Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Donia's Summary For TQM
Donia's Summary For TQM
Uploaded by
Dønia Àymàn Èid0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views1 pageQuality control focuses on finished products and ensures they meet quality standards through inspection, testing, and audits. It is reactive in nature and aims to identify and correct defects. Quality assurance is more proactive as it focuses on processes and aims to prevent defects by ensuring processes are designed and controlled properly through documentation, training, process improvement, and risk management. It involves all team members and uses tools like statistical process control and process audits to verify and review processes.
Original Description:
Original Title
Donia's summary for TQM
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentQuality control focuses on finished products and ensures they meet quality standards through inspection, testing, and audits. It is reactive in nature and aims to identify and correct defects. Quality assurance is more proactive as it focuses on processes and aims to prevent defects by ensuring processes are designed and controlled properly through documentation, training, process improvement, and risk management. It involves all team members and uses tools like statistical process control and process audits to verify and review processes.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views1 pageDonia's Summary For TQM
Donia's Summary For TQM
Uploaded by
Dønia Àymàn ÈidQuality control focuses on finished products and ensures they meet quality standards through inspection, testing, and audits. It is reactive in nature and aims to identify and correct defects. Quality assurance is more proactive as it focuses on processes and aims to prevent defects by ensuring processes are designed and controlled properly through documentation, training, process improvement, and risk management. It involves all team members and uses tools like statistical process control and process audits to verify and review processes.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
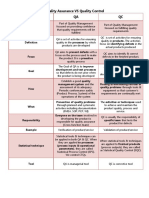
Differences between Quality control and Quality assurance
Feature Quality Control (QC) Quality Assurance (QA)
Focus Finished products Processes used to make products
Action Reactive: Identifies and corrects defects Proactive: Prevents defects
Ensure processes are designed and
controlled to produce high-quality
Goal Ensure products meet quality standards products
Documentation, training, process
Activities Inspection, testing, audits improvement, risk management
All team members involved in product
Responsibility Dedicated QC team development
Statistical quality control (SQC), Statistical process control (SPC), risk
Tools inspection checklists assessment tools, process audits
Verification, Design reviews, supplier
Example Software testing, final product inspection evaluation, training programs
Corrective (fixes the problem after it Preventive (avoids problems before they
Nature occurs) occur)
Primarily direct costs associated with QC Primarily indirect costs associated with QA
Cost activities activities
Improves product quality, reduces return, Reduces production costs, improves
Benefits enhances customer satisfaction process efficiency, minimizes rework
References
- Total Quality Management Third Edition Poornima M. Charantimath
- American Society for Quality (ASQ)
- Oakland (2003); Dale & Oakland (1997) - Emerald
Under supervision: Dr. Mohammad Abdulwakeel Ata – February 22, 2024
You might also like
- Quality Assurance Vs Quality ControlDocument1 pageQuality Assurance Vs Quality Controlpsathishthevan100% (1)
- Textile Testing & Quality ControlDocument7 pagesTextile Testing & Quality ControlMahmuda Chowdhury100% (3)
- QA Vs QCDocument1 pageQA Vs QCBaljeetNo ratings yet
- Difference Between QA & QC.Document1 pageDifference Between QA & QC.bkumar.ece91No ratings yet
- Quality Control Vs AssuranceDocument1 pageQuality Control Vs AssuranceBani MarweinNo ratings yet
- Ality Control and Quality AssuranceDocument22 pagesAlity Control and Quality AssuranceAlice MakeNo ratings yet
- Qa QCDocument22 pagesQa QCAnnisa RahmatinaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Introduction To Quality ManagementDocument43 pagesChapter 1 Introduction To Quality ManagementNafis SprataNo ratings yet
- Quality Assurance VS Quality Control Category QA QCDocument1 pageQuality Assurance VS Quality Control Category QA QCirc.indusNo ratings yet
- QM MergedDocument76 pagesQM MergedSneha Giji SajiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Introduction To Quality Management (Autosaved)Document43 pagesChapter 1 Introduction To Quality Management (Autosaved)Arvin RajNo ratings yet
- QA Vs QCDocument4 pagesQA Vs QCBalaNo ratings yet
- QCR Chapter 1Document48 pagesQCR Chapter 1praveenkumarnitkkrNo ratings yet
- Chapter-1: Introduction To Textile TestingDocument5 pagesChapter-1: Introduction To Textile TestingsatexNo ratings yet
- QualityDocument38 pagesQualityserviceNo ratings yet
- QA Basic Testing IntroductionV06 - 20012021Document105 pagesQA Basic Testing IntroductionV06 - 20012021Harold CamachoNo ratings yet
- Assignment 01: Department of Mechatronic Nust College of Electrical and Mechanical EngineeringDocument3 pagesAssignment 01: Department of Mechatronic Nust College of Electrical and Mechanical EngineeringUsama IhazNo ratings yet
- Welcome To Quality SESSION: QC QADocument30 pagesWelcome To Quality SESSION: QC QAAbou Tebba SamNo ratings yet
- Lecture # 1 - SlidesDocument73 pagesLecture # 1 - SlidesDeny AnsariNo ratings yet
- Control Vs Quality AssuranceDocument14 pagesControl Vs Quality Assuranceumama amjadNo ratings yet
- Quality Assurance vs. Quality Control: Ms. Soomaiya HamidDocument14 pagesQuality Assurance vs. Quality Control: Ms. Soomaiya Hamidumama amjadNo ratings yet
- Quality Control Vs Quality AssuranceDocument14 pagesQuality Control Vs Quality AssuranceSoomaiya HamidNo ratings yet
- Concept of QA & QCDocument16 pagesConcept of QA & QCVidit OberoiNo ratings yet
- QC & Qa PDFDocument22 pagesQC & Qa PDFAmr El-BahnasawyNo ratings yet
- QC Exam QuestionDocument30 pagesQC Exam QuestionMd. Ahedul IslamNo ratings yet
- Quality Assurance & GMPDocument39 pagesQuality Assurance & GMPVaishnavi KarmveerNo ratings yet
- Dr. Masoom Qa 1-Qa 1-Qa 1Document42 pagesDr. Masoom Qa 1-Qa 1-Qa 1Muhammad Masoom AkhtarNo ratings yet
- Quality Management (Quality AssuranceDocument79 pagesQuality Management (Quality AssuranceMrym NbNo ratings yet
- Introduction TTQC IIIDocument42 pagesIntroduction TTQC IIIRounoque ShishirNo ratings yet
- Important Questions of Cpa EditedDocument58 pagesImportant Questions of Cpa EditedMohammed TayyabNo ratings yet
- Verification & Validation LimitationsDocument10 pagesVerification & Validation LimitationsSparsh Gupta ASET, JaipurNo ratings yet
- محاضرة 1 جودةDocument29 pagesمحاضرة 1 جودةAmira HossamNo ratings yet
- Administración de ProyectosDocument7 pagesAdministración de Proyectosyennis de arcoNo ratings yet
- QA Interview QuestionsDocument45 pagesQA Interview Questionsmagiofficial97No ratings yet
- Slide DeckDocument45 pagesSlide Deckpranjal.mathurNo ratings yet
- Q1 A) Distinguish Between Quality Control Quality Assurance and Total Quality ManagementDocument1 pageQ1 A) Distinguish Between Quality Control Quality Assurance and Total Quality Managementsaravananpg8697No ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - Introduction To QCQA PDFDocument11 pagesLecture 1 - Introduction To QCQA PDFAli shayanNo ratings yet
- محاضرة 1 جودةDocument29 pagesمحاضرة 1 جودةsalmanasserr95No ratings yet
- Session-2 & 3 Quality - Evolution of QualityDocument20 pagesSession-2 & 3 Quality - Evolution of Qualitymatten yahyaNo ratings yet
- Prezentare Ppt. Engleza de AfaceriDocument14 pagesPrezentare Ppt. Engleza de AfaceriCristinaFlorentinaSoraNo ratings yet
- Module 01Document100 pagesModule 01Essam ZatoutNo ratings yet
- Quality ManagementDocument30 pagesQuality ManagementAlamin KhanNo ratings yet
- Qa & QCDocument18 pagesQa & QCEdgardo Ed RamirezNo ratings yet
- 2 Total Quality ManagementDocument33 pages2 Total Quality Managementzenia thea dulayNo ratings yet
- TQM Unit 1Document15 pagesTQM Unit 1utkarshtyagi2307No ratings yet
- QA Vs QCDocument1 pageQA Vs QCAshutosh SinghNo ratings yet
- Quality in Construction Works: An Introduction To QA/QC Concept and Quality Management System Based On ISO 9001:2008Document38 pagesQuality in Construction Works: An Introduction To QA/QC Concept and Quality Management System Based On ISO 9001:2008sid_calayag100% (2)
- Quality Assurance Vs Quality Control: Team MembersDocument21 pagesQuality Assurance Vs Quality Control: Team MembersMuhib UllahNo ratings yet
- Quality Assurance Quality Control and Testing WhitepaperDocument39 pagesQuality Assurance Quality Control and Testing WhitepaperJairo Israel Alvarez CordovaNo ratings yet
- Inleiding Tot de Logistiek (3542) : Prof. Dr. Kris BraekersDocument75 pagesInleiding Tot de Logistiek (3542) : Prof. Dr. Kris BraekersJoost VerheyenNo ratings yet
- QC Module2Document26 pagesQC Module2Ulah LaliNo ratings yet
- Concept & Evolution of QC QADocument20 pagesConcept & Evolution of QC QARyan 1112No ratings yet
- IE 3 Reviewer LESSON 1 6Document13 pagesIE 3 Reviewer LESSON 1 6Tina RetaNo ratings yet
- Software Quality Assurance and QA IssuesDocument21 pagesSoftware Quality Assurance and QA IssuesLij Melkam AbuhayNo ratings yet
- CGMP Process ValidationDocument30 pagesCGMP Process Validationliyevig969No ratings yet
- Pendahuluan ManajemenDocument10 pagesPendahuluan ManajemenwandizeeNo ratings yet
- SQA IntroductionDocument16 pagesSQA IntroductionAsad AkhlaqNo ratings yet
- Quality Definations, by DoniaDocument1 pageQuality Definations, by DoniaDønia Àymàn ÈidNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 6 Intr CorporationsDocument9 pagesTutorial 6 Intr CorporationsDønia Àymàn ÈidNo ratings yet
- Strategic ManagementDocument35 pagesStrategic ManagementDønia Àymàn ÈidNo ratings yet
- Advanced StudiesDocument18 pagesAdvanced StudiesDønia Àymàn ÈidNo ratings yet
- Chapter Six: Products, Services, and Brands: Building Customer ValueDocument60 pagesChapter Six: Products, Services, and Brands: Building Customer ValueDønia Àymàn ÈidNo ratings yet