Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lesson 1
Lesson 1
Uploaded by
Earl Vincent MergildoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lesson 1
Lesson 1
Uploaded by
Earl Vincent MergildoCopyright:
Available Formats
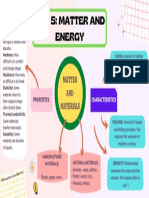
MATTER
Matter is anything that has mass and occupies space. Everything on earth
Has mass and takes up space.
PARTICLES COMPOSING MATTER
ATOMS - these are the smallest unit of matter that can’t be broken down chemically.
MOLECULES – these are groups of two or more atoms that are chemically bonded.
IONS – these are particles that have gained or lost one or more of their valence electrons
GENERAL PROPERTIES OF MATTER
• Mass
• Weight
• Volume
• Density
• Specific gravity
MASS – the amount of water in an object (the more matter is present in an object means
the greater its mass. It is usually expressed in grams (g) or kilograms (kg)
Weight – is the measure of force that acts on an object. Expressed as the amount of matter
(mass) multiplied by the gravitational force that acts on it. Expressed in Newtons (N)
Volume - amount of space occupied by matter. - it can be measured using instrument with
graduations or by getting the dimensions of the object. - expressed in Liters (L) for liquids, or
cubie length (19) for solid.
Density - ratio between mass and volume. - expressed in kilograms per cubic meter
(Kg/m3) or grams per cubic centimeter (g/cm). - tells how compact an object is. * An object
with greater mass has more compact particles than the lighter ones.
Specific Gravity - ratio of a substance's density to a standard substance. - also known as
relative density. - it is a dimensionless quantity.
rd = mw/ms ->mass of ->mass of
Properties of Matters
Physical Chemical
Extensive - Reactivity
-Depends of the amount of matter -Biodegradability
-Mass - Flammability
-Volume - Combustibility
Intensive
- Does not depend of the amount of matter
-Density -Weight - Metallic
-Specific gravity - boiling melting - Freezing
Melting point - temperature at which a solid matter changes to liquid
Freezing point- temperature at which a liquid turns into a solid matter.
Boiling Point - temperature at which liquid corporates.
- vapor precure is equal to the pressure of its surrounding liquid at this temperature.
Solubility - Ability of a solute to dissolve in given solvent. - varies depending on its
composition.
Metallic Properties - qualities that are observed specifically in metals.
a) Conductivity - ability of a material to allow heat or electric changers to pass through
easily - materials can be thermal or electrical conductors.
b) Malleability - ability of a material to be flattened into thin sheets.
c) Ductility - ability of a material to be easily drawn into wires. (stretchable)
You might also like
- Properties of Matter Notes Grade 8Document1 pageProperties of Matter Notes Grade 8Maristela Paraan MacaranasNo ratings yet
- Extensive and Intensive Properties FinalDocument16 pagesExtensive and Intensive Properties FinalCentener CalcetaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry For Engineers REVIEWEEERDocument26 pagesChemistry For Engineers REVIEWEEERJames Philip Relleve100% (6)
- 1st Q 1st TopicDocument43 pages1st Q 1st TopicAlexandra TabucanonNo ratings yet
- GenChem 1.4Document5 pagesGenChem 1.4MichelleNo ratings yet
- Properties of MatterDocument12 pagesProperties of MatterKriz ZiaNo ratings yet
- MixtureDocument11 pagesMixturebkbkjNo ratings yet
- Matter and Its Properties 2Document21 pagesMatter and Its Properties 2jsvalzado1515No ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1 Matter, MeasurementsDocument23 pagesCHAPTER 1 Matter, MeasurementsRusher SigueNo ratings yet
- PS Lesson 3Document2 pagesPS Lesson 3euginNo ratings yet
- Matter and Its PropertiesDocument10 pagesMatter and Its PropertiesGerald CatiponNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 CHEMISTRY HandoutsDocument3 pagesGrade 7 CHEMISTRY HandoutsCestlavi Santos100% (2)
- MatterDocument40 pagesMatterMarianne B. HingpesNo ratings yet
- Matter: Gracie Ann M. DyDocument24 pagesMatter: Gracie Ann M. DyLee Claudine BonifacioNo ratings yet
- Genchem1 ReviewerDocument4 pagesGenchem1 ReviewerCrystal Anne CastilloNo ratings yet
- Physical Properties of Matter Are Categorized As Either Intensive or ExtensiveDocument2 pagesPhysical Properties of Matter Are Categorized As Either Intensive or ExtensiveCamille Rose CruzNo ratings yet
- Material Properties Physical PropertiesDocument11 pagesMaterial Properties Physical PropertiesXiedrick SibongaNo ratings yet
- Module 3Document4 pagesModule 3delunaluisa19No ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1 - PocDocument1 pageCHAPTER 1 - PocloremipsumperNo ratings yet
- SHS-General Chemistry 1Document32 pagesSHS-General Chemistry 1JC PerezNo ratings yet
- Ice 3Document9 pagesIce 3Gabriel CortesNo ratings yet
- Week 1 - 2 - Properties of MatterDocument53 pagesWeek 1 - 2 - Properties of MatterAngelica Marie ZamoraNo ratings yet
- Module 5 Mathematics, Science, and TechnologyDocument3 pagesModule 5 Mathematics, Science, and TechnologyMarianne Bag-aoNo ratings yet
- CHM01Document17 pagesCHM01Daphne DimamayNo ratings yet
- Concept MapDocument5 pagesConcept MapMar YaNo ratings yet
- Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry 11th NotesDocument10 pagesSome Basic Concepts of Chemistry 11th NotesRʌĸɘsʜ GɘʜɭotNo ratings yet
- Sda, M, NDocument51 pagesSda, M, NUD ATNo ratings yet
- Unit 5: Matter and EnergyDocument1 pageUnit 5: Matter and EnergyanaNo ratings yet
- 3rd MASTERY - CHEM 1Document3 pages3rd MASTERY - CHEM 1Rhasher YbañezNo ratings yet
- Intensive, ExtensiveuhiuDocument1 pageIntensive, ExtensiveuhiuSepehr SaNo ratings yet
- Chem 1 L1 W1Document51 pagesChem 1 L1 W1Desire JoyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Study of ChangeDocument7 pagesChapter 1 Study of ChangeMark Julius Felix PagudNo ratings yet
- Chem HandoutDocument11 pagesChem HandoutEllen Mae PrincipeNo ratings yet
- Group C Material ScienceDocument71 pagesGroup C Material ScienceOrap-Orap, Jay Person F.No ratings yet
- GenChem 1.3Document12 pagesGenChem 1.3MichelleNo ratings yet
- Chem. Lesson 1Document31 pagesChem. Lesson 1Ashlee Talento100% (1)
- Class 9 - Chemistry HW - 18 April 2023Document3 pagesClass 9 - Chemistry HW - 18 April 2023Rishabh SinghNo ratings yet
- Gen ChemDocument2 pagesGen ChemLyresh Ellaine VillegasNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Reviewer 1Document13 pagesChemistry Reviewer 1John Van Dave TaturoNo ratings yet
- Chemistry ReviewerDocument7 pagesChemistry Reviewerback upNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document21 pagesChapter 1Lorraine Dacuro OcaslaNo ratings yet
- CMTTTTDocument24 pagesCMTTTTLealyn Pagsinuhin BobadillaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Chem IDocument11 pagesChapter 1 Chem IStudy LionNo ratings yet
- Science Outline CHAPTER10Document2 pagesScience Outline CHAPTER10Ben JeNo ratings yet
- Matter and Its Properties: Physical Science Week 3 HandoutsDocument2 pagesMatter and Its Properties: Physical Science Week 3 HandoutsBenj Jamieson DuagNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument4 pagesChemistryRhea Kristine C. MateoNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry (Reviewer) : Charisse Manlongat STEM301 SY. 2021-2022Document5 pagesGeneral Chemistry (Reviewer) : Charisse Manlongat STEM301 SY. 2021-2022Chandler ManlongatNo ratings yet
- Beige Brown Minimal Aesthetic Thesis Defense PresentationDocument8 pagesBeige Brown Minimal Aesthetic Thesis Defense PresentationCASUL, ARAVELANo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 1Document4 pagesGeneral Chemistry 1Jelou LumakinNo ratings yet
- GenchemDocument9 pagesGenchemGelan AiumtNo ratings yet
- Matter and Its Components - 1Document7 pagesMatter and Its Components - 1TenacityNo ratings yet
- Handout On Matter (2018)Document9 pagesHandout On Matter (2018)scientistgenerosoNo ratings yet
- Unit 7 Matter: Natural ScienceDocument10 pagesUnit 7 Matter: Natural ScienceClase Tercero ANo ratings yet
- Objectives:: Key Questions and Terms NotesDocument2 pagesObjectives:: Key Questions and Terms NotesfelishaNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document19 pagesModule 1Romel AlojadoNo ratings yet
- A. Extensive PropertiesDocument1 pageA. Extensive PropertiesAgnes Llanes CruzNo ratings yet
- Genchem1 Lesson 1 2 PrelimDocument33 pagesGenchem1 Lesson 1 2 PrelimXhander MacanasNo ratings yet
- GENERAL CHEMISTRY 2Document20 pagesGENERAL CHEMISTRY 2Jin LianNo ratings yet
- Module 4 - PROPERTIES OF MATTERDocument11 pagesModule 4 - PROPERTIES OF MATTERJBM 0531No ratings yet
- Thermo 3 Cyclic ProcessesDocument13 pagesThermo 3 Cyclic ProcessesFebrian RomanNo ratings yet
- Design and Development of Energy Efficient Solar Tunnel Dryer For Industrial DryingDocument9 pagesDesign and Development of Energy Efficient Solar Tunnel Dryer For Industrial DryingManish JoshiNo ratings yet
- SPH Bearing Draft (09.06.11)Document38 pagesSPH Bearing Draft (09.06.11)Dave ThompsonNo ratings yet
- FLR DR: 0 Its Velocity and Displacement Are + Vyoi, + V ODocument19 pagesFLR DR: 0 Its Velocity and Displacement Are + Vyoi, + V OSüshãñt SåhâÿNo ratings yet
- Wa0008.Document61 pagesWa0008.Praveen SingupurapuNo ratings yet
- Miniproject BatchesDocument4 pagesMiniproject BatchesDhanush SarnaikNo ratings yet
- Resonance and Damping NOTESDocument1 pageResonance and Damping NOTESThash ANo ratings yet
- Ice Core Records of Atmospheric CO2Document4 pagesIce Core Records of Atmospheric CO2Lucia Bascoy OteroNo ratings yet
- Chinese Standard For Pressure VesselDocument40 pagesChinese Standard For Pressure VesselirfanlarikhotmailcomNo ratings yet
- Material Characterization - Lecture 4Document18 pagesMaterial Characterization - Lecture 4Nilesh BondreNo ratings yet
- Chemical Kinetics Class 12 Notes Chemistry Chapter 4 - CBSE LabsDocument5 pagesChemical Kinetics Class 12 Notes Chemistry Chapter 4 - CBSE Labsavinash kishoreNo ratings yet
- Advanced Fluid DynamicsDocument281 pagesAdvanced Fluid Dynamicspeyvand100% (3)
- 01.1 - J. B. Shukla, Et Al - Effect of Global Warming On Sea Level Rise A Modeling StudyDocument12 pages01.1 - J. B. Shukla, Et Al - Effect of Global Warming On Sea Level Rise A Modeling StudyM. Alfi ZahamsyahNo ratings yet
- DLP SCIENCE 4 Q4 Practice Safety Precautions On The Effects of The SunDocument6 pagesDLP SCIENCE 4 Q4 Practice Safety Precautions On The Effects of The SunMark-Christopher Roi Pelobello MontemayorNo ratings yet
- Science 4: Third - Quarter Written Test No. 3Document5 pagesScience 4: Third - Quarter Written Test No. 3Melanie Dela Cruz CayabyabNo ratings yet
- Engineering Chemistry 9781783323555 9781783325702 1783323558 - CompressDocument381 pagesEngineering Chemistry 9781783323555 9781783325702 1783323558 - Compressotherwork3757No ratings yet
- Advanced Powder Technology: Shuangqing Su, Hongwen Ma, Xiuyun ChuanDocument6 pagesAdvanced Powder Technology: Shuangqing Su, Hongwen Ma, Xiuyun ChuanNELLY KARINA PEREZ GONZALEZNo ratings yet
- 55.JSS GOH PC850-8R1 Ulimanitra 10 Desember 2022Document21 pages55.JSS GOH PC850-8R1 Ulimanitra 10 Desember 2022doni granadaNo ratings yet
- Basic CalculationsDocument3 pagesBasic CalculationsMohammad J HaddadNo ratings yet
- Name: Sajeel Khan Roll#: M.phil-SSP-03-F19 Class: M.phil SSP (Morning) Subject: Magnetism in Condensed Matter Submitted To: Dr. Imran Sadiq SBDocument10 pagesName: Sajeel Khan Roll#: M.phil-SSP-03-F19 Class: M.phil SSP (Morning) Subject: Magnetism in Condensed Matter Submitted To: Dr. Imran Sadiq SBAnonymous f7wV1lQKRNo ratings yet
- The Journal of Supercritical FluidsDocument11 pagesThe Journal of Supercritical FluidsẢfnì Ădrỉànâ SịnãgăNo ratings yet
- Pengajuan Peralatan Fiber Optik: Fusion Splicer AI9C SIGNAL FIREDocument2 pagesPengajuan Peralatan Fiber Optik: Fusion Splicer AI9C SIGNAL FIRENanda KhoiriNo ratings yet
- Alpha-Voltaic Power Source DesignsDocument3 pagesAlpha-Voltaic Power Source DesignsMelvin BlackNo ratings yet
- Oxidation-Reduction Potential of The Ferro-Ferricyanide System in Buffer SolutionsDocument7 pagesOxidation-Reduction Potential of The Ferro-Ferricyanide System in Buffer SolutionsscribedbioaNo ratings yet
- Learning Plan in Science Grade 5Document7 pagesLearning Plan in Science Grade 5Marsha EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- Process Utility: By: Anupam Manoj B.Tech (Chemical Engg) 6 SemesterDocument14 pagesProcess Utility: By: Anupam Manoj B.Tech (Chemical Engg) 6 SemesterAnupam Manoj0% (1)
- Pinch TechnologyDocument26 pagesPinch TechnologyrajatNo ratings yet
- Science7 - Wheeldon, Stuber, Dierking - April7Document9 pagesScience7 - Wheeldon, Stuber, Dierking - April7Lea Bondoc LimNo ratings yet
- Principle of Fire SafetyDocument28 pagesPrinciple of Fire SafetySaraswatapalitNo ratings yet
- Normal Modes of Continuous SystemsDocument20 pagesNormal Modes of Continuous SystemsrohitNo ratings yet