Professional Documents
Culture Documents
J249 04 Paper Dec 17
J249 04 Paper Dec 17
Uploaded by
yufm2008Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- WPH15 01 MSC 20210304Document16 pagesWPH15 01 MSC 20210304Little Wizard67% (3)
- Year 11 Prelim Exams PhysicsDocument22 pagesYear 11 Prelim Exams PhysicsTimothy KurbyNo ratings yet
- Astrophysical Plasmas Exam 2021Document8 pagesAstrophysical Plasmas Exam 2021SarbajitMannaNo ratings yet
- Nsaa s1 Specimen Explained AnswersDocument45 pagesNsaa s1 Specimen Explained AnswersKatia La PlacaNo ratings yet
- J249 03 Paper Dec 17Document24 pagesJ249 03 Paper Dec 17yufm2008No ratings yet
- J249 03 Paper Dec 17Document25 pagesJ249 03 Paper Dec 17yufm2008No ratings yet
- PAT 2006 Paper PDFDocument9 pagesPAT 2006 Paper PDFchjggfNo ratings yet
- Cluster Level Question Bank (Ahmedabad & Gandhinagar Cluster)Document33 pagesCluster Level Question Bank (Ahmedabad & Gandhinagar Cluster)manpreetsingh3458417No ratings yet
- Quantum Physics Exam Questions 69 QuestionsDocument145 pagesQuantum Physics Exam Questions 69 QuestionsVedant BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Friday 8 October 2021 - Morning: AS Level Physics ADocument20 pagesFriday 8 October 2021 - Morning: AS Level Physics ATankioNo ratings yet
- Unit h156 01 Breadth in Physics Sample Assessment MaterialsDocument44 pagesUnit h156 01 Breadth in Physics Sample Assessment Materialsmarjan familiNo ratings yet
- 702765 Topic Test Understanding ProcessesDocument22 pages702765 Topic Test Understanding Processesaidenflecky07No ratings yet
- H556-02 QP Jun22Document28 pagesH556-02 QP Jun22Vaibhav MehraNo ratings yet
- 4.4 Waves - Wave Motion QPDocument52 pages4.4 Waves - Wave Motion QPwill hayNo ratings yet
- Stars-Spectra Ch19 PDFDocument39 pagesStars-Spectra Ch19 PDFSaraii cgzzNo ratings yet
- Question Paper Unit h556 02 Exploring Physics PDFDocument32 pagesQuestion Paper Unit h556 02 Exploring Physics PDFHumaira MohungooNo ratings yet
- WPH15 01 MSC Jan-2022 UNUSEDDocument16 pagesWPH15 01 MSC Jan-2022 UNUSEDchemtrailsoverNo ratings yet
- wph15 01 Rms 20240307Document15 pageswph15 01 Rms 20240307shakera.khatun74No ratings yet
- January 2021 (IAL) MSDocument16 pagesJanuary 2021 (IAL) MSJannati Saba NawarNo ratings yet
- CBSE Board Paper Solution-2020Document51 pagesCBSE Board Paper Solution-2020SsNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 MCQ CollectionDocument11 pagesUnit 5 MCQ CollectionNirmani RodrigoNo ratings yet
- January 2023 MSDocument17 pagesJanuary 2023 MSSavva LazarevNo ratings yet
- Pat2015 PDFDocument22 pagesPat2015 PDFノエル ビクトリアNo ratings yet
- Marking Scheme Physics 10Document8 pagesMarking Scheme Physics 10Suleman AwanNo ratings yet
- JEE Main 2023 31st Jan Shift 1 QPDocument30 pagesJEE Main 2023 31st Jan Shift 1 QPhemantNo ratings yet
- Physical Sciences P1 Grade 11 Nov 2017 EngDocument18 pagesPhysical Sciences P1 Grade 11 Nov 2017 EngravenswayproNo ratings yet
- June 2016 QP - Paper 1 OCR (A) Physics AS-LevelDocument28 pagesJune 2016 QP - Paper 1 OCR (A) Physics AS-LevelDhanBahadurNo ratings yet
- Physics P1 2016Document15 pagesPhysics P1 2016onalennapoha263No ratings yet
- Y20 jc2 Physics H2 Prelim MIDocument86 pagesY20 jc2 Physics H2 Prelim MIGigitaran LiemNo ratings yet
- 61 InequalitiesDocument40 pages61 InequalitiesshanthiNo ratings yet
- Canadian Association of Physicists 1999 Prize Exam Part A: Multiple ChoiceDocument5 pagesCanadian Association of Physicists 1999 Prize Exam Part A: Multiple Choiceelty TanNo ratings yet
- 4.4 Waves - Electromagnetic Waves QPDocument30 pages4.4 Waves - Electromagnetic Waves QPwillowchenchenNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure: Mcqs 4 Course OutlineDocument13 pagesAtomic Structure: Mcqs 4 Course OutlineMansoor SarwarNo ratings yet
- Model Set B (2080)Document6 pagesModel Set B (2080)gautamraman444No ratings yet
- AS Challenge 2017Document16 pagesAS Challenge 2017KrishnamohanNo ratings yet
- Foundations Forces Motion - MC QuestionsDocument18 pagesFoundations Forces Motion - MC QuestionslollolNo ratings yet
- Question Paper Breadth in PhysicsDocument28 pagesQuestion Paper Breadth in PhysicsRafay BilalNo ratings yet
- RevisionFinalExamPhysics2 2022 1Document4 pagesRevisionFinalExamPhysics2 2022 1221003ddtNo ratings yet
- 2017 CBSE Board XII Physics Paper SolDocument25 pages2017 CBSE Board XII Physics Paper SolAbhishek Saini100% (3)
- IAL Physics Unit 1 MCQ QP PDFDocument49 pagesIAL Physics Unit 1 MCQ QP PDFMir Faiyaz HossainNo ratings yet
- Triple Physics Higher Multiple Choice PractiseDocument14 pagesTriple Physics Higher Multiple Choice PractiseDominic Wynes-DevlinNo ratings yet
- 11th Full Book PaperDocument3 pages11th Full Book PaperAhsan KhanNo ratings yet
- 11 Physics23 24sp01Document18 pages11 Physics23 24sp01shagunarya71No ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument18 pagesPhysicsHarsh AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Final Model Paper Physics HSSC-I RevisedDocument7 pagesFinal Model Paper Physics HSSC-I ReviseddasddaNo ratings yet
- November 2020 QP - Paper 1 OCR (A) Physics A-LevelDocument32 pagesNovember 2020 QP - Paper 1 OCR (A) Physics A-LevelVaibhav MehraNo ratings yet
- 9702 m22+s22 P1Document65 pages9702 m22+s22 P1Zubair AhmadNo ratings yet
- James Ruse 2020 Physics Trials & SolutionsDocument59 pagesJames Ruse 2020 Physics Trials & Solutionsanew.name5245nNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: Physics 9702/12Document16 pagesCambridge International AS & A Level: Physics 9702/12Herman HermanNo ratings yet
- CombinepdfDocument308 pagesCombinepdfFurious GraveNo ratings yet
- 2020 Jrahs Physics Trial JrahsDocument40 pages2020 Jrahs Physics Trial Jrahsthinhandre12No ratings yet
- Dwnload Full Principles of Physics A Calculus Based Text 5th Edition Serway Solutions Manual PDFDocument36 pagesDwnload Full Principles of Physics A Calculus Based Text 5th Edition Serway Solutions Manual PDFimbreedjejunity.8hi2yz100% (14)
- Friday 09 October 2020 - Morning: A Level Physics ADocument32 pagesFriday 09 October 2020 - Morning: A Level Physics AJude PereraNo ratings yet
- Answers To Further Questions: in GCSE Physics For You (5th Edition)Document5 pagesAnswers To Further Questions: in GCSE Physics For You (5th Edition)Mencam AsongNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Sample Physics QN PaperDocument5 pagesClass 11 Sample Physics QN PaperAnish ShakyaNo ratings yet
- Physics 7Document2 pagesPhysics 7Ishan SubediNo ratings yet
- Physics SSC-II SolutionDocument9 pagesPhysics SSC-II SolutionFarhatullah Muhammad100% (1)
- Physics Ssc-Ii: Answer Sheet No.Document7 pagesPhysics Ssc-Ii: Answer Sheet No.Maryam KhanNo ratings yet
- SSC-II Physics (All Sets With Solutions) - CombinedDocument46 pagesSSC-II Physics (All Sets With Solutions) - CombinedNaveed Haider MirzaNo ratings yet
- Board PhysicsDocument9 pagesBoard PhysicsDurgesh Yadav100% (1)
- Barron's Physics Practice Plus: 400+ Online Questions and Quick Study ReviewFrom EverandBarron's Physics Practice Plus: 400+ Online Questions and Quick Study ReviewNo ratings yet
- Question Paper Unit b731 01 Modules b1 b2 b3 Foundation TierDocument28 pagesQuestion Paper Unit b731 01 Modules b1 b2 b3 Foundation Tieryufm2008No ratings yet
- Biology Paper 3 MSDocument8 pagesBiology Paper 3 MSyufm2008No ratings yet
- Mathematics Paper 1 QPDocument16 pagesMathematics Paper 1 QPyufm2008No ratings yet
- Ilovepdf MergedDocument25 pagesIlovepdf Mergedyufm2008No ratings yet
- Unit j257 03 Breadth in Biology Higher Tier Paper 3 Sample Assessment MaterialDocument52 pagesUnit j257 03 Breadth in Biology Higher Tier Paper 3 Sample Assessment Materialyufm2008No ratings yet
- PPSC Past Papers Chemistry MCQS: Malik XufyanDocument14 pagesPPSC Past Papers Chemistry MCQS: Malik XufyanchemistryNo ratings yet
- National Instruction 6 of 1999 Hazardous Substances PDFDocument6 pagesNational Instruction 6 of 1999 Hazardous Substances PDFAnonymous TVEog38No ratings yet
- DU-M.Sc. 2016Document8 pagesDU-M.Sc. 2016Abhishek PantNo ratings yet
- 1st Mock Test MDCAT-2021 - by RKian MCAT ServiceDocument15 pages1st Mock Test MDCAT-2021 - by RKian MCAT ServiceKhan100% (1)
- Waec Physics 2010 AnswersDocument12 pagesWaec Physics 2010 Answerssamuelakpuri5No ratings yet
- 2016 Specimen Paper 4 Mark SchemeDocument6 pages2016 Specimen Paper 4 Mark SchemeMaheerNo ratings yet
- Nuclei in One Shot - Class Notes - LEC-6 - PPT-6 - Physics - Nuclei - Vijeta Series - Kshitiz Kanik Sir - RAM NIWASDocument61 pagesNuclei in One Shot - Class Notes - LEC-6 - PPT-6 - Physics - Nuclei - Vijeta Series - Kshitiz Kanik Sir - RAM NIWASprajwal jhaNo ratings yet
- IMO Classes: Class 1: ExplosivesDocument6 pagesIMO Classes: Class 1: ExplosivesbertNo ratings yet
- Quantum & Atomic Physics (Eg Photoelectric Affect) Formula Sheet & Study Tool Physics ADocument2 pagesQuantum & Atomic Physics (Eg Photoelectric Affect) Formula Sheet & Study Tool Physics AMark Riley100% (2)
- Fallout Theme - GenesysDocument20 pagesFallout Theme - GenesysRoberto Padron100% (1)
- October November 23 Paper 12Document16 pagesOctober November 23 Paper 12avanishh914No ratings yet
- Car ScheduleDocument13 pagesCar Scheduledubai eyeNo ratings yet
- Pauli-Jung Letters - Atom and ArchetypeDocument313 pagesPauli-Jung Letters - Atom and ArchetypeMiguelAngelBroc100% (18)
- 19 SolutionsDocument8 pages19 SolutionsRainierGo0% (1)
- Module1 - Exponential FunctionsDocument28 pagesModule1 - Exponential Functionsstepharry08No ratings yet
- Full Download Nuclear Engineering Fundamentals A Practical Perspective 1st Masterson Solution Manual PDF Full ChapterDocument36 pagesFull Download Nuclear Engineering Fundamentals A Practical Perspective 1st Masterson Solution Manual PDF Full Chapterstraik.zetetics.yn5u100% (21)
- Answers & Solutions: For For For For For NEET (UG) Phase-II - 2016Document28 pagesAnswers & Solutions: For For For For For NEET (UG) Phase-II - 2016sumit kumarNo ratings yet
- Fizik K1+Skema Trial SPM SMK ST Luke Sri Aman 2019Document15 pagesFizik K1+Skema Trial SPM SMK ST Luke Sri Aman 2019David Chang0% (1)
- Level Ii QuestionsDocument19 pagesLevel Ii QuestionsAmit Sindhya0% (1)
- Pulse Chase ExperimentDocument7 pagesPulse Chase ExperimentNikhil Govind Bharambe50% (2)
- Modern Physics: Larry D. Buban, Ph.D. (Scied - Physics)Document47 pagesModern Physics: Larry D. Buban, Ph.D. (Scied - Physics)Hannah Grace Romano ViceralNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary EducationDocument20 pagesCambridge International General Certificate of Secondary EducationBeshkaNo ratings yet
- GCSE Physics SpecificationDocument36 pagesGCSE Physics SpecificationsheelahaiNo ratings yet
- 2020 MAM Manual 1 - Part 2 Revision ExercisesDocument127 pages2020 MAM Manual 1 - Part 2 Revision ExercisesHykal FaridNo ratings yet
- Basic ChemistryDocument13 pagesBasic ChemistryNurharis MunandarNo ratings yet
- Radiation Safety TrainingDocument118 pagesRadiation Safety TrainingZibiao SunNo ratings yet
- Physical Science LPDocument16 pagesPhysical Science LPHenno Nickole Vince A. BugtongNo ratings yet
J249 04 Paper Dec 17
J249 04 Paper Dec 17
Uploaded by
yufm2008Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
J249 04 Paper Dec 17
J249 04 Paper Dec 17
Uploaded by
yufm2008Copyright:
Available Formats
Oxford Cambridge and RSA
H
GCSE (9–1) Physics A (Gateway Science)
J249/04 Paper 4, P5 – P8 and P9 (Higher Tier)
Year 11 Test
Time allowed: 1 hour 45 minutes
You must have:
• a ruler (cm/mm)
• the Data Sheet for GCSE Physics A
You may use:
• a scientific or graphical calculator
• an HB pencil
First name
Last name
Centre Candidate
number number
INSTRUCTIONS
• Use black ink. You may use an HB pencil for graphs and diagrams.
• Complete the boxes above with your name, centre number and candidate number.
• Answer all the questions.
• Write your answer to each question in the space provided. Additional paper may be
used if required but you must clearly show your candidate number, centre number and
question number(s).
• Do not write in the barcodes.
INFORMATION
• The total mark for this paper is 90.
• The marks for each question are shown in brackets [ ].
• Quality of extended responses will be assessed in the questions marked with an
asterisk (*).
• This document consists of 24 pages.
© OCR 2017 Practice paper OCR is an exempt Charity
DC (KS/TP) 162084/5 Turn over
2
SECTION A
Answer all the questions.
1 Which sentence about electromagnetic waves is true?
A They are longitudinal waves, transmitted through space with the same velocity.
B They are transverse waves, transmitted through air with the same velocity.
C They are transverse waves, transmitted through space with different velocities.
D They are transverse waves, transmitted through space with the same velocity.
Your answer [1]
2 Light from other galaxies can be red-shifted.
Which sentence about red-shift is true?
A Light from galaxies moving away from us undergoes red-shift.
B Light from galaxies moving towards us undergoes red-shift.
C Nearby galaxies show more red-shift than distant galaxies.
D Stationary galaxies undergo red-shift.
Your answer [1]
3 Which row in the table about nuclear fission is true?
A Uranium-235 Hit by neutron Splits into smaller nuclei and more neutrons
B Uranium-235 Hit by proton Creates larger nuclei and fewer neutrons
C Uranium-235 Hit by electron Splits into smaller nuclei and more neutrons
D Uranium-235 Hit by neutron Creates larger nuclei and more neutrons
Your answer [1]
© OCR 2017 Practice paper J249/04
3
4 Which wave has the longest wavelength and is used in radiotherapy for cancer treatment?
A Gamma-ray
B Infrared
C Ultraviolet
D X-ray
Your answer [1]
5 A student wants to calculate the kinetic energy (KE) of a toy car.
Which equation does she use?
1
A KE = × mass × velocity
2
1
B KE = × mass × velocity × 2
2
1
C KE = × (mass × velocity)2
2
1
D KE = × mass × (velocity)2
2
Your answer [1]
© OCR 2017 Practice paper J249/04 Turn over
4
6 Which ray diagram shows the action of a strong concave lens?
Your answer [1]
© OCR 2017 Practice paper J249/04
5
7 Which sentence about the nuclear fusion of hydrogen is true?
A When hydrogen atomic nuclei join to make a large nucleus, energy is absorbed.
B When hydrogen atomic nuclei join to make a large nucleus, energy is emitted.
C When hydrogen atomic nuclei split to make a large nucleus, energy is emitted.
D When hydrogen atomic nuclei split to make a large nucleus, energy is absorbed.
Your answer [1]
8 A lorry accelerates from 0 km / h to 100 km / h in about 25 s.
Estimate the acceleration of the lorry.
A 1 m / s2
B 3 m / s2
C 6 m / s2
D 10 m / s2
Your answer [1]
9 Which statement describes Newton’s 3rd law of motion?
A Energy can be neither created or destroyed
B Every action has an equal and opposite reaction
C Force = mass × acceleration
D Objects with balanced forces acting on them will stay at rest, or in constant motion
Your answer [1]
10 Which formula is correct?
A Pressure (N) = force normal to a surface (N) / area of that surface (m3)
B Pressure (Pa) = force normal to a surface (kg) / area of that surface (m2)
C Pressure (Pa) = force normal to a surface (N) / area of that surface (m)
D Pressure (Pa) = force normal to a surface (N) / area of that surface (m2)
Your answer [1]
© OCR 2017 Practice paper J249/04 Turn over
6
11 Which sentence about pressure in liquids is correct?
A Pressure causes a net force at all angles to any surface.
B Pressure causes a net force at right angles to any surface.
C Pressure causes a net force downwards to any surface.
D Pressure causes a net force upwards on any surface.
Your answer [1]
12 A radio wave has a frequency of 3 × 106 Hz and a velocity of 3 × 108 m / s.
What is the wavelength of this radio wave?
A 1m
B 10 m
C 100 m
D 1000 m
Your answer [1]
13 A moving rocket has a velocity of 20 m / s and a momentum of 24 000 kgm / s.
Calculate the mass of the rocket.
A 48 000 kg
B 24 000 kg
C 12 000 kg
D 1200 kg
Your answer [1]
© OCR 2017 Practice paper J249/04
7
14 A lunar lander weighs 24 500 N on the moon and has a mass of 15 100 kg.
Calculate the gravitational field strength (g) on the surface of the moon.
A 0.616 m / s2
B 1.62 m / s2
C 10.00 m / s2
D 3.70 × 108 m / s2
Your answer [1]
15 A power supply provides 48 000 C of charge which transfers 24 000 J of energy to a circuit.
Calculate the voltage of the power supply.
A 0.5 V
B 2V
C 12 V
D 1.152 MV
Your answer [1]
© OCR 2017 Practice paper J249/04 Turn over
8
SECTION B
Answer all the questions.
16 Students in a class investigate stopping distances using bicycles.
They compare the stopping distances for one student riding a bicycle at different speeds.
Look at the results they collected.
Speed Thinking distance Braking distance Stopping distance
(m / s) (m) (m) (m)
2 1.6 1.2 2.8
4 3.2 4.8 8.0
6 4.8 10.8 15.6
8
(a) Describe how halving the speed affects the thinking distance.
...................................................................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................................................. [1]
(b) Describe how tripling (×3) the speed affects the braking distance.
...................................................................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................................................. [1]
(c) The student travels at a new speed. He has to brake suddenly.
The reaction time for the student is 0.8 s and the thinking distance is 7.2 m.
Use the formula: distance = speed × time
Calculate the initial speed of the student.
Answer = .................................................. m / s [2]
(d) The student now travels at 8 m / s.
Calculate the stopping distance at this new speed.
Answer = ..................................................... m [3]
© OCR 2017 Practice paper J249/04
9
(e) Five other students in the class measure their reaction time.
Look at their results.
Student Reaction time
(s)
A 0.82
B 0.77
C 0.78
D 0.83
E
The average reaction time for the students is 0.81 m / s.
Calculate the reaction time of student E.
Answer = ....................................................... s [2]
(f) It is difficult to measure the thinking distance for the student on the bicycle.
Suggest why.
...................................................................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................................................. [1]
(g) Name two different factors that may increase reaction time when riding a bicycle.
1 ................................................................................................................................................
2 ................................................................................................................................................
[2]
(h) Name two different factors that may increase braking distance when riding a bicycle.
1 ................................................................................................................................................
2 ................................................................................................................................................
[2]
© OCR 2017 Practice paper J249/04 Turn over
10
17 Our Sun formed from a large cloud of dust and gas in space.
Explain how this dust and gas changed to produce a star that is now in a long stable period of
energy production.
..........................................................................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................................................................
..................................................................................................................................................... [4]
© OCR 2017 Practice paper J249/04
11
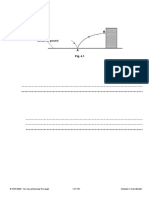
18 A rollercoaster car at A is lifted up the slope by an electric motor. It is lifted up the slope until it
reaches B.
Rollercoaster car B
E
C G
Pool of water
A
D F H
At B, the electric motor is switched off. The rollercoaster car rolls down the slope past C.
It continues its journey until it is slowed by the pool of water at H.
(a) Explain what happens to the energy stored by the rollercoaster car when it reaches the pool
of water at H.
...................................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................................................. [3]
(b) The highest part of the rollercoaster ride is B. Part G is lower than part E.
Explain why the height of the slope must reduce along the rollercoaster ride.
Use ideas about the conservation of energy in your answer.
...................................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................................................. [4]
(c) The rollercoaster car has a mass of 1200 kg. It gains 240 kJ of energy when lifted to B.
Calculate the height of the slope in metres (m).
The acceleration due to gravity (g) = 10 m / s2.
Answer = ..................................................... m [4]
© OCR 2017 Practice paper J249/04 Turn over
12
BLANK PAGE
© OCR 2017 Practice paper J249/04
13
19 This question is about radioactivity.
(a) Radon (Rn) is a radioactive element. It decays by emitting an alpha particle to form
polonium (Po). The polonium decays to lead (Pb) and then bismuth (Bi).
Complete the four spaces in the decay series.
4 4 0
α α .............
2 2 –1
220 ........... 212 ..........
Rn Po Pb Bi
86 84 82 ..........
[4]
(b) Carbon is an element. It has 6 protons in its nucleus.
Carbon-12, carbon-13 and carbon-14 are isotopes of carbon.
Complete the six spaces to show the differences between these isotopes of carbon.
carbon-12 carbon-13 carbon-14
................ ................ ................
C C C
................ ................ ................
[2]
© OCR 2017 Practice paper J249/04 Turn over
14
(c)* Carbon-14 is a radioactive isotope produced in the atmosphere by cosmic rays.
It is taken in by trees as they grow. When the trees die they stop taking in carbon-14.
The carbon-14 already in the trees decays.
Carbon-14 has a half-life of 5.73 × 103 years and is used to find the age of ancient trees.
Two scientists collect information about living and ancient trees. They examine the same size
samples from each tree.
Tree Type of tree Mass of carbon-14 Age of tree
in sample since death
(g) (years)
A Living tree 1.95 0
B Ancient tree 0.06
C Ancient tree 0.12
They have different conclusions about the data.
Scientist one – Tree C is the oldest as there is more carbon-14 left.
Scientist two – Tree B is the oldest. It is twice the age of tree C.
© OCR 2017 Practice paper J249/04
15
Use the data to evaluate the conclusions made by the two scientists and use the data to
determine the ages since death of trees B and C.
...................................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................................................. [6]
© OCR 2017 Practice paper J249/04 Turn over
16
20 This question is about energy generation in the UK.
(a) Power stations burn fuels to provide the kinetic energy needed to generate electricity.
(i) Look at the information about a coal power station.
10 000 MJ 3500 MJ
input from Coal power station useful
coal electrical
output
3500 MJ heat 3000 MJ heat lost through condensed steam.
lost through This goes into cooling towers and is dumped
chimney into the river.
Use the formula: efficiency = useful output energy transfer (J) ÷ input energy transfer (J)
Calculate the % of energy wasted by the coal power station.
Answer = ..................................................... % [3]
© OCR 2017 Practice paper J249/04
17
(ii) Community power stations are more efficient.
Look at the information about a community power station.
10 000 MJ 3500 MJ
input from Community power station useful
coal electrical
output
2600 MJ heat 3900 MJ heat used to heat
lost through homes, hospitals, public
chimney buildings and schools
Using the data, show how the efficiency of a community power station is more than
double the efficiency of a coal power station.
...........................................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................... [4]
(iii) Unfortunately, in the UK, there are very few community power stations.
Suggest why.
...........................................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................... [2]
© OCR 2017 Practice paper J249/04 Turn over
18
(b) Power stations use transformers to change the potential difference (p.d.).
Look at the diagram of a transformer.
Primary p.d. across the coils Secondary p.d. across the coils
= 20 000 V = 400 000 V
Primary coil = 520 turns Secondary coil
potential difference across primary coil number of turns in primary coil
Use the formula: =
potential difference across secondary coil number of turns in secondary coil
Calculate the number of turns in the secondary coil.
Answer = ......................................................... [3]
(c) This transformer changes the p.d. across the coils from 20 000 V to 400 000 V.
The transformer is designed to work in ambient temperatures up to 50 °C and must be
surrounded by oil.
(i) Suggest one reason why the transformer must be surrounded by oil.
...........................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................... [1]
© OCR 2017 Practice paper J249/04
19
(ii) Suggest why the temperature of 50 °C cannot be exceeded.
...........................................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................... [2]
(d) The national grid has power lines.
Electricity is sent through national grid power lines A and B.
Power line Potential difference Current Resistance Power loss
(V) (A) (Ω) (W)
A 400 000 250 3
B 275 000 5 000 80
(i) Calculate the power loss for each power line.
Power line A
Answer = .......................................................... W
Power line B
Answer = .......................................................... W
[4]
(ii) Explain why power line A, with a potential difference of 400 000 V, is usually used in the
national grid.
...........................................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................... [2]
© OCR 2017 Practice paper J249/04 Turn over
20
21 Mains electricity is used in homes to power the heater in a metal hair dryer.
The three wires used in mains electricity are:
• Live wire
• Neutral wire
• Earth wire.
Look at the simple diagram including the circuit for a heater in a metal hair dryer.
Switch in the
hair dryer
Fuse Live wire Heater
Mains switch Earth wire Neutral wire
in the plug connected to
socket metal case of
heater
If there is an electrical fault, the fuse and earth wire work together to keep the person using the
metal hair dryer safe. Explain how.
..........................................................................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................................................................
..................................................................................................................................................... [3]
© OCR 2017 Practice paper J249/04
21
22 A student uses energy from the Sun to heat cold water.
She puts cold water into a black teapot and measures the temperature of the water.
Thermometer
Infra-red waves
from the Sun
Black teapot
containing water
Look at the results she gets.
Temperature (°C)
45
20
0 200 Time (minutes)
(a) State why the water gets hotter in the first 200 minutes.
...................................................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................................. [1]
(b) Explain why the black teapot remains at a steady temperature after 200 minutes.
...................................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................................. [3]
© OCR 2017 Practice paper J249/04 Turn over
22
23 A student puts a trolley on a horizontal surface.
The trolley is at rest and has a string attached which runs over a pulley.
A force supplied by the weight makes the trolley move in the direction of the arrow.
Look at the diagram.
Trolley String
Pulley
Horizontal
surface
Weight
(a) Explain how the student could determine the acceleration of the trolley.
...................................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................................. [2]
© OCR 2017 Practice paper J249/04
23
(b) The student uses a 5 N weight (force) to pull the trolley.
He repeats the experiment a few times with trolleys of different masses and calculates the
average acceleration of each trolley.
Look at his results.
Force on string Mass of trolley Average acceleration
(N) (kg) (m / s2)
5 1.0 3.96
5 1.5 2.66
5 2.0 2.02
5 2.5 1.59
5 3.0 1.34
(i) Plot the five points for mass of trolley against average acceleration.
4.0
3.0
Average
acceleration
(m / s2) 2.0
1.0
0.0
0.0 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 3.0 3.5 4.0
Mass of trolley (kg)
[1]
(ii) Use the graph to estimate the acceleration of a 4 kg trolley.
Answer = ................................................ m / s2 [1]
© OCR 2017 Practice paper J249/04 Turn over
24
(iii) The student wants to improve his results.
The acceleration seems to be much lower than he expects.
Suggest two ways of improving his results so the acceleration is higher.
Improvement 1 ..................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................................
Improvement 2 ..................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................................
[2]
END OF QUESTION PAPER
Oxford Cambridge and RSA
Copyright Information
OCR is committed to seeking permission to reproduce all third-party content that it uses in its assessment materials. OCR has attempted to identify and contact all copyright holders
whose work is used in this paper. To avoid the issue of disclosure of answer-related information to candidates, all copyright acknowledgements are reproduced in the OCR Copyright
Acknowledgements Booklet. This is produced for each series of examinations and is freely available to download from our public website (www.ocr.org.uk) after the live examination series.
If OCR has unwittingly failed to correctly acknowledge or clear any third-party content in this assessment material, OCR will be happy to correct its mistake at the earliest possible
opportunity.
For queries or further information please contact the Copyright Team, First Floor, 9 Hills Road, Cambridge CB2 1GE.
OCR is part of the Cambridge Assessment Group; Cambridge Assessment is the brand name of University of Cambridge Local Examinations Syndicate (UCLES), which is itself a
department of the University of Cambridge.
© OCR 2017 Practice paper J249/04
You might also like
- WPH15 01 MSC 20210304Document16 pagesWPH15 01 MSC 20210304Little Wizard67% (3)
- Year 11 Prelim Exams PhysicsDocument22 pagesYear 11 Prelim Exams PhysicsTimothy KurbyNo ratings yet
- Astrophysical Plasmas Exam 2021Document8 pagesAstrophysical Plasmas Exam 2021SarbajitMannaNo ratings yet
- Nsaa s1 Specimen Explained AnswersDocument45 pagesNsaa s1 Specimen Explained AnswersKatia La PlacaNo ratings yet
- J249 03 Paper Dec 17Document24 pagesJ249 03 Paper Dec 17yufm2008No ratings yet
- J249 03 Paper Dec 17Document25 pagesJ249 03 Paper Dec 17yufm2008No ratings yet
- PAT 2006 Paper PDFDocument9 pagesPAT 2006 Paper PDFchjggfNo ratings yet
- Cluster Level Question Bank (Ahmedabad & Gandhinagar Cluster)Document33 pagesCluster Level Question Bank (Ahmedabad & Gandhinagar Cluster)manpreetsingh3458417No ratings yet
- Quantum Physics Exam Questions 69 QuestionsDocument145 pagesQuantum Physics Exam Questions 69 QuestionsVedant BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Friday 8 October 2021 - Morning: AS Level Physics ADocument20 pagesFriday 8 October 2021 - Morning: AS Level Physics ATankioNo ratings yet
- Unit h156 01 Breadth in Physics Sample Assessment MaterialsDocument44 pagesUnit h156 01 Breadth in Physics Sample Assessment Materialsmarjan familiNo ratings yet
- 702765 Topic Test Understanding ProcessesDocument22 pages702765 Topic Test Understanding Processesaidenflecky07No ratings yet
- H556-02 QP Jun22Document28 pagesH556-02 QP Jun22Vaibhav MehraNo ratings yet
- 4.4 Waves - Wave Motion QPDocument52 pages4.4 Waves - Wave Motion QPwill hayNo ratings yet
- Stars-Spectra Ch19 PDFDocument39 pagesStars-Spectra Ch19 PDFSaraii cgzzNo ratings yet
- Question Paper Unit h556 02 Exploring Physics PDFDocument32 pagesQuestion Paper Unit h556 02 Exploring Physics PDFHumaira MohungooNo ratings yet
- WPH15 01 MSC Jan-2022 UNUSEDDocument16 pagesWPH15 01 MSC Jan-2022 UNUSEDchemtrailsoverNo ratings yet
- wph15 01 Rms 20240307Document15 pageswph15 01 Rms 20240307shakera.khatun74No ratings yet
- January 2021 (IAL) MSDocument16 pagesJanuary 2021 (IAL) MSJannati Saba NawarNo ratings yet
- CBSE Board Paper Solution-2020Document51 pagesCBSE Board Paper Solution-2020SsNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 MCQ CollectionDocument11 pagesUnit 5 MCQ CollectionNirmani RodrigoNo ratings yet
- January 2023 MSDocument17 pagesJanuary 2023 MSSavva LazarevNo ratings yet
- Pat2015 PDFDocument22 pagesPat2015 PDFノエル ビクトリアNo ratings yet
- Marking Scheme Physics 10Document8 pagesMarking Scheme Physics 10Suleman AwanNo ratings yet
- JEE Main 2023 31st Jan Shift 1 QPDocument30 pagesJEE Main 2023 31st Jan Shift 1 QPhemantNo ratings yet
- Physical Sciences P1 Grade 11 Nov 2017 EngDocument18 pagesPhysical Sciences P1 Grade 11 Nov 2017 EngravenswayproNo ratings yet
- June 2016 QP - Paper 1 OCR (A) Physics AS-LevelDocument28 pagesJune 2016 QP - Paper 1 OCR (A) Physics AS-LevelDhanBahadurNo ratings yet
- Physics P1 2016Document15 pagesPhysics P1 2016onalennapoha263No ratings yet
- Y20 jc2 Physics H2 Prelim MIDocument86 pagesY20 jc2 Physics H2 Prelim MIGigitaran LiemNo ratings yet
- 61 InequalitiesDocument40 pages61 InequalitiesshanthiNo ratings yet
- Canadian Association of Physicists 1999 Prize Exam Part A: Multiple ChoiceDocument5 pagesCanadian Association of Physicists 1999 Prize Exam Part A: Multiple Choiceelty TanNo ratings yet
- 4.4 Waves - Electromagnetic Waves QPDocument30 pages4.4 Waves - Electromagnetic Waves QPwillowchenchenNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure: Mcqs 4 Course OutlineDocument13 pagesAtomic Structure: Mcqs 4 Course OutlineMansoor SarwarNo ratings yet
- Model Set B (2080)Document6 pagesModel Set B (2080)gautamraman444No ratings yet
- AS Challenge 2017Document16 pagesAS Challenge 2017KrishnamohanNo ratings yet
- Foundations Forces Motion - MC QuestionsDocument18 pagesFoundations Forces Motion - MC QuestionslollolNo ratings yet
- Question Paper Breadth in PhysicsDocument28 pagesQuestion Paper Breadth in PhysicsRafay BilalNo ratings yet
- RevisionFinalExamPhysics2 2022 1Document4 pagesRevisionFinalExamPhysics2 2022 1221003ddtNo ratings yet
- 2017 CBSE Board XII Physics Paper SolDocument25 pages2017 CBSE Board XII Physics Paper SolAbhishek Saini100% (3)
- IAL Physics Unit 1 MCQ QP PDFDocument49 pagesIAL Physics Unit 1 MCQ QP PDFMir Faiyaz HossainNo ratings yet
- Triple Physics Higher Multiple Choice PractiseDocument14 pagesTriple Physics Higher Multiple Choice PractiseDominic Wynes-DevlinNo ratings yet
- 11th Full Book PaperDocument3 pages11th Full Book PaperAhsan KhanNo ratings yet
- 11 Physics23 24sp01Document18 pages11 Physics23 24sp01shagunarya71No ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument18 pagesPhysicsHarsh AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Final Model Paper Physics HSSC-I RevisedDocument7 pagesFinal Model Paper Physics HSSC-I ReviseddasddaNo ratings yet
- November 2020 QP - Paper 1 OCR (A) Physics A-LevelDocument32 pagesNovember 2020 QP - Paper 1 OCR (A) Physics A-LevelVaibhav MehraNo ratings yet
- 9702 m22+s22 P1Document65 pages9702 m22+s22 P1Zubair AhmadNo ratings yet
- James Ruse 2020 Physics Trials & SolutionsDocument59 pagesJames Ruse 2020 Physics Trials & Solutionsanew.name5245nNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: Physics 9702/12Document16 pagesCambridge International AS & A Level: Physics 9702/12Herman HermanNo ratings yet
- CombinepdfDocument308 pagesCombinepdfFurious GraveNo ratings yet
- 2020 Jrahs Physics Trial JrahsDocument40 pages2020 Jrahs Physics Trial Jrahsthinhandre12No ratings yet
- Dwnload Full Principles of Physics A Calculus Based Text 5th Edition Serway Solutions Manual PDFDocument36 pagesDwnload Full Principles of Physics A Calculus Based Text 5th Edition Serway Solutions Manual PDFimbreedjejunity.8hi2yz100% (14)
- Friday 09 October 2020 - Morning: A Level Physics ADocument32 pagesFriday 09 October 2020 - Morning: A Level Physics AJude PereraNo ratings yet
- Answers To Further Questions: in GCSE Physics For You (5th Edition)Document5 pagesAnswers To Further Questions: in GCSE Physics For You (5th Edition)Mencam AsongNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Sample Physics QN PaperDocument5 pagesClass 11 Sample Physics QN PaperAnish ShakyaNo ratings yet
- Physics 7Document2 pagesPhysics 7Ishan SubediNo ratings yet
- Physics SSC-II SolutionDocument9 pagesPhysics SSC-II SolutionFarhatullah Muhammad100% (1)
- Physics Ssc-Ii: Answer Sheet No.Document7 pagesPhysics Ssc-Ii: Answer Sheet No.Maryam KhanNo ratings yet
- SSC-II Physics (All Sets With Solutions) - CombinedDocument46 pagesSSC-II Physics (All Sets With Solutions) - CombinedNaveed Haider MirzaNo ratings yet
- Board PhysicsDocument9 pagesBoard PhysicsDurgesh Yadav100% (1)
- Barron's Physics Practice Plus: 400+ Online Questions and Quick Study ReviewFrom EverandBarron's Physics Practice Plus: 400+ Online Questions and Quick Study ReviewNo ratings yet
- Question Paper Unit b731 01 Modules b1 b2 b3 Foundation TierDocument28 pagesQuestion Paper Unit b731 01 Modules b1 b2 b3 Foundation Tieryufm2008No ratings yet
- Biology Paper 3 MSDocument8 pagesBiology Paper 3 MSyufm2008No ratings yet
- Mathematics Paper 1 QPDocument16 pagesMathematics Paper 1 QPyufm2008No ratings yet
- Ilovepdf MergedDocument25 pagesIlovepdf Mergedyufm2008No ratings yet
- Unit j257 03 Breadth in Biology Higher Tier Paper 3 Sample Assessment MaterialDocument52 pagesUnit j257 03 Breadth in Biology Higher Tier Paper 3 Sample Assessment Materialyufm2008No ratings yet
- PPSC Past Papers Chemistry MCQS: Malik XufyanDocument14 pagesPPSC Past Papers Chemistry MCQS: Malik XufyanchemistryNo ratings yet
- National Instruction 6 of 1999 Hazardous Substances PDFDocument6 pagesNational Instruction 6 of 1999 Hazardous Substances PDFAnonymous TVEog38No ratings yet
- DU-M.Sc. 2016Document8 pagesDU-M.Sc. 2016Abhishek PantNo ratings yet
- 1st Mock Test MDCAT-2021 - by RKian MCAT ServiceDocument15 pages1st Mock Test MDCAT-2021 - by RKian MCAT ServiceKhan100% (1)
- Waec Physics 2010 AnswersDocument12 pagesWaec Physics 2010 Answerssamuelakpuri5No ratings yet
- 2016 Specimen Paper 4 Mark SchemeDocument6 pages2016 Specimen Paper 4 Mark SchemeMaheerNo ratings yet
- Nuclei in One Shot - Class Notes - LEC-6 - PPT-6 - Physics - Nuclei - Vijeta Series - Kshitiz Kanik Sir - RAM NIWASDocument61 pagesNuclei in One Shot - Class Notes - LEC-6 - PPT-6 - Physics - Nuclei - Vijeta Series - Kshitiz Kanik Sir - RAM NIWASprajwal jhaNo ratings yet
- IMO Classes: Class 1: ExplosivesDocument6 pagesIMO Classes: Class 1: ExplosivesbertNo ratings yet
- Quantum & Atomic Physics (Eg Photoelectric Affect) Formula Sheet & Study Tool Physics ADocument2 pagesQuantum & Atomic Physics (Eg Photoelectric Affect) Formula Sheet & Study Tool Physics AMark Riley100% (2)
- Fallout Theme - GenesysDocument20 pagesFallout Theme - GenesysRoberto Padron100% (1)
- October November 23 Paper 12Document16 pagesOctober November 23 Paper 12avanishh914No ratings yet
- Car ScheduleDocument13 pagesCar Scheduledubai eyeNo ratings yet
- Pauli-Jung Letters - Atom and ArchetypeDocument313 pagesPauli-Jung Letters - Atom and ArchetypeMiguelAngelBroc100% (18)
- 19 SolutionsDocument8 pages19 SolutionsRainierGo0% (1)
- Module1 - Exponential FunctionsDocument28 pagesModule1 - Exponential Functionsstepharry08No ratings yet
- Full Download Nuclear Engineering Fundamentals A Practical Perspective 1st Masterson Solution Manual PDF Full ChapterDocument36 pagesFull Download Nuclear Engineering Fundamentals A Practical Perspective 1st Masterson Solution Manual PDF Full Chapterstraik.zetetics.yn5u100% (21)
- Answers & Solutions: For For For For For NEET (UG) Phase-II - 2016Document28 pagesAnswers & Solutions: For For For For For NEET (UG) Phase-II - 2016sumit kumarNo ratings yet
- Fizik K1+Skema Trial SPM SMK ST Luke Sri Aman 2019Document15 pagesFizik K1+Skema Trial SPM SMK ST Luke Sri Aman 2019David Chang0% (1)
- Level Ii QuestionsDocument19 pagesLevel Ii QuestionsAmit Sindhya0% (1)
- Pulse Chase ExperimentDocument7 pagesPulse Chase ExperimentNikhil Govind Bharambe50% (2)
- Modern Physics: Larry D. Buban, Ph.D. (Scied - Physics)Document47 pagesModern Physics: Larry D. Buban, Ph.D. (Scied - Physics)Hannah Grace Romano ViceralNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary EducationDocument20 pagesCambridge International General Certificate of Secondary EducationBeshkaNo ratings yet
- GCSE Physics SpecificationDocument36 pagesGCSE Physics SpecificationsheelahaiNo ratings yet
- 2020 MAM Manual 1 - Part 2 Revision ExercisesDocument127 pages2020 MAM Manual 1 - Part 2 Revision ExercisesHykal FaridNo ratings yet
- Basic ChemistryDocument13 pagesBasic ChemistryNurharis MunandarNo ratings yet
- Radiation Safety TrainingDocument118 pagesRadiation Safety TrainingZibiao SunNo ratings yet
- Physical Science LPDocument16 pagesPhysical Science LPHenno Nickole Vince A. BugtongNo ratings yet