Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Esophageal Atresia
Esophageal Atresia
Uploaded by
kudzaimuregidubeOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Esophageal Atresia
Esophageal Atresia
Uploaded by
kudzaimuregidubeCopyright:
Available Formats
Esophageal Atresia
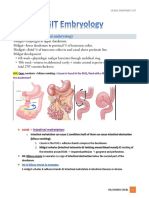
Esophageal atresia (EA) with distal tracheo-esophageal fistula (TEF) is the most common
congenital anomaly of the esophagus, followed by EA without TEF also known as pure
esophageal atresia and pure TEF.
Incidence is one in every 2500 live births.
Development - The trachea and esophagus begin as a ventral diverticulum of the foregut
during the third intrauterine week of life. A proliferation of endodermal cells appears on
the lateral aspect of this growing diverticulum. These cell masses will divide the foregut
into trachea and esophageal tubes.
There is interruption of this normal event
during tracheal growth atresia of the esophagus results because of fistulous
fixation of the esophagus to the trachea
. Polyhydramnios is seen in pure EA.
Newbors- EA causes
excessive salivation,
choking,
coughing,
regurgitation with first feed
inability to pass a feeding tube into the stomach.
Management - X ray with tube in situ – shows obstruction
Correct dehydration,
acid-base disturbances,
respiratory distress
decompress proximal esophageal pouch
Evaluate for associated conditions such as VACTERL association.
-Vertebral anomalies i.e. hemivertebrae, spina bifida
-Anal malformations i.e. imperforate anus
-Cardiac malformations i.e. VSD, ASD, Tetralogy Fallot
-Tracheo-Esophageal fistula (must be one of the associated conditions)
-Renal deformities i.e. absent kidney, hypospadia, etc.
-Limb dysplasia
Early surgical repair (transpleural or extrapleural) is undertaken for those babies with
adequate arterial blood gases, adequate weight (>1200 gm) and no significant associated
anomalies.
Delayed repair (gastrostomy first) for all other patients.
Repair
thoracotomy,
closure of TEF
primary anastomosis.
Esophagogram is done 7-10 days after repair.
Prognosis depends on –
birth weight,
severity of pulmonary dysfuntion,
presence of major congenital cardiac disease.
Complications after surgery:
anastomotic leak,
stricture,
gastroesophageal reflux,
tracheomalacia
recurrent TEF.
most common complications after surgery: are in order of frequency: stricture, leakage
and recurrent TEF.
You might also like
- Normal Gastrointestinal Embryology: Intestinal MalrotationDocument159 pagesNormal Gastrointestinal Embryology: Intestinal MalrotationDaNy ChiriacNo ratings yet
- Esophageal AtresiaDocument70 pagesEsophageal Atresiahayssam rashwan100% (1)
- PEDI 2. Embryologic Basis of GI Malformations 2021Document54 pagesPEDI 2. Embryologic Basis of GI Malformations 2021Hayle MaryamNo ratings yet
- Summary and Conclusion Esophageal Atresia (Or Oesophageal AtresiaDocument3 pagesSummary and Conclusion Esophageal Atresia (Or Oesophageal AtresiaSanket TelangNo ratings yet
- Esophageal Atresia: DR - Ibrahim AlsbouDocument21 pagesEsophageal Atresia: DR - Ibrahim Alsbouraed faisalNo ratings yet
- Congenital AnomaliesDocument10 pagesCongenital Anomaliesربيع ضياء ربيعNo ratings yet
- Tracheo Esophageal FistulaDocument6 pagesTracheo Esophageal Fistulablast2111No ratings yet
- GastroentrologyDocument204 pagesGastroentrologyahmed_abu_alrobNo ratings yet
- Curs 4 Gastro IDocument23 pagesCurs 4 Gastro In bNo ratings yet
- PATHO 4-3 Diseases of The EsophagusDocument7 pagesPATHO 4-3 Diseases of The EsophagusMiguel Cuevas DolotNo ratings yet
- Esophageal Atresia and Tracheoesophageal Fistula: A Guide For ParentsDocument4 pagesEsophageal Atresia and Tracheoesophageal Fistula: A Guide For ParentsMaya Asharie HarahapNo ratings yet
- Atresia EsofagusDocument7 pagesAtresia EsofagusTommysNo ratings yet
- Disorders of EsophagusDocument27 pagesDisorders of EsophagusFranci Kay SichuNo ratings yet
- A Tracheoesophageal FistulaDocument11 pagesA Tracheoesophageal FistulaaparnaprasadmNo ratings yet
- Congenital Development Disorder of Esophagus, Stomach, Duodenum, Abdomen Wall, Anus and RectumDocument56 pagesCongenital Development Disorder of Esophagus, Stomach, Duodenum, Abdomen Wall, Anus and RectumSarah Nabella PutriNo ratings yet
- Esophagus Atresia: Dwi Rezki Amalia Medical Faculty of Lambung Mangkurat UniversityDocument26 pagesEsophagus Atresia: Dwi Rezki Amalia Medical Faculty of Lambung Mangkurat UniversityDwi Rezky AmaliaNo ratings yet
- Diseases of EsophagusDocument46 pagesDiseases of EsophagusPlày GameNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2022-05-30 at 9.43.21 PMDocument23 pagesScreenshot 2022-05-30 at 9.43.21 PMAZNo ratings yet
- Clinical Approach To A Patient With Dysphagia: Medicine UpdateDocument3 pagesClinical Approach To A Patient With Dysphagia: Medicine UpdateAnonymous XFDJfsGviNo ratings yet
- VACTERL-association EN PDFDocument12 pagesVACTERL-association EN PDFAuliaRahmanNo ratings yet
- Bedah Anak: Kelainan Kongenital Gastrointestinal Anak Kedaruratan AnakDocument52 pagesBedah Anak: Kelainan Kongenital Gastrointestinal Anak Kedaruratan AnakalifNo ratings yet
- Surgical ConditionsDocument116 pagesSurgical ConditionsFan EliNo ratings yet
- Pediatric SurgeryDocument167 pagesPediatric Surgerynanialex800No ratings yet
- ESOPHAGEAL:Gastritis DiseaseDocument25 pagesESOPHAGEAL:Gastritis DiseaseraNo ratings yet
- Neonatal Surgical EmergenciesDocument17 pagesNeonatal Surgical EmergenciesfaisaldanyaniNo ratings yet
- Dysphagia Lusoria: A Comprehensive ReviewDocument6 pagesDysphagia Lusoria: A Comprehensive ReviewDante ChavezNo ratings yet
- Common Pediatric Surgery ProblemsDocument141 pagesCommon Pediatric Surgery Problemssedaka26100% (4)
- Test 2 NotesDocument38 pagesTest 2 Notesbjpalmer100% (2)
- Emergencies in GITDocument7 pagesEmergencies in GITsssajiNo ratings yet
- 5-Esophageal Diseases: Hugh K. Duckworth M.DDocument5 pages5-Esophageal Diseases: Hugh K. Duckworth M.DJames FlanneryNo ratings yet
- Oesophagealatresia 120920081900 Phpapp01Document37 pagesOesophagealatresia 120920081900 Phpapp01Mulugeta AbenehNo ratings yet
- Muhimbili University of Health and Allied Sciences. School of NursingDocument21 pagesMuhimbili University of Health and Allied Sciences. School of NursingJerilee SoCute WattsNo ratings yet
- BaldwinDocument6 pagesBaldwinalexafarrenNo ratings yet
- Esophageal Atresia and Tracheoesophageal FistulaDocument21 pagesEsophageal Atresia and Tracheoesophageal FistulaIslam AmerNo ratings yet
- K26 Ileus ObsDocument18 pagesK26 Ileus ObsmitrajoeNo ratings yet
- 19-Pediatric SurgeryDocument39 pages19-Pediatric Surgerycallisto3487No ratings yet
- Jejunal and Ileal AtresiasDocument37 pagesJejunal and Ileal AtresiasABDUL RAHIM UMAR FAROUKNo ratings yet
- Bladder News 10 HydroDocument3 pagesBladder News 10 HydrosaidyanzNo ratings yet
- Fanaroff Anormalidades GastrointestinalesDocument28 pagesFanaroff Anormalidades GastrointestinalesDome HerreraNo ratings yet
- Presentacion GastrointestinalDocument228 pagesPresentacion GastrointestinalNb + XB = AVNo ratings yet
- Esophageal AtresiaDocument21 pagesEsophageal AtresiaOktania Putri Kusnawan100% (2)
- MiniOSCE Surgery 1Document329 pagesMiniOSCE Surgery 1Mohammad BanisalmanNo ratings yet
- Non-Neoplastic Disorders of Esophagus: Dr. Naw May Emerald Faculty of Medicine & Health Sciences UCSI UniversityDocument32 pagesNon-Neoplastic Disorders of Esophagus: Dr. Naw May Emerald Faculty of Medicine & Health Sciences UCSI UniversitySindhu BabuNo ratings yet
- Intestinal Atresia and StenosisDocument7 pagesIntestinal Atresia and StenosisMichael NafarinNo ratings yet
- Hrkansh NotesDocument424 pagesHrkansh NotesAhmed RagabNo ratings yet
- Intestinal Obstruction, Colorectal CancerDocument49 pagesIntestinal Obstruction, Colorectal CancermeghanaNo ratings yet
- 1-s2.0-S2213576622003608-mainDocument5 pages1-s2.0-S2213576622003608-mainAdam DanuartaNo ratings yet
- What Is Intestinal ObstructionDocument5 pagesWhat Is Intestinal ObstructionmatrixtrinityNo ratings yet
- Duodenal AtresiaDocument18 pagesDuodenal AtresiaRianto Noviady RamliNo ratings yet
- Anesthesia For Tracheoesophageal Fistula RepairDocument29 pagesAnesthesia For Tracheoesophageal Fistula RepairArop AkechNo ratings yet
- A3. Esophageal Diverticles and Tracheo-Esophageal FistulesDocument4 pagesA3. Esophageal Diverticles and Tracheo-Esophageal FistulesSaman SadeghiNo ratings yet
- AtresiaDocument5 pagesAtresiakirtiNo ratings yet
- Esophagus: Comments On Embryology of EsophagusDocument14 pagesEsophagus: Comments On Embryology of EsophagusDave AbrahamNo ratings yet
- Congenital Anomalies of The Esophagus PDFDocument3 pagesCongenital Anomalies of The Esophagus PDFSpecialName100% (1)
- 4 U1.0 B978 1 4160 6189 2..00012 3..DOCPDFDocument9 pages4 U1.0 B978 1 4160 6189 2..00012 3..DOCPDFJuan HernandezNo ratings yet
- Dysphagia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandDysphagia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Esophageal Varices, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandEsophageal Varices, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet