Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ortega, Beverly Bea. Activity-1
Ortega, Beverly Bea. Activity-1
Uploaded by
Beverly OrtegaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ortega, Beverly Bea. Activity-1
Ortega, Beverly Bea. Activity-1
Uploaded by
Beverly OrtegaCopyright:
Available Formats
Orrega, Beverly Bea D.
BSHM 3D
Statistics: Activity 1
Introduction to Statistics
Answer the following:
A. Classify whether the following situations will make use of descriptive or inferential statistics.
Write your answer before the number.
Descriptive Statistics1. A sari-sari store owner computes her daily sales.
Descriptive Statistics2. A mother recorded their monthly expenses.
Inferential Statistics 3. A psychologist investigates if there is a significant relationship between
the size of the head and the IQ score.
Descriptive Statistics 4. The secretary of department posted the list of students who qualified for
dean’s lister.
Inferential Statistics 5. A psychometrician studies whether there is a significant difference
between the grade of students who watch anime and who did not watch anime.
B. Tell whether the following is quantitative or qualitative data:
Qualitative 1. Civil Status
Qualitative 2. Color of the eyes
Quantitative 3. Number of bags
Qualitative 4. Military ranks
Quantitative 5. Suicide rates
Qualitative 6. Cellphone numbers
Quantitative 7. Age of teachers
Qualitative 8. Kinds of books
Quantitative 9. Income
Quantitative 10. Score in exam
C. Identify each of the following as discrete of continuous:
Continuous Variable1. Speed of tricycle
Continuous Variable2. Volume of water
Continuous Variable 3. Length of room
Discrete Variable 4. Number of books
Discrete Variable 5. Number of customers in a shop.
D. Determine the scale of measurement for each of the following
Nominal 1. Brand of bags Nominal 6. Language
Ratio 2. Weight Interval 7. Temperature
Nominal 3. Nationality Ordinal 8. Academic Rank
Nominal 4. Kinds of works Ratio 9. Distance
Nominal 5. Course of student Ratio 10. Average Salary
E. A researcher would like to investigate the perception of students of Psychology major about the
issue of suicide. He divided the population based on the year of the student
1. Use stratified random sampling if the sampling to be drawn consists of 500 students.
2. Compute for the sample size using Slovin’s formula with 5% of margin of error and use it
for construction of strata.
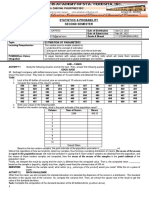
1.
Number of Students Percentage Number of the Student
in the sample
First Year 2,500 500/2500= 0.2 0.2 (500)= 100
Second Year 1,500 500/1500= 0.33 0.33(500)= 165
Third year 1,500 500/1500= 0.33 0.33(500)=165
Fourth Year 1,000 500/1000= 0.5 0.5 (500)= 250
Number of Students Percentage Number of the Student
in the sample
First Year 2,000 500/2000= 0.25 0.25(500)= 125
Second Year 1,500 500/1500=0.33 0.33(500)=165
Third Year 1,500 500/1500=0.33 0.33(500)=165
Fourth Year 1,000 500/1000=0.5 0.5(500)= 250
2. Slovin Formula
1 2
2500/(1+(2500)(0.05)²) 2000/(1+(2000)(0.05)²)
2500/(1+(2500)(0.0025)) 2000/(1+(2000)(0.0025))
2500/(1+6.25) 2000/(1+5)
2500/7.25 2000/6
=344.83 =333.33
1500/(1+(1500)(0.05)²) 1500/(1+(1500)(0.05)²)
1500/(1+(1500)(0.0025)) 1500/(1+(1500)(0.0025))
1500/(1+3.75) 1500/(1+3.75)
1500/4.75 1500/4.75
=315.79 =315.79
1500/(1+(1500)(0.05)²) 1500/(1+(1500)(0.05)²)
1500/(1+(1500)(0.0025)) 1500/(1+(1500)(0.0025))
1500/(1+3.75) 1500/(1+3.75)
1500/4.75 1500/4.75
=315.79 =315.79
1000/(1+(1000)(0.05)²) 1000/(1+(1000)(0.05)²)
1000/(1+(1000)(0.0025)) 1000/(1+(1000)(0.0025))
1000/(1+2.5) 1000/(1+2.5)
1000/3.5 1000/3.5
=285.71 =285.71
You might also like
- 2621 - Free Numerical Reasoning Test Questions Answers PDFDocument18 pages2621 - Free Numerical Reasoning Test Questions Answers PDFMartha Veraida SilaenNo ratings yet
- Statistics - Probability - Q3 - Mod7 - Percentile and T-DistributionDocument23 pagesStatistics - Probability - Q3 - Mod7 - Percentile and T-DistributionSheebei Sheebei83% (29)
- Olympiad Sample Paper 2: Useful for Olympiad conducted at School, National & International levelsFrom EverandOlympiad Sample Paper 2: Useful for Olympiad conducted at School, National & International levelsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- Freud Eros and ThanatosDocument5 pagesFreud Eros and Thanatossicoastrologo_5No ratings yet
- Basics of English Speaking For Workplace RevisedDocument170 pagesBasics of English Speaking For Workplace Revisedravi96100% (4)
- It Is Quite True That Man Lives by Bread AloneDocument4 pagesIt Is Quite True That Man Lives by Bread AloneReham PNo ratings yet
- Epanto - Designing & Planning Phase ExercisesDocument2 pagesEpanto - Designing & Planning Phase ExercisesCharmagne Joci EpantoNo ratings yet
- SYLLABUS OF 7th CLASS 2010Document30 pagesSYLLABUS OF 7th CLASS 2010kapilfreindNo ratings yet
- Std06 II MSSS EM PDFDocument112 pagesStd06 II MSSS EM PDFspsarathyNo ratings yet
- Mathematics: Quarter 4: Week 6-8Document28 pagesMathematics: Quarter 4: Week 6-8Larry MarNo ratings yet
- Statistics: Lesson 5Document11 pagesStatistics: Lesson 5Mark Jether GasmenNo ratings yet
- 6 STD Text Book Part 2Document112 pages6 STD Text Book Part 2Parthasarathy SeshadriNo ratings yet
- Slovins FormulaDocument20 pagesSlovins FormulashimissNo ratings yet
- LM9 Stat&probab TasksDocument2 pagesLM9 Stat&probab TaskskhlneNo ratings yet
- Mba ProjectsDocument19 pagesMba ProjectsGowsic RoolzNo ratings yet
- Stat and Prob Set ADocument20 pagesStat and Prob Set AAubrey CasocoNo ratings yet
- The Aga Khan University Sample Test Paper 2020 Graduate Programme Section I English Time Allowed: 1 HourDocument12 pagesThe Aga Khan University Sample Test Paper 2020 Graduate Programme Section I English Time Allowed: 1 HourDost Ali Deedar AliNo ratings yet
- The Aga Khan University Sample Test Paper 2020 Graduate Programme Section I English Time Allowed: 1 HourDocument11 pagesThe Aga Khan University Sample Test Paper 2020 Graduate Programme Section I English Time Allowed: 1 HourswasahmedNo ratings yet
- Problem Solving 1 Sampling Techniques: First Semester 2018 - 2019Document6 pagesProblem Solving 1 Sampling Techniques: First Semester 2018 - 2019John Louie NunezNo ratings yet
- GE 4 MMW Reviewer AutosavedDocument12 pagesGE 4 MMW Reviewer AutosavedKyle SarcosNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper - PHD Agh KhanDocument11 pagesSample Paper - PHD Agh KhanSayed Faraz Ali ShahNo ratings yet
- Mba201 Action ResearchDocument14 pagesMba201 Action ResearchRiz ZhaNo ratings yet
- Data Interpretation For SBI PO - 2014Document3 pagesData Interpretation For SBI PO - 2014Furin KatoNo ratings yet
- Instructional Module in Statistics and Probability For ResearchDocument5 pagesInstructional Module in Statistics and Probability For ResearchKatlyn FaithNo ratings yet
- Olympiad Sample Paper 5: Useful for Olympiad conducted at School, National & International levelsFrom EverandOlympiad Sample Paper 5: Useful for Olympiad conducted at School, National & International levelsNo ratings yet
- Math10 q4 Week8 Hybrid Version2Document17 pagesMath10 q4 Week8 Hybrid Version2Hanna Ciubal HonradeNo ratings yet
- Exam MLC 2013 FallDocument54 pagesExam MLC 2013 Fallsteellord123No ratings yet
- Wipro Model Placement PaperDocument24 pagesWipro Model Placement PaperSakshi KirpalaniNo ratings yet
- Sampling Technique SDocument18 pagesSampling Technique Sjoseph dave pregonerNo ratings yet
- Statistics and Probability: Learner'S Activity Sheet Quarter 3 - Week 5: Sampling Distribution of Sample MeansDocument10 pagesStatistics and Probability: Learner'S Activity Sheet Quarter 3 - Week 5: Sampling Distribution of Sample MeansRuben100% (1)
- Semi Detailed Lesson Plan in Stat. & Prob 11Document6 pagesSemi Detailed Lesson Plan in Stat. & Prob 11Marinella Mauro100% (1)
- Math 6 DLP 4 - Naming A Decimal For A Given Model - Region - Blocks, Money, Number Line and GridDocument8 pagesMath 6 DLP 4 - Naming A Decimal For A Given Model - Region - Blocks, Money, Number Line and GridZyreen Joy ServanesNo ratings yet
- 5.1 Ratio and ProportionDocument5 pages5.1 Ratio and ProportionXiaolinChenNo ratings yet
- Saurav ExamDocument9 pagesSaurav ExamShrijan BasnetNo ratings yet
- 3rd Periodical Examination in Mathematics 5Document3 pages3rd Periodical Examination in Mathematics 5klia.1No ratings yet
- Module 1Document43 pagesModule 1Jypsy PardillaNo ratings yet
- Std06 II MSSS EM 1Document48 pagesStd06 II MSSS EM 1vino5boraNo ratings yet
- StatsDocument12 pagesStatsdeez nutsNo ratings yet
- Math HandoutDocument4 pagesMath Handoutdennis delrosarioNo ratings yet
- Numerical Test Questions AnswersDocument18 pagesNumerical Test Questions AnswersVivian Law50% (2)
- ...Document11 pages...Kaira SabieNo ratings yet
- Math6 Q1 Module4Document28 pagesMath6 Q1 Module4Aslainie D. CasarNo ratings yet
- Statistics and Probability 7Document23 pagesStatistics and Probability 7zeromanzaxNo ratings yet
- General Mathematics: Quarter 1 - Module 5Document22 pagesGeneral Mathematics: Quarter 1 - Module 5April Grace Montebano100% (1)
- Cse Mock Exam (Edited)Document21 pagesCse Mock Exam (Edited)kayNo ratings yet
- Chichewa STD 8 District Mock 2023Document8 pagesChichewa STD 8 District Mock 2023fickyboy713No ratings yet
- Sample Size Thru Slovin's PDFDocument8 pagesSample Size Thru Slovin's PDFCyndy VillapandoNo ratings yet
- Generating Patterns LP1Document5 pagesGenerating Patterns LP1cynthia palisocNo ratings yet
- Statistics and Probability RANDOM SAMPLINGDocument8 pagesStatistics and Probability RANDOM SAMPLINGfaith marceloNo ratings yet
- Stat ProbDocument22 pagesStat ProbEmpreomNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Lesson 1Document39 pagesChapter 4 Lesson 1Ikay RicarteNo ratings yet
- Stat - Prob 11 - Q3 - SLM - WK5Document12 pagesStat - Prob 11 - Q3 - SLM - WK5Angelica CamaraoNo ratings yet
- Olympiad Sample Paper 3: Useful for Olympiad conducted at School, National & International levelsFrom EverandOlympiad Sample Paper 3: Useful for Olympiad conducted at School, National & International levelsRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Summative Test Set BDocument1 pageSummative Test Set BRobert UmandalNo ratings yet
- Edu 2012 11 MLC ExamDocument54 pagesEdu 2012 11 MLC Examcorlears56No ratings yet
- Writing Level 1Document69 pagesWriting Level 1tranngoc21122004No ratings yet
- INFERENCIAL ACTIVITIES MAED UpdatedDocument14 pagesINFERENCIAL ACTIVITIES MAED UpdatedMel Rose CabreraNo ratings yet
- UK Colleges Told To Be Truthful About Online Lessons, EBAU TestDocument3 pagesUK Colleges Told To Be Truthful About Online Lessons, EBAU TestGaraNo ratings yet
- Professional Writing Textbook For EFLDocument32 pagesProfessional Writing Textbook For EFLbaedaebokNo ratings yet
- Hemh105 PDFDocument20 pagesHemh105 PDFhoneygarg1986No ratings yet
- Statistics Probability Q4 Mod3 Test Statistic On Population MeanDocument28 pagesStatistics Probability Q4 Mod3 Test Statistic On Population MeanYsabel Villanueva100% (1)
- GR 7 Summer H.WDocument33 pagesGR 7 Summer H.WfatzimaNo ratings yet
- Math 2 Lesson 6Document13 pagesMath 2 Lesson 6Marc Graham NacuaNo ratings yet
- Journal of Cleaner Production: ReviewDocument13 pagesJournal of Cleaner Production: ReviewChristy SetiawanNo ratings yet
- Web Hosting Server DetailsDocument11 pagesWeb Hosting Server DetailsTarun VBRSITNo ratings yet
- Elimination Round Level Questions AnswersDocument4 pagesElimination Round Level Questions AnswersThắng Thông TháiNo ratings yet
- Exercise 2.6Document4 pagesExercise 2.6mohitgaba19No ratings yet
- Report On Military Justice SystemDocument79 pagesReport On Military Justice SystemWarren Wyndell DP SarsagatNo ratings yet
- Salaria v. Buenviaje G.R. No. L 45642 DIGESTDocument2 pagesSalaria v. Buenviaje G.R. No. L 45642 DIGESTMikee BornforThis MirasolNo ratings yet
- A Little Guide To Academic Writing Skills 2009Document11 pagesA Little Guide To Academic Writing Skills 2009Ramona AmorasNo ratings yet
- Motion Modifying The Freeze of AssetsDocument4 pagesMotion Modifying The Freeze of AssetsThe Daily SentinelNo ratings yet
- Effective Written CommunicationDocument10 pagesEffective Written CommunicationFilja JohnNo ratings yet
- 2015 Eccentric or Concentric Exercises For The Treatment of Tendinopathies...Document11 pages2015 Eccentric or Concentric Exercises For The Treatment of Tendinopathies...Castro WeithNo ratings yet
- Corporate Communication - Unit 3Document37 pagesCorporate Communication - Unit 3Hạnh LinhNo ratings yet
- Dashamgranth ChhandasDocument12 pagesDashamgranth ChhandassomapriyNo ratings yet
- Semantic Configuration of Sexist Idioms: Radical Networks and Cultural ScriptsDocument7 pagesSemantic Configuration of Sexist Idioms: Radical Networks and Cultural ScriptsgangancristinaNo ratings yet
- MS07 Combined PDFDocument322 pagesMS07 Combined PDFSarin John SkariaNo ratings yet
- When Marnie Was ThereDocument2 pagesWhen Marnie Was ThereChloie Marie Rosalejos0% (1)
- Parental Socialization, Peer Influence, Self Control and Financial Literacy As Determinants of Saving Behavior of The Workforce of A State College in Davao de OroDocument11 pagesParental Socialization, Peer Influence, Self Control and Financial Literacy As Determinants of Saving Behavior of The Workforce of A State College in Davao de OroPsychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary JournalNo ratings yet
- Attock Refinery FM Assignment#3Document13 pagesAttock Refinery FM Assignment#3Vishal MalhiNo ratings yet
- The Prevalence of Musculoskeletal Disorders and Their Association With Risk Factors in Auto Rickshaw Drivers - A Survey in Guntur CityDocument8 pagesThe Prevalence of Musculoskeletal Disorders and Their Association With Risk Factors in Auto Rickshaw Drivers - A Survey in Guntur CityijphyNo ratings yet
- The Theory of Unemployment by Professor A. C. PigouDocument21 pagesThe Theory of Unemployment by Professor A. C. PigouMathias MachadoNo ratings yet
- Cse SyllabusDocument34 pagesCse SyllabusVaishnavi MittalNo ratings yet
- The Relationship Between Introverted Student Behavior and TeacherDocument83 pagesThe Relationship Between Introverted Student Behavior and TeacherJulline Althea PorcadillaNo ratings yet
- Let Gen Ed Preboard 2015Document21 pagesLet Gen Ed Preboard 2015nicaella pedroNo ratings yet
- Qatar National Physical Activity GuidelinesDocument97 pagesQatar National Physical Activity GuidelinesMohammed BadieNo ratings yet
- Chemistry PG 2015 Admn On05sept2015Document96 pagesChemistry PG 2015 Admn On05sept2015ZiyadNo ratings yet
- CPBFI - 2.0 - Online - Lesson 7-Session 1Document11 pagesCPBFI - 2.0 - Online - Lesson 7-Session 1Mahima SonsareNo ratings yet
- Tpa Task 2 Final - ShafferDocument3 pagesTpa Task 2 Final - Shafferapi-608197412No ratings yet
- 0607 s15 QP 42Document20 pages0607 s15 QP 42Philip WhiteNo ratings yet