Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter-1 PHT
Chapter-1 PHT
Uploaded by
fg0t1zn0Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter-1 PHT
Chapter-1 PHT
Uploaded by
fg0t1zn0Copyright:
Available Formats
PROCESS HEAT TRANSFER (3340501)
FUNDAMENTALS OF HEAT TRANSFER
HEAT TRANSFER:
Heat transfer deals with the study of rates at which exchange of heat takes
place between hot source and cold receiver.
In process industry there are many operations which involve transfer of
energy in the form of heat. E.g. Evaporation, distillation, drying etc.
Also the chemical reactions carried on commercial scale take place with
evolution or absorption of heat.
Industrial Applications:
Heat transfer methods find a variety of applications in the chemical process
industries.
Heating and Cooling of Batch Tanks……..
This application will allow the user to calculate the time it takes to heat up
and then cool a batch vessel or tank.
The heating methods supported are:
Steam Jacketing or Coil
Electrical Heating Jacket
The cooling methods supported are:
Water Jacketing or Coil
External Cooler (Heat Exchanger)
CONDUCTION:
It is the transfer of heat from one part of a body to another part of a same
body or from one body to another which is in physical contact with it,
without appreciable displacement of particles of a body.
When heat is transferred through conduction, the substance itself does not
flow; rather, heat is transferred internally, by vibrations of atoms and
molecules. Electrons are also carry heat, which is the reason metals are
generally very good conductors of heat. Metals have many free electrons,
PREPARED BY RAKESH VASAVA
PROCESS HEAT TRANSFER (3340501)
which move around randomly; these can transfer heat from one part of the
metal to another.
CONVECTION:
It is the transfer of heat from one point to another point within a fluid (gas
or liquid) by mixing of hot and cold portions of the fluid.
RADIATION:
Radiation refers to the transfer of heat energy from one body to another, not
in contact with it, by electromagnetic waves through space.
STEADY STATE AND UNSTEADY STATE HEAT TRANSFER
Heat transfer is the transfer of thermal e from a body, at a high
temperature, to another at a lower temperature. This transfer of thermal
energy may occur under steady or unsteady state conditions. Under Steady
state conditions the temperature within the system does not change with
time. Conversely, under unsteady state conditions the temperature within
the system does vary with time.
Examples of steady state heat transfer
A steam turbine in a power plant is operating at constant load, constant
temperature, constant flow hour after hour while there is steady state heat
transfer of heat lost from the turbine's housing to the room air.
Examples of unsteady state heat transfer
Think about when you cook an egg, for those of you who do not cook, just
pretend. When you take an egg out of the refrigerator it is at a temperature
of about 5 oC . If you place it in a pot of boiling water, heat is transferred
from the egg’s surface to its center. The temperature throughout the egg is
changing with time, eventually cooking the egg.
PREPARED BY RAKESH VASAVA
PROCESS HEAT TRANSFER (3340501)
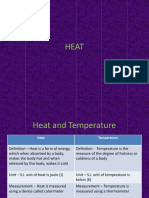
Temperature
Temperature is the measure of the average thermal energy in a system or
body. We use three common scales to measure temperature: Fahrenheit,
Celsius and Kelvin. The Fahrenheit scale sets the freezing point of water to
32 ⁰ F and the boiling point of water to be 212 ⁰ F, whereas the Celsius
scale sets the freezing point of water to be 0 ⁰ C and the boiling point of
water to be 100 ⁰ C. The Kelvin scale is an adaptation of Celsius that sets
absolute zero to be 0 K. At absolute zero, atoms cease to move and there is
no longer any thermal energy. For reference, one of the coldest materials
that is frequently used is liquid nitrogen, which has a temperature of 77 K,
which is -196 ⁰ C or -321 ⁰ F.
Heat
Heat is an important concept for both scientist and engineers. The term
"heat" is different from temperature in that it is not the measure of thermal
energy, but rather the measure of the transfer of thermal energy
PREPARED BY RAKESH VASAVA
You might also like
- Chapter Four Heat and ThermodynamicsDocument44 pagesChapter Four Heat and ThermodynamicsmesfinNo ratings yet
- BMS Group 1Document32 pagesBMS Group 1sandaliNo ratings yet
- Lighting Dan HeatDocument118 pagesLighting Dan HeatAndri Fayrina RamadhaniNo ratings yet
- Temperature, Heat & Thermal: Physics Thermodynamics Energy System Thermal Contact WorkDocument12 pagesTemperature, Heat & Thermal: Physics Thermodynamics Energy System Thermal Contact WorkAmirul ZahariNo ratings yet
- P 6Document4 pagesP 6Mark Joseph MalaluanNo ratings yet
- Heat and Temperature by ArchieGBDocument43 pagesHeat and Temperature by ArchieGBArchiemedez BatanganNo ratings yet
- Temperature and HeatDocument38 pagesTemperature and Heatmistymint.crewneticNo ratings yet
- Unit: 1 Refrigeration System and Refrigeration EquipmentsDocument13 pagesUnit: 1 Refrigeration System and Refrigeration EquipmentsrajasekarNo ratings yet
- Heat Chapter NotesDocument9 pagesHeat Chapter NotesMaanya KumarNo ratings yet
- Kavita - Int Sci Heat TransferDocument10 pagesKavita - Int Sci Heat Transfer27h4fbvsy8No ratings yet
- Heat TransferDocument11 pagesHeat TransferArnab HazraNo ratings yet
- HeatDocument10 pagesHeatdivya singhNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer: LT Col G. Junior Virgo Ext. 3263Document23 pagesHeat Transfer: LT Col G. Junior Virgo Ext. 3263DubistWhiteNo ratings yet
- Warming The Earth and The AtmosphereDocument46 pagesWarming The Earth and The AtmosphereSalih TrexieNo ratings yet
- HEAT Class 7Document50 pagesHEAT Class 7Raynaah100% (1)
- Chapter 3 Energy (Calorimetry)Document74 pagesChapter 3 Energy (Calorimetry)zed santosNo ratings yet
- ApoyDocument23 pagesApoyKaneki KenNo ratings yet
- Hvac 2Document41 pagesHvac 2skyNo ratings yet
- Hvac 2HGHDHDocument32 pagesHvac 2HGHDHskyNo ratings yet
- LO10 Session 08 ThermodynamicsDocument44 pagesLO10 Session 08 ThermodynamicsAbo Alphotoh GamingNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer - Lecture Notes 2023 - 122022 PDFDocument46 pagesHeat Transfer - Lecture Notes 2023 - 122022 PDFJuliusNo ratings yet
- Cdi8reporting Sabbang&saldaDocument7 pagesCdi8reporting Sabbang&saldacelino.euniceeNo ratings yet
- ThermodynamicsDocument5 pagesThermodynamicsSabyasachiNo ratings yet
- Elements of Mechanical Engineering - B22ME0103: Unit - IDocument21 pagesElements of Mechanical Engineering - B22ME0103: Unit - IKartik RaghuwanshiNo ratings yet
- 9th - Ch6 Part A - Heat and Energy - NOTES-4Document17 pages9th - Ch6 Part A - Heat and Energy - NOTES-4Xyann PlaysNo ratings yet
- Tehnički Engleski Jezik 1. Translate The Following SentencesDocument2 pagesTehnički Engleski Jezik 1. Translate The Following SentencesSelmaNo ratings yet
- Shortnote About Temperature and HeatDocument18 pagesShortnote About Temperature and Heatsample nameNo ratings yet
- Heat and Mass Flow Process 1Document50 pagesHeat and Mass Flow Process 1Suleman ZahoorNo ratings yet
- Fire Protection AND Arson Investigation: Mark Lester E. Caranay, RcrimDocument10 pagesFire Protection AND Arson Investigation: Mark Lester E. Caranay, RcrimGemel John CatapNo ratings yet
- Temperature and Heat - FDocument44 pagesTemperature and Heat - Fmostafa_m_ibrahim2444100% (1)
- Warming The Earth and The AtmosphereDocument46 pagesWarming The Earth and The AtmosphereKylene AlimNo ratings yet
- Heat and TemperatureDocument6 pagesHeat and Temperaturesachinjangra98No ratings yet
- Physics ProjectDocument19 pagesPhysics Projectaditya varteNo ratings yet
- Heat Notes 2024Document5 pagesHeat Notes 2024saesha2801No ratings yet
- HeatDocument12 pagesHeatMayukh ChoudhuryNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 CH 6 To SendDocument36 pagesGrade 10 CH 6 To SendZynx DixonNo ratings yet
- CSEC Physics 12 Hour Crash Course Sections B and C Student Version-2Document107 pagesCSEC Physics 12 Hour Crash Course Sections B and C Student Version-2Mrs MendezNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 ThermodynamicsDocument40 pagesLecture 1 Thermodynamicsshahid9641181No ratings yet
- Thermodynamics: Thermo:Heat, Dynamics: Power, MotionDocument43 pagesThermodynamics: Thermo:Heat, Dynamics: Power, MotionAl MahmudNo ratings yet
- Temperature MeasurementsDocument58 pagesTemperature Measurements22-00191No ratings yet
- Air Conditioning: Basic Refrigeration Principles: Unit-1Document16 pagesAir Conditioning: Basic Refrigeration Principles: Unit-1Prabha Karen PalanisamyNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer: What Is Matter?Document3 pagesHeat Transfer: What Is Matter?danial kashifNo ratings yet
- Triple Point of Water - AssignmentDocument13 pagesTriple Point of Water - AssignmentpatilsspNo ratings yet
- HEAT SRGDocument67 pagesHEAT SRGBharat JadhavNo ratings yet
- Curved Mirrors Concave and ConvexDocument48 pagesCurved Mirrors Concave and ConvexGeorge SsebNo ratings yet
- Temperature SystemsDocument10 pagesTemperature SystemsrajaraghuramvarmaNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics ReviewerDocument118 pagesThermodynamics ReviewerRenz Karl DeclaroNo ratings yet
- 4 PhyDocument64 pages4 PhymesfinNo ratings yet
- 8-Lecture 1 - Introduction To Heat Transfer-11-Jul-2018 - Reference Material I - Lecture 1Document20 pages8-Lecture 1 - Introduction To Heat Transfer-11-Jul-2018 - Reference Material I - Lecture 1Nikhil BabuNo ratings yet
- 01 Thermal Expansion 1Document23 pages01 Thermal Expansion 1Ashok PradhanNo ratings yet
- Heat and TemperatureDocument125 pagesHeat and TemperatureNovelynLozano-EdrosoNo ratings yet
- The Heat Energy (Q)Document5 pagesThe Heat Energy (Q)KIPNGENO EMMANUELNo ratings yet
- Heat and Mass TransferDocument4 pagesHeat and Mass TransferSuhaib AshrafNo ratings yet
- Module in SEd 211Document95 pagesModule in SEd 211Sherryl MontalboNo ratings yet
- Heat and Mass Transfer LAB: Ma'am Hibbah AkhtarDocument14 pagesHeat and Mass Transfer LAB: Ma'am Hibbah AkhtarTauQeer ShahNo ratings yet
- Caress Be Je Co FinalDocument24 pagesCaress Be Je Co FinalSheen Leigh MahusayNo ratings yet
- “Foundations to Flight: Mastering Physics from Curiosity to Confidence: Cipher 4”: “Foundations to Flight: Mastering Physics from Curiosity to Confidence, #4From Everand“Foundations to Flight: Mastering Physics from Curiosity to Confidence: Cipher 4”: “Foundations to Flight: Mastering Physics from Curiosity to Confidence, #4Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)