Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CHAPTER 1 - The Indian Contract Act 1872
CHAPTER 1 - The Indian Contract Act 1872
Uploaded by
khanak bodraOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
CHAPTER 1 - The Indian Contract Act 1872
CHAPTER 1 - The Indian Contract Act 1872
Uploaded by
khanak bodraCopyright:
Available Formats
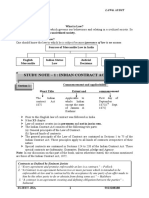
CHAPTER 1- The Indian Contract Act 1872
Saturday, 10 February 2024 7:11 PM
Law- "the body of principles recognized and applied
Salmond- by the state in administration of justice
OR
"rule of external human action enforced by
Holland- sovereign political academy"
OR
Austin- "a rule of conduct imposed and enforced by the sovereign"
Purpose of the TICA- control various kinds of business and commercial activities
WHAT IS BUSINESS LAW?
- A branch of legal system that regulates business activities and provides for an
orderly conduct of business affairs and also for settlement of genuine
disputes in a systematic manner.
AGREEMENTS
What is an agreement- every promise and set of promises forming the
consideration for each other is an agreement.
Agreement= offer + acceptance
TYPES OF AGREEMENTS
→ Valid agreement- one which is enforceable by law
→ Void agreement- not enforceable by law, as it has no legal existence at all and
is without any legal effect
→ Enforceable agreement- an agreement enforceable by law is a conduct
→ Voidable agreement- it is enforceable by law at the option of one or more of
the parties thereto but not at the option of the other or others.
→ Unenforceable agreement- it is valid in law but is incapable of proof because
of some technical defect
→ Voidable agreement- it is enforceable by law at the option of one or more of
the parties thereto but not at the option of the other or others.
→ Unenforceable agreement- it is valid in law but is incapable of proof because
of some technical defect
→ Illegal agreement- it is something against the law and public policy a.k.a. void
ab initio
What is a contract?
- An agreement enforceable by law
- Contract= an agreement + enforceable by law
Essential elements of a void contract
a) Offer and acceptance- these should be a 'lawful offer' by one party and
'lawful acceptance by other'
b) Legal relationship- without a legal relationship, the contract is not there. Eg- a
friendly agreement cannot be called contract
c) Lawful consideration- price for which promise of another is bought. In this a
promise should be made ad both parties should benefit too.
d) Capacity of parties- the parties involved must be competent to the contract,
if important contract is not valid. Eg- minors, unsound mind, convict,
insolvent, alien enemy
e) Free consent- in this parties must have agreed upon the same thing in the
same sense. There should be no use of force.
f) Lawful object- the object of an agreement must be valid. It is unlawful when,
i) it is forbidden by law, ii) its nature, iii) it is fraudulent, iv) it is harmful to
another person, v) court regard it is as immoral
g) Agreement not declared void by law- i) agreement in restraint of trade, ii)
agreement in restraint of marriage, iii) agreement in restraint of legal
proceedings
h) Possibility of performance- the act should not be impossible in itself,
physically, or legally, hence cannot be enforced by law. Eg- lets discover
treasure by magic
i) Certainty of terms- the agreement should consist of terms ad they should be
certain and ultra modern décor, the contract here is void as the term 'ultra
modern' is not certain.
You might also like
- Housing and Land Use Regulatory Board: Draft DecisionDocument9 pagesHousing and Land Use Regulatory Board: Draft DecisionGene Abot100% (10)
- Indian Contract Act 1872,,by Risabh GaurDocument315 pagesIndian Contract Act 1872,,by Risabh GaurDibyani DashNo ratings yet
- Martial Arts WaiverDocument2 pagesMartial Arts WaiverkltonNo ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument6 pagesCase Studykevin ariasNo ratings yet
- Contract-1 (1) LL BDocument65 pagesContract-1 (1) LL Bgoyal.anilirNo ratings yet
- BRF Unit IDocument34 pagesBRF Unit ILatha Priya100% (1)
- Indian Contract Act 1872Document6 pagesIndian Contract Act 1872subhash dalviNo ratings yet
- Assignment ON Corporate Legal EnvironmentDocument6 pagesAssignment ON Corporate Legal EnvironmentDeependra BishtNo ratings yet
- Indian Contract Act 1872Document62 pagesIndian Contract Act 1872Pranav IyengarNo ratings yet
- BLAWDocument68 pagesBLAWhamedi1No ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: Q1: Define A Contract and Describe The Essentials of A Valid ContractDocument8 pagesThis Study Resource Was: Q1: Define A Contract and Describe The Essentials of A Valid ContractchangumanguNo ratings yet
- Essential Elements of Valid ContractDocument4 pagesEssential Elements of Valid Contractricha.joseph052714No ratings yet
- Unit 2. Law of ContractDocument29 pagesUnit 2. Law of Contractste100% (2)
- Law of Contract 1Document314 pagesLaw of Contract 1Sapna AgarwalNo ratings yet
- SEM V NotesDocument45 pagesSEM V NotesMEGHA KARWANo ratings yet
- Legal Issues Chapter 1Document5 pagesLegal Issues Chapter 1sdfghjkNo ratings yet
- Unit I LAB - FairDocument44 pagesUnit I LAB - Fairmurugesan.NNo ratings yet
- Sbaa 1206Document138 pagesSbaa 1206Arpit ChaurasiaNo ratings yet
- Unit - 1 Indian Contract Act, 1872 NotesDocument43 pagesUnit - 1 Indian Contract Act, 1872 NotesshobhanaNo ratings yet
- Contract Law Notes MS EDU PrintDocument127 pagesContract Law Notes MS EDU Printskhan skhanbirNo ratings yet
- UNIT 2 (Online MBA) With Ref.Document30 pagesUNIT 2 (Online MBA) With Ref.Janane jananeNo ratings yet
- What Is An Agreement?: For ExampleDocument165 pagesWhat Is An Agreement?: For ExampleAyesha jamesNo ratings yet
- Intro To Contract ActDocument28 pagesIntro To Contract ActRahulNo ratings yet
- Contract IDocument8 pagesContract IDhananjaya BkNo ratings yet
- Contract PPT (All Notes)Document62 pagesContract PPT (All Notes)Praveen kumarNo ratings yet
- SBAA1302Document130 pagesSBAA1302prabal parasharNo ratings yet
- Via This: Q1: Define A Contract and Describe The Essentials of A Valid ContractDocument14 pagesVia This: Q1: Define A Contract and Describe The Essentials of A Valid ContractchangumanguNo ratings yet
- BUSINESS LAW Unit 1Document65 pagesBUSINESS LAW Unit 1Deepak TongliNo ratings yet
- Formation of Valid ContractDocument27 pagesFormation of Valid ContractMeghaNo ratings yet
- Business Laws (RTU) - Module 1Document54 pagesBusiness Laws (RTU) - Module 1aparna kallaNo ratings yet
- SUJEET JHA Indian Contract Act NotesDocument61 pagesSUJEET JHA Indian Contract Act Notes2050101 A YUVRAJ100% (1)
- Contract NotesDocument60 pagesContract NotesAayushi PruthiNo ratings yet
- Contract NotesDocument303 pagesContract NotesRasteNo ratings yet
- Indian Contract Act 1872 SummaryDocument85 pagesIndian Contract Act 1872 Summaryagpoorvi02No ratings yet
- ST - Joseph's Degree & PG College Business Law Unit1Document14 pagesST - Joseph's Degree & PG College Business Law Unit1Saud Waheed KhanNo ratings yet
- Manonmaniam Sundaranar University: B.B.A. - Ii YearDocument140 pagesManonmaniam Sundaranar University: B.B.A. - Ii YearAKASH JOEL DAVIDNo ratings yet
- Legal Aspects Unit 1Document74 pagesLegal Aspects Unit 1Vetri VelanNo ratings yet
- Indian Contract Semester 1Document173 pagesIndian Contract Semester 1Pramod ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Assignment ON Legal Aspect of BusinessDocument10 pagesAssignment ON Legal Aspect of BusinessPriyanka JainNo ratings yet
- Unit - 1: Contract LawDocument56 pagesUnit - 1: Contract LawPremendra SahuNo ratings yet
- ContractDocument114 pagesContractAishwaryaSasiNairNo ratings yet
- Business LawDocument28 pagesBusiness LawlovkushsinghNo ratings yet
- Legal Aspects Unit 1Document74 pagesLegal Aspects Unit 1Vetri VelanNo ratings yet
- Law of Contract Notes Part 1Document33 pagesLaw of Contract Notes Part 1Priyanshi BhatiaNo ratings yet
- BELAB Unit-3 (INDIAN CONTRACT ACT, 1872)Document41 pagesBELAB Unit-3 (INDIAN CONTRACT ACT, 1872)aryansrivastava2645No ratings yet
- Formation of A ContractDocument26 pagesFormation of A Contractchanakya8999No ratings yet
- Contract 1Document302 pagesContract 1Sahaj MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- legal contract 1 pdfDocument8 pageslegal contract 1 pdfAman guptaNo ratings yet
- Indian Contract Law Notes-1-85Document85 pagesIndian Contract Law Notes-1-85Harsh100% (1)
- Indian Contract Act 1872: Legal Framework of Business and ManagementDocument27 pagesIndian Contract Act 1872: Legal Framework of Business and Managementluvnica6477No ratings yet
- Defination and Nature of ContractDocument12 pagesDefination and Nature of Contractayushchaudhary22790No ratings yet
- Business LawDocument2 pagesBusiness LawMd. RuHul A.No ratings yet
- Contract Act, ModifiedDocument20 pagesContract Act, ModifiedhamidfarahiNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Law of Contract: 1.1 ObjectivesDocument43 pagesUnit 1 Law of Contract: 1.1 ObjectivesgaardiNo ratings yet
- Legal Chapter-2 Contract PDFDocument19 pagesLegal Chapter-2 Contract PDFNusrat Jahan RimuNo ratings yet
- Commercial LawDocument49 pagesCommercial LawPrince AntonyNo ratings yet
- Contract LawDocument46 pagesContract LawAyesha jamesNo ratings yet
- CONTRACTS PSDA Shiksha PDFDocument9 pagesCONTRACTS PSDA Shiksha PDFShiksha GaurNo ratings yet
- BlawDocument68 pagesBlawLawangen MalikKhelNo ratings yet
- A Simple Guide for Drafting of Conveyances in India : Forms of Conveyances and Instruments executed in the Indian sub-continent along with Notes and TipsFrom EverandA Simple Guide for Drafting of Conveyances in India : Forms of Conveyances and Instruments executed in the Indian sub-continent along with Notes and TipsNo ratings yet
- How to Break (or renegotiate) ANY ContractFrom EverandHow to Break (or renegotiate) ANY ContractRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- TRAVELERS INDEMNITY COMPANY OF ILLINOIS Et Al v. CLARENDON AMERICAN INSURANCE COMPANY Et Al ComplaintDocument41 pagesTRAVELERS INDEMNITY COMPANY OF ILLINOIS Et Al v. CLARENDON AMERICAN INSURANCE COMPANY Et Al ComplaintACELitigationWatchNo ratings yet
- Obligation and Contracts MCQDocument4 pagesObligation and Contracts MCQLynNo ratings yet
- Intengan v. Court of AppealsDocument11 pagesIntengan v. Court of AppealssescuzarNo ratings yet
- Notes On Companies Act 1956Document87 pagesNotes On Companies Act 1956Pranay KinraNo ratings yet
- 7 Calalas v. Court of Appels G.R. No. 122039, May 31, 2000Document4 pages7 Calalas v. Court of Appels G.R. No. 122039, May 31, 2000Ian Kenneth MangkitNo ratings yet
- Cunanan - Diloy - Escanilla - Fabella - Francisco - Hernandez - Lamado - Punsalan 1Document23 pagesCunanan - Diloy - Escanilla - Fabella - Francisco - Hernandez - Lamado - Punsalan 1Ronald FloresNo ratings yet
- Unitrans International Vs Insurance Company of North AmericaDocument17 pagesUnitrans International Vs Insurance Company of North AmericaBea AlduezaNo ratings yet
- TORTS - 41. Child Learning Center, Inc. v. TagorioDocument7 pagesTORTS - 41. Child Learning Center, Inc. v. TagorioMark Gabriel B. MarangaNo ratings yet
- Dar 12312017Document6 pagesDar 12312017Fauquier NowNo ratings yet
- 3 - International Express Travel V CA G.R. No. 119002Document4 pages3 - International Express Travel V CA G.R. No. 119002Renz Francis LimNo ratings yet
- Raymundo Vs BandongDocument5 pagesRaymundo Vs BandongJessa PuerinNo ratings yet
- 403 OBLICON Review Case Digests Part 1Document116 pages403 OBLICON Review Case Digests Part 1Harold CasalemNo ratings yet
- Arcilla Vs CADocument5 pagesArcilla Vs CACatherine MerillenoNo ratings yet
- Apprac. Digest No. 1Document13 pagesApprac. Digest No. 1Jm CruzNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - PowerpointDocument43 pagesLecture 2 - PowerpointYUK LAM WONGNo ratings yet
- SL (34) Luzon Brokerage Vs Maritime Building - BRILLANTESDocument1 pageSL (34) Luzon Brokerage Vs Maritime Building - BRILLANTESJuan Carlos BrillantesNo ratings yet
- 03 Limketkai Sons Milling, Inc. vs. Court of AppealsDocument20 pages03 Limketkai Sons Milling, Inc. vs. Court of AppealsMark Anthony Javellana SicadNo ratings yet
- Discharge of ContractDocument12 pagesDischarge of ContractlakshamuNo ratings yet
- Quern V Jordan, 440 US 332 (1979)Document35 pagesQuern V Jordan, 440 US 332 (1979)nolu chanNo ratings yet
- Metro Bottled Water Corp v. Andrada ConstructionDocument3 pagesMetro Bottled Water Corp v. Andrada ConstructionKarla Lois de Guzman100% (1)
- Hawkins v. McGeeDocument3 pagesHawkins v. McGeeRonnie Barcena Jr.No ratings yet
- De Castro vs. Judicial and Bar Council (JBC) : 640 Supreme Court Reports AnnotatedDocument35 pagesDe Castro vs. Judicial and Bar Council (JBC) : 640 Supreme Court Reports AnnotatedCJNo ratings yet
- Coblaw 1 NotesDocument12 pagesCoblaw 1 NotesJoshua KhoNo ratings yet
- Legal Ethics - Case DigestsDocument51 pagesLegal Ethics - Case DigestsanntomarongNo ratings yet
- Republic Vs CA, 154 SCRA 428Document7 pagesRepublic Vs CA, 154 SCRA 428Add AllNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Tradisi A'borong Dalam Penyelesaian Sengketa Di Tanah Toa KajangDocument8 pagesJurnal Tradisi A'borong Dalam Penyelesaian Sengketa Di Tanah Toa Kajangrahmat Fauzi ramdhanNo ratings yet
- Alvarez vs. Iac - DigestDocument8 pagesAlvarez vs. Iac - Digestnia_artemis3414No ratings yet