Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 viewsNetwork
Network
Uploaded by
robigew824DNS maps domain names to IP addresses to make it easier for humans to identify machines. It is a distributed and hierarchical system necessary because a centralized directory would be too large and prone to failure. DNS uses primary and secondary servers that maintain zones of the domain name space and perform name lookups by either recursively or iteratively querying other servers. Caching is used to optimize the process.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Cryptool LabDocument11 pagesCryptool Labimbo9No ratings yet
- Application Layer Unit 7 Cse 3Document83 pagesApplication Layer Unit 7 Cse 3VADAPALLY PRAVEEN KUMARNo ratings yet
- CN - 5Document37 pagesCN - 5SivaRamanNo ratings yet
- Computer NetworksDocument22 pagesComputer NetworksRISHINo ratings yet
- Unit-5 Q&ADocument16 pagesUnit-5 Q&AMunawar MohammedNo ratings yet
- ASCII Strings Into Network Addresses.: How DNS WorksDocument6 pagesASCII Strings Into Network Addresses.: How DNS WorksAnup PaulNo ratings yet
- Application LayerDocument42 pagesApplication LayerAnubhav KumarNo ratings yet
- Unit-V CNDocument35 pagesUnit-V CNchinnupyariNo ratings yet
- Application Layer: Prepared byDocument35 pagesApplication Layer: Prepared byIhab AmerNo ratings yet
- Computer Networks (1) - 157-172Document16 pagesComputer Networks (1) - 157-172Harini VelrajNo ratings yet
- Computer Networks - Unit - 5 Y3/S5: Unit - V Application LayerDocument32 pagesComputer Networks - Unit - 5 Y3/S5: Unit - V Application LayerSanthosh RockyNo ratings yet
- Lecture 17-DNS, Email, Telnet, FTP, SNMPDocument10 pagesLecture 17-DNS, Email, Telnet, FTP, SNMPyesmuraliNo ratings yet
- WINSEM2020-21 CSE1004 ETH VL2020210504039 Reference Material I 20-May-2021 Application LayerDocument44 pagesWINSEM2020-21 CSE1004 ETH VL2020210504039 Reference Material I 20-May-2021 Application LayerDivij BahlNo ratings yet
- CN Tutorial 5Document15 pagesCN Tutorial 5Hîмanî JayasNo ratings yet
- UNIT - II - Computer NetworksDocument8 pagesUNIT - II - Computer Networkssankalpsamant2001No ratings yet
- Unit 5 CNDocument19 pagesUnit 5 CNnavya goneNo ratings yet
- Computer Networks Administration, Strong Understanding of TCP/IP, DNS, Network Routing/switching, and Network Best Practices For Complex EnvironmentsDocument14 pagesComputer Networks Administration, Strong Understanding of TCP/IP, DNS, Network Routing/switching, and Network Best Practices For Complex EnvironmentsAlex LucaNo ratings yet
- Protocols & ApplicationDocument32 pagesProtocols & ApplicationS M AkashNo ratings yet
- Domain Name SystemDocument11 pagesDomain Name SystemJeng DevNo ratings yet
- Application Layer ProtocolsDocument33 pagesApplication Layer ProtocolsSarah AliNo ratings yet
- CN Unit-5Document14 pagesCN Unit-5dhosheka123No ratings yet
- Unit 5: The Above Figure Is An Example To ShowDocument18 pagesUnit 5: The Above Figure Is An Example To ShowDeepti SinghNo ratings yet
- CN Unit V R18Document27 pagesCN Unit V R18Sahithi Priya AttiliNo ratings yet
- CCNA 1 Chapter 3 SummaryDocument6 pagesCCNA 1 Chapter 3 SummaryzanarutoNo ratings yet
- Traditional Applications - Electronic Mail (SMTP, POP3, IMAP, MIME) - HTTP - Web Services - DNS-SNMPDocument39 pagesTraditional Applications - Electronic Mail (SMTP, POP3, IMAP, MIME) - HTTP - Web Services - DNS-SNMPanish.t.pNo ratings yet
- The Application Layer Includes The Following FunctionsDocument15 pagesThe Application Layer Includes The Following FunctionsCaptain AmericaNo ratings yet
- Unit-V: Dns-Domain Name SpaceDocument33 pagesUnit-V: Dns-Domain Name SpaceMr.T.Vijayakumar Assistant ProfessorNo ratings yet
- Cube Notes For DNSDocument17 pagesCube Notes For DNSoli_via_roNo ratings yet
- Unit 4Document16 pagesUnit 4anjworl3614No ratings yet
- Presentation Layer & Session LayerDocument45 pagesPresentation Layer & Session LayertopherskiNo ratings yet
- Application LayerDocument21 pagesApplication Layerrajpurohitpriyanshi2511No ratings yet
- Cse3039 Module 7Document134 pagesCse3039 Module 7jtrttttttttttttttttttttttNo ratings yet
- Computer Networks UNIT 5Document21 pagesComputer Networks UNIT 5thefamousbro123No ratings yet
- Application layer-DNS, E-MailDocument24 pagesApplication layer-DNS, E-MailVenkata Ganesh GorlaNo ratings yet
- Application Layer - Email-DNSDocument33 pagesApplication Layer - Email-DNSJimmi NadapdapNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 CNDocument28 pagesUnit 5 CNkumargpj7091No ratings yet
- BSC IT 63 Advanced Computer NetworksDocument24 pagesBSC IT 63 Advanced Computer NetworksAshutosh SaraswatNo ratings yet
- Unit-1.2 Internet and World Wide WebDocument40 pagesUnit-1.2 Internet and World Wide Webco22352No ratings yet
- Lecture2 DOMAIN NAME SYSTEM (DNS) Part 1Document22 pagesLecture2 DOMAIN NAME SYSTEM (DNS) Part 1Kas7W 5kNo ratings yet
- DNS (Domain Name Service) - TCP and Udp 53: The Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP)Document13 pagesDNS (Domain Name Service) - TCP and Udp 53: The Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP)Suraj Singh RajputNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 CNDocument73 pagesUnit 5 CNnikitha.veeramalluNo ratings yet
- Unit VDocument22 pagesUnit V20H51A04P3-PEDAPUDI SHAKTHI GANESH B.Tech ECE (2020-24)No ratings yet
- CSMA (Carrier Sense Multiple Access)Document4 pagesCSMA (Carrier Sense Multiple Access)Mahi sharmaNo ratings yet
- Assg 11 - DNS LOOPK UPDocument5 pagesAssg 11 - DNS LOOPK UP2108 Aniket BankapurNo ratings yet
- CN5Document11 pagesCN5ECE 3 VNRNo ratings yet
- CN Manual A11Document5 pagesCN Manual A11Sneha KanwadeNo ratings yet
- CN Unit 5Document38 pagesCN Unit 533 ABHISHEK WAGHNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 CNDocument73 pagesUnit 5 CNHemasai 6909No ratings yet
- Presentation Layer & Session LayerDocument51 pagesPresentation Layer & Session LayerAnonymous fp8NP80% (1)
- Unit-5 Computer NetworkDocument10 pagesUnit-5 Computer NetworkShivansh tomarNo ratings yet
- Au Satdns PDFDocument12 pagesAu Satdns PDFFrance CalNo ratings yet
- Application ProtocolsDocument28 pagesApplication Protocolsrez habloNo ratings yet
- DNS, SMTP, Pop, FTP, HTTPDocument9 pagesDNS, SMTP, Pop, FTP, HTTPBapuji ValabojuNo ratings yet
- Computer Networks Chapter 2 Application Layer NotesDocument5 pagesComputer Networks Chapter 2 Application Layer NotesderguenhartNo ratings yet
- Networking ShortDocument9 pagesNetworking ShortPiyush PriyankNo ratings yet
- Server ConfigurationDocument12 pagesServer ConfigurationHaresh JiNo ratings yet
- 1.1 What Is A Computer Network?Document9 pages1.1 What Is A Computer Network?Mmichael123456789No ratings yet
- DNSDocument19 pagesDNSAkash BhaiyyeNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Some SMTP Testing, Email Verification, Header Analysis, SSL Checkers, Email Delivery, Email Forwarding and WordPress Email ToolsFrom EverandEvaluation of Some SMTP Testing, Email Verification, Header Analysis, SSL Checkers, Email Delivery, Email Forwarding and WordPress Email ToolsNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Some SMTP Testing, SSL Checkers, Email Delivery, Email Forwarding and WP Email Tools: Evaluation of Some SMTP Testing, SSL Checkers, Email Delivery, Email Forwarding and WordPress Email ToolsFrom EverandEvaluation of Some SMTP Testing, SSL Checkers, Email Delivery, Email Forwarding and WP Email Tools: Evaluation of Some SMTP Testing, SSL Checkers, Email Delivery, Email Forwarding and WordPress Email ToolsNo ratings yet
- Hacking Network Protocols: Unlocking the Secrets of Network Protocol AnalysisFrom EverandHacking Network Protocols: Unlocking the Secrets of Network Protocol AnalysisNo ratings yet
- CS8792 CNS QBank PITDocument49 pagesCS8792 CNS QBank PITVignesh BaskeyNo ratings yet
- Secure Wireless Data Transmission ReportDocument75 pagesSecure Wireless Data Transmission Reportdeeptrivedi61950% (2)
- A Survey On Various Cryptography TechniquesDocument7 pagesA Survey On Various Cryptography TechniquesDNo ratings yet
- Ics Mcqs Shift2Document5 pagesIcs Mcqs Shift2Aishwarya KulkarniNo ratings yet
- CISSP Domain 3 v2 CompleteDocument178 pagesCISSP Domain 3 v2 CompleteJeff Edstrom100% (1)
- RU19 - CSE - Course Structure - Syllabus - VII SEMESTERDocument20 pagesRU19 - CSE - Course Structure - Syllabus - VII SEMESTERsohail shaikNo ratings yet
- Cryptograpy and Network Security HandoutDocument78 pagesCryptograpy and Network Security HandoutDr Narayana Swamy RamaiahNo ratings yet
- A Comparative Study of Symmetric Key Encryption Algorithms: Amit Jain, Divya BhatnagarDocument6 pagesA Comparative Study of Symmetric Key Encryption Algorithms: Amit Jain, Divya BhatnagarrebwarpcNo ratings yet
- Groebert Automatic - Identification.of - Cryptographic.primitives - In.softwareDocument115 pagesGroebert Automatic - Identification.of - Cryptographic.primitives - In.softwareassimilatNo ratings yet
- Final NSMDocument185 pagesFinal NSMErSweety MittalNo ratings yet
- Comparison of Encryption Algorithms: AES, Blowfish and Twofish For Security of Wireless NetworksDocument5 pagesComparison of Encryption Algorithms: AES, Blowfish and Twofish For Security of Wireless NetworksPuji SetiadiNo ratings yet
- Classical Encryption Techniques: M. Odeo LecturerDocument39 pagesClassical Encryption Techniques: M. Odeo LecturerSNo ratings yet
- Understanding Cryptography Chapter3Document4 pagesUnderstanding Cryptography Chapter3AliXmetecNo ratings yet
- Abstract. This Paper Presents A 64-Bit Lightweight Block Cipher TWINEDocument24 pagesAbstract. This Paper Presents A 64-Bit Lightweight Block Cipher TWINEاليزيد بن توهاميNo ratings yet
- Seminar - Report - Cover - Front PagesDocument7 pagesSeminar - Report - Cover - Front PagesArchan rajNo ratings yet
- CNS Course Plan - Iv CDocument9 pagesCNS Course Plan - Iv CMohana SubbuNo ratings yet
- Rijndael FinalDocument23 pagesRijndael FinalNur RachmatNo ratings yet
- Comparative Analysis of Block Cipher Modes of Operation: November 2017Document5 pagesComparative Analysis of Block Cipher Modes of Operation: November 2017Cristhian ChahuayoNo ratings yet
- 4.cryptography Handout 2Document87 pages4.cryptography Handout 2Miki AberaNo ratings yet
- Unit Ii: Block Ciphers & Public Key CryptographyDocument109 pagesUnit Ii: Block Ciphers & Public Key CryptographyDhivyabharathi ANo ratings yet
- Unit - Ii: Traditional Symmetric-Key CiphersDocument124 pagesUnit - Ii: Traditional Symmetric-Key Cipherssanthosh RNo ratings yet
- Ma Chan Myae Thu (For Third Seminar)Document47 pagesMa Chan Myae Thu (For Third Seminar)Dr. Myat Mon KyawNo ratings yet
- Block Ciphers and The Data Encryption Standard (DES)Document17 pagesBlock Ciphers and The Data Encryption Standard (DES)Vasantha KumariNo ratings yet
- Irjet V5i4919Document5 pagesIrjet V5i4919ghada sayedNo ratings yet
- Lecture4 (With Notes)Document61 pagesLecture4 (With Notes)amr ahmedNo ratings yet
- Foundations of Cryptography (CYS 602) : Lecture #2 Stream CiphersDocument18 pagesFoundations of Cryptography (CYS 602) : Lecture #2 Stream CiphersWafaa AlshaikhiNo ratings yet
- The KLEIN Block CipherDocument18 pagesThe KLEIN Block Ciphertorchbearer one100% (1)
- Secure Online Voting SystemDocument178 pagesSecure Online Voting SystemMichael Chinwuba92% (13)
- CNS (Vikram)Document121 pagesCNS (Vikram)Shreyas BaligaNo ratings yet
Network
Network
Uploaded by
robigew8240 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views9 pagesDNS maps domain names to IP addresses to make it easier for humans to identify machines. It is a distributed and hierarchical system necessary because a centralized directory would be too large and prone to failure. DNS uses primary and secondary servers that maintain zones of the domain name space and perform name lookups by either recursively or iteratively querying other servers. Caching is used to optimize the process.
Original Description:
Network imp questions
Original Title
network
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentDNS maps domain names to IP addresses to make it easier for humans to identify machines. It is a distributed and hierarchical system necessary because a centralized directory would be too large and prone to failure. DNS uses primary and secondary servers that maintain zones of the domain name space and perform name lookups by either recursively or iteratively querying other servers. Caching is used to optimize the process.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views9 pagesNetwork
Network
Uploaded by
robigew824DNS maps domain names to IP addresses to make it easier for humans to identify machines. It is a distributed and hierarchical system necessary because a centralized directory would be too large and prone to failure. DNS uses primary and secondary servers that maintain zones of the domain name space and perform name lookups by either recursively or iteratively querying other servers. Caching is used to optimize the process.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 9
what is DNS?
what is the Purpose of DNS Secondary servers – A secondary server
DNS – Domain Name system. retrieves information from another primary or
Purpose of DNS – Machines on the internet secondary server and stores this information
are identified by a unique IP address. It is (Zone transfer). It does not create or update
difficult to people to remember the the file. If updating is required, it must be
addresses. Humans are more comfortable done by the primary server, which sends the
with name rather than numbers. Hence, it updated version to the secondary.
would be easier to identify the machine using Domain Name Space – Domain Name Space is
name instead of an address. A system is the implementation of the hierarchical name
needed that can map a name to an address. space. In this space, the names are defined in
This task is handled by Domain name system an inverted tree structure with the root at the
(DNS). Domain Name Space-It Is basically a top. The hierarchical structure (tree) can have
client server application that maps host only 128 levels; level 0 (root) to level 127
names to IP Addresses on the internet. Domain: A domain is a subtree of the domain
Write short notes on DNS name space. The name of the domain is the
Ans. – Machines on the internet are identified name of the node at the top of the tree. A
by a unique IP address. It is difficult to people domain itself can be divided into subdomains
to remember the addresses. Humans are Zone: Each DNS server is responsible for or
more comfortable with name rather than has authority over a zone. A zone is a
numbers. Hence, it would be easier to identify continuous part of the domain tree. If a server
the machine using name instead of an stores the entire domain, the zone and
address. A system is needed that can map a domain are the same. If the server divides the
name to an address. This task is handled by domain into subdomains and assigns
Domain name system (DNS). Domain Name responsibility to different servers, zone and
Space-It Is basically a client server application domain are different.
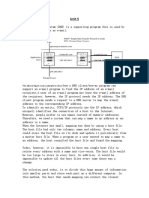
that maps host names to IP Addresses on the What is Caching ?
internet. Since the Internet is a huge network, Ans – Each time a server receives a query for a
a central directory system cannot hold all the name that is not in its domain, it needs to
mapping. If the entire mapping is stored in a search its database for a server IP address.
single computer, the file size will be very Thus, the query proceeds by working down
large. Moreover, it will cause a lot of traffic to the tree of name servers. This can be time
the computer. If this computer crashes, the consuming and can lead to inefficiency.
entire system would fail. Thus, a distributed, Internet name servers use name caching to
hierarchical system is needed to perform the optimize the search cost.
mapping efficiently.
Write short note on MIME
Define MIME – (Multipurpose Internet Mail
Root Server – A root server is a DNS server Extensions) The mail transfer protocol. Allows
whose zone consists of the whole tree only ASCII characters to be included in the
normally; it does not store any information mail. It does not support characters from
about domains but delegates its authority to other languages and scripts, images, audio,
the other server. There are many roots server etc., it specifies the protocol version.
around the world, each covering the whole Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions
domain name space. Protocol is a supplementary protocol used
Primary server – A primary server stores with SMTP in order to allow non-ASCII data
information about the zone in a file on the like images etc. to be sent in the email. MIME
local disk. It responsible for updating and transforms non- ASCII data at the sender to
maintaining all information about the zone. It ASCII data and delivers it to the client MTA.
sends this information to the other secondary The message at the receiving site is
servers when requested. transformed back to the original data.
What is the port no of DNS? Explain architecture of email with different
Ans – Port no of DNS is UDP 53 scenarios
What is resolution? Explain its types --> email allows user to exchange messages. It
Resolution – the process of mapping name to is probably the most widely used service
an address or an address to a name is called associated with computer networks.
resolution. Email system has 3 different agents:
Recursive name-address resolution: In this 1.User Agent (UA)
method, the DNS client sends a request to a 2.Message Transfer Agent (MTA)
server for resolution. If the server can resolve 3.Message Access Agent (MAA)
the name-address then it responds Scenario 1: Sender and receiver connected to
immediately. If the server does not have same server – the sender and receiver are
authority of domain name, then it sends user on same system. Each user has a mailbox
request to another server and waits for in system. Each message carries the mailbox
response. address of sender and receiver. When A wants
Iterative resolution: In iterative resolution, to send mail to B, A uses a User agent (UA) to
the DNS client may send its requests to create message and send a mail B’s mailbox. B
multiple servers before getting the answer. If can read message in B’s mailbox anytime
a server cannot resolve the query, it returns according to convenience
the IP address of another server. The query is Scenario 2: Sender and receiver connected to
then sent to this server and the process different server – the sender and receiver are
continues till the query is resolved. users on different system. The mail has to be
Write short notes on DNS in the internet sent from user A in system to user B in
OR another system. The mail may have to be sent
Describe generic, country, inverse domains. over the internet. Thus, we need 2 User
Ans – The DNS protocol is designed to work Agents (UA) and 2 Message Transfer Agents
on different systems. The DNS for Internet (MTA). The UA’s allows A and B to send and
provides a mechanism that implements retrieve messages. The MTA’s are needed to
machine name hierarchy for TCP/IP, DNS can actually do the transmission from A’s server
use the services of UDP or TCP using the well- to B’s server.
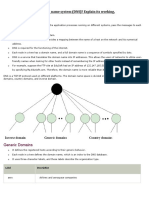
known port 53. There are 3 types of domain Scenario 3: One user is remote user – In this
i. Generic domain: It allows organizations to Scenario, the retriever B is connected to his
be grouped by organizational types. When an system directly. But A is not connected to
organization wants to participate in DNS, it system. A is remote user. A connects to the
registers under that scheme. There are 14 system using LAN or WAN link.
generic domains which describe the Scenario 4: both users are remote
organization types. In this scenario A connects to his mail server
ii. Country domain: This divides the servers by using LAN or WAN link. Receiver B also
country. This scheme uses two-character connects to his mail server through LAN or
country abbreviations. For example, uk-for WAN connection.
United Kingdom, us-for United states, in-for Write short note on SMTP
India etc. SMTP – stands for simple mail transfer
iii. Inverse domain: This is used to map an protocol.
address to a name. For example, if a server This protocol defines the communication
receives a request from a client and the server between MTA client and MTA server. It is also
has only the IP addresses of the clients in its known as Push protocol (it pushes the
list then the server asks its resolver to query message from the client to server). It is simple
to the DNS server to map the IP address to ASCII protocol. (all information in the mail is
name to verify if the client is authorized. This sent un the form of ASCII Characters). It uses
type of query is also called inverse query or TCP for communication at port 25.
pointer query (PTR query). The MTA client and server establish a
connection before communicating.
Que. Short note on user agent and its I. Monoalphabetic substitution cipher: In
different types monoalphabetic substitution, the relationship
User Agent: A User Agent is an important between a symbol in the plaintext to a symbol
component of the email architecture. It in the ciphertext is always one-to-one. This
provides service to the user to make the means that a letter or symbol is always
process of sending and receiving a message replaced by the same letter or symbol in the
easier. It is software that provides the ciphertext, irrespective of its position in the
following important services: plaintext. For example, if the encryption
i. Composing messages: Process of creating scheme is to replace A by letter X, then every
mails. The user agent provides a template A in the plaintext is replaced by letter X.
which helps the user fill in different fields. It Terminology
can also perform spell check and provide text i. Cryptography: Cryptography is the art and
formatting capabilities. science of transforming messages for secure
ii. Reading messages: Process of displaying communication. Cryptography is the art of
messages in the appropriate format. The achieving security by encoding messages to
message size, the sender and a part of the make them non-readable. The word
subject. cryptography combines two Greek words
ill. Replying to messages: Process of replying 'cryptos meaning hidden and 'graphene'
to received messages. The user agent allows meaning writing. So Cryptography means
the recipient to reply to the received 'secret writing
message. ii. Plaintext: The original message to be
iv. Forwarding messages: Process of sending encrypted is called plaintext. It is the
a received message to other users. information that can be directly read by
Forwarding sends the message to a third humans or a machine without the need of any
party. transformation.
v. Handling mailboxes: Process of handling Ciphertext: The secret message which is
inbox, outbox and customized mailboxes transmitted is called ciphertext. It is the
Users can create mailboxes to store the mails output of Encryption process.
efficiently. iv. Cipher: It is an algorithm for transforming
i. Command driven: This type of user agent the plaintext message into one that is
uses a Command based Interface i.e., a unintelligible. i.e. a cipher transforms
Character User Interface (CUI). The user has plaintext into ciphertext.
to type the commands to perform various UA Cipher Key: The cipher key is some critical
actions. Example: mail, pine, elm etc. information used by the cipher, known only to
ii. GUI based: Modern User Agents are GUI the sender and receiver.
based. They use GUI components like buttons, V. e Encryption: The process of converting the
menu's, lists etc. to make the mail creation plaintext to ciphertext using an encryption
task easier and more interactive. Example: function E and a cipher key.
Eudora, Outlook etc. vi. Decryption: The process to retrieve the
Q.1 Substitution Cipher plaintext from the ciphertext using Decryption
The substitution cipher technique is very 4 function D and cipher key.
simple. It replaces a letter or group of letters vii. Cryptanalysis: The study of principles and
by another letter or group of letters. If the methods of transforming an unintelligible
plaintext is viewed as a sequence of bits, then message back into an intelligible message
substitution involves replacing plaintext bit without knowledge of the key. Also
patterns with ciphertext bit patterns. called code breaking.
If one letter is replaced by another, it is
monoalphabetic substitution cipher. If a group
of letters is replaced by another group, it is
polyalphabetic substitution cipher.
The components of the encryption model A symmetric key cryptography
are: This is also called public key cryptography. In
i. Sender: In this model, the sender is the this method, each entity has two keys:
source of the message. It generates a plain
text message to be sent securely to a receiver. i.A public key known to all
ii. Plaintext: The plaintext message is ii. A private key known only to itself.
generated by the sender. It is in a human or When A wants to send a private message to B.
machine-readable form i.e. it can be read and A encrypts the message using B's public key. B
understood by the sender, receiver and also then decrypts the message using his own
anyone else who can access it. private key. Hence, a different key is used for
iii.Encryption algorithm: If the plaintext has to encryption and decryption. For B to
be sent securely from the sender to the communicate with A. B encrypts the message
receiver, it has to be transformed so that with A's public key and A decrypts the
anyone else (ex: intruder) who gets access to message using A's private key.
the message is unable to understand its Advantages of Symmetric
contents. The Encryption algorithm takes two 1 Only one key is needed for encryption as
inputs the plaintext and the encryption key. It well as decryption.
transforms the plaintext into ciphertext by 2. Symmetric key algorithms are very fast and
using some Encryption method E. The output efficient.
of the Encryption algorithm is the Ciphertext. 3. Symmetric key encryption algorithms are
iv. Encryption key: The Encryption algorithm easy and simple to implement.
uses an Encryption key to convert the The sender and receiver have a choice of
plaintext to ciphertext. This key may be various methods for key generation and
private (symmetric key cryptography) or sharing.
public (asymmetric key cryptography). The Disadvantages of Symmetric
sender and receiver generate and share the The key must be kept secret. If it is
key using various algorithms and mechanisms. compromised, the whole process fails. Key
V. Ciphertext: The output of the encryption generation and sharing is a complex process
algorithm is the ciphertext. It is the and requires additional overheads. The key
transformed message to be sent to the must be shared through a secure channel.
receiver. 3. Each communicating pair needs one secret
vi. Communication channel: The sender and key. Hence, if a sender is communicating with
receiver use a communication channel to n receivers, the sender needs to remember n
communicate with each other. The ciphertext secret keys. This is a huge overhead. In
is sent to the receiver through a general, if there are 'n' communicating
communication channel. In most cases, this devices in a system, the total number of
channel is a public, shared channel which is symmetric keys are n(n-1)/2.
insecure or untrustworthy. Hence, the 4 The secret key must be stored securely.
plaintext message must be encrypted before 5. Where only a few keys are involved in the
transmission. network, key management overhead is low.
Types of Cryptography However, if there are many keys, handling and
All cryptographic algorithms are divided into storage is a huge problem.
two categories: 4.1 Traditional Ciphers
Cryptography Symmetric key Traditional ciphers are based on symmetric
Asymmetric key key encryption. Symmetric encryption was the
Symmetric key cryptography only type of encryption in use before to the
This is also called Secret key or Private key development of public key encryption in the
cryptography. In this method, the same key is 1970s. The only security service these systems
used for encryption and decryption. provide is confidentiality of information. It is
Hence,the key is shared by the sender and still the most widely used of the two types of
receiver and must be kept a secret. encryptions.
Transposition Cipher The ciphertext is:
In a substitution cipher, the plaintext symbol dnetlhseedheswloteateftaafcl
is replaced by another symbol. Thus, the If the key = 4 i.e. 4 rails, the transposition is as
characters se disguised but the order of follows:
characters is preserved. A very different kind The ciphertext is:
of mapping is served by. of permutation on dttfsedhswotatfneaalhcleelee
the plaintext letters. This technique is referred To decrypt, the ciphertext is written in row-
to as a transposition cipher wise manner across the rails and read in a zig-
In the transposition cipher, the plaintext is not zag manner.
replaced but the characters are reordered or Advantages of Transposition Cipher
rearranged in some pattern i.e. they are not 1. Looking at the ciphertext, it is difficult to
disguised but their order is changed. For understand that it is transposition cipher.
example, a character may appear at position 3 2. Not knowing the sequence of columns
in the plaintext but at position 9 in the makes it harder to break.
ciphertext. The reordering is done using a key. Symmetric key ciphers can be classified into
two types
i. Simple Columnar Transposition: This is the Block cipher: It is a symmetric key cipher
simplest transposition cipher. To obtain the where a block of data is encrypted at a time.
transposition cipher, the following method is This results in a block of ciphertext of the
used: same size. This cipher encrypts an n bit block
a. Use a key which is a word or a phrase. It of plaintext or decrypts an n bit block of
should not contain any repeating ciphertext. The encryption or decryption
characters. algorithm uses a k-bit key
Stream cipher: It is a symmetric key cipher
For example, CIPHER, MAGNETIC, KEYWORD where the plaintext is processed in the form
etc. can be used as keys. of bits, 'r' bits at a time. Bitwise operations
b. The plaintext is organized into a two- are performed on the plaintext using key bits
dimensional table whose columns = number to give the ciphertext bits. We have a
of characters in key. plaintext bit stream P=p_{n}...p_{2}p_{1} , a
C. Write the plaintext in a row-wise manner in ciphertext bit stream C=c_{1}...c_{2},c_{1} and
the table. Extra spaces are padded. a key bit stream K=k_{n}...k_{2},k_{1}, in
d. The columns are numbered according to which p_{i},c_{i} and k_{i} are r-bit words.
the alphabetic order of the characters in the 4.3 Modern Block Cipher
key. For example, if the keyword is KEYWORD, A modern block cipher can be designed to act
the first letter in the key that appears first in as a substitution cipher or a transposition
the alphabetic order is D. Hence, the last cipher or a combination of the two.
column in numbered 1. The next character is Disadvantages
E, hence, column 2 is numbered 2 and so on. 1.Since the letters are only reordered, the
Rail fence transposition cipher: The rail fence frequency characteristics are similar to
cipher is a simple transposition cipher that plaintext.
permutes the letters in the plaintext by 2. If the intruder knows that it is a
writing them in a zig-zag manner (downwards transposition, this can then often be
and diagonally) along parallel rails. The key is anagramming i.e. sliding pieces of ciphertext
the number of rails. The ciphertext is read around, then looking for sections that look
along the rails in a row-wise manner. like anagrams of English words, and solving
For example, let us consider the plaintext as the anagrams. attacked by
"Defendtheeastwallofthecastle" and key = 3 Comparison of Substitution and Transposition
i.e. 3 rails. Cipher
The plaintext letters are written along the The following table illustrates some important
three rails as shown: differences between substitution and
transposition cipher.
Split and Combine: The split operations split a
4.2 Simple Modern Ciphers block of bits into multiple parts and the
Traditional ciphers mainly worked on plaintext combine operation combines multiple sub-
in the form of alphabets and characters. blocks of bits into a single block.
However, when computers are used for The design of a modern block cipher is based
encryption and decryption, we need to on satisfying two important aspects:
perform bit-oriented encryption and i. Diffusion: It hides the relationship between
decryption. Computers deal with information the ciphertext and the plaintext.
in various forms: simple text, numbers, ii. Confusion: It hides the relationship
images, audio and video. Hence it is between the ciphertext and the key.
convenient to perform encryption and Components of a Modern Block cipher
decryption on different formats of i. S-box: An S-box (substitution-box) is a basic
information in the form of a stream of bits. component of symmetric key algorithms
Because symmetric key cryptography is much which performs substitution. In general, an S-
faster than asymmetric key cryptography, box takes some number of input bits, m, and
modern ciphers are built using the principles transforms them into some number of output
of symmetric key cryptography. bits, n, where n is not necessarily equal to m
The S-Box is used to provide confusion, as it
4.4 Modern Round Cipher hides the relationship between the key and
Shannon introduced the concept of a product the ciphertext.
cipher. A product cipher is a complex cipher ii. P-box: A p-box is used to transpose bits. P-
combining substitution, permutation, and boxes are typically classified as compression
other components of the modern block (output bits < input bits), expansion (output
cipher. In a product cipher, diffusion and bits > input bits), and straight ((output bits =
confusion can be achieved using iterated input bits). Only straight P-boxes are
product ciphers where each iteration is a invertible.
combination of S-boxes, P-boxes, and other simplified Feistel structure with two rounds.
components. Such iterations are called The plaintext is divided into two parts: Left
rounds. Modern block ciphers are all product and Right. An encryption function is applied
ciphers, and many are based on the Feistel on the right half using a round key. The
cipher. output of the function is XORed with the Left
Feistel cipher part. The two parts are swapped for the next
The Feistel Cipher model is a general structure round.Many modern algorithms such as DES,
or a design which is based on symmetric key AES, IDEA etc. use the Feistel structure.
encryption and decryption. The plaintext is Data Encryption Standard (DES)
divided into blocks and one block is encrypted DES is a symmetric block cipher designed and
at a time. The Feistel structure consists of published in the 1970's by NIST (National
multiple rounds. Each round consists of a Institute of Standards and Technology). The
substitution step followed by a permutation algorithm is based on the Feistel structure. It
step. A different key is used for each round. encrypts a 64-bit plaintext block and
YOR: An important component in most block generates a 64-bit ciphertext block using a 64-
ciphers is the exclusive-or operation. Five bit key (converted to 56 bits).
properties of the exclusive-or operation
makes it a very important component for use Rotation cipher: In the rotation cipher, the
in a block cipher: closure, associativity, input bits are rotated to the left or right. It can
commutativity, existence of identity, and be keyed or keyless. In keyed rotation, the key
forsteen of inverse defines the number of rotations. In keyless
Circular Shift: Another component found in rotation, the number of rotations in fixed. It
some modern block ciphers is the circular shift can be considered as a special case of
operation. This shifts the bits of the block to transpositional cipher using bits instead of
the left or the right. characters.
Que. Difference between flat name space
4.4 Modern Round Cipher and hierarchical name space.
Shannon introduced the concept of a product Flat name space. Hierarchical name
cipher. A product cipher is a complex cipher space
combining substitution, permutation, and 1 Each name Each name is
other components of the modern block consists of made up of
cipher. In a product cipher, diffusion and sequence of several parts,
confusion can be achieved using iterated characters each defining
product ciphers where each iteration is a without any level of hierarchy.
combination of S-boxes, P-boxes, and other further structure.
components. Such iterations are called 2 Names are stored Names are
rounds. Modern block ciphers are all product at central distributed.
ciphers, and many are based on the Feistel location.
cipher. 3 Centralized Decentralized
control. control.
Feistel cipher 4 Easy to resolve Resolution is
The Feistel Cipher model is a general structure names and more complex
or a design which is based on symmetric key address. due to
encryption and decryption. The plaintext is hierarchical
divided into blocks and one block is encrypted structure.
at a time. The Feistel structure consists of 5 As the names are Even if parts of
multiple rounds. Each round consists of a drawn from a the names are
substitution step followed by a permutation single set of same, the whole
step. A different key is used for each round. identifiers, the address is unique.
potential for
DES Steps conflicts
i. Plaintext is encrypted in blocks of size 64 increases.
bits each, which produces 64 bits of 6 Easy to Difficult to
ciphertext. implement. implement.
ii. The initial key consists of 64 bits. Every 8th 7 Does not require Requires
bit of the key is discarded. i.e., bit positions 8, communication communication
16, 24, 32, 40, 48, 56, and 64 are discarded, and coordination and coordination
producing a 56-bit key. between several between several
iii. The 64-bit plaintext is applied an Initial authorities. authorities.
Permutation (IP). Que. Difference between FQDN and PQDN.
iv The IP produces two halves of the FQDN PQDN
permuted block; Left Plain Text (LPT) and
Right Plain Text (RPT). 1 Path from node to Path does not
V. Each of LPT and RPT goes through 16 root. contain root.
rounds of encryption process, each with its 2 Can be used Cannot us
own round key independently. independently.
3 Ends with dots(.). Does not end with
What is the port no of SMTP? dots.
Ans: SMTP port no is Port 25 4 Requires more Requires less
space to store. space in DNS
tables.
5 No additional Full domain name
suffix needs to be of the parent
added. should be added
as suffix.
Que. Difference between substitution and
transposition cipher
Substitution Transposition
cipher cipher
1 Plaintext letters Plaintext letters
are disguised are not disguised
2 Plaintext letters Plaintext letters
are not recorded are recorded
3 Does not frequency
preserve distribution of
frequency plaintext letters is
distribution of preserved.
plaintext
4 Easier to break if Requires higher
language work factor to
characters are break
known
5 Encryption and Encryption and
decryption are decryption are
easy to more complex
implement
6 Example: Playfair, Example: simple
Caesar columnar,
RailFence
POP3 IMAP4
1 Simple protocol, it only allows to download Advance and more powerful protocol.
messages from the mailbox to the computer.
2 Uses port 110. Uses port 143.
3 All emails must be downloaded for reading Does not need to be downloaded.
4 Users cannot organize the emails in the Provides a facility to organize email in the
mailbox. mailbox.
5 Easy to setup use. Complicated to setup and use.
6 Speed is fast. Speed is slow.
7 Works on 2 modes: i) delete mode Emails are always kept in the mailbox and
ii) keep mode also the other servers. Deleted emails can
be retrieved.
8 Since mails are downloaded, the mailbox size Size of the mailbox must be sufficiently
can be smaller. large to hold all emails.
You might also like
- Cryptool LabDocument11 pagesCryptool Labimbo9No ratings yet
- Application Layer Unit 7 Cse 3Document83 pagesApplication Layer Unit 7 Cse 3VADAPALLY PRAVEEN KUMARNo ratings yet
- CN - 5Document37 pagesCN - 5SivaRamanNo ratings yet
- Computer NetworksDocument22 pagesComputer NetworksRISHINo ratings yet
- Unit-5 Q&ADocument16 pagesUnit-5 Q&AMunawar MohammedNo ratings yet
- ASCII Strings Into Network Addresses.: How DNS WorksDocument6 pagesASCII Strings Into Network Addresses.: How DNS WorksAnup PaulNo ratings yet
- Application LayerDocument42 pagesApplication LayerAnubhav KumarNo ratings yet
- Unit-V CNDocument35 pagesUnit-V CNchinnupyariNo ratings yet
- Application Layer: Prepared byDocument35 pagesApplication Layer: Prepared byIhab AmerNo ratings yet
- Computer Networks (1) - 157-172Document16 pagesComputer Networks (1) - 157-172Harini VelrajNo ratings yet
- Computer Networks - Unit - 5 Y3/S5: Unit - V Application LayerDocument32 pagesComputer Networks - Unit - 5 Y3/S5: Unit - V Application LayerSanthosh RockyNo ratings yet
- Lecture 17-DNS, Email, Telnet, FTP, SNMPDocument10 pagesLecture 17-DNS, Email, Telnet, FTP, SNMPyesmuraliNo ratings yet
- WINSEM2020-21 CSE1004 ETH VL2020210504039 Reference Material I 20-May-2021 Application LayerDocument44 pagesWINSEM2020-21 CSE1004 ETH VL2020210504039 Reference Material I 20-May-2021 Application LayerDivij BahlNo ratings yet
- CN Tutorial 5Document15 pagesCN Tutorial 5Hîмanî JayasNo ratings yet
- UNIT - II - Computer NetworksDocument8 pagesUNIT - II - Computer Networkssankalpsamant2001No ratings yet
- Unit 5 CNDocument19 pagesUnit 5 CNnavya goneNo ratings yet
- Computer Networks Administration, Strong Understanding of TCP/IP, DNS, Network Routing/switching, and Network Best Practices For Complex EnvironmentsDocument14 pagesComputer Networks Administration, Strong Understanding of TCP/IP, DNS, Network Routing/switching, and Network Best Practices For Complex EnvironmentsAlex LucaNo ratings yet
- Protocols & ApplicationDocument32 pagesProtocols & ApplicationS M AkashNo ratings yet
- Domain Name SystemDocument11 pagesDomain Name SystemJeng DevNo ratings yet
- Application Layer ProtocolsDocument33 pagesApplication Layer ProtocolsSarah AliNo ratings yet
- CN Unit-5Document14 pagesCN Unit-5dhosheka123No ratings yet
- Unit 5: The Above Figure Is An Example To ShowDocument18 pagesUnit 5: The Above Figure Is An Example To ShowDeepti SinghNo ratings yet
- CN Unit V R18Document27 pagesCN Unit V R18Sahithi Priya AttiliNo ratings yet
- CCNA 1 Chapter 3 SummaryDocument6 pagesCCNA 1 Chapter 3 SummaryzanarutoNo ratings yet
- Traditional Applications - Electronic Mail (SMTP, POP3, IMAP, MIME) - HTTP - Web Services - DNS-SNMPDocument39 pagesTraditional Applications - Electronic Mail (SMTP, POP3, IMAP, MIME) - HTTP - Web Services - DNS-SNMPanish.t.pNo ratings yet
- The Application Layer Includes The Following FunctionsDocument15 pagesThe Application Layer Includes The Following FunctionsCaptain AmericaNo ratings yet
- Unit-V: Dns-Domain Name SpaceDocument33 pagesUnit-V: Dns-Domain Name SpaceMr.T.Vijayakumar Assistant ProfessorNo ratings yet
- Cube Notes For DNSDocument17 pagesCube Notes For DNSoli_via_roNo ratings yet
- Unit 4Document16 pagesUnit 4anjworl3614No ratings yet
- Presentation Layer & Session LayerDocument45 pagesPresentation Layer & Session LayertopherskiNo ratings yet
- Application LayerDocument21 pagesApplication Layerrajpurohitpriyanshi2511No ratings yet
- Cse3039 Module 7Document134 pagesCse3039 Module 7jtrttttttttttttttttttttttNo ratings yet
- Computer Networks UNIT 5Document21 pagesComputer Networks UNIT 5thefamousbro123No ratings yet
- Application layer-DNS, E-MailDocument24 pagesApplication layer-DNS, E-MailVenkata Ganesh GorlaNo ratings yet
- Application Layer - Email-DNSDocument33 pagesApplication Layer - Email-DNSJimmi NadapdapNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 CNDocument28 pagesUnit 5 CNkumargpj7091No ratings yet
- BSC IT 63 Advanced Computer NetworksDocument24 pagesBSC IT 63 Advanced Computer NetworksAshutosh SaraswatNo ratings yet
- Unit-1.2 Internet and World Wide WebDocument40 pagesUnit-1.2 Internet and World Wide Webco22352No ratings yet
- Lecture2 DOMAIN NAME SYSTEM (DNS) Part 1Document22 pagesLecture2 DOMAIN NAME SYSTEM (DNS) Part 1Kas7W 5kNo ratings yet
- DNS (Domain Name Service) - TCP and Udp 53: The Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP)Document13 pagesDNS (Domain Name Service) - TCP and Udp 53: The Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP)Suraj Singh RajputNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 CNDocument73 pagesUnit 5 CNnikitha.veeramalluNo ratings yet
- Unit VDocument22 pagesUnit V20H51A04P3-PEDAPUDI SHAKTHI GANESH B.Tech ECE (2020-24)No ratings yet
- CSMA (Carrier Sense Multiple Access)Document4 pagesCSMA (Carrier Sense Multiple Access)Mahi sharmaNo ratings yet
- Assg 11 - DNS LOOPK UPDocument5 pagesAssg 11 - DNS LOOPK UP2108 Aniket BankapurNo ratings yet
- CN5Document11 pagesCN5ECE 3 VNRNo ratings yet
- CN Manual A11Document5 pagesCN Manual A11Sneha KanwadeNo ratings yet
- CN Unit 5Document38 pagesCN Unit 533 ABHISHEK WAGHNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 CNDocument73 pagesUnit 5 CNHemasai 6909No ratings yet
- Presentation Layer & Session LayerDocument51 pagesPresentation Layer & Session LayerAnonymous fp8NP80% (1)
- Unit-5 Computer NetworkDocument10 pagesUnit-5 Computer NetworkShivansh tomarNo ratings yet
- Au Satdns PDFDocument12 pagesAu Satdns PDFFrance CalNo ratings yet
- Application ProtocolsDocument28 pagesApplication Protocolsrez habloNo ratings yet
- DNS, SMTP, Pop, FTP, HTTPDocument9 pagesDNS, SMTP, Pop, FTP, HTTPBapuji ValabojuNo ratings yet
- Computer Networks Chapter 2 Application Layer NotesDocument5 pagesComputer Networks Chapter 2 Application Layer NotesderguenhartNo ratings yet
- Networking ShortDocument9 pagesNetworking ShortPiyush PriyankNo ratings yet
- Server ConfigurationDocument12 pagesServer ConfigurationHaresh JiNo ratings yet
- 1.1 What Is A Computer Network?Document9 pages1.1 What Is A Computer Network?Mmichael123456789No ratings yet
- DNSDocument19 pagesDNSAkash BhaiyyeNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Some SMTP Testing, Email Verification, Header Analysis, SSL Checkers, Email Delivery, Email Forwarding and WordPress Email ToolsFrom EverandEvaluation of Some SMTP Testing, Email Verification, Header Analysis, SSL Checkers, Email Delivery, Email Forwarding and WordPress Email ToolsNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Some SMTP Testing, SSL Checkers, Email Delivery, Email Forwarding and WP Email Tools: Evaluation of Some SMTP Testing, SSL Checkers, Email Delivery, Email Forwarding and WordPress Email ToolsFrom EverandEvaluation of Some SMTP Testing, SSL Checkers, Email Delivery, Email Forwarding and WP Email Tools: Evaluation of Some SMTP Testing, SSL Checkers, Email Delivery, Email Forwarding and WordPress Email ToolsNo ratings yet
- Hacking Network Protocols: Unlocking the Secrets of Network Protocol AnalysisFrom EverandHacking Network Protocols: Unlocking the Secrets of Network Protocol AnalysisNo ratings yet
- CS8792 CNS QBank PITDocument49 pagesCS8792 CNS QBank PITVignesh BaskeyNo ratings yet
- Secure Wireless Data Transmission ReportDocument75 pagesSecure Wireless Data Transmission Reportdeeptrivedi61950% (2)
- A Survey On Various Cryptography TechniquesDocument7 pagesA Survey On Various Cryptography TechniquesDNo ratings yet
- Ics Mcqs Shift2Document5 pagesIcs Mcqs Shift2Aishwarya KulkarniNo ratings yet
- CISSP Domain 3 v2 CompleteDocument178 pagesCISSP Domain 3 v2 CompleteJeff Edstrom100% (1)
- RU19 - CSE - Course Structure - Syllabus - VII SEMESTERDocument20 pagesRU19 - CSE - Course Structure - Syllabus - VII SEMESTERsohail shaikNo ratings yet
- Cryptograpy and Network Security HandoutDocument78 pagesCryptograpy and Network Security HandoutDr Narayana Swamy RamaiahNo ratings yet
- A Comparative Study of Symmetric Key Encryption Algorithms: Amit Jain, Divya BhatnagarDocument6 pagesA Comparative Study of Symmetric Key Encryption Algorithms: Amit Jain, Divya BhatnagarrebwarpcNo ratings yet
- Groebert Automatic - Identification.of - Cryptographic.primitives - In.softwareDocument115 pagesGroebert Automatic - Identification.of - Cryptographic.primitives - In.softwareassimilatNo ratings yet
- Final NSMDocument185 pagesFinal NSMErSweety MittalNo ratings yet
- Comparison of Encryption Algorithms: AES, Blowfish and Twofish For Security of Wireless NetworksDocument5 pagesComparison of Encryption Algorithms: AES, Blowfish and Twofish For Security of Wireless NetworksPuji SetiadiNo ratings yet
- Classical Encryption Techniques: M. Odeo LecturerDocument39 pagesClassical Encryption Techniques: M. Odeo LecturerSNo ratings yet
- Understanding Cryptography Chapter3Document4 pagesUnderstanding Cryptography Chapter3AliXmetecNo ratings yet
- Abstract. This Paper Presents A 64-Bit Lightweight Block Cipher TWINEDocument24 pagesAbstract. This Paper Presents A 64-Bit Lightweight Block Cipher TWINEاليزيد بن توهاميNo ratings yet
- Seminar - Report - Cover - Front PagesDocument7 pagesSeminar - Report - Cover - Front PagesArchan rajNo ratings yet
- CNS Course Plan - Iv CDocument9 pagesCNS Course Plan - Iv CMohana SubbuNo ratings yet
- Rijndael FinalDocument23 pagesRijndael FinalNur RachmatNo ratings yet
- Comparative Analysis of Block Cipher Modes of Operation: November 2017Document5 pagesComparative Analysis of Block Cipher Modes of Operation: November 2017Cristhian ChahuayoNo ratings yet
- 4.cryptography Handout 2Document87 pages4.cryptography Handout 2Miki AberaNo ratings yet
- Unit Ii: Block Ciphers & Public Key CryptographyDocument109 pagesUnit Ii: Block Ciphers & Public Key CryptographyDhivyabharathi ANo ratings yet
- Unit - Ii: Traditional Symmetric-Key CiphersDocument124 pagesUnit - Ii: Traditional Symmetric-Key Cipherssanthosh RNo ratings yet
- Ma Chan Myae Thu (For Third Seminar)Document47 pagesMa Chan Myae Thu (For Third Seminar)Dr. Myat Mon KyawNo ratings yet
- Block Ciphers and The Data Encryption Standard (DES)Document17 pagesBlock Ciphers and The Data Encryption Standard (DES)Vasantha KumariNo ratings yet
- Irjet V5i4919Document5 pagesIrjet V5i4919ghada sayedNo ratings yet
- Lecture4 (With Notes)Document61 pagesLecture4 (With Notes)amr ahmedNo ratings yet
- Foundations of Cryptography (CYS 602) : Lecture #2 Stream CiphersDocument18 pagesFoundations of Cryptography (CYS 602) : Lecture #2 Stream CiphersWafaa AlshaikhiNo ratings yet
- The KLEIN Block CipherDocument18 pagesThe KLEIN Block Ciphertorchbearer one100% (1)
- Secure Online Voting SystemDocument178 pagesSecure Online Voting SystemMichael Chinwuba92% (13)
- CNS (Vikram)Document121 pagesCNS (Vikram)Shreyas BaligaNo ratings yet