Professional Documents
Culture Documents
9 95565err
9 95565err
Uploaded by
Guette SyOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
9 95565err
9 95565err
Uploaded by
Guette SyCopyright:
Available Formats
DATA PRIVACY AND ETHICS
Definition of Data Privacy
Data Privacy, also called Information Privacy, is the aspect of information technology (IT) that
deals with the ability an organization or individual has to determine what data in a computer system
can be shared with third parties.
Source: peoplematters.in
Definition of Data Ethics
“A specialized area of Data Governance and Stewardship” where data can be “productionalized and,
in large part, automated through the use of good tooling.” (Andrew Brust, Tech Crunch)
Not only moral guidance as to “what data should be collected and how it should be used,” but also
“who gets to make those decisions in the first place.” (James Arvanitakis, et al., Phys.org)
A code of conduct or ethics for Data Scientists, similar to the purpose of the Hippocratic Oath in
guiding medical professionals. (Natalie Evans Harris, BrightHive)
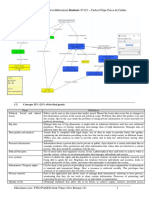
Data Privacy and Ethics
Data Governance: A process of management and oversight for information access according
to established best practice standards to ensure:
Data Integrity
Security
Privacy and Confidentiality
© 2023 Athena Global Education. All Rights Reserved
Data Integrity: The entire set of characteristics associated with data quality. These
include data content, including, currency (whether data are up to date or current), relevance to
the decision-making purpose, and accuracy (whether data are correct); scope
(comprehensiveness); level of detail composition (issues involved in database structure and the
definition of entities and attributes) consistency, including both semantic consistency
(consistency in the definitions of data elements, such as “patient number”, across entity types,
such as “patient” and “encounter”) and structural consistency (consistency in the business
rules that define the relationships among data elements) and reaction to change, which
concerns how data elements are updated, deleted or added to a database.
Data Security: Physical and electronic protection of integrity, availability, and
confidentiality of computer-based information and the resources used to enter, store,
process, and communicate it. The means to control access and protect information from
accidental or intentional disclosure.
Data Quality: The data owner is also accountable for maintaining the quality of the
information. This may include determining and setting user data quality expectations,
instituting gauges and measurements of the levels of data quality, and providing reports on the
conformance to data quality. This also includes defining data quality policies for all data that
flows into the system and any data cleansing, standardization, or other preparation for user
applications.
© 2023 Athena Global Education. All Rights Reserved
© 2023 Athena Global Education. All Rights Reserved
You might also like
- Case Study: Léa Hartmann - ID 18860 Jocelyn Rodriguez-Piedra - ID 19081 Guan Zihan - ID 19179Document11 pagesCase Study: Léa Hartmann - ID 18860 Jocelyn Rodriguez-Piedra - ID 19081 Guan Zihan - ID 19179Leah100% (1)
- An Extended Privacy Calculus Model For E-Commerce Transactions., - ISR, - 2006Document21 pagesAn Extended Privacy Calculus Model For E-Commerce Transactions., - ISR, - 2006dburnama100% (1)
- Chapter 2 Data Handling Ethics - DONE DONE DONEDocument15 pagesChapter 2 Data Handling Ethics - DONE DONE DONERoche ChenNo ratings yet
- Salaam InsuranceDocument23 pagesSalaam InsuranceNur Alia100% (1)
- TASK 4 Foundation of EducationDocument3 pagesTASK 4 Foundation of Educationalabanzasalthea100% (1)
- Nursing Informatics 1-2Document15 pagesNursing Informatics 1-2Jenny Agustin Fabros100% (2)
- Ethical Principles For Pharmacy TechniciansDocument6 pagesEthical Principles For Pharmacy TechniciansGilbert OfeiNo ratings yet
- Lee vs. TambagoDocument3 pagesLee vs. TambagoAnj100% (3)
- The Boy Who Broke The Bank PDFDocument4 pagesThe Boy Who Broke The Bank PDFsobia khan86% (28)
- Personal Data AnonymizationDocument7 pagesPersonal Data AnonymizationDraganNo ratings yet
- Data Governance Checklist: PTAC-CL, Dec 2011Document7 pagesData Governance Checklist: PTAC-CL, Dec 2011Tejeswara RaoNo ratings yet
- The Study On Data Science - Ethics and Privacy - HBRP PublicationDocument12 pagesThe Study On Data Science - Ethics and Privacy - HBRP PublicationsxtkateNo ratings yet
- Securing History: Privacy and Accountability in Database SystemsDocument10 pagesSecuring History: Privacy and Accountability in Database SystemsHarsha AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Database PDFDocument10 pagesDatabase PDFEegnayb Majait CuizonNo ratings yet
- PHD InterviewDocument2 pagesPHD InterviewviyasarmoulyNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Information, Information Science, and Information SystemsDocument65 pagesIntroduction To Information, Information Science, and Information SystemsTeover RamosNo ratings yet
- Blockchain-Enabled Security Solutions For Medical Device Integrity and Provenance in Cloud EnvironmentsDocument13 pagesBlockchain-Enabled Security Solutions For Medical Device Integrity and Provenance in Cloud EnvironmentsInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Big Data PrivacyDocument30 pagesBig Data Privacymr_ton1e46No ratings yet
- Big Data and Perioperative Nursing: Bonnie L. Westra, PHD, RN, Faan, Facmi Jessica J. Peterson, PHD-C, RN, CrnaDocument7 pagesBig Data and Perioperative Nursing: Bonnie L. Westra, PHD, RN, Faan, Facmi Jessica J. Peterson, PHD-C, RN, Crnadeny gunawanNo ratings yet
- Privacy Study in Sultan Ismail Hospital Johor BahruDocument4 pagesPrivacy Study in Sultan Ismail Hospital Johor BahruLim LeePingNo ratings yet
- Ch14 - Administrative and Clinical Health Information SystemsDocument68 pagesCh14 - Administrative and Clinical Health Information SystemsmarkdemonteverdeNo ratings yet
- Data Security - Challenges and Research OpportunitiesDocument5 pagesData Security - Challenges and Research Opportunities22ec10va480No ratings yet
- Data Management ReviewerDocument3 pagesData Management ReviewerhidalgomaxenejaneNo ratings yet
- Data Moning Seminar ReportDocument12 pagesData Moning Seminar ReportSankalp MishraNo ratings yet
- Electronics: A Systematic Literature Review On Privacy by Design in The Healthcare SectorDocument27 pagesElectronics: A Systematic Literature Review On Privacy by Design in The Healthcare SectorcdmaaNo ratings yet
- Data Mining in Medical Records For The Enhancement of Strategic Decisions: A Case StudyDocument10 pagesData Mining in Medical Records For The Enhancement of Strategic Decisions: A Case StudySasa TrifkovicNo ratings yet
- The Security DomainsDocument14 pagesThe Security DomainsBava IstamNo ratings yet
- Health Information Privacy and SecurityDocument9 pagesHealth Information Privacy and SecurityHafsa AkhtarNo ratings yet
- (Q1) Conceptual Analysis: Macieira AntunesDocument4 pages(Q1) Conceptual Analysis: Macieira AntuneskucaantunesNo ratings yet
- Value Added Privacy Services For Healthcare Data: Luvai Motiwalla and Xiaobai (Bob) LiDocument8 pagesValue Added Privacy Services For Healthcare Data: Luvai Motiwalla and Xiaobai (Bob) LiPUNEETH KUMAR T PNo ratings yet
- Data Governance Checklist - 0Document5 pagesData Governance Checklist - 0Muhammad Ammad100% (1)
- A Data Warehouse Architecture For Clinical Data Warehousing: Tony R. Sahama and Peter R. CrollDocument6 pagesA Data Warehouse Architecture For Clinical Data Warehousing: Tony R. Sahama and Peter R. CrollIrna SenikaNo ratings yet
- Diploma in Strategic ManagementDocument4 pagesDiploma in Strategic ManagementmushahidshahidNo ratings yet
- Literature Survey of Association Rule Based Techniques For Preserving PrivacyDocument6 pagesLiterature Survey of Association Rule Based Techniques For Preserving PrivacyIjact EditorNo ratings yet
- 7 Quality of DataDocument2 pages7 Quality of Datazbidi seifeddineNo ratings yet
- Analytical Techniques For Decision Making: Big DataDocument4 pagesAnalytical Techniques For Decision Making: Big Datasingh testNo ratings yet
- Bio Final Report BTDocument15 pagesBio Final Report BTK NandanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document16 pagesChapter 5Raed AlmalkiNo ratings yet
- Adibi 2008Document4 pagesAdibi 2008WENDY ELIZABETH SANTANA ROMERONo ratings yet
- Blockchain: A Panacea For Healthcare Cloud-Based Data Security and Privacy?Document7 pagesBlockchain: A Panacea For Healthcare Cloud-Based Data Security and Privacy?omarNo ratings yet
- On Ethics and Decision Support Systems Development: Rob Meredith and David ArnottDocument14 pagesOn Ethics and Decision Support Systems Development: Rob Meredith and David ArnottHari DubeyNo ratings yet
- Nursing Informatics: Data and Data ProcessingDocument17 pagesNursing Informatics: Data and Data Processinglea mae andoloyNo ratings yet
- BigdataDocument12 pagesBigdataTGOWNo ratings yet
- Data Governance BookDocument11 pagesData Governance BookAbhishek PrasadNo ratings yet
- YOYO's SISDocument13 pagesYOYO's SISbeaubeauyoNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S1877050917329563 MainDocument8 pages1 s2.0 S1877050917329563 Maintylermichael912No ratings yet
- Health Informatics Terminologies:: An IntroductionDocument33 pagesHealth Informatics Terminologies:: An IntroductionAriel Delos ReyesNo ratings yet
- Data Curation and Managment Chap1-5 1-5Document31 pagesData Curation and Managment Chap1-5 1-5yukoo2034No ratings yet
- The More Secure The Better? A Study of Information Security ReadinessDocument19 pagesThe More Secure The Better? A Study of Information Security Readinesspatyal20No ratings yet
- 88.challenges and Opportunities in Maintaining Data IntegrityDocument7 pages88.challenges and Opportunities in Maintaining Data Integrityeternitebeautiful21No ratings yet
- NCM 110 Module 3 - Health Data Standards and InteroperabilityDocument16 pagesNCM 110 Module 3 - Health Data Standards and InteroperabilityVincentus BinNo ratings yet
- Data GovernanceDocument7 pagesData GovernancesamydogNo ratings yet
- What Is InformaticsDocument38 pagesWhat Is Informaticsapi-239123914No ratings yet
- Ethical Considerations in Data Analysis - Essay 4Document2 pagesEthical Considerations in Data Analysis - Essay 4Nabeel MughalNo ratings yet
- 3 - Nelson DIKW ModelDocument32 pages3 - Nelson DIKW ModelAngela May Pustasa AllamNo ratings yet
- Topic 12 Manipulating Data: Prepared By: Mohammad Nabeel ArshadDocument24 pagesTopic 12 Manipulating Data: Prepared By: Mohammad Nabeel ArshadBLADE LEMON100% (1)
- Information Systems Security Versus Privacy 1 Running Head: Information Systems SecurityDocument9 pagesInformation Systems Security Versus Privacy 1 Running Head: Information Systems SecurityJamesPriceNo ratings yet
- Data Mining in MedicineDocument42 pagesData Mining in MedicineAna-Maria RaileanuNo ratings yet
- ATARC AIDA Guidebook - FINAL 3nDocument6 pagesATARC AIDA Guidebook - FINAL 3ndfgluntNo ratings yet
- Data MGMT - Some PointsDocument9 pagesData MGMT - Some Pointsphaltu_No ratings yet
- Pulkit Emerging Threats & Countermeas - EditedDocument7 pagesPulkit Emerging Threats & Countermeas - EditedEdwin SoimoNo ratings yet
- Data HandlingDocument15 pagesData HandlingFarzana HossainNo ratings yet
- CYBERSECURITYDocument3 pagesCYBERSECURITYOgunfodunrin RemilekunNo ratings yet
- ATARC AIDA Guidebook - FINAL TDocument1 pageATARC AIDA Guidebook - FINAL TdfgluntNo ratings yet
- Big Data in Healthcare Systems and ResearchDocument4 pagesBig Data in Healthcare Systems and ResearchInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- EL112 SURVEY OF AFRO ReviewerDocument5 pagesEL112 SURVEY OF AFRO ReviewerUkulele PrincessNo ratings yet
- DPR - Panchayat Raj Office ComplexDocument11 pagesDPR - Panchayat Raj Office ComplexD.V.Srinivasa RaoNo ratings yet
- Nilesh G Luharia Quiz !Document2 pagesNilesh G Luharia Quiz !Nilesh LuhariyaNo ratings yet
- Dwi Herinanto-Semnas DJ 2021 Old 2Document9 pagesDwi Herinanto-Semnas DJ 2021 Old 2Bernadhita HerindriNo ratings yet
- Tausug (Any)Document15 pagesTausug (Any)Fharhan Dacula100% (2)
- Tumasik or Old SingaporeDocument6 pagesTumasik or Old SingaporeAdrian TanNo ratings yet
- Loan SchemesDocument48 pagesLoan SchemesbalwinderNo ratings yet
- Crate Escape ScenarioDocument1 pageCrate Escape ScenarioBladiebla84No ratings yet
- WFC Conference Renewable EnergyDocument1 pageWFC Conference Renewable EnergyVincs KongNo ratings yet
- Dndaf Security Views Vince Quesnel 19 March 2013Document47 pagesDndaf Security Views Vince Quesnel 19 March 2013Isaac jebaduraiNo ratings yet
- Sole Proprietorship: Your Company's Form Will AffectDocument4 pagesSole Proprietorship: Your Company's Form Will AffectPauline ApiladoNo ratings yet
- STR502 Workplace Project Task 3 Assessors ChecklistDocument9 pagesSTR502 Workplace Project Task 3 Assessors ChecklistCong Tuan HuynhNo ratings yet
- Case - Make in IndiaDocument15 pagesCase - Make in IndiaMrinal Mantravadi100% (1)
- Ajay Gehlot CVDocument8 pagesAjay Gehlot CVRvi MahayNo ratings yet
- Lucian and Flaubert: David MarshDocument56 pagesLucian and Flaubert: David MarshAttila Lébényi-PalkovicsNo ratings yet
- Vol Ume 1: Mai N: Classification OF Wetlands OF BangladeshDocument261 pagesVol Ume 1: Mai N: Classification OF Wetlands OF BangladeshMd. Tanvir Hasan 1812974042No ratings yet
- College Schedule: Thursday Friday Saturday Sunday MondayDocument5 pagesCollege Schedule: Thursday Friday Saturday Sunday MondayGomv ConsNo ratings yet
- Maricalum Mining Corp. vs. FlorentinodocxDocument6 pagesMaricalum Mining Corp. vs. FlorentinodocxMichelle Marie TablizoNo ratings yet
- FC CantocoralvocalDocument320 pagesFC Cantocoralvocalfelix miguelNo ratings yet
- CSR-Reading Note-Workplace Marketplace Environment and Community-Lec 6-Prereading XrmI39M105 PDFDocument7 pagesCSR-Reading Note-Workplace Marketplace Environment and Community-Lec 6-Prereading XrmI39M105 PDFAnshuman DashNo ratings yet
- Certificate of Registration Registration No:: Code Subject Unit Class Days Time Room FacultyDocument2 pagesCertificate of Registration Registration No:: Code Subject Unit Class Days Time Room FacultyKael Matt Paul BesmonteNo ratings yet
- WFP ToR For Assistance To Syrian Refugees PDFDocument38 pagesWFP ToR For Assistance To Syrian Refugees PDFRuNo ratings yet
- Organic Organizational DesignDocument9 pagesOrganic Organizational DesignANGELA MARIA CAÑIZARES RAMIREZNo ratings yet
- Municipality of San Narciso Vs Mendez Sr. DigestDocument2 pagesMunicipality of San Narciso Vs Mendez Sr. DigestMark MlsNo ratings yet