Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Test 2 2020 Biology1a03 Without Answers
Test 2 2020 Biology1a03 Without Answers
Uploaded by
proplayer910Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Aqa A Level Biology p1 QPDocument36 pagesAqa A Level Biology p1 QPJaden MistryNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Molecular Biology 5th Edition Robert WeaverDocument11 pagesTest Bank For Molecular Biology 5th Edition Robert WeaverMelindaYangtpeg100% (38)
- Cell Communication Practice TestDocument5 pagesCell Communication Practice Testapi-237801056100% (2)
- AP Bio CH 18-20 Take Home FinalDocument14 pagesAP Bio CH 18-20 Take Home Finalheeraangelwingz0% (1)
- Biochemistry FinalDocument71 pagesBiochemistry FinalJanie-Vi Gorospe100% (2)
- MCQDocument10 pagesMCQNasir Ahmed100% (1)
- Cell Final ExamDocument8 pagesCell Final ExamJorge GomezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 03Document4 pagesChapter 03Teehee JonesNo ratings yet
- Bio1A03 Practice Test 2Document11 pagesBio1A03 Practice Test 2cbox4273No ratings yet
- Molecular Cell Biology Practice QuestionsDocument9 pagesMolecular Cell Biology Practice Questionssahana2791100% (1)
- BIO230 Sample Midterm With Answers UpdatedDocument9 pagesBIO230 Sample Midterm With Answers Updatedfgb9qfb7x6No ratings yet
- Test 2 Winter 2020 AnswersDocument10 pagesTest 2 Winter 2020 Answersproplayer910No ratings yet
- BCMB20002 MST2 Sem1 2016Document6 pagesBCMB20002 MST2 Sem1 2016kfqhnmh87hNo ratings yet
- Molecular Cell Biology Lodish 6th Edition Test Bank DownloadDocument9 pagesMolecular Cell Biology Lodish 6th Edition Test Bank Downloadjohndanielswrydmzokge100% (32)
- Chapter 13 RNA Test NAME Abdullah Alabdullah CLASS 9A DATEDocument7 pagesChapter 13 RNA Test NAME Abdullah Alabdullah CLASS 9A DATEAbdullah AlabdullahNo ratings yet
- Must Review ThisDocument19 pagesMust Review Thispmp123456No ratings yet
- Test Bank For Brock Biology of Microorganisms 14th Edition Michael T Madigan Download DownloadDocument20 pagesTest Bank For Brock Biology of Microorganisms 14th Edition Michael T Madigan Download Downloadstevenstevensjgzaryxbdp100% (28)
- Bio Practice Questions For Final Exam Biol 1101Document5 pagesBio Practice Questions For Final Exam Biol 1101Megadirectioner 21No ratings yet
- SampleQuiz-Ch11 18 PDFDocument2 pagesSampleQuiz-Ch11 18 PDFNguyễn Đức ÝNo ratings yet
- t2 Bio Revision Ex 1 Answer SchemeDocument15 pagest2 Bio Revision Ex 1 Answer SchemeNicholas OwNo ratings yet
- SamplepapeDocument7 pagesSamplepapeYogesh Verma ParjapatiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 Test A RNA and Protein Synthesis ANSWERS PDFDocument6 pagesChapter 13 Test A RNA and Protein Synthesis ANSWERS PDFxspiiirONo ratings yet
- StudentDocument12 pagesStudent김예진No ratings yet
- Test On Molecular Biology NEETDocument4 pagesTest On Molecular Biology NEETSadananda KumbhakarNo ratings yet
- MCQDocument9 pagesMCQpkm7929No ratings yet
- Lodish6e ch07Document8 pagesLodish6e ch07nNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 Rna Test Name Class DateDocument7 pagesChapter 13 Rna Test Name Class DateAbdullah AlabdullahNo ratings yet
- Science 10 Summative Test 2 Quarter 3 With Answer KeyDocument3 pagesScience 10 Summative Test 2 Quarter 3 With Answer KeyRowena Nim100% (2)
- Cytogenetics Final ExamDocument20 pagesCytogenetics Final ExamMICHAEL JOHN AGUILARNo ratings yet
- SSN SBPM Workshop Exam One Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument10 pagesSSN SBPM Workshop Exam One Multiple Choice QuestionsAG KhanNo ratings yet
- Principles of Cell Biology Exam 2 Spring 2020 March 26, 2020Document13 pagesPrinciples of Cell Biology Exam 2 Spring 2020 March 26, 2020Zachary D AbramsNo ratings yet
- CBT 2 Paper PDFDocument140 pagesCBT 2 Paper PDFkarthikNo ratings yet
- 2014Document14 pages2014Samuel RobertsNo ratings yet
- Ôn Thi SHPTDocument7 pagesÔn Thi SHPTHạ Thi LêNo ratings yet
- AP BioDocument12 pagesAP BioThomas Lim100% (2)
- Test Bank MetabolismDocument6 pagesTest Bank MetabolismWanga CharleneNo ratings yet
- DNA SamplexDocument6 pagesDNA SamplexNelica RotoniNo ratings yet
- 2020 Midterm 2 Questions W AnswersDocument12 pages2020 Midterm 2 Questions W AnswersKingsley ZhengNo ratings yet
- Biology 9648/01: Anderson Junior College Higher 2Document30 pagesBiology 9648/01: Anderson Junior College Higher 2saffronNo ratings yet
- Molecular Biology Examination (BSC) 2020/2021-Teneng Section A: McqsDocument3 pagesMolecular Biology Examination (BSC) 2020/2021-Teneng Section A: McqsTeneng Fidelis AwaNo ratings yet
- Bio 366 Sdsu Exam 2Document6 pagesBio 366 Sdsu Exam 2caseyvegarraNo ratings yet
- Genetics Chapter 8Document19 pagesGenetics Chapter 8Zahraa TermosNo ratings yet
- K101PracEx4 SP19 KeyDocument10 pagesK101PracEx4 SP19 KeyBraxton PhillipsNo ratings yet
- Paper II Part 2Document8 pagesPaper II Part 2Kritika MishraNo ratings yet
- Exam 1 Lectures 4 & 5 Q'sDocument6 pagesExam 1 Lectures 4 & 5 Q'sBlaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 &10 - Gene ExpressionDocument4 pagesChapter 9 &10 - Gene ExpressionMahmOod GhNo ratings yet
- 2010 A Level h2 Biology Dunman HighDocument46 pages2010 A Level h2 Biology Dunman HighStephyNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry FinalDocument60 pagesBiochemistry FinalAndrassy Twinkle Alinea100% (2)
- Biology MCQ Base KROK-1Document27 pagesBiology MCQ Base KROK-1Aswin JayakumarNo ratings yet
- IB DNA and Protein Synthesis Unit Test HL2 STUDENTDocument7 pagesIB DNA and Protein Synthesis Unit Test HL2 STUDENT167101No ratings yet
- Biochemistry Book Additional PlatesDocument8 pagesBiochemistry Book Additional PlatesKiana TehraniNo ratings yet
- Dr. Harvey Laranang MicrobiologyDocument9 pagesDr. Harvey Laranang MicrobiologyPatricia L.No ratings yet
- AP Biology Unit 5 ExamDocument13 pagesAP Biology Unit 5 ExamLana Sage CummingsNo ratings yet
- CellDocument14 pagesCellSyrian AsadNo ratings yet
- Microbiology A Human Perspective 7th Edition Nester Test BankDocument40 pagesMicrobiology A Human Perspective 7th Edition Nester Test Bankmagnusngah7aaz100% (33)
- Lecture COPEG Qns (Last Lect)Document8 pagesLecture COPEG Qns (Last Lect)Wesley TanNo ratings yet
- Gene RegulationsDocument11 pagesGene Regulationsmahadi.infsduNo ratings yet
- General Biology Ii: Engineering and Mathematics Science, TechnologyDocument3 pagesGeneral Biology Ii: Engineering and Mathematics Science, TechnologyKeirby CayanongNo ratings yet
- 6Document17 pages6AmaniNo ratings yet
- Microbial PhysiologyFrom EverandMicrobial PhysiologyAlbert G. MoatNo ratings yet
- Animal Physiology MCQsDocument3 pagesAnimal Physiology MCQsShafiq Azam RumiNo ratings yet
- Alfa 1 AntitripsinDocument4 pagesAlfa 1 AntitripsinDwitaRiadiniNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Bacteria: Structure and ReplicationDocument19 pagesIntroduction To Bacteria: Structure and ReplicationFort SalvadorNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Diagnosis of Sexually Transmited DiseasesDocument31 pagesLaboratory Diagnosis of Sexually Transmited DiseasesrikarzNo ratings yet
- Biotechnology and Its ApplicationsDocument8 pagesBiotechnology and Its ApplicationsS SURAJNo ratings yet
- Randox ControlDocument17 pagesRandox ControlLuis Ferdinand Dacera-Gabronino Gamponia-Nonan100% (1)
- June 2018 QP - Paper 1 AQA Biology A-LevelDocument44 pagesJune 2018 QP - Paper 1 AQA Biology A-LevelreneehandsNo ratings yet
- Therapeutic Dosages22Document11 pagesTherapeutic Dosages22Rishikesh AsthanaNo ratings yet
- 001assessment Exam ImmunohemaDocument25 pages001assessment Exam ImmunohemaFrankenstein MelancholyNo ratings yet
- Bact Alert Culture Media - 0Document4 pagesBact Alert Culture Media - 0Corporativo DRLABNo ratings yet
- LymphomaDocument20 pagesLymphomaChairul Adilla Ardy100% (1)
- Thrombolytics-1Document3 pagesThrombolytics-1Shayan ShayanNo ratings yet
- NLBL Bio Tech ApplicationsDocument5 pagesNLBL Bio Tech Applicationsyogeshwaran09102005No ratings yet
- Dental Caries DefinitionDocument11 pagesDental Caries DefinitioncartoonNo ratings yet
- 2325-300 Free PSA AccuBind ELISA Rev 5Document2 pages2325-300 Free PSA AccuBind ELISA Rev 5Emma MNo ratings yet
- Vaccine Race Is Over Ready or NotDocument6 pagesVaccine Race Is Over Ready or NotInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- 0710 Biology Past Questions From June 2000 To June 2021Document46 pages0710 Biology Past Questions From June 2000 To June 2021Stella DjuikomNo ratings yet
- Antileukotriene Agents in The Management of Asthma - UpToDateDocument30 pagesAntileukotriene Agents in The Management of Asthma - UpToDateAmr MohamedNo ratings yet
- Metabolism of NucleotidesDocument24 pagesMetabolism of NucleotidesAditya NayakNo ratings yet
- R J Epstein-Human Molecular Biology - An Introduction To The Molecular Basis of Health and Disease-Cambridge University Press (2002)Document655 pagesR J Epstein-Human Molecular Biology - An Introduction To The Molecular Basis of Health and Disease-Cambridge University Press (2002)Libros a Color ConceNo ratings yet
- PG StatementDocument6 pagesPG StatementDede RosadiNo ratings yet
- TranslationDocument37 pagesTranslationFarhana AnuarNo ratings yet
- Csec HSB June 2008 p2Document26 pagesCsec HSB June 2008 p2Sachin BahadoorsinghNo ratings yet
- H-046-019558-00 SARS-CoV-2 IgG-CEDocument2 pagesH-046-019558-00 SARS-CoV-2 IgG-CERenato DesideriNo ratings yet
- Liver Cirrhosis TreatmentDocument5 pagesLiver Cirrhosis TreatmentPrajith NairNo ratings yet
- Topic: Corona Virus Topic Sentence: Corona Virus Is A Virus That Can Be Conquered With The Right ActionsDocument2 pagesTopic: Corona Virus Topic Sentence: Corona Virus Is A Virus That Can Be Conquered With The Right ActionsArifah RamadhaniNo ratings yet
- African Healthcare Setting VHF PDFDocument209 pagesAfrican Healthcare Setting VHF PDFWill TellNo ratings yet
- Topic 5 Genhisto NotesDocument6 pagesTopic 5 Genhisto NotesShiina MashiroNo ratings yet
- Blood: Lecture Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor Florence-Darlington Technical CollegeDocument71 pagesBlood: Lecture Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor Florence-Darlington Technical CollegeCath TabasNo ratings yet
Test 2 2020 Biology1a03 Without Answers
Test 2 2020 Biology1a03 Without Answers
Uploaded by
proplayer910Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Test 2 2020 Biology1a03 Without Answers
Test 2 2020 Biology1a03 Without Answers
Uploaded by
proplayer910Copyright:
Available Formats
lOMoARcPSD|17391941
Test 2 2020- Biology1A03 (without answers)
Biology (McMaster University)
StuDocu is not sponsored or endorsed by any college or university
Downloaded by Photo Account (photos.riyad.asgarali@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|17391941
BIOLOGY 1A03 - Practice Test 2 Answers
PART A: MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS (worth 30 marks)
DR. DA SILVA’S MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
1. All of the following are considered examples of housekeeping genes except
A. RNA polymerase gene.
B. translation elongation factor genes.
C. histone genes.
D. lactose permease gene.
2. Regulated genes
A. have CpG islands in their promoters that are never methylated.
B. include genes that are only expressed when there is a change in an environmental condition.
C. code for proteins that are needed all the time in a cell.
D. are always kept on by histone acetyl transferase proteins.
3. CpG island methylation within a promoter
A. enhances the binding of transcription factors to the promoter region.
B. inhibits the activity of the histone deacetylase protein.
C. prevents the binding of transcription factors to the promoter.
D. changes the shape of RNA polymerase that binds to the promoter.
4. Transcription factors binding to a promoter region is an example of a _____________molecule
binding with DNA.
A. protein
B. carbohydrate
C. lipid
D. DNA
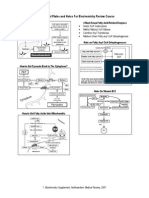
5. Based on the image shown below, which region represents the gene that codes for the repressor
protein of the lac operon?
A. promoter
B. operator
C. lac I coding sequence
D. lacY coding sequence
Downloaded by Photo Account (photos.riyad.asgarali@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|17391941
6. Which of the following is false when considering the lac operon in E. coli?
A. Lac operon messenger RNA is monocistronic mRNA.
B. The operon is never fully off.
C. Beta galactosidase can only be produced when the repressor protein is not bound to the
operator.
D. The lac operon has one promoter for both the beta galactosidase and the lactose permease
genes.
7. The following image shows the growth of E. coli in an environment containing both glucose and
lactose. At which point would you expect to see the lowest expression of the beta galactosidase gene
once glucose is used up?
A. Time point A
B. Time point B
C. Time point C
D. Time point D
8.The lac operon
A. is expressed at the highest levels in the presence of high levels of glucose.
B. is negatively regulated by the CRP-cAMP complex.
C. is positively regulated in the presence of lactose.
D. expresses high levels of lactose permease with the inhibition of the adenylyl cyclase enzyme.
9.Which of the following is the most appropriate definition of a promoter, in the context of prokaryotic
gene expression?
A. A DNA-binding protein that regulates gene expression.
B. A cluster of genes that are regulated by a single promoter.
C. A non-coding regulatory DNA sequence that is bound by RNA polymerase.
D. A non-coding regulatory DNA sequence that is bound by a repressor protein.
Downloaded by Photo Account (photos.riyad.asgarali@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|17391941
10. When considering eukaryotic transcription
A. the enhancer sequence is always within the promoter.
B. the transcriptional activator proteins that bind to the enhancer regions do not interact at all with
the transcription factors at the core promoter.
C. the TATA box region is part of the enhancer sequence of the regulatory promoter.
D. the TATA box and BRE regions are always relatively close to the transcription start site.
11. Which of the following are not matched correctly with regards to regulation of gene expression?
A. miRNA binding to its target → causes mRNA destruction by the RISC complex
B. DNA methylation → occurs in the nucleus
C. post translational modifications → includes amino acid phosphorylation
D. nucleosome compaction → inhibits transcription
12. When regulating gene expression,
A. miRNAs bind as double stranded RNA to the RISC complex.
B. miRNA in the RISC complex binds in an exact manner to the target mRNA sequence.
C. siRNAs lead to the inhibition of transcription.
D. siRNA molecules are exact complementary sequences of their mRNA target.
13. During the course of human development,
A. the alpha globin gene is only expressed in a fetus.
B. the beta globin gene is only expressed in adults.
C. the gamma globin gene is only expressed in adults.
D. a fetus will have a lower oxygen affinity than an adult.
14. A pregnant woman will tend to be short of breath because her
A. alpha globin gene expression is always off.
B. gamma globin gene expression is off and beta globin gene expression is on.
C. gamma globin gene expression is on and beta globin gene expression is on.
D. beta globin gene expression is on and alpha globin gene expression is off.
15. Proteasome protein complexes
A. utilize GTP as a source of energy.
B. add ubiquitin tags to proteins.
C. regulate gene expression at the post-translational level.
D. regulate mRNA processing.
16. Individuals with galactosemia
A. have a decreased ability to digest lactose into galactose after weaning.
B. are able to breakdown lactose into glucose and galactose.
C. have gene mutations in the coding region of the lactase gene.
D. will accumulate toxic levels of lactose in the liver.
17. When considering how cells are able to respond to external signals and modify gene expression,
A. signal transduction cascades only lead to quick, short term changes in the cell.
B. short term responses include modifications of gene expression.
C. long term responses include post-translational protein modifications.
D. short term responses include metabolic cell changes.
Downloaded by Photo Account (photos.riyad.asgarali@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|17391941
18. _________________ regulation is the fastest way to control gene expression.
A. Transcriptional
B. RNA processing
C. Translational
D. Post-Translational
19. Epigenetic differences arise during the lifetime of monozygotic twins. Previous research has
shown that these include
A. the epigenetic drift of gene expression in monozygotic twin pairs with age.
B. younger twin pairs having large differences in DNA methylation patterns.
C. older twin pairs having very similar DNA methylation patterns.
D. younger twin pairs having large differences in histone protein acetylation.
20. Which of the following is true regarding individuals with lactase non-persistance after weaning?
A. These individuals have a sustained ability to digest lactose very well after weaning.
B.These individuals lose the ability to transport any digested lactose products across the
membranes of the absorptive microvilli of the small intestine.
C. A mutation in a neighbouring regulatory gene keeps the lactase gene permanently on.
D. These individuals are born with congenital lactose intolerance.
DR. KAJIURA’S MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
21.Which of the following describes a step during the initiation of translation in eukaryotes?
A. STOP codons on the mRNA bind to special proteins, rather than to tRNA molecules
B. initiation factors recruit the small ribosomal subunit and tRNAMet and scan the mRNA for the
AUG codon
C. a peptide bond forms between amino acids attached to nearby tRNA’s on the ribosome
D. the ribosomal subunits are broken apart and disassembled
E. the ribosome recognizes a UGA codon and combines with the E site
22. rRNA sequences are not translated because rRNA is:
A. directly used to make new strands of DNA
B. not important to the functioning of the cell
C. a structural component of the cell
D. not made of the same bases as messenger RNA or transfer RNA
E. both A & D
23. After the process of translation has completed, the ribosome:
A. breaks into large and small subunits
B. joins with other ribosomes to continue translation
C. stays intact and searches for another AUG codon to begin translation
D. will remain connected to the mRNA
E. moves back to the first AUG codon of the mRNA to begin the process again
Downloaded by Photo Account (photos.riyad.asgarali@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|17391941
24. Recall the experiments regarding the one-gene, one-enzyme hypothesis via the investigation of
the arginine biosynthetic pathway in the Neurospora crassa. In order to find cells with mutations in the
arginine biosynthetic pathway, they exposed cell s to mutagenic radiation and screened the cells for:
A. cells that are poisoned by arginine
B. cells that no longer make any enzymes
C. cells with high levels of mutations in their DNA
D. cells that cannot grow unless arginine is provided as a supplement
25. When an individual, such as actress/singer, Eden Atwood, possesses the condition known as
androgen insensitivity syndrome (AIS), which of the following correctly describes the AIS condition
from a cellular and molecular biology perspective?
A. Eden Atwood has only one X chromosome
B. Eden Atwood has a rare mutation, which changes the nucleotide sequence of a gene, which
results a high quantity of estrogen being produced in her body
C. Eden Atwood has two extra Y chromosomes and only one X chromosome
D. Eden Atwood does not have functional androgen receptor proteins, therefore her cells are not
able to respond to testosterone
E. Eden Atwood has only one Y chromosome
26.Suppose that a diploid organism is homozygous for a mutation which converts substance B to
substance C (i.e. enzyme b is not produced). In that situation, you would expect that:
A. Substance B will increase in concentration
B. Substance A will decrease in concentration
C. Substance D will increase in concentration
D. Substance C will increase in concentration
27. Which of the following occurs during the transition from preproinsulin to the formation of
proinsulin?
A. The removal of the A chain and the formation of 2 disulphide bonds
B. The formation of 3 disulphide bridges and the removal of the signal sequence.
C. The addition of 3 phosphodiester linkages and the removal of the B chain
D. The removal of the C chain
28. As indicated during the Biology 1A03 Theme 2 Modules 3 & 4 Review Lecture, what is the
significance of having intracellular signals amplified?
A. It is significant, since it shows that the process can be slow
B. It is significant, since it permits the intracellular signals to broken down at an intermediate rate
in the cytoplasm
C. It is significant, since it can stop the release of enzymes, which could be recycled by the cell
D. It is significant, since it allows the process to be more efficient and occur more quickly
Downloaded by Photo Account (photos.riyad.asgarali@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|17391941
29. Recall in Bio 1A03 Theme 2 Module 3 & 4 review lecture, that we discussed the relationships
between genes and the products they produce. We considered three different hypotheses. Which of
the following is currently considered the best hypothesis?
A. It is the hypothesis that suggests that the function of a gene is to determine the production of a
specific enzyme.
B. It is the hypothesis that suggests that the function of the gene is to determine the production of
a specific polypeptide.
C. It is the hypothesis called “one-gene -…”, that suggests that the function of the gene is to
determine the production of a specific polypeptide and also takes into consideration post
translational modifications which may occur
D. Both A & B
30. The accuracy in the translation of mRNA into the primary structure of a polypeptide depends on
specificity in the ______________________________.
A. attachment of amino acids to tRNAs
B. tRNAs which have anticodons that base pair with the codons of the mRNA
C. the shape of the E site and A site of the small ribosomal subunit
D. the substitution of the N terminus of the polypeptide for the C terminus
E. Both A & B
Downloaded by Photo Account (photos.riyad.asgarali@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|17391941
PART B: WRITTEN ANSWER-STYLE QUESTIONS 31 – 39 (worth 10 marks)
DR. DA SILVA’S WRITTEN ANSWER QUESTIONS (7 marks)
31. (Total 2.5 marks) As we have learned, maternal diet can influence the coat colour of genetically
identical Agouti mice siblings and can be an indication of Agouti gene expression.
A. What would be the predominant offspring coat colour observed if a yellow Agouti mother receives
no prenatal folic acid supplementation? (0.5 mark)
32. B. What epigenetic mechanism is involved with determining the coat colour in Agouti mice, and
how does this relate to and explain the offspring coat colour observed in part (a) above? (0.5 + 0.5 +
0.5 + 0.5 = 2 marks)
33. (Total 2 marks) The table below shows the fecal beta galactosidase activity that is detected in
the intestines of lactose intolerant individuals before (baseline period), during supplementation, and
during a follow-up period of treatment with yogurt.
Is intestinal lactase enzyme activity stimulated in these patients? Why or why not? In addition,
explain why these patients have an increased ability to digest lactose and less diarrhea during the
supplementation period. (0.5 + 0.5 + 0.5 + 0.5 = 2 marks)
Downloaded by Photo Account (photos.riyad.asgarali@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|17391941
34. (Total 2.5 marks) The image below shows the results of a microarray analysis comparing the
expression of 3 genes in both normal breast epithelial cells and breast cancer cells. The tumor
suppressor gene p53 codes for a protein that inhibits the growth of tumours while the EGFR gene
codes for a receptor that binds the epidermal growth factor protein that stimulates cell growth.
A. Based on the microarray data, why are the breast cancer cells able to grow and divide faster than
the normal breast epithelial cells? (0.5 + 0.5 = 1 mark)
35. B. True or False? The differences in gene expression between these cells as seen in the
microarray comes down to mutations that have occured in the EGFR and p53 genes. Explain your
answer using the cancer cells example that was discussed in class. (0.5 + 0.5 + 0.5 = 1.5 marks)
DR. KAJIURA’S WRITTEN ANSWER QUESTIONS (3 marks)
36. (Total 1.5 marks) Is the animal the Kermode (Spirit) bear an albino bear, since it has white fur?
Describe the research finding of Ritland and co-workers, which explains why the Kermode bear’s fur
appears white in colour. (0.5 + 0.5 + 0.5 =1.5 marks)
Downloaded by Photo Account (photos.riyad.asgarali@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|17391941
37. (Total 1.5 marks) Recall the Biology 1A03 Applied Lecture Theme 2 Module 3 & 4 Applied
lecture.
A. What is the specific name of the translated protein produced by Mytilus mussels? (0.5 mark)
38. B. What function does this protein serve in the natural marine environment of the Mytilus
mussels? (0.5 mark)
39. C) What do genetic engineers want to do with Mytilus mussels? (0.5 mark)
THIS BIOLOGY 1A03 TEST #2 IS THE INTELLECTUAL & ACADEMIC PROPERTY OF DR. KAJIURA, DR. DA
SILVA, & DR. MAHALINGAM. ANY REPRODUCTION, DISTRIBUTION, OR COMMUNICATION IN ANY FORM
USING ANY MEDIA IS STRICTLY PROHIBITED. ANY USE OF THIS COPYRIGHT MATERIAL MUST HAVE
WRITTEN EXPRESSED PERMISSION FROM DR. KAJIURA, DR. DA SILVA, & DR. MAHALINGAM.
Copyright © Winter 2021 Biology 1A03 L. Kajiura, R. DaSilva, S. Mahalingam, A. Tracey, Department of Biology, McMaster University,
Hamilton, Ontario. Canada.
Downloaded by Photo Account (photos.riyad.asgarali@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|17391941
Downloaded by Photo Account (photos.riyad.asgarali@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|17391941
BIOLOGY 1A03 - Practice Test 2 Answers
PART A: MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS (worth 30 marks)
DR. DA SILVA’S MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
1. All of the following are considered examples of housekeeping genes except
A. RNA polymerase gene.
B. translation elongation factor genes.
C. histone genes.
D. lactose permease gene.
2. Regulated genes
A. have CpG islands in their promoters that are never methylated.
B. include genes that are only expressed when there is a change in an environmental condition.
C. code for proteins that are needed all the time in a cell.
D. are always kept on by histone acetyl transferase proteins.
3. CpG island methylation within a promoter
A. enhances the binding of transcription factors to the promoter region.
B. inhibits the activity of the histone deacetylase protein.
C. prevents the binding of transcription factors to the promoter.
D. changes the shape of RNA polymerase that binds to the promoter.
4. Transcription factors binding to a promoter region is an example of a _____________molecule
binding with DNA.
A. protein
B. carbohydrate
C. lipid
D. DNA
5. Based on the image shown below, which region represents the gene that codes for the repressor
protein of the lac operon?
A. promoter
B. operator
C. lac I coding sequence
D. lacY coding sequence
Downloaded by Photo Account (photos.riyad.asgarali@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|17391941
6. Which of the following is false when considering the lac operon in E. coli?
A. Lac operon messenger RNA is monocistronic mRNA.
B. The operon is never fully off.
C. Beta galactosidase can only be produced when the repressor protein is not bound to the
operator.
D. The lac operon has one promoter for both the beta galactosidase and the lactose permease
genes.
7. The following image shows the growth of E. coli in an environment containing both glucose and
lactose. At which point would you expect to see the lowest expression of the beta galactosidase gene
once glucose is used up?
A. Time point A
B. Time point B
C. Time point C
D. Time point D
8.The lac operon
A. is expressed at the highest levels in the presence of high levels of glucose.
B. is negatively regulated by the CRP-cAMP complex.
C. is positively regulated in the presence of lactose.
D. expresses high levels of lactose permease with the inhibition of the adenylyl cyclase enzyme.
9.Which of the following is the most appropriate definition of a promoter, in the context of prokaryotic
gene expression?
A. A DNA-binding protein that regulates gene expression.
B. A cluster of genes that are regulated by a single promoter.
C. A non-coding regulatory DNA sequence that is bound by RNA polymerase.
D. A non-coding regulatory DNA sequence that is bound by a repressor protein.
Downloaded by Photo Account (photos.riyad.asgarali@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|17391941
10. When considering eukaryotic transcription
A. the enhancer sequence is always within the promoter.
B. the transcriptional activator proteins that bind to the enhancer regions do not interact at all with
the transcription factors at the core promoter.
C. the TATA box region is part of the enhancer sequence of the regulatory promoter.
D. the TATA box and BRE regions are always relatively close to the transcription start site.
11. Which of the following are not matched correctly with regards to regulation of gene expression?
A. miRNA binding to its target → causes mRNA destruction by the RISC complex
B. DNA methylation → occurs in the nucleus
C. post translational modifications → includes amino acid phosphorylation
D. nucleosome compaction → inhibits transcription
12. When regulating gene expression,
A. miRNAs bind as double stranded RNA to the RISC complex.
B. miRNA in the RISC complex binds in an exact manner to the target mRNA sequence.
C. siRNAs lead to the inhibition of transcription.
D. siRNA molecules are exact complementary sequences of their mRNA target.
13. During the course of human development,
A. the alpha globin gene is only expressed in a fetus.
B. the beta globin gene is only expressed in adults.
C. the gamma globin gene is only expressed in adults.
D. a fetus will have a lower oxygen affinity than an adult.
14. A pregnant woman will tend to be short of breath because her
A. alpha globin gene expression is always off.
B. gamma globin gene expression is off and beta globin gene expression is on.
C. gamma globin gene expression is on and beta globin gene expression is on.
D. beta globin gene expression is on and alpha globin gene expression is off.
15. Proteasome protein complexes
A. utilize GTP as a source of energy.
B. add ubiquitin tags to proteins.
C. regulate gene expression at the post-translational level.
D. regulate mRNA processing.
16. Individuals with galactosemia
A. have a decreased ability to digest lactose into galactose after weaning.
B. are able to breakdown lactose into glucose and galactose.
C. have gene mutations in the coding region of the lactase gene.
D. will accumulate toxic levels of lactose in the liver.
17. When considering how cells are able to respond to external signals and modify gene expression,
A. signal transduction cascades only lead to quick, short term changes in the cell.
B. short term responses include modifications of gene expression.
C. long term responses include post-translational protein modifications.
D. short term responses include metabolic cell changes.
Downloaded by Photo Account (photos.riyad.asgarali@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|17391941
18. _________________ regulation is the fastest way to control gene expression.
A. Transcriptional
B. RNA processing
C. Translational
D. Post-Translational
19. Epigenetic differences arise during the lifetime of monozygotic twins. Previous research has
shown that these include
A. the epigenetic drift of gene expression in monozygotic twin pairs with age.
B. younger twin pairs having large differences in DNA methylation patterns.
C. older twin pairs having very similar DNA methylation patterns.
D. younger twin pairs having large differences in histone protein acetylation.
20. Which of the following is true regarding individuals with lactase non-persistance after weaning?
A. These individuals have a sustained ability to digest lactose very well after weaning.
B.These individuals lose the ability to transport any digested lactose products across the
membranes of the absorptive microvilli of the small intestine.
C. A mutation in a neighbouring regulatory gene keeps the lactase gene permanently on.
D. These individuals are born with congenital lactose intolerance.
DR. KAJIURA’S MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
21.Which of the following describes a step during the initiation of translation in eukaryotes?
A. STOP codons on the mRNA bind to special proteins, rather than to tRNA molecules
B. initiation factors recruit the small ribosomal subunit and tRNAMet and scan the mRNA for the
AUG codon
C. a peptide bond forms between amino acids attached to nearby tRNA’s on the ribosome
D. the ribosomal subunits are broken apart and disassembled
E. the ribosome recognizes a UGA codon and combines with the E site
22. rRNA sequences are not translated because rRNA is:
A. directly used to make new strands of DNA
B. not important to the functioning of the cell
C. a structural component of the cell
D. not made of the same bases as messenger RNA or transfer RNA
E. both A & D
23. After the process of translation has completed, the ribosome:
A. breaks into large and small subunits
B. joins with other ribosomes to continue translation
C. stays intact and searches for another AUG codon to begin translation
D. will remain connected to the mRNA
E. moves back to the first AUG codon of the mRNA to begin the process again
Downloaded by Photo Account (photos.riyad.asgarali@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|17391941
24. Recall the experiments regarding the one-gene, one-enzyme hypothesis via the investigation of
the arginine biosynthetic pathway in the Neurospora crassa. In order to find cells with mutations in the
arginine biosynthetic pathway, they exposed cell s to mutagenic radiation and screened the cells for:
A. cells that are poisoned by arginine
B. cells that no longer make any enzymes
C. cells with high levels of mutations in their DNA
D. cells that cannot grow unless arginine is provided as a supplement
25. When an individual, such as actress/singer, Eden Atwood, possesses the condition known as
androgen insensitivity syndrome (AIS), which of the following correctly describes the AIS condition
from a cellular and molecular biology perspective?
A. Eden Atwood has only one X chromosome
B. Eden Atwood has a rare mutation, which changes the nucleotide sequence of a gene, which
results a high quantity of estrogen being produced in her body
C. Eden Atwood has two extra Y chromosomes and only one X chromosome
D. Eden Atwood does not have functional androgen receptor proteins, therefore her cells are not
able to respond to testosterone
E. Eden Atwood has only one Y chromosome
26.Suppose that a diploid organism is homozygous for a mutation which converts substance B to
substance C (i.e. enzyme b is not produced). In that situation, you would expect that:
A. Substance B will increase in concentration
B. Substance A will decrease in concentration
C. Substance D will increase in concentration
D. Substance C will increase in concentration
27. Which of the following occurs during the transition from preproinsulin to the formation of
proinsulin?
A. The removal of the A chain and the formation of 2 disulphide bonds
B. The formation of 3 disulphide bridges and the removal of the signal sequence.
C. The addition of 3 phosphodiester linkages and the removal of the B chain
D. The removal of the C chain
28. As indicated during the Biology 1A03 Theme 2 Modules 3 & 4 Review Lecture, what is the
significance of having intracellular signals amplified?
A. It is significant, since it shows that the process can be slow
B. It is significant, since it permits the intracellular signals to broken down at an intermediate rate
in the cytoplasm
C. It is significant, since it can stop the release of enzymes, which could be recycled by the cell
D. It is significant, since it allows the process to be more efficient and occur more quickly
Downloaded by Photo Account (photos.riyad.asgarali@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|17391941
29. Recall in Bio 1A03 Theme 2 Module 3 & 4 review lecture, that we discussed the relationships
between genes and the products they produce. We considered three different hypotheses. Which of
the following is currently considered the best hypothesis?
A. It is the hypothesis that suggests that the function of a gene is to determine the production of a
specific enzyme.
B. It is the hypothesis that suggests that the function of the gene is to determine the production of
a specific polypeptide.
C. It is the hypothesis called “one-gene -…”, that suggests that the function of the gene is to
determine the production of a specific polypeptide and also takes into consideration post
translational modifications which may occur
D. Both A & B
30. The accuracy in the translation of mRNA into the primary structure of a polypeptide depends on
specificity in the ______________________________.
A. attachment of amino acids to tRNAs
B. tRNAs which have anticodons that base pair with the codons of the mRNA
C. the shape of the E site and A site of the small ribosomal subunit
D. the substitution of the N terminus of the polypeptide for the C terminus
E. Both A & B
Downloaded by Photo Account (photos.riyad.asgarali@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|17391941
PART B: WRITTEN ANSWER-STYLE QUESTIONS 31 – 39 (worth 10 marks)
DR. DA SILVA’S WRITTEN ANSWER QUESTIONS (7 marks)
31. (Total 2.5 marks) As we have learned, maternal diet can influence the coat colour of genetically
identical Agouti mice siblings and can be an indication of Agouti gene expression.
A. What would be the predominant offspring coat colour observed if a yellow Agouti mother receives
no prenatal folic acid supplementation? (0.5 mark)
The colour of most offspring would be yellow (0.5 mark).
32. B. What epigenetic mechanism is involved with determining the coat colour in Agouti mice, and
how does this relate to and explain the offspring coat colour observed in part (a) above? (0.5 + 0.5 +
0.5 + 0.5 = 2 marks)
CpG Island (0.5 mark) methylation determines coat colour (0.5 mark).
Without a methyl source, (0.5 mark) there was no methylation of the Agouti gene promoter (0.5
mark) (with gene expressed, mice are yellow).
33. (Total 2 marks) The table below shows the fecal beta galactosidase activity that is detected in
the intestines of lactose intolerant individuals before (baseline period), during supplementation, and
during a follow-up period of treatment with yogurt.
Is intestinal lactase enzyme activity stimulated in these patients? Why or why not? In addition,
explain why these patients have an increased ability to digest lactose and less diarrhea during the
supplementation period. (0.5 + 0.5 + 0.5 + 0.5 = 2 marks)
These patients do not have functional lactase enzyme (0.5 mark) because they are lactose intolerant
(0.5 mark)
They have better ability to digest lactose because the bacterial beta-galactosidase levels increase in
the intestine (0.5 mark), leading to digesting of lactose and less entering large intestine (reducing
symptoms of diarrhea) (0.5 mark).
Downloaded by Photo Account (photos.riyad.asgarali@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|17391941
34. (Total 2.5 marks) The image below shows the results of a microarray analysis comparing the
expression of 3 genes in both normal breast epithelial cells and breast cancer cells. The tumor
suppressor gene p53 codes for a protein that inhibits the growth of tumours while the EGFR gene
codes for a receptor that binds the epidermal growth factor protein that stimulates cell growth.
A. Based on the microarray data, why are the breast cancer cells able to grow and divide faster than
the normal breast epithelial cells? (0.5 + 0.5 = 1 mark)
The breast cancer cells have a greater expression of the EGFR gene, which promotes cell growth(0.5
mark).
They also have a lower or no expression of p53 gene, which leads to no inhibition of their growth,
while the normal cells do (0.5 mark).
35. B. True or False? The differences in gene expression between these cells as seen in the
microarray comes down to mutations that have occured in the EGFR and p53 genes. Explain your
answer using the cancer cells example that was discussed in class. (0.5 + 0.5 + 0.5 = 1.5 marks)
False (0.5 mark): the difference can also be due to differences caused by epigenetic mechanisms
(0.5 mark)
For example, cancer cells can overmethylate promoters to some genes and undermethylate
promoters for other genes (leading to differences in gene expression) (0.5 mark).
DR. KAJIURA’S WRITTEN ANSWER QUESTIONS (3 marks)
36. (Total 1.5 marks) Is the animal the Kermode (Spirit) bear an albino bear, since it has white fur?
Describe the research finding of Ritland and co-workers, which explains why the Kermode bear’s fur
appears white in colour. (0.5 + 0.5 + 0.5 =1.5 marks)
No, the Kermode (Spirit) bear is not an albino (0.5 mark).
Ritland & co-workers discovered that a single nucleotide mutation results in modified protein product
from the MC1R gene melanocortin 1 receptor gene (0.5 mark).
The MC1R gene encodes for a protein, which serves to regulate skin and hair colour (0.5 mark).
Downloaded by Photo Account (photos.riyad.asgarali@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|17391941
37. (Total 1.5 marks) Recall the Biology 1A03 Applied Lecture Theme 2 Module 3 & 4 Applied
lecture.
A. What is the specific name of the translated protein produced by Mytilus mussels? (0.5 mark)
The translated protein is called byssus (0.5 mark).
38. B. What function does this protein serve in the natural marine environment of the Mytilus
mussels? (0.5 mark)
Byssus helps the mussels cling (attach) to rocks in their marine environment (0.5 mark) OR
Byssus helps the mussels by making them more resistant to the pounding waves (0.5 mark) OR
Byssus helps the mussels attach to rocks, thereby providing them with less chance of them falling
into the water and being preyed upon by their predators (0.5 mark)
39. C) What do genetic engineers want to do with Mytilus mussels? (0.5 mark)
Genetic engineers want to insert the segments of mussel DNA that are associated with the production
of byssus into yeast cells, so that they can serve as production “factories” for producing the byssus
adhesive (0.5 mark).
THIS BIOLOGY 1A03 TEST #2 IS THE INTELLECTUAL & ACADEMIC PROPERTY OF DR. KAJIURA, DR. DA
SILVA, & DR. MAHALINGAM. ANY REPRODUCTION, DISTRIBUTION, OR COMMUNICATION IN ANY FORM
USING ANY MEDIA IS STRICTLY PROHIBITED. ANY USE OF THIS COPYRIGHT MATERIAL MUST HAVE
WRITTEN EXPRESSED PERMISSION FROM DR. KAJIURA, DR. DA SILVA, & DR. MAHALINGAM.
Copyright © Winter 2021 Biology 1A03 L. Kajiura, R. DaSilva, S. Mahalingam, A. Tracey, Department of Biology, McMaster University,
Hamilton, Ontario. Canada.
Downloaded by Photo Account (photos.riyad.asgarali@gmail.com)
You might also like
- Aqa A Level Biology p1 QPDocument36 pagesAqa A Level Biology p1 QPJaden MistryNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Molecular Biology 5th Edition Robert WeaverDocument11 pagesTest Bank For Molecular Biology 5th Edition Robert WeaverMelindaYangtpeg100% (38)
- Cell Communication Practice TestDocument5 pagesCell Communication Practice Testapi-237801056100% (2)
- AP Bio CH 18-20 Take Home FinalDocument14 pagesAP Bio CH 18-20 Take Home Finalheeraangelwingz0% (1)
- Biochemistry FinalDocument71 pagesBiochemistry FinalJanie-Vi Gorospe100% (2)
- MCQDocument10 pagesMCQNasir Ahmed100% (1)
- Cell Final ExamDocument8 pagesCell Final ExamJorge GomezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 03Document4 pagesChapter 03Teehee JonesNo ratings yet
- Bio1A03 Practice Test 2Document11 pagesBio1A03 Practice Test 2cbox4273No ratings yet
- Molecular Cell Biology Practice QuestionsDocument9 pagesMolecular Cell Biology Practice Questionssahana2791100% (1)
- BIO230 Sample Midterm With Answers UpdatedDocument9 pagesBIO230 Sample Midterm With Answers Updatedfgb9qfb7x6No ratings yet
- Test 2 Winter 2020 AnswersDocument10 pagesTest 2 Winter 2020 Answersproplayer910No ratings yet
- BCMB20002 MST2 Sem1 2016Document6 pagesBCMB20002 MST2 Sem1 2016kfqhnmh87hNo ratings yet
- Molecular Cell Biology Lodish 6th Edition Test Bank DownloadDocument9 pagesMolecular Cell Biology Lodish 6th Edition Test Bank Downloadjohndanielswrydmzokge100% (32)
- Chapter 13 RNA Test NAME Abdullah Alabdullah CLASS 9A DATEDocument7 pagesChapter 13 RNA Test NAME Abdullah Alabdullah CLASS 9A DATEAbdullah AlabdullahNo ratings yet
- Must Review ThisDocument19 pagesMust Review Thispmp123456No ratings yet
- Test Bank For Brock Biology of Microorganisms 14th Edition Michael T Madigan Download DownloadDocument20 pagesTest Bank For Brock Biology of Microorganisms 14th Edition Michael T Madigan Download Downloadstevenstevensjgzaryxbdp100% (28)
- Bio Practice Questions For Final Exam Biol 1101Document5 pagesBio Practice Questions For Final Exam Biol 1101Megadirectioner 21No ratings yet
- SampleQuiz-Ch11 18 PDFDocument2 pagesSampleQuiz-Ch11 18 PDFNguyễn Đức ÝNo ratings yet
- t2 Bio Revision Ex 1 Answer SchemeDocument15 pagest2 Bio Revision Ex 1 Answer SchemeNicholas OwNo ratings yet
- SamplepapeDocument7 pagesSamplepapeYogesh Verma ParjapatiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 Test A RNA and Protein Synthesis ANSWERS PDFDocument6 pagesChapter 13 Test A RNA and Protein Synthesis ANSWERS PDFxspiiirONo ratings yet
- StudentDocument12 pagesStudent김예진No ratings yet
- Test On Molecular Biology NEETDocument4 pagesTest On Molecular Biology NEETSadananda KumbhakarNo ratings yet
- MCQDocument9 pagesMCQpkm7929No ratings yet
- Lodish6e ch07Document8 pagesLodish6e ch07nNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 Rna Test Name Class DateDocument7 pagesChapter 13 Rna Test Name Class DateAbdullah AlabdullahNo ratings yet
- Science 10 Summative Test 2 Quarter 3 With Answer KeyDocument3 pagesScience 10 Summative Test 2 Quarter 3 With Answer KeyRowena Nim100% (2)
- Cytogenetics Final ExamDocument20 pagesCytogenetics Final ExamMICHAEL JOHN AGUILARNo ratings yet
- SSN SBPM Workshop Exam One Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument10 pagesSSN SBPM Workshop Exam One Multiple Choice QuestionsAG KhanNo ratings yet
- Principles of Cell Biology Exam 2 Spring 2020 March 26, 2020Document13 pagesPrinciples of Cell Biology Exam 2 Spring 2020 March 26, 2020Zachary D AbramsNo ratings yet
- CBT 2 Paper PDFDocument140 pagesCBT 2 Paper PDFkarthikNo ratings yet
- 2014Document14 pages2014Samuel RobertsNo ratings yet
- Ôn Thi SHPTDocument7 pagesÔn Thi SHPTHạ Thi LêNo ratings yet
- AP BioDocument12 pagesAP BioThomas Lim100% (2)
- Test Bank MetabolismDocument6 pagesTest Bank MetabolismWanga CharleneNo ratings yet
- DNA SamplexDocument6 pagesDNA SamplexNelica RotoniNo ratings yet
- 2020 Midterm 2 Questions W AnswersDocument12 pages2020 Midterm 2 Questions W AnswersKingsley ZhengNo ratings yet
- Biology 9648/01: Anderson Junior College Higher 2Document30 pagesBiology 9648/01: Anderson Junior College Higher 2saffronNo ratings yet
- Molecular Biology Examination (BSC) 2020/2021-Teneng Section A: McqsDocument3 pagesMolecular Biology Examination (BSC) 2020/2021-Teneng Section A: McqsTeneng Fidelis AwaNo ratings yet
- Bio 366 Sdsu Exam 2Document6 pagesBio 366 Sdsu Exam 2caseyvegarraNo ratings yet
- Genetics Chapter 8Document19 pagesGenetics Chapter 8Zahraa TermosNo ratings yet
- K101PracEx4 SP19 KeyDocument10 pagesK101PracEx4 SP19 KeyBraxton PhillipsNo ratings yet
- Paper II Part 2Document8 pagesPaper II Part 2Kritika MishraNo ratings yet
- Exam 1 Lectures 4 & 5 Q'sDocument6 pagesExam 1 Lectures 4 & 5 Q'sBlaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 &10 - Gene ExpressionDocument4 pagesChapter 9 &10 - Gene ExpressionMahmOod GhNo ratings yet
- 2010 A Level h2 Biology Dunman HighDocument46 pages2010 A Level h2 Biology Dunman HighStephyNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry FinalDocument60 pagesBiochemistry FinalAndrassy Twinkle Alinea100% (2)
- Biology MCQ Base KROK-1Document27 pagesBiology MCQ Base KROK-1Aswin JayakumarNo ratings yet
- IB DNA and Protein Synthesis Unit Test HL2 STUDENTDocument7 pagesIB DNA and Protein Synthesis Unit Test HL2 STUDENT167101No ratings yet
- Biochemistry Book Additional PlatesDocument8 pagesBiochemistry Book Additional PlatesKiana TehraniNo ratings yet
- Dr. Harvey Laranang MicrobiologyDocument9 pagesDr. Harvey Laranang MicrobiologyPatricia L.No ratings yet
- AP Biology Unit 5 ExamDocument13 pagesAP Biology Unit 5 ExamLana Sage CummingsNo ratings yet
- CellDocument14 pagesCellSyrian AsadNo ratings yet
- Microbiology A Human Perspective 7th Edition Nester Test BankDocument40 pagesMicrobiology A Human Perspective 7th Edition Nester Test Bankmagnusngah7aaz100% (33)
- Lecture COPEG Qns (Last Lect)Document8 pagesLecture COPEG Qns (Last Lect)Wesley TanNo ratings yet
- Gene RegulationsDocument11 pagesGene Regulationsmahadi.infsduNo ratings yet
- General Biology Ii: Engineering and Mathematics Science, TechnologyDocument3 pagesGeneral Biology Ii: Engineering and Mathematics Science, TechnologyKeirby CayanongNo ratings yet
- 6Document17 pages6AmaniNo ratings yet
- Microbial PhysiologyFrom EverandMicrobial PhysiologyAlbert G. MoatNo ratings yet
- Animal Physiology MCQsDocument3 pagesAnimal Physiology MCQsShafiq Azam RumiNo ratings yet
- Alfa 1 AntitripsinDocument4 pagesAlfa 1 AntitripsinDwitaRiadiniNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Bacteria: Structure and ReplicationDocument19 pagesIntroduction To Bacteria: Structure and ReplicationFort SalvadorNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Diagnosis of Sexually Transmited DiseasesDocument31 pagesLaboratory Diagnosis of Sexually Transmited DiseasesrikarzNo ratings yet
- Biotechnology and Its ApplicationsDocument8 pagesBiotechnology and Its ApplicationsS SURAJNo ratings yet
- Randox ControlDocument17 pagesRandox ControlLuis Ferdinand Dacera-Gabronino Gamponia-Nonan100% (1)
- June 2018 QP - Paper 1 AQA Biology A-LevelDocument44 pagesJune 2018 QP - Paper 1 AQA Biology A-LevelreneehandsNo ratings yet
- Therapeutic Dosages22Document11 pagesTherapeutic Dosages22Rishikesh AsthanaNo ratings yet
- 001assessment Exam ImmunohemaDocument25 pages001assessment Exam ImmunohemaFrankenstein MelancholyNo ratings yet
- Bact Alert Culture Media - 0Document4 pagesBact Alert Culture Media - 0Corporativo DRLABNo ratings yet
- LymphomaDocument20 pagesLymphomaChairul Adilla Ardy100% (1)
- Thrombolytics-1Document3 pagesThrombolytics-1Shayan ShayanNo ratings yet
- NLBL Bio Tech ApplicationsDocument5 pagesNLBL Bio Tech Applicationsyogeshwaran09102005No ratings yet
- Dental Caries DefinitionDocument11 pagesDental Caries DefinitioncartoonNo ratings yet
- 2325-300 Free PSA AccuBind ELISA Rev 5Document2 pages2325-300 Free PSA AccuBind ELISA Rev 5Emma MNo ratings yet
- Vaccine Race Is Over Ready or NotDocument6 pagesVaccine Race Is Over Ready or NotInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- 0710 Biology Past Questions From June 2000 To June 2021Document46 pages0710 Biology Past Questions From June 2000 To June 2021Stella DjuikomNo ratings yet
- Antileukotriene Agents in The Management of Asthma - UpToDateDocument30 pagesAntileukotriene Agents in The Management of Asthma - UpToDateAmr MohamedNo ratings yet
- Metabolism of NucleotidesDocument24 pagesMetabolism of NucleotidesAditya NayakNo ratings yet
- R J Epstein-Human Molecular Biology - An Introduction To The Molecular Basis of Health and Disease-Cambridge University Press (2002)Document655 pagesR J Epstein-Human Molecular Biology - An Introduction To The Molecular Basis of Health and Disease-Cambridge University Press (2002)Libros a Color ConceNo ratings yet
- PG StatementDocument6 pagesPG StatementDede RosadiNo ratings yet
- TranslationDocument37 pagesTranslationFarhana AnuarNo ratings yet
- Csec HSB June 2008 p2Document26 pagesCsec HSB June 2008 p2Sachin BahadoorsinghNo ratings yet
- H-046-019558-00 SARS-CoV-2 IgG-CEDocument2 pagesH-046-019558-00 SARS-CoV-2 IgG-CERenato DesideriNo ratings yet
- Liver Cirrhosis TreatmentDocument5 pagesLiver Cirrhosis TreatmentPrajith NairNo ratings yet
- Topic: Corona Virus Topic Sentence: Corona Virus Is A Virus That Can Be Conquered With The Right ActionsDocument2 pagesTopic: Corona Virus Topic Sentence: Corona Virus Is A Virus That Can Be Conquered With The Right ActionsArifah RamadhaniNo ratings yet
- African Healthcare Setting VHF PDFDocument209 pagesAfrican Healthcare Setting VHF PDFWill TellNo ratings yet
- Topic 5 Genhisto NotesDocument6 pagesTopic 5 Genhisto NotesShiina MashiroNo ratings yet
- Blood: Lecture Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor Florence-Darlington Technical CollegeDocument71 pagesBlood: Lecture Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor Florence-Darlington Technical CollegeCath TabasNo ratings yet