Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Assignment #3
Assignment #3
Uploaded by
Ian James Calanza0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views2 pagesAlexander Graham Bell is considered the father of multiplexing in telephony. Multiplexing refers to combining multiple data streams into a single transmission channel to efficiently use bandwidth and resources, allowing multiple users to share infrastructure without interfering. The four main types of multiplexing are frequency division, time division, code division, and space division multiplexing.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentAlexander Graham Bell is considered the father of multiplexing in telephony. Multiplexing refers to combining multiple data streams into a single transmission channel to efficiently use bandwidth and resources, allowing multiple users to share infrastructure without interfering. The four main types of multiplexing are frequency division, time division, code division, and space division multiplexing.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views2 pagesAssignment #3
Assignment #3
Uploaded by
Ian James CalanzaAlexander Graham Bell is considered the father of multiplexing in telephony. Multiplexing refers to combining multiple data streams into a single transmission channel to efficiently use bandwidth and resources, allowing multiple users to share infrastructure without interfering. The four main types of multiplexing are frequency division, time division, code division, and space division multiplexing.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
Name: Ian James V.
Calanza BSIT-3A Subject: Mobile Computing
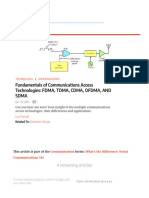
1. What is Multiplexing in Mobile Computing?
- Multiplexing in mobile computing refers to the technique of combining multiple data
streams or signals into a single transmission channel or medium. The purpose of multiplexing is
to efficiently utilize the available bandwidth and resources, enabling multiple users or devices to
share the same communication infrastructure without interfering with each other.
2. Who is the father of Multiplexing in telephony?
- The father of multiplexing in telephony is considered to be Alexander Graham Bell.
Bell's invention of the telephone in 1876 marked the beginning of modern
telecommunications. He made significant contributions to the development of multiplexing
techniques, particularly in the early days of telephone communication. One of Bell's notable
achievements was the invention of the harmonic telegraph, also known as the "harmonic
multiplexer," which allowed multiple telegraph signals to be transmitted simultaneously over a
single wire.
3. What are the four types of Multiplexing?
The four main types of multiplexing are:
Frequency Division Multiplexing (FDM): In FDM, the available bandwidth is divided
into multiple non-overlapping frequency bands, and each band is allocated to a
different communication channel. This allows multiple signals to be transmitted
simultaneously without interfering with each other. FDM is commonly used in
applications such as traditional analog television and radio broadcasting.
Time Division Multiplexing (TDM): TDM divides the transmission channel into
sequential time slots, and each user or device is allocated one or more time slots for
data transmission. Users take turns transmitting their data during their designated
time slots, enabling multiple signals to share the same communication channel
without overlapping. TDM is widely used in digital communication systems, including
telecommunications networks and digital subscriber lines (DSL).
Code Division Multiplexing (CDM): CDM assigns a unique code to each user or
data stream, and all users transmit simultaneously over the same frequency
spectrum. The receiver uses the appropriate decoding mechanism to extract the
intended data stream based on the assigned code. CDMA (Code Division Multiple
Access) is a popular example of CDM used in mobile communication systems.
Space Division Multiplexing (SDM): SDM involves the allocation of separate
physical paths or spatial domains within the transmission medium to different users or
data streams. This can be achieved through techniques like multiple antennas (MIMO
- Multiple Input Multiple Output) or beamforming, allowing multiple users to transmit
simultaneously without interfering with each other. SDM is commonly used in wireless
communication systems to increase capacity and improve signal quality.
You might also like
- Mobile and Wireless Communication Complete Lecture Notes #1Document22 pagesMobile and Wireless Communication Complete Lecture Notes #1Student Lecture Notes100% (3)
- Multiplexing Is A Technique Used in Telecommunications and Computer Networks To Combine Multiple Signals Into One MediumDocument14 pagesMultiplexing Is A Technique Used in Telecommunications and Computer Networks To Combine Multiple Signals Into One Mediumhemantha dalugamaNo ratings yet
- What Is MultiplexingDocument11 pagesWhat Is Multiplexinghemantha dalugamaNo ratings yet
- Multiplexing FDM TDM and TCM PDFDocument8 pagesMultiplexing FDM TDM and TCM PDFQuang Nghĩa VõNo ratings yet
- Overview: Techniques. Furthermore, We'll Present The Basic Idea Behind TheseDocument51 pagesOverview: Techniques. Furthermore, We'll Present The Basic Idea Behind Thesejowelantonio20No ratings yet
- College of Engineering and TechnologDocument12 pagesCollege of Engineering and TechnologSã MïNo ratings yet
- Multiplexing in Mobile ComputingDocument5 pagesMultiplexing in Mobile ComputingKarthikeyan RamajayamNo ratings yet
- LTI Mobile Computing3Document3 pagesLTI Mobile Computing3Abdul LaNo ratings yet
- Multiple Access Tech and DS CDMA 03 Feb 23Document154 pagesMultiple Access Tech and DS CDMA 03 Feb 23Tanmoy PandeyNo ratings yet
- Multiplexing PDFDocument2 pagesMultiplexing PDFparas3775No ratings yet
- "Introduction To Communication Systems": Chapter-1Document15 pages"Introduction To Communication Systems": Chapter-1Mohamed SaeeDNo ratings yet
- Code-Division Multiple AccessDocument11 pagesCode-Division Multiple AccessMr. Akhil WaliaNo ratings yet
- Multiplexing - Theory and ConceptDocument6 pagesMultiplexing - Theory and ConceptsolayanoNo ratings yet
- Seminar CdmaDocument21 pagesSeminar CdmaMohit BansalNo ratings yet
- Introduction About Telecom: TelecommunicationDocument29 pagesIntroduction About Telecom: TelecommunicationChandra Prakash BhartiNo ratings yet
- Group 2Document12 pagesGroup 2Tolu AyanaNo ratings yet
- Fdmatdmacdma 181225151208Document43 pagesFdmatdmacdma 181225151208Nada A. AminNo ratings yet
- 13.channel Estimation For Wireless Communication.Document1 page13.channel Estimation For Wireless Communication.Sameer NandanNo ratings yet
- Differences Between TDMA, CDMA, and FDMADocument1 pageDifferences Between TDMA, CDMA, and FDMAKarthik Mohan KNo ratings yet
- Assignment#1 OF Mobile and ADHOC NetworksDocument13 pagesAssignment#1 OF Mobile and ADHOC NetworksRajesh RanaNo ratings yet
- CD MaDocument28 pagesCD MaParminder SinghNo ratings yet
- Introduction (Report Comms)Document3 pagesIntroduction (Report Comms)Gerard GuangcoNo ratings yet
- Difference Between OFDM and OFDMADocument4 pagesDifference Between OFDM and OFDMAskshna100% (1)
- Cdma Deepak Final 1Document83 pagesCdma Deepak Final 1deepak18mNo ratings yet
- Department OF Electronics & Communication: Lab Manual (It 501) " Data Communication"Document45 pagesDepartment OF Electronics & Communication: Lab Manual (It 501) " Data Communication"Deeksha KulshresthaNo ratings yet
- Multiplexing & DemultiplexingDocument4 pagesMultiplexing & DemultiplexingJabal JaisNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document24 pagesChapter 5Alexander VoltaNo ratings yet
- MC Mid1 SaqDocument4 pagesMC Mid1 SaqDJ Narotham SaiNo ratings yet
- Basic of MultiplexingDocument4 pagesBasic of MultiplexingÁñúrāG 444No ratings yet
- Multiple Input-Multiple Output Ofdm SystemsDocument36 pagesMultiple Input-Multiple Output Ofdm SystemsLoukya KuttiNo ratings yet
- WMC Practical FileDocument25 pagesWMC Practical FileDilpalNo ratings yet
- MUTIPLEXINGDocument5 pagesMUTIPLEXINGMadhu SwtyNo ratings yet
- Eee Presentation Fully Completed 111111Document11 pagesEee Presentation Fully Completed 111111Mohitha BandiNo ratings yet
- Access Methods For Mobile Networks - ShavaneDocument2 pagesAccess Methods For Mobile Networks - ShavaneDrumz Staff50% (2)
- Multiplexing: Figure 1: Concept of MultiplexingDocument4 pagesMultiplexing: Figure 1: Concept of MultiplexingMohammad Afiq AbidinNo ratings yet
- Unit 8 Multiplexing: StructureDocument15 pagesUnit 8 Multiplexing: StructurelandNo ratings yet
- Abhishek Sharma - Generations - of - Wireless - Communication - FRDocument9 pagesAbhishek Sharma - Generations - of - Wireless - Communication - FRscheeleNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Multiplexing TechniqDocument7 pagesChapter 3 Multiplexing TechniqJoshua DomaNo ratings yet
- 4th Lecture Access TechniquesDocument2 pages4th Lecture Access TechniquesAyesha NawazNo ratings yet
- Activity 3 Multiple Access Channeling ProtocolsDocument6 pagesActivity 3 Multiple Access Channeling ProtocolsJames Rannel BayonaNo ratings yet
- CD MaDocument8 pagesCD MaDheeraj BahadurNo ratings yet
- Mobile & Wireless Lecture # 1 by Engr. Sajjad KarimDocument21 pagesMobile & Wireless Lecture # 1 by Engr. Sajjad KarimShah Zeb YousafzaiNo ratings yet
- Multiplexing:: ApllicationsDocument6 pagesMultiplexing:: ApllicationsMominaIdreesNo ratings yet
- Wireless Mobile CommunicationDocument6 pagesWireless Mobile Communicationduyttcute1989No ratings yet
- Frequency Domain MultiplexingDocument1 pageFrequency Domain Multiplexingunivcj30No ratings yet
- Frequency Reuse: Channel Access MethodDocument6 pagesFrequency Reuse: Channel Access MethodBassy KaserNo ratings yet
- An Efficient Strategy For Multiuser Detection in CdmaDocument40 pagesAn Efficient Strategy For Multiuser Detection in CdmaNiveli NaiviNo ratings yet
- 1 MultiplexingDocument19 pages1 Multiplexingdalisoullemu02No ratings yet
- Technology Digest: Evolu On of Mobile Communica Ons (1G, 2G and 3G) - Part IDocument6 pagesTechnology Digest: Evolu On of Mobile Communica Ons (1G, 2G and 3G) - Part IManoharNo ratings yet
- Time Division Multiple Access (TDMA) Is A Channel Access MethodDocument59 pagesTime Division Multiple Access (TDMA) Is A Channel Access MethodMaheshwar KumarNo ratings yet
- MUltiplexing FinalDocument6 pagesMUltiplexing FinalPratham KangraNo ratings yet
- Wireless Communication: An OverviewDocument10 pagesWireless Communication: An Overviewmihir_damNo ratings yet
- Sdma - Tdma - Fdma - Cdma.Document11 pagesSdma - Tdma - Fdma - Cdma.julie MNo ratings yet
- Multiple Access TDMADocument5 pagesMultiple Access TDMAJasman SinghNo ratings yet
- MC Answer Key 1Document47 pagesMC Answer Key 1Neeraj SinghNo ratings yet
- Computer Networks Assignment-2: Topic-Working of Physical Layer in 1G, 2G, 3G and 4G NetworksDocument12 pagesComputer Networks Assignment-2: Topic-Working of Physical Layer in 1G, 2G, 3G and 4G NetworksPunit KyalNo ratings yet
- Multiple XingDocument34 pagesMultiple XingRafia ShoukatNo ratings yet
- CDMA TextDocument7 pagesCDMA TextNriman ShehadehNo ratings yet
- Term Paper On CDMADocument5 pagesTerm Paper On CDMATaufeeq Malik100% (1)
- SLA Ortega Review IH 29Document1 pageSLA Ortega Review IH 29muttieNo ratings yet
- Management Information Systems Research Center, University of Minnesota Is Collaborating With JSTOR ToDocument18 pagesManagement Information Systems Research Center, University of Minnesota Is Collaborating With JSTOR ToMohd DaruziNo ratings yet
- Good and Poor Design Comparison (Template)Document3 pagesGood and Poor Design Comparison (Template)Samantha De CárdenasNo ratings yet
- Impact of Using CellphonesDocument31 pagesImpact of Using CellphonesJames Baryl GarceloNo ratings yet
- Cps InfographicDocument1 pageCps Infographicapi-665846419No ratings yet
- Cell Bridge - RESUME - SharifDocument2 pagesCell Bridge - RESUME - SharifBoby SharifNo ratings yet
- 4.8 Consequences of Uses of ComputingDocument2 pages4.8 Consequences of Uses of ComputinglouistestevensNo ratings yet
- Impact of English Camp To StudentsDocument20 pagesImpact of English Camp To StudentsJanella SeNo ratings yet
- UBBP - HuaweiDocument18 pagesUBBP - HuaweiVod MonkeyNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect - Complete Spanish GrammarrDocument3 pagesPractice Makes Perfect - Complete Spanish Grammarrgweber.gw6380No ratings yet
- Two - Track Approach PresentationDocument32 pagesTwo - Track Approach PresentationDivine Grace Samortin89% (18)
- (Human Cognitive Processing, V. 26) Graham Low - Et Al-Researching and Applying Metaphor in The Real World (2010)Document400 pages(Human Cognitive Processing, V. 26) Graham Low - Et Al-Researching and Applying Metaphor in The Real World (2010)yo_yo9_1No ratings yet
- HCIDocument22 pagesHCIHimanshu ThakurNo ratings yet
- RPP Vocabulary Ok DikonversiDocument8 pagesRPP Vocabulary Ok DikonversiMiftahul JannahNo ratings yet
- LESSON PLAN BlankDocument6 pagesLESSON PLAN BlankDaniela CebotariNo ratings yet
- Big Data - Introduction: RavichandranDocument44 pagesBig Data - Introduction: RavichandranVaidyanathan RavichandranNo ratings yet
- 10 Case StudiesDocument29 pages10 Case StudiesKr Chandra ShekharNo ratings yet
- Pendekatan Etika KristenDocument19 pagesPendekatan Etika KristenVelLa Lilinsa AsbanuNo ratings yet
- Principles of MKTG Module Jan 11-29Document18 pagesPrinciples of MKTG Module Jan 11-29Roz AdaNo ratings yet
- TRF - JanetDocument3 pagesTRF - Janetjudelyn jamilNo ratings yet
- DC Module1 PDFDocument63 pagesDC Module1 PDFAfraNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Letter WritingDocument20 pagesMechanics of Letter WritingNavneet NandaNo ratings yet
- Summary TeflDocument4 pagesSummary TeflAlVin AryaGiansNo ratings yet
- Steps in Development of Media PlanDocument4 pagesSteps in Development of Media PlanSeemaNo ratings yet
- 3 - LanguageDocument5 pages3 - Languagepablodarko84No ratings yet
- Intoducing Product: Coco Peat Batok Kelapa Minyak SerehDocument46 pagesIntoducing Product: Coco Peat Batok Kelapa Minyak SerehMohamadFatihRidwanMangkudewoNo ratings yet
- English Proficiency of Grade 9 Junior High StudentsDocument24 pagesEnglish Proficiency of Grade 9 Junior High StudentsEditor IJTSRD100% (1)
- Computer Networking: A Top-Down Approach Featuring The InternetDocument27 pagesComputer Networking: A Top-Down Approach Featuring The InternetmssacNo ratings yet
- Pivot 4A: School Teacher Teaching Date Teaching TimeDocument3 pagesPivot 4A: School Teacher Teaching Date Teaching TimeMam Lorna Es GeeNo ratings yet
- UNIT - I Coding-DecodingDocument24 pagesUNIT - I Coding-DecodingChandan SinghNo ratings yet