Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Tissues Comprehensive Notes
Tissues Comprehensive Notes
Uploaded by
Muhammad SaadOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Tissues Comprehensive Notes
Tissues Comprehensive Notes
Uploaded by
Muhammad SaadCopyright:
Available Formats
6.1 Are Plants and Animals Made of Same Types of Tissues?
1. Multi-cellular organisms show division of labour. Judge the statement.
In human beings, muscle cells contract and relax to cause movement, nerve cells carry messages,
blood flows to transport oxygen, food, hormones and waste material and so on. In plants, vascular
tissues conduct food and water from one part of the plant to other parts. So, multi-cellular organisms
show division of labour
2. What is tissue?
A group of cells that are similar in structure and/or work together to achieve a particular function
forms a tissue.e.g Blood, phloem and muscle are all examples of tissues
3. Are Plants and Animals Made of Same Types of Tissues? Why or why not?
No,
4. What is the utility of tissues in multi-cellular organisms?
In multicellular organisms, several cells are grouped to form tissues. These tissues perform particular
function at a definite place in the body. For example, nerve cells from the nervous tissue which helps
in transmission of messages. This is known as division of labour in multicellular organisms. Because
of this division of labour, multicellular organisms are able to perform all functions perfectly.
5. The growth of plants occurs only in certain specific regions.Why?
This is because the dividing tissue, also known as meristematic tissue, is located only at these points.
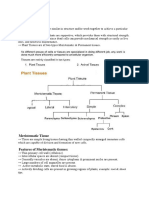
6. 6.2 Plant Tissues 6.2.1 MERISTEMATIC TISSUE
COMPREHENSIVE QUESTION BANK IN BIOLOGY, CLASS IX
THE INDIAN HIGH SCHOOL, DUBAI Page 1
Name the dividing tissues in plants. How it is classified?
Meristem.
Depending on the region where they are present, meristematic tissues are classified as apical, lateral
and intercalary
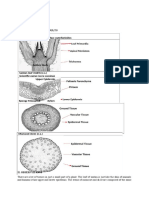
7. Illustrate the location, role and occurance of types of meristem.
8. How does meristematic tissue structurally adapted for its function?
As the cells of this tissue are very active, they have dense cytoplasm, thin cellulose walls and
prominent nuclei. They lack vacuoles.
9. Why meristematic tissue lack vacuole?
Since the cells are always dividing, there will be no waste products or materials to store in the cell.
Thus they don’t have vacuoles.
10. Tabulate the types, location and role of meristem.
11. 6.2. PERMANENT TISSUE
Show classification of plant tissues .
COMPREHENSIVE QUESTION BANK IN BIOLOGY, CLASS IX
THE INDIAN HIGH SCHOOL, DUBAI Page 2
12. A plant cannot survive only with meristematic tissue, as it has to perform various life activities to
sustain life. What happens to the cells formed by meristematic tissue?
They take up a specific role and lose the ability to divide. As a result, they form a permanent tissue.
This process of taking up a permanent shape, size, and a function is called differentiation. Cells of
meristematic tissue differentiate to form different types of permanent tissue.
13. Name the process by which meristem changes to permanent tissue.
Differentiation
14. Differentiate between meristem and permanent tissue.
15. List types of permanent tissues.
Simple permanent tissue
COMPREHENSIVE QUESTION BANK IN BIOLOGY, CLASS IX
THE INDIAN HIGH SCHOOL, DUBAI Page 3
Complex permanent tissue
16. Tabulate features of simple permanent tissues. (Learn any 3 differences)
17. Identify complex permanent tissue.
COMPREHENSIVE QUESTION BANK IN BIOLOGY, CLASS IX
THE INDIAN HIGH SCHOOL, DUBAI Page 4
18. Differentiate between types of complex permanent tissues/ Xylem and Phloem
19. Draw and label section of phloem.
COMPREHENSIVE QUESTION BANK IN BIOLOGY, CLASS IX
THE INDIAN HIGH SCHOOL, DUBAI Page 5
20. Identify the tissue, after analyzing features:
*Form the basic packing tissue
*A type of permanent tissue
*Relatively unspecialised cells with thin cell walls
*They are live cells.
*They are usually loosely packed, (intercellular spaces)
*This tissue provides support to plants and also stores food
The tissue is parenchyma.
21. Tabulate basic tissues in vascular plants:
COMPREHENSIVE QUESTION BANK IN BIOLOGY, CLASS IX
THE INDIAN HIGH SCHOOL, DUBAI Page 6
22. Make a concept map for tissues in plants:
23. Explain how parenchyma evolved into different types to perform varied role.
In some situations, it contains chlorophyll and performs photosynthesis, and then it is called
chlorenchyma. In aquatic plants, large air cavities are present in parenchyma to give buoyancy to the
plants to help them float. Such a parenchyma type is called aerenchyma.
24. Tabulate the features, role and occurance of collenchymas.
Features Occurance Role
The cells of this tissue are This tissue in leaf stalks Provide flexibility in plants. It
living, elongated and below the epidermis. allows easy bending in
irregularly thickened at the various parts of a plant (leaf,
corners. There is very little stem) without breaking. It
intercellular space also provides mechanical
support to plants.
25. Tabulate the features, role and occurance of sclerenchyma.
Features Occurance Role
The cells of this tissue are This tissue is present in It is the tissue which makes
dead. They are long and stems, around vascular the plant hard and stiff. . It
narrow as the walls are bundles, in the veins of leaves provides strength to the plant
thickened due to lignin (a and in the hard covering of parts.
chemical substance which seeds and nuts also in the
acts as cement and hardens husk of a coconut.
COMPREHENSIVE QUESTION BANK IN BIOLOGY, CLASS IX
THE INDIAN HIGH SCHOOL, DUBAI Page 7
them). Often these walls are
so thick that there is no
internal space inside the cell.
26.
Identify A- D
A- GUARD CELLS
B- EPIDERMAL CELL
C- STOMATA
D- GUARD CELL
27. Write features of epidermis.
It is the outermost layer of cells
The epidermis is usually made of a single layer of cells. Since it has a protective role to play, cells of
epidermal tissue form a continuous layer without intercellular spaces. Most epidermal cells are
relatively flat. Often their outer and side walls are thicker than the inner wall.
28. How epidermis adapted to perform its protective role?
In some plants living in very dry habitats, the epidermis may be thicker since protection against
water loss is critical. The entire surface of a plant has this outer covering of epidermis. It protects all
the parts of the plant. Epidermal cells on the aerial parts of the plant often secrete a waxy, water-
resistant layer on their outer surface. This aids in protection against loss of water, mechanical injury
and invasion by parasitic fungi.
29. What you call for small pores on the leaf epidermis?
Stomata.
30. Name the cells enclosing stomata.
Guard cell.
31. List the functions of stomata.
They are necessary for exchanging gases with the atmosphere. Transpiration (loss of water in the
form of water vapour) also takes place through stomata.
32 How do epidermal cells of root modified?
Epidermal cells of the roots, whose function is water absorption, commonly bear long hair-like parts
that greatly increase the total absorptive surface area.
33. What kind of modification is seen in epidermis of desert plant?
COMPREHENSIVE QUESTION BANK IN BIOLOGY, CLASS IX
THE INDIAN HIGH SCHOOL, DUBAI Page 8
In desert plants, epidermis has a thick waxy coating of cutin (chemical substance with waterproof
quality) on its outer surface to reduce water loss.
34 Is the outer layer of a branch of a tree different from the outer layer of a young stem? Support your
answer.
As plants grow older, the outer protective tissue undergoes certain changes. A strip of secondary
meristem replaces the epidermis of the stem. Cells on the outside are cut off from this layer. This
forms the several-layer thick cork or the bark of the tree. Cells of cork are dead and compactly
arranged without intercellular spaces.They also have a chemical called suberin in their walls that
makes them impervious to gases and water.
35. Identify the specific component of xylem.
a) transport water and minerals vertically
b) stores food and helps in the sideways conduction of water
c) supportive
a) Tracheids and vessels
b) Parenchyma
c) Fibres
36. Identify the specific component of phloem.
a) tubular cells with perforated walls.
b) Non living component
a) Sieve tube
b) Fibres
37. 6.3 Animal Tissues
Make a classification chart for animal tissues
37. Tabulate types of epithelial tissue , location and functions.
COMPREHENSIVE QUESTION BANK IN BIOLOGY, CLASS IX
THE INDIAN HIGH SCHOOL, DUBAI Page 9
38. What is a glandular epithelium?
Epithelial cells often acquire additional specialisation as gland cells, which can secrete substances at
the epithelial surface. Sometimes a portion of the epithelial tissue folds inward, and a multicellular
gland is formed. This is glandular epithelium.
39 How does stratified squamous epithelium formed?
COMPREHENSIVE QUESTION BANK IN BIOLOGY, CLASS IX
THE INDIAN HIGH SCHOOL, DUBAI Page 10
Stratified squamous epithelium: -.
Skin epithelial cells are arranged in many layers to prevent wear and tear. Since they are arranged in
a pattern of layers, the epithelium is called stratified squamous epithelium.
40. Identify the tissue.
a. Extremely thin and flat and form a delicate lining- simple squamous epithelium
b. The tissue lining oesophagus and the lining of the mouth - squamous epithelium
c. Cells are arranged in many layers to prevent wear and tear- Stratified squamous epithelium
d. Absorption and secretion occur, as in the inner lining of the intestine- Cuboidal epithelium
e. Epithelium that facilitates movement across the epithelial barrier- Columnar epithelium
f. Respiratory tract – Ciliated columnar epithelium
g. Forms the lining of kidney tubules and ducts of salivary glands- Cuboidal epithelium
h. Provide mechanical support- Cuboidal epithelium
i. Epithelial tissue folded inward to secrete- Glandular epithelium
*** It is important to mention epithelium once you identify a epithelial tissue.
41. 6.3.2 CONNECTIVE TISSUE
Show classification of connective tissue.
42. What are features of a connective tissue?
The cells of connective tissue are loosely spaced and embedded in an intercellular matrix . The matrix
may be jelly like, fluid, dense or rigid. The nature of matrix differs in concordance with the function of
COMPREHENSIVE QUESTION BANK IN BIOLOGY, CLASS IX
THE INDIAN HIGH SCHOOL, DUBAI Page 11
the particular connective tissue.
43. Enumerate the components and functions of blood.
Blood has a fluid (liquid) matrix called plasma, in which red blood cells (RBCs), white blood cells
(WBCs) and platelets are suspended. The plasma contains proteins, salts and hormones. Blood flows
and transports gases, digested food, hormones and waste materials to different parts of the body.
44. Why blood is called a fluid connective tissue ?
Blood is a fluid connective tissue because the main feature of fluid connective tissue is connecting
different tissues or parts of the body and having matrix.
45. Tabulate the details of connective tissue.
COMPREHENSIVE QUESTION BANK IN BIOLOGY, CLASS IX
THE INDIAN HIGH SCHOOL, DUBAI Page 12
46. Identify the tissue
a. Fills the space between the organs- Adipose connective tissue
b. Tissue found between skin and muscles- Areolar connective tissue
c. Below skin- Adipose connective tissue
d. Fills the space inside internal organs- Areolar connective tissue
e. Transport respiratory gases- Blood
47. Differentiate between tendon and ligament.
48. What is a muscle fibre?
COMPREHENSIVE QUESTION BANK IN BIOLOGY, CLASS IX
THE INDIAN HIGH SCHOOL, DUBAI Page 13
Muscular tissue consists of elongated cells, also called muscle fibres.
49. How is a muscle tissue structurally adapted to promote movement?
Muscular tissue consists of elongated cells, also called muscle fibres.
Muscles contain special proteins called contractile proteins, which contract and relax to cause
movement.
50. Tabulate the details of muscular tissue
51. What are voluntary and involuntary muscles?
Voluntary muscles: Muscles which can be moved by our conscious will. E.g. Muscles present in
our limbs
Involuntary muscles:-Muscles which cannot be moved according to our will .E.g..-Found in
alimentary canal, iris of eye
52. Identify the muscle and parts labeled as A and B.
The muscle is Striated or skeletal muscle.
A- Nucleus
B- Striations
53. Identify the muscle and parts labeled as A and B.
COMPREHENSIVE QUESTION BANK IN BIOLOGY, CLASS IX
THE INDIAN HIGH SCHOOL, DUBAI Page 14
A- Spindle shaped muscle cell
B- Nucleus
The given tissue is smooth muscle tissue or non striated muscle tissue.
54. Identify the muscle and parts labeled as A and B.
Enumerate special or unique features of this tissue
A- Striations
B- Nucleus
The given tissue is cardiac muscle tissue
This tissue show rhythmic contraction and relaxation throughout life.
Heart muscle cells are cylindrical, branched and uninucleate.
55. 6.3.4 NERVOUS TISSUE
Sketch and label nerve tissue or neuron
56. What is the role of nervous tissue?
Impulse transmission.
57. All cells possess the ability to respond to stimuli. How ?
Cells of the nervous tissue are highly specialised for being stimulated and then transmitting the
COMPREHENSIVE QUESTION BANK IN BIOLOGY, CLASS IX
THE INDIAN HIGH SCHOOL, DUBAI Page 15
stimulus very rapidly from one place to another within the body.
58. Enlist the location of nervous tissue.
The brain, spinal cord and nerves are all composed of the nervous tissue. The cells of this tissue are
called nerve cells or neurons.
59. Briefly describe the structure of Nervous tissue. Are nervous tissue and neuron same?
A neuron consists of a cell body with a nucleus and cytoplasm, from which long thin hair-like parts
arise . Usually each neuron has a single long part, called the axon, and many short, branched parts
called dendrites. An individual nerve cell may be up to a metre long.
No,nervous tissue and neuron same are not same.
Many nerve fibres bound together by connective tissue make up a nerve.
60. What mechanism helps animals to move rapidly in response to stimuli?
Nerve impulses allow us to move our muscles when we want to. The functional
combination of nerve and muscle tissue is fundamental to most animals. This combination enables
animals to move rapidly in response to stimuli.
COMPREHENSIVE QUESTION BANK IN BIOLOGY, CLASS IX
THE INDIAN HIGH SCHOOL, DUBAI Page 16
You might also like
- Phlebotomy Course OutlineDocument7 pagesPhlebotomy Course OutlineDegee GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Health Assessment Exam 1 Study GuideDocument8 pagesHealth Assessment Exam 1 Study GuideDharati Patel100% (1)
- Practice Guide: Heart Awakening & Total LoveDocument7 pagesPractice Guide: Heart Awakening & Total LoveElena GrigorescuNo ratings yet
- SCFHS Diagnostic Radiology ExamsDocument123 pagesSCFHS Diagnostic Radiology ExamsDr-Khaled Shaaban100% (1)
- I. Meristematic Tissue (Dividing Tissue) :: 6. Tissues Q.1 What Is A Tissue? or Define The Term TissueDocument10 pagesI. Meristematic Tissue (Dividing Tissue) :: 6. Tissues Q.1 What Is A Tissue? or Define The Term Tissuetara tuitionNo ratings yet
- Chapter-6 TISSUESDocument36 pagesChapter-6 TISSUESSATYAM RATHOURNo ratings yet
- PLANT TISSUE AND SEC GROWTH For 9 11Document6 pagesPLANT TISSUE AND SEC GROWTH For 9 11Khushbu PandyaNo ratings yet
- Edu246 Botany 2Document8 pagesEdu246 Botany 2ANNE MARGUERITE BARETENo ratings yet
- Life Sciences Term 2 Content Workshopplant Tissues, Plant OrgansDocument29 pagesLife Sciences Term 2 Content Workshopplant Tissues, Plant Organsonthabiseng mathNo ratings yet
- Notes 9 Tissues New 2021Document9 pagesNotes 9 Tissues New 2021Arjun AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Report SheetDocument11 pagesReport SheetMikhail LandichoNo ratings yet
- BIOL223-Lab 10Document60 pagesBIOL223-Lab 10chicken friesNo ratings yet
- TissuesDocument12 pagesTissueschandankrdumkaNo ratings yet
- TissuesDocument6 pagesTissuesRahul SinghNo ratings yet
- TissuesDocument6 pagesTissuessrianshNo ratings yet
- Report SheetDocument6 pagesReport SheetMikhail LandichoNo ratings yet
- L-2 Tissues - 210822Document22 pagesL-2 Tissues - 210822hridaanNo ratings yet
- TissueDocument14 pagesTissueBarkha Agrawal100% (1)
- Ix Biology 6 1, PPTDocument35 pagesIx Biology 6 1, PPTShruti TiwariNo ratings yet
- Kebo 106Document8 pagesKebo 106Mohamed Fayaz Sheik DawoodNo ratings yet
- Notes of CH Tissues Class 9Document20 pagesNotes of CH Tissues Class 9PrabhaNo ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Biology Chapter 6 Anatomy of Flowering PlantsDocument8 pagesNCERT Solutions For Class 11 Biology Chapter 6 Anatomy of Flowering PlantsyashNo ratings yet
- Asgn 5974128103Document7 pagesAsgn 5974128103rappycatNo ratings yet
- Class 9 Plant Tissues Notes - 1, 2022-23Document4 pagesClass 9 Plant Tissues Notes - 1, 2022-23collins thomasNo ratings yet
- 642020112334AM-Class 9 Biology Notes-Chapter-6 Plant TissueDocument14 pages642020112334AM-Class 9 Biology Notes-Chapter-6 Plant Tissuekmdmohideen2297100% (1)
- TISSUESDocument9 pagesTISSUEStyrtNo ratings yet
- Plant TissueDocument19 pagesPlant TissueKAMESH .G100% (1)
- Plant Tissue - Study NotesDocument11 pagesPlant Tissue - Study NotesrockyajeetNo ratings yet
- B-9-T1 - 02 Tissues PDFDocument26 pagesB-9-T1 - 02 Tissues PDFriddhi100% (1)
- L-3 Epidermal-Tissues - 210822Document12 pagesL-3 Epidermal-Tissues - 210822hridaanNo ratings yet
- Tissues - Comprehensive NotesDocument4 pagesTissues - Comprehensive NotesRatheesh HrishikeshNo ratings yet
- Lakhmir Singh Solutions Class 9 Biology Chapter 3Document7 pagesLakhmir Singh Solutions Class 9 Biology Chapter 3DarshilNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Flowering Plants Revision Notes For Class 11 Biology CH 6Document30 pagesAnatomy of Flowering Plants Revision Notes For Class 11 Biology CH 6Anubhav MamgainNo ratings yet
- Plant TissuesDocument11 pagesPlant TissuesRudra Patel100% (1)
- Gist of The Topic: BiologyDocument14 pagesGist of The Topic: BiologyDhanya BalasundarrajNo ratings yet
- Biology:: ObjectiveDocument6 pagesBiology:: Objectivesreehaasini kandregulaNo ratings yet
- 7.plant TissueDocument3 pages7.plant TissueRAVINDRA PRASADNo ratings yet
- TISSUES (Prashant Kirad)Document9 pagesTISSUES (Prashant Kirad)abhijotsinghas83No ratings yet
- Tissue - Class 9Document9 pagesTissue - Class 9Rohit Jain100% (1)
- 8 June Support and Transport Systems in PlantsDocument25 pages8 June Support and Transport Systems in Plantsmaduanekabelo08No ratings yet
- Plant Tissue ARDocument34 pagesPlant Tissue ARAnna Grace Lobigas RanocoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Flowering PlantsDocument10 pagesAnatomy of Flowering PlantssuryababaNo ratings yet
- Cell Organization in Plants: Form 4 Biology Chapter 2 (B) Cell OrganisationDocument9 pagesCell Organization in Plants: Form 4 Biology Chapter 2 (B) Cell OrganisationMei QiiNo ratings yet
- Exercise 5 (PLANT TISSUES)Document8 pagesExercise 5 (PLANT TISSUES)BARRIENTOS, MARIE NICOLENo ratings yet
- Tissue 9th BiologyDocument8 pagesTissue 9th BiologyNestor Bong Bordaje NemeñoNo ratings yet
- Tissues Just NotesDocument20 pagesTissues Just NotesSudesh Sharma100% (1)
- Tissues: Chapter - 6Document17 pagesTissues: Chapter - 6Aditya Jha100% (1)
- Class 9 Science CH 6 NotesDocument13 pagesClass 9 Science CH 6 NotesChetan GargNo ratings yet
- Simple Permanent TissueDocument9 pagesSimple Permanent Tissueking100% (1)
- Notes Plant TissuesDocument7 pagesNotes Plant TissuesHariprasanthNo ratings yet
- Young Stems and RootsDocument11 pagesYoung Stems and RootsHailey CoutuNo ratings yet
- Tissues Class 9 Extra Questions Very Short Answer TypeDocument31 pagesTissues Class 9 Extra Questions Very Short Answer TypeAyushi VermaNo ratings yet
- 9tissuesppt 150802072720 Lva1 App6892Document29 pages9tissuesppt 150802072720 Lva1 App6892Vipul GuptaNo ratings yet
- Plant PrintsDocument11 pagesPlant PrintsWARDAH SHOAIBNo ratings yet
- Topic 4 Edexcel - 240101 - 190205Document57 pagesTopic 4 Edexcel - 240101 - 190205Ovina RanasingheNo ratings yet
- Bio - CH 2 TissuesDocument92 pagesBio - CH 2 TissuesPagli MonkeyNo ratings yet
- Atomic Energy Education Society: Handout Class Ix Biology - 6 TISSUES (Module 1)Document6 pagesAtomic Energy Education Society: Handout Class Ix Biology - 6 TISSUES (Module 1)Bhawan malhiNo ratings yet
- Tissue ClassworkDocument5 pagesTissue ClassworkRajesh Kanna A亗No ratings yet
- CropSci101 Module 3Document11 pagesCropSci101 Module 3Jetro Neil GapasinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Plant Tissues - Class 9th - BiologyDocument6 pagesChapter 6 Plant Tissues - Class 9th - BiologyPreeti BhullarNo ratings yet
- Biology Tissue Notes of Class 9thDocument12 pagesBiology Tissue Notes of Class 9thrishabhraj.adzNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Flowering PlantDocument7 pagesAnatomy of Flowering Plantjimmy902437No ratings yet
- OsmosislabDocument8 pagesOsmosislabapi-328190492No ratings yet
- Treating Low Back PainDocument18 pagesTreating Low Back PainWilliam Tell50% (2)
- GoniosDocument14 pagesGoniosJayricDepalobosNo ratings yet
- Antioxidants an-WPS OfficeDocument6 pagesAntioxidants an-WPS OfficeGowri RNo ratings yet
- Daftar PustakaDocument5 pagesDaftar PustakaRizky Rachmat KurniawanNo ratings yet
- London Examinations GCE: Human Biology Ordinary LevelDocument20 pagesLondon Examinations GCE: Human Biology Ordinary Levelwilsky05No ratings yet
- Pelatihan Dry NeedleDocument101 pagesPelatihan Dry NeedleAri SudarsonoNo ratings yet
- S TPHA Liquid: Design VerificationDocument9 pagesS TPHA Liquid: Design VerificationTanveerNo ratings yet
- El Sayed2005Document7 pagesEl Sayed2005Romeo Pomarí JuárezNo ratings yet
- Nervous System I: Basic Structure and FunctionDocument4 pagesNervous System I: Basic Structure and FunctionrohitNo ratings yet
- Physical Chemistry For The Life SciencesDocument1 pagePhysical Chemistry For The Life SciencessnowblindedNo ratings yet
- Phylogenetic Trees Activity - Farizah AliDocument2 pagesPhylogenetic Trees Activity - Farizah AliFarizah AliNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Song by MR ParrDocument1 pageRespiratory Song by MR ParrRanulfo MayolNo ratings yet
- BTS Guidelines For Emergency Oxygen Use in Adults PatiensDocument81 pagesBTS Guidelines For Emergency Oxygen Use in Adults PatiensarmitadewiNo ratings yet
- Muscles of The Head and NeckDocument31 pagesMuscles of The Head and NeckMontassar DridiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 20 - Postpartum Physiologic ChangesDocument10 pagesChapter 20 - Postpartum Physiologic ChangesJill Hill100% (2)
- The Open Field Test. A Critical ReviewDocument23 pagesThe Open Field Test. A Critical Reviewgoutham278No ratings yet
- Abs Bench 500 Manual 3esDocument15 pagesAbs Bench 500 Manual 3esmaremotusNo ratings yet
- Soal Uts Bahasa Inggris Kelas 3 Tahun 2018Document2 pagesSoal Uts Bahasa Inggris Kelas 3 Tahun 2018J Sathu KediriNo ratings yet
- NCMB 316 M1 Cu1Document23 pagesNCMB 316 M1 Cu1Maica Lectana100% (1)
- Limbic SystemDocument18 pagesLimbic SystemPankajNo ratings yet
- QowdoDocument1 pageQowdoRSCERIA KANDANGANNo ratings yet
- SLE211 Week 4 Class 2 - Skeletal Muscle Physiology (1) - 4 Slides Per PageDocument8 pagesSLE211 Week 4 Class 2 - Skeletal Muscle Physiology (1) - 4 Slides Per PagehasNo ratings yet
- The Molecular Cytoarchitecture of The Adult Mouse BrainDocument28 pagesThe Molecular Cytoarchitecture of The Adult Mouse BrainVictor Rodrigues SantosNo ratings yet
- Anti Parasit A RiosDocument14 pagesAnti Parasit A RiosYuukiAuclair100% (2)
- Pharmacology Practice QuestionsDocument5 pagesPharmacology Practice QuestionsVipin JainNo ratings yet