Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Physics 2
Physics 2
Uploaded by
mathiasshereni243Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Physics 2
Physics 2
Uploaded by
mathiasshereni243Copyright:
Available Formats
Question
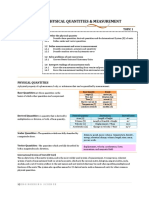
1) What are physical quantities.
2) State any four base quantities and their SI Units
3) Define length
4) Three instruments used to measure length
Answers
1) Physical quantity is a property of an object or substance that can be measured using an appropriate measuring instrument.
2) Base quantities and their SI Units
Quantity SI Unit
Length meter
Temperature kelvins
Mass kilograms
Time seconds
Electric current Amphere
Amount of substance moles
c) Length is a straight line distance between two points along an object.
d) Instruments used to measure length.
i. Vernier caliper
ii. Ruler
iii. Screw gauge micrometer
Question
a) Write notes on
i. Ruler/measuring tape
ii. Vernier caliper
iii. Screw gauge micrometer
b) SI Unit stands for
Ruler….
Have markings as small as a cm, each cm is divided into 10 divisions which are mm.
When taking measurements your eye must be directly above the reading to avoid parallax errors.
Place the object to be measured in the line with the zero error
Rulers can measure to the nearest mm.
Vernier Caliper…
A tool that is used for taking highly accurate measurements.
It has two scales, a main scale with the markings similar to those on a ruler and a Vernier caliper scale with the markings in 0,1mm
increments.
Vernier caliper are especially useful in measuring the diameter of objects such as pipes.
Screw gauge micrometer…
Can measure smaller lengths than Vernier calipers
It can measure small objects to 0,001cm
One revelation of the thimble opens accurately flat, parallel jaws by one division on the scale on the shaft of the gauge, it is usually one
and a half mm that is 0.05cm
If the thimble has a scale of 50 divisions round it, then rotation of the drum by one division open the jaws by 0,05 over 50 = 0,001 cm
A friction clutch ensures that the jaws exact the same force when the object is gripped.
How to read a caliper
To measure the internal, external diameter
Take the mm from the main scale markings before the zero on the Vernier mark to consider with a main scale mark.
Add the two readings.
Derived units.
i. The units of all other quantities are derived from these base units.
Derived Quantity How it is derived Unit
Density M/V mass Kg/m^3
volume
Area LXL m^2
Length X Length
Velocity L/T Length m/s
Time
Acceleration V/T Velocity m/s^2
Time
Question.. (Mechanical systems)
a) Define a machine
b) What do you understand by the following terms
i. Mechanical advantage
ii. Velocity ratio
iii. Efficiency
Answers
a) A machine is a device that causes a change in the way that forces it to make hard work easier.
A mechanical system designed to make hard work easier e . g (1) inclined planes
(2) gears
(3) livers by using less applied force to carry heavy things.
i. Mechanical advantage.
It is the measure of how much easier is it to complete using a simple machine.
The greater the (MA) the easier it is to do work.
The ratio of two forces.
Mechanical advantage (MA) = LOAD/EFFORT
ii. Velocity ratio.
It is the ratio of two distances such as distance moved by the effort and distance moved by load.
VR = DISTANCE EFFORT/DISTANCE LOAD.
You might also like
- Science Form1 Chapter 1Document56 pagesScience Form1 Chapter 1Halizah Ramthan88% (17)
- A-level Physics Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Physics Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (10)
- Chapter 1 Physical Quantities and Measurement Lecturer Only1Document45 pagesChapter 1 Physical Quantities and Measurement Lecturer Only1Jerome FizzowNo ratings yet
- Matter? Matter Is Everything That We See and Interact With Which Has Mass and Occupies Some SpaceDocument264 pagesMatter? Matter Is Everything That We See and Interact With Which Has Mass and Occupies Some SpacedickouyuNo ratings yet
- 2019 - 2020 Session SS1 Physics NoteDocument33 pages2019 - 2020 Session SS1 Physics NoteMuhammad AzamuddinNo ratings yet
- 1st Sec. - Physics Full SummaryDocument57 pages1st Sec. - Physics Full SummaryWalaa AmrNo ratings yet
- TenthClass Content EM Physics 01-MeasurementOfLengthDocument10 pagesTenthClass Content EM Physics 01-MeasurementOfLengthArindam GuhaNo ratings yet
- Measurement and Significant Figures: Pre-Lab Study QuestionsDocument3 pagesMeasurement and Significant Figures: Pre-Lab Study QuestionsUmer farooqNo ratings yet
- Tyhjmnf 767Document6 pagesTyhjmnf 767sneha sharmaNo ratings yet
- Phy NotesDocument222 pagesPhy NotesNunu KheesNo ratings yet
- Meaurement and Physical Quantities SPDocument14 pagesMeaurement and Physical Quantities SPsurabhiNo ratings yet
- Chapter One PDFDocument12 pagesChapter One PDFMohamed AbdelghanyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - System of Units UpdatedDocument16 pagesChapter 1 - System of Units UpdatedRN Builder IpohNo ratings yet
- Physics Quick RevisionDocument27 pagesPhysics Quick RevisionAayan AhmadNo ratings yet
- Olevel Physics Revised Edition 2016Document426 pagesOlevel Physics Revised Edition 2016rasheedlukman9No ratings yet
- Phy NotesDocument232 pagesPhy NotesTshegofatso LegadikoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-ADocument1 pageChapter 1-AJoshuaNo ratings yet
- Week - 1 HLAS Q1Document19 pagesWeek - 1 HLAS Q1Cheena Francesca LucianoNo ratings yet
- L1 - Units and Dimensions PDFDocument74 pagesL1 - Units and Dimensions PDFविभूति गर्गNo ratings yet
- Physics Grade 10 To 12 PamphletDocument156 pagesPhysics Grade 10 To 12 PamphletChílënî LengalengaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Notes: Physical Quantities, Units & MeasurementDocument8 pagesChapter 1 Notes: Physical Quantities, Units & MeasurementterrygohNo ratings yet
- Measurement Physics NotesDocument6 pagesMeasurement Physics NotesAhmed OmarNo ratings yet
- DPS Worksheet C01 (Teacher)Document5 pagesDPS Worksheet C01 (Teacher)Regie Sacil EspiñaNo ratings yet
- General Physics BlockDocument43 pagesGeneral Physics Blockmdridomd15No ratings yet
- HBSC4103 Topic 1Document41 pagesHBSC4103 Topic 1atun28No ratings yet
- Physics Notes L1Document9 pagesPhysics Notes L1Dalal NabeelNo ratings yet
- Physics Grade 10 To 12 PamphletDocument156 pagesPhysics Grade 10 To 12 PamphletFrancis BwalyaNo ratings yet
- Physics: Physical QuantitiesDocument28 pagesPhysics: Physical QuantitiesNoorshikha NeupaneNo ratings yet
- 03 - ICSE9th - Physics BookLet 27 May 21Document99 pages03 - ICSE9th - Physics BookLet 27 May 21Vivaan GandhiNo ratings yet
- Phy NotesDocument222 pagesPhy Notesitzprincechichi077No ratings yet
- Besaran Dan SatuanDocument90 pagesBesaran Dan SatuanVerena NatasiaNo ratings yet
- Makalah Units of MeasurementDocument10 pagesMakalah Units of MeasurementRaihan WibawaNo ratings yet
- Unit, Dimension & MeasurementDocument21 pagesUnit, Dimension & MeasurementgginrearrangeitproperlyNo ratings yet
- 1.units and MeasurementsDocument27 pages1.units and Measurementsahmed khanNo ratings yet
- Exp 1 Precision Measurements Lab ManualDocument3 pagesExp 1 Precision Measurements Lab Manualwapaisinixson03No ratings yet
- Grade 10 12 Physics NotesDocument68 pagesGrade 10 12 Physics NotesERIC ZULUNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Physics Notes 2023-24 Chapter 2 Units and MeasurementsDocument35 pagesClass 11 Physics Notes 2023-24 Chapter 2 Units and Measurementsnick tyagiNo ratings yet
- 2018-Quantities, Measurement, Significant Figures, Scientific Notation, Conversion of UnitsDocument50 pages2018-Quantities, Measurement, Significant Figures, Scientific Notation, Conversion of UnitsErika Mae Naparato Pepaño100% (1)
- Chibesa Physics PDFDocument156 pagesChibesa Physics PDFMusanta Simmon SimzNo ratings yet
- 2020 SPM Physics: Chapter 1 Introduction To Physics Scalar and VectorDocument73 pages2020 SPM Physics: Chapter 1 Introduction To Physics Scalar and VectorsharveenaNo ratings yet
- Netsolving Problems Involving Conversion of Units of MeasurementDocument28 pagesNetsolving Problems Involving Conversion of Units of MeasurementFynn NiallNo ratings yet
- Chem101 Ho1Document12 pagesChem101 Ho1Jordan DingayanNo ratings yet
- Unit-Dimensions & Basic Maths PDFDocument40 pagesUnit-Dimensions & Basic Maths PDFSambasivarao GalabaNo ratings yet
- Physics Notes Form 5Document221 pagesPhysics Notes Form 5tonikay219No ratings yet
- Measurements of Physical QuantityDocument8 pagesMeasurements of Physical Quantitycjjorphen24No ratings yet
- Unit and Dimension & Basic Mathematics: Theory and Exercise BookletDocument1,715 pagesUnit and Dimension & Basic Mathematics: Theory and Exercise BookletRekha BhasinNo ratings yet
- Measurement NotesDocument16 pagesMeasurement NotesMurtaza SohailNo ratings yet
- Vernier and Micrometer Caliper-DoneDocument4 pagesVernier and Micrometer Caliper-DoneJAMEL DENYSE FERNANDEZNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument11 pagesPhysicsKeeertththana SaravananNo ratings yet
- CHP 2 Physics BsekDocument9 pagesCHP 2 Physics BsekRaza AliNo ratings yet
- MeasurementDocument2 pagesMeasurementSav OliNo ratings yet
- Introduction To PhysicsDocument135 pagesIntroduction To PhysicsDennis CheruiyotNo ratings yet
- Unite 1 Revision Physics Ms. EsraaDocument14 pagesUnite 1 Revision Physics Ms. Esraamqwe59281No ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument61 pagesPhysicsEmaleku FavourNo ratings yet
- Complete Olevel PhysicsDocument105 pagesComplete Olevel PhysicsSarim AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Making Measurements CMDocument37 pagesMaking Measurements CMelezabethNo ratings yet
- P-9-T1 - 01 Measurement Units - Dimensions PDFDocument32 pagesP-9-T1 - 01 Measurement Units - Dimensions PDFriddhiNo ratings yet
- Chap7 - Dimensions, Units and ConversionsDocument28 pagesChap7 - Dimensions, Units and ConversionsalsinanhananNo ratings yet
- Handbook of Mechanical and Materials EngineeringFrom EverandHandbook of Mechanical and Materials EngineeringRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)