Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Math 121 Module 4
Math 121 Module 4
Uploaded by
Azhel0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views1 pageThe document discusses exact differential equations. It defines an exact differential equation as one that involves the derivative of one variable with respect to another and can be solved directly without special techniques. It explains that a first-order differential equation is exact if it can be written as the result of a simple differentiation. The document provides an example of determining if a given differential equation is exact and, if so, solving for the general solution. It outlines the process of partial integration and combining terms to find the general solution.
Original Description:
MATH 121 - Module 4 in College
Original Title
MATH 121 MODULE 4
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses exact differential equations. It defines an exact differential equation as one that involves the derivative of one variable with respect to another and can be solved directly without special techniques. It explains that a first-order differential equation is exact if it can be written as the result of a simple differentiation. The document provides an example of determining if a given differential equation is exact and, if so, solving for the general solution. It outlines the process of partial integration and combining terms to find the general solution.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views1 pageMath 121 Module 4
Math 121 Module 4
Uploaded by
AzhelThe document discusses exact differential equations. It defines an exact differential equation as one that involves the derivative of one variable with respect to another and can be solved directly without special techniques. It explains that a first-order differential equation is exact if it can be written as the result of a simple differentiation. The document provides an example of determining if a given differential equation is exact and, if so, solving for the general solution. It outlines the process of partial integration and combining terms to find the general solution.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
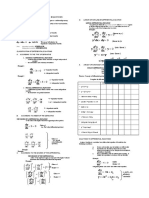
MIDTERM EXAMPLE: Determine whether the DE 2xydx + (1+x2) dy = 0 is exact.
If so, solve for the general solution.
WEEK/MODULE- 4 Solution:
EXACT DIFFERENTIAL EQUATION
Exact differential equation definition is an equation which contains one
or more terms. It involves the derivative of one variable (dependent
variable) with respect to the other variable (independent variable).
Type of differential equation that can be solved directly without the use
of any of the special techniques in the subject. A first-order differential
equation (of one variable) is called exact, or an exact differential, if it is
the result of a simple differentiation.
EXAMPLE: Find the general solution of the differential equation, (2x +
y -3) dx + (x- 4y+1) dy = 0.
Solution:
(The subscripts in this equation indicate which variable the partial
derivative is taken with respect to.)
∫ M(x, y) 𝑑𝑥 = A partial integration (variables other than x will be
treated as constant)
∫ N(x, y) 𝑑𝑦 = B partial integration (variables other than y will be
treated as constant)
For the general solution: Combine A and B (common expressions will
become single unit)
1 MATH 121 | D I F F E R E N T I A L E Q U A T I O N
You might also like
- Engineering Mathematics by Mohammad Abdul HalimDocument249 pagesEngineering Mathematics by Mohammad Abdul HalimArnobNo ratings yet
- Module 4 - Math 121Document1 pageModule 4 - Math 121AzhelNo ratings yet
- Module Chapter 2 Variable Separable Differential EquationDocument5 pagesModule Chapter 2 Variable Separable Differential EquationChristian Jay Miano BojosNo ratings yet
- Differential Equations BasicDocument4 pagesDifferential Equations BasicBenjaminNo ratings yet
- Differential EquationDocument7 pagesDifferential EquationRonaldNo ratings yet
- Calculus Assignment FinalDocument16 pagesCalculus Assignment FinalYared DemissieNo ratings yet
- Differential Equations-1st Order, 1st DegreeDocument9 pagesDifferential Equations-1st Order, 1st DegreeVince Rabin CandidatoNo ratings yet
- Differential EquationsDocument5 pagesDifferential EquationsJoe Randy100% (2)
- Differential Equations: Solution by Direct IntegrationDocument7 pagesDifferential Equations: Solution by Direct IntegrationGlennmark RodriguesNo ratings yet
- MTH312 NotesDocument98 pagesMTH312 NotesAnmol PanchalNo ratings yet
- First Order ODEDocument15 pagesFirst Order ODEKevin JinNo ratings yet
- LP-1-Differential EquationDocument25 pagesLP-1-Differential EquationHaya BusaNo ratings yet
- Math 206 - Differential Equations Andy Rosen Please Sign inDocument23 pagesMath 206 - Differential Equations Andy Rosen Please Sign inAston RiceNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - Math 121Document3 pagesModule 1 - Math 121Nicko Candia ReyesNo ratings yet
- Separable Differential EquationsDocument7 pagesSeparable Differential EquationsLeopold LasetNo ratings yet
- 18.034 Honors Differential Equations: Mit OpencoursewareDocument4 pages18.034 Honors Differential Equations: Mit OpencoursewareParatus AlcántaraNo ratings yet
- Differential Equations ReviewDocument20 pagesDifferential Equations Reviewsaimom sarkerNo ratings yet
- Chapter One 1.1 Differential Equation: (Also, Mention What A Solution of Differential Equation Means)Document10 pagesChapter One 1.1 Differential Equation: (Also, Mention What A Solution of Differential Equation Means)aaryan khanalNo ratings yet
- Well-Posed Problems of An IvpDocument3 pagesWell-Posed Problems of An IvpJustin PerezNo ratings yet
- Project Work MTH 400Document19 pagesProject Work MTH 400chukwudiemmanuel154No ratings yet
- Ordinary Differential EquationsDocument16 pagesOrdinary Differential EquationsShehroze Khan Nyaze Noori khelNo ratings yet
- First Order Ordinary Linear Differential EquationsDocument23 pagesFirst Order Ordinary Linear Differential EquationsRobinNo ratings yet
- Exact EquationsDocument11 pagesExact EquationsNelsonMoseMNo ratings yet
- App Mathematics III-1Document15 pagesApp Mathematics III-1FikruNo ratings yet
- Ch.1 Introduction To Differential EquationsDocument23 pagesCh.1 Introduction To Differential EquationsHazem AlmasryNo ratings yet
- Differential Equations Basic Concepts, Definitions, and ClassificationDocument53 pagesDifferential Equations Basic Concepts, Definitions, and ClassificationCivil Engineering 1CNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Mathematics of FinanceDocument19 pagesIntroduction To Mathematics of FinanceMehroze ElahiNo ratings yet
- C&DE Unit - IVDocument11 pagesC&DE Unit - IV2103a51450No ratings yet
- General and Particular Differential Equations Solutions - Videos, Examples PDFDocument1 pageGeneral and Particular Differential Equations Solutions - Videos, Examples PDFTakudzwa ZengeraniNo ratings yet
- ODE SectionDocument11 pagesODE SectionPraneeth AnjanaNo ratings yet
- ES 21 Second Exam D.E.1 - NotesDocument5 pagesES 21 Second Exam D.E.1 - NotesGil Kenneth San MiguelNo ratings yet
- 4 Ordinary Differential EquationsDocument91 pages4 Ordinary Differential EquationsKai CaoNo ratings yet
- Level 3 Ebe Odes (Updated)Document29 pagesLevel 3 Ebe Odes (Updated)Cloyd Vincent De CastroNo ratings yet
- What Are Differential Equations ?Document17 pagesWhat Are Differential Equations ?Nidaa FlaihNo ratings yet
- Session 2 (20)Document10 pagesSession 2 (20)supriti83No ratings yet
- Differential Equations PDFDocument5 pagesDifferential Equations PDF2001divya1959No ratings yet
- Differential Equations IntroDocument29 pagesDifferential Equations IntroMansi NanavatiNo ratings yet
- University of Zimbabwe: Linear Algebra and Probability For EngineeringDocument18 pagesUniversity of Zimbabwe: Linear Algebra and Probability For EngineeringPromise GwaindepiNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Dela Sem. II B.tech. Ma0211Document4 pagesUnit 1 Dela Sem. II B.tech. Ma0211BHADORIYA ADITYASINHNo ratings yet
- Module 3 - Math 121Document1 pageModule 3 - Math 121AzhelNo ratings yet
- MATH2860 ODE Lecture0 IntroDocument8 pagesMATH2860 ODE Lecture0 IntroDanah Al ShemarieNo ratings yet
- First Order Ordinary Differential EquationsDocument11 pagesFirst Order Ordinary Differential Equationstobianimashaun99No ratings yet
- Differential Equation Area Under The Curve 1645520155242Document50 pagesDifferential Equation Area Under The Curve 1645520155242Abhishek KothariNo ratings yet
- Solutions of Some 1 Order, 1 Degree D.E.: Differential EquationsDocument23 pagesSolutions of Some 1 Order, 1 Degree D.E.: Differential EquationsMay Ann AceraNo ratings yet
- 11 3 Higher DerivativesDocument10 pages11 3 Higher Derivativestarek mahmoudNo ratings yet
- Notes For Diffrentai EquationsDocument10 pagesNotes For Diffrentai EquationsAksyNo ratings yet
- AP3114 Lecture WK10 Solving Differential Eqautions IDocument35 pagesAP3114 Lecture WK10 Solving Differential Eqautions IGuoXuanChanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Ordinary Diffrential Equations-JADocument27 pagesChapter 1 Ordinary Diffrential Equations-JAعبدالكريم الدليميNo ratings yet
- Chapter 01 by M.A.HALIMDocument5 pagesChapter 01 by M.A.HALIMArnobNo ratings yet
- First Order and First Degree Differential EquationDocument22 pagesFirst Order and First Degree Differential EquationHi HiNo ratings yet
- OdeDocument47 pagesOdeReiniel AllanicNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 - Homogeneous DEDocument15 pagesTopic 3 - Homogeneous DESelaras KyleNo ratings yet
- Dif LecturenotesDocument168 pagesDif LecturenotesbaransakirhvhNo ratings yet
- Week 014 Differential Equations - Separable EquationsDocument3 pagesWeek 014 Differential Equations - Separable Equationsvit.chinnajiginisaNo ratings yet
- Differential EquationDocument16 pagesDifferential Equationशिवम् सुनील कुमारNo ratings yet
- STEP Support Programme STEP 3 Differential Equations Topic NotesDocument2 pagesSTEP Support Programme STEP 3 Differential Equations Topic NotesNani AhmedNo ratings yet
- Best Approach: Differential EquationDocument31 pagesBest Approach: Differential EquationTanmay SagarNo ratings yet
- Chapters 1-2 Lecture NotesDocument62 pagesChapters 1-2 Lecture NotespastelgorengNo ratings yet
- Mathematics 1St First Order Linear Differential Equations 2Nd Second Order Linear Differential Equations Laplace Fourier Bessel MathematicsFrom EverandMathematics 1St First Order Linear Differential Equations 2Nd Second Order Linear Differential Equations Laplace Fourier Bessel MathematicsNo ratings yet
- Green's Function Estimates for Lattice Schrödinger Operators and Applications. (AM-158)From EverandGreen's Function Estimates for Lattice Schrödinger Operators and Applications. (AM-158)No ratings yet
- Module 4 - Es 125Document1 pageModule 4 - Es 125AzhelNo ratings yet
- Module 5 - Math 121Document1 pageModule 5 - Math 121AzhelNo ratings yet
- Art Appreciation Report 5Document7 pagesArt Appreciation Report 5AzhelNo ratings yet
- Hydrographic Survey FinalDocument1 pageHydrographic Survey FinalAzhelNo ratings yet
- Theories and Views On GenderDocument2 pagesTheories and Views On GenderAzhelNo ratings yet