Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Eapp Reviewer
Eapp Reviewer
Uploaded by
Cloe Miranda0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
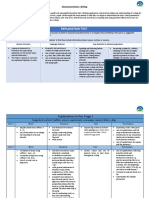
8 views5 pages1. The document discusses various text structures used in academic texts including definition, description, sequence, cause-effect, problem-solution, comparison, enumeration, and classification.
2. It also covers approaches for determining text structures such as noting language cues, graphic presentations, and outlining. Outlining principles include division, classification, coordination, and subordination.
3. Language and text structures are discussed across different disciplines including math, business, social sciences, natural sciences, and literature/arts. Each discipline employs certain terminology, symbols, and conventions in texts.
Original Description:
Original Title
eapp-reviewer
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1. The document discusses various text structures used in academic texts including definition, description, sequence, cause-effect, problem-solution, comparison, enumeration, and classification.
2. It also covers approaches for determining text structures such as noting language cues, graphic presentations, and outlining. Outlining principles include division, classification, coordination, and subordination.
3. Language and text structures are discussed across different disciplines including math, business, social sciences, natural sciences, and literature/arts. Each discipline employs certain terminology, symbols, and conventions in texts.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views5 pagesEapp Reviewer
Eapp Reviewer
Uploaded by
Cloe Miranda1. The document discusses various text structures used in academic texts including definition, description, sequence, cause-effect, problem-solution, comparison, enumeration, and classification.
2. It also covers approaches for determining text structures such as noting language cues, graphic presentations, and outlining. Outlining principles include division, classification, coordination, and subordination.
3. Language and text structures are discussed across different disciplines including math, business, social sciences, natural sciences, and literature/arts. Each discipline employs certain terminology, symbols, and conventions in texts.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 5
ENGLISH FOR ACADEMIC AND PROFESSIONAL constitute a concept, presented in
PURPOSES REVIEWER hierarchical order
Made by: JP De Guzman o Key words: several type/kinds, another
-Kung mahal mo, magreview ka muna! kind of, divided to
• Thesis-evidence
I. READING ACADEMIC TEXTS
o Serves the purposes of arguing a
A. Informational Text Structures point/position or interpretation
o Key words: assert/claim, prove/show
• Definition/Elucidation that, support, allege that
o Explains nature of something and
describes the thing being defined and B. Approaches to Determine Text Structures
cites examples
• Noting Language cues (key words)
o Key words: is/are, is defined as, means,
• Make Graphic presentation of the text
involves, as appears to be, a type of, a
• Outlining (main ideas and subtopics)
kind of
o Framework of a text through division
• Description
and subdivision of ideas
o Concrete details of appearance,
o Basic Principles and Rules in
characteristics, and actions
Outlining
o Key words: describes size, shape, color,
▪ Principle of Division
position, texture, adverbs of manner,
➢ every part of an outline
adjective phrases
that has subtopics
• Recount of a Sequence
should have at least two
o Chronological narration and sequential
parts or subsections
description of a process/procedure
▪ Principle of Classification
o Key words: first, second, now, before,
➢ Similar ideas should go
after, then, finally, while, meanwhile,
together
during
▪ Principle of Coordination
• Cause-Effect ➢ Coordinate headings
o Explains reasons why something must be expressed in
happened/effect of something parallel construction
o Key words: Effect-so, so that, as a ▪ Principle of Subordination
result, Cause-due to, because of, a ➢ There are big ideas and
cause of small idea
• Problem-Solution o Types of Outlines
o Starts with negative situations ends with ▪ Sentences Outline
a positive situation ▪ Topic Outline
o Key words: the problem/dilemma is, o Outline Format
if/then, so that, solves, an answer to, ▪ Traditional Outline
addresses the problem of ➢ Main ideas are labeled
• Comparison and Contrast with Roman numerals
o Similarities and differences are ▪ Non-Traditional Outline
presented
o Similarities key words: Similarly, in like C. Language and Text Structures across Disciplines
manner, in the same way
• Math
Differences key words: On the other
o Use of symbols and expressions in
hand, on the contrary, the opposite,
place of words
compared to, in contrast, although,
o Exact, precise language
unless, however
• Business
• Enumeration
o Use of business jargons and letters
o List of parts, of characteristics, of
o Compound nouns are standard
examples,
expressions
o Key words: To start with, first, second, in
addition, next, then, another, finally • Social Science
o Analysis of graphs and tables
• Classification
o Political Science, Economics, Sociology
o Present groupings, types, classes,
and Psychology
categories, and sub-categories that
• Natural Science o People’s evaluation can help improve
o Technical terms, symbols, one’s skill or craft
abbreviations, diagrams and drawings o Guide to help people make decisions
o Science texts are dense and o Critique
information-heavy ▪ Assess/evaluate the merits of a
• Literature and the Arts work
o Connotative language and figures of ▪ Objective, using a criteria
speech; vivid language for images and o Reaction Paper
impressions ▪ Evaluation of the works,
o Creativity weighs as much as content experiencesfeelings in relation
to the work being evaluated
D. Stating the Main Idea of a Text ▪ Subjective, how the work affects
the writer
• The thesis or main point of an informational text
o Subjectivity sets the difference between
• Types
reaction papers and critiques
o Deductive
o Both provides accurate descriptions of
▪ Stated ate the beginning;
the work being evaluated
followed by the supporting ideas
o Inductive B. Facts and Opinions
▪ Stated at the end; earlier
statements are details/specifics • Facts
that build up the main point o Verifiable statements
o Can be proven as true or false
E. Summarizing and Paraphrasing o Tested through direct experience
• Opinions
• Summary
o Expression of a person’s “feelings,
o Short/abbreviated version of a longer
attitudes, or beliefs, that are neither true
text
nor false”
• Paraphrase
o Can never be proven as true or false
o A restatement/restructuring of ideas for
o But may be difficult to prove as true or
the purpose of clarifying the meaning of
false because of ambiguous wordings
a text
C. Content and Organization of Critiques and
Reaction Papers
• Characteristics of a Good Critique/Reaction
Paper
o Accurate
▪ Accurate description
II. WRITING CRITIQUES AND REACTION PAPERS ▪ Summary/background details (5
A. Critical Thinking, Reading, and Writing W’s)
o Evaluative
• Critical Thinking ▪ Writer’s overall judgement
o Evaluative thinking ▪ 3 or more supporting
o Judgements can be both positive and evaluations
negative o Balanced
o Judgements = to criticize and evaluate ▪ Pointing out the weaknesses
• Critical Reading ▪ Recognizing the strong points
o Applying critical thinking skills upon the • Writing process
things we read that includes many kinds o Know well the nature of the writing
of materials that we encounter everyday assignment
o Important because it is not just used in o See, listen to, or otherwise experience
academics but is a life skill the work assigned for evaluation
• Critical Writing o Outline your presentation
o Result of critical thinking and reading o Draft and edit your paper
o Way of judging a student’s critical
thinking ability
o Way to determine how students feel
about the assigned subject
B. Writing a Position Paper
III. THE POSITION PAPER
• Choosing an issue for a topic
A. The Nature of a Position Paper • Collective information on the issue
o Logical Appeals
• Position Paper
▪ Use facts in order to support a
o Also called argumentative
position and persuade the
paper/manifesto
audience by targeting their
o Presents a person/group’s position or
thinking
stand on a particular issue
▪ Types of Arguments
o Convince the reader of the acceptability
➢ Transitivity
of the writer’s position
✓ Involves 3
• Uses of a Position Paper terms
o To express sentiments on an issue associated
o Any kind of situation in which there is a through the
significant issue that needs to be process of
addressed classification
o Helps others to become aware of certain ➢ Incompatibility
problems in society and possibly ✓ 2contradictory
become more involved in finding the choices
solution to it ➢ Reciprocity
• Parts of a Position Paper ✓ Individuals and
o Issue situations that
▪ An idea or question which can be put
people are divided together under
▪ Also called controversy the same
o Thesis category should
▪ A statement that expresses the be treated in the
stand or position on the issue same way
▪ Also called the claim ➢ Comparison
o Reasons ✓ argues that 2
▪ Explanation why the position is situations will
logical, acceptable, and have the same
believable outcome
▪ Also called arguments because of the
o Support similarities
▪ Evidences or ideas to between these
substantiate the reasons situations
▪ Types ➢ Generalization
➢ Facts - figures and the ✓ Use 1 member
writer’s own of a population
observations/reports to make
from scholarly studies conclusions
➢ Comparisons – about the entire
similarities/differentiatio population
n between two ideas, ➢ Examples
concepts, or situations ✓ use a group of
➢ Examples - real-life examples
demonstrations of an ➢ Cause
idea ✓ posits that A is
➢ Opinions - the author’s caused by B
feelings/generalizations
o Counterarguments ➢ Sign
▪ Opposing viewpoints give the ✓ uses a sign or
arguments opposing your stand indicator X to
▪ Refutes by showing argue for the
weaknesses existence of
condition Y
o Emotional Appeals o Conclusion
▪ Use the audience’s feelings and ▪ Summarize your arguments
values in order to persuade ▪ Reiterate your position
▪ Used only in addition to Logical
appeals to ensure balanced IV. THE CONCEPT PAPER
approach A. The Nature of a Concept Paper
▪ Types of Emotional Appeals
➢ Bandwagon Appeal • Concept Paper
✓ Uses people’s o An in-depth analysis of any idea,
tendency to situation or practice
conform with o It can be on anything that you find
the majority significant: feeling, a cultural practice, a
➢ Appeal to Common belief, a situation
Folk o It could be on something you feel strong
✓ the persuasion about or something you are very familiar
is done by with
pointing out that o Examines the “what-ness” or nature of
a person is no something
different from
ordinary people B. The Concept Paper as Extended Definition
➢ False Authority • Written to inform if the topic or concept is
✓ A type of false unknown to the audience
reasoning in • Written to introduce new information/dimension
which a person that gives new perspective to the concept if the
speaks as audience knows the subjects
expert on
• Definition Paper and Project Proposal
something on
o Definition Paper: Targets the
which he / she
explanation of an idea, theory, practice,
has no
or principle for the purpose of informing
expertise,
the audience
➢ Name Calling/Ad
o Project Proposal: Seeks to present an
Hominem
idea for consideration by others,
✓ uses labels with
possibly for support; hence, a concept
negative
paper also entails persuasive intent
meanings to
• Formal Definition
cast one’s
o Give the class to which the term belongs
opponent in a
• Informal Definition
bad light
o Based on a person’s personal views
➢ Association
✓ done by • Technical Definition
creating a link o Makes use of the technical language or
between one specialized vocabulary of a field
thing or idea • Popular Definition
and another o Makes use of the layman’s language is
one that people easy to understand
have a positive • Deductive Order > Organization > > Negative to
or negative Positive & Chronological Order
feelings for • Present tense for defining a term;
Past tense for tracing the historical
development > Indefinite article in the 1st part of
the definition > Restrictive clause in the 2nd part
• Organizing the Content of the definition
o Introduction C. Rhetorical Strategies used to Extend a Definition
▪ Introduce the issue
▪ State the claim on the issue • Examples
o Body o Fitting strategy if the term is abstract
▪ Present the opposing viewpoint • Comparison and Contrast
▪ Present your arguments
o Used when the term is not familiar or ▪ Free of emotionally loaded or
popular to the audience biased words so that the report
• Giving Details appears neutral and factual
o Physical description: shape, size, color, o Nondiscriminatory Writing
texture; non-physical: characteristics ▪ Treats all people equally and
• Giving Historical Background respectfully: gender, age,
o Used when a definition has gone disability
through changes in time
B. Parts of a Report
• Analysis
o Discussing the idea’s components • Prefatory Elements
and/or its implications o Title Page
o Abstract
D. The Concept Paper as a Project Proposal
• Report Proper
• Serves as an initial stage in the process of o Introduction
preparing a project proposal o Procedures
• A summary of proposed project o Results and Discussion
• Serve the twin purposes of informing and o Conclusion
persuading o Appendix
• Sections of Project Concept Paper o References
o Introduction C. Field Report
▪ Arouse the interest of the
reader/target sponsor by • Documents and interprets a researcher’s
showing your understanding of observation of behaviors usually in relation to a
their mission theory
o Purpose • Participants’ behaviors are carefully recorded,
▪ a problem or need of the reader described, and classified in order to show
that you wish to address patterns and/or unique instances.
o Project Description • Assigned to allow students to connect a theory
▪ Describe the activities that your to real life
project will undertake to address • Parts of a Field Report
the problem/need. o Introduction
o Objectives ▪ Orients the readers about the
▪ SMART observation done
o Methodology/Project Design o Description
▪ steps/procedures to implement ▪ provides the details of what you
the project have experienced
o Project Needs ▪ Scope
▪ a list that will be needed to carry ▪ Subjects
out the project ▪ Obsevations
o Timetable o Interpretation and Analysis
▪ an estimate of the time it will ▪ explains what you have seen
take for the completion of the from the perspective of the
project theory
o Conclusions and Recommendations
V. WRITING A FIELD REPORT
▪ summarizes the findings of the
A. Basic Report Writing Principles paper
▪ Summary of the findings
• Writing Style for Reports ▪ Recommendations
o Concise Writing ▪ Limitations
▪ Efficient writing; text should o Appendix
state an idea with the least ▪ the “extras” that you don’t need
number of words without affect in the body, but are related to
meaning the study
o Clear Writing o References
▪ Transmits to the reader the ▪ presents the complete
exact idea you have in mind bibliographic information of all
o Objective Writing the sources cited in the paper
You might also like
- Graphic Design Dissertation ExamplesDocument4 pagesGraphic Design Dissertation ExamplesWhereCanIBuyResumePaperSingapore100% (1)
- Overall Assessment Structure Critical ThinkingDocument2 pagesOverall Assessment Structure Critical ThinkingOun KimhengNo ratings yet
- Rodgers L Ethical Issues Concept Map Intro PageDocument2 pagesRodgers L Ethical Issues Concept Map Intro Pageapi-539642478No ratings yet
- RW Reviewer BAWAL ISHAREDocument5 pagesRW Reviewer BAWAL ISHAREIvan TrinidadNo ratings yet
- Eapp ReviewerDocument4 pagesEapp Reviewertimbolmarissa21No ratings yet
- New Syllabus Mathematics 1 (7th Edition)Document6 pagesNew Syllabus Mathematics 1 (7th Edition)Omer punjabNo ratings yet
- EOYE Class 6 SyllabusDocument6 pagesEOYE Class 6 Syllabuszeeshanajia1No ratings yet
- R and W (Topic 5)Document2 pagesR and W (Topic 5)JEANNE G. LLAVENo ratings yet
- Reading and Writing Skills - Midterm ReviewerDocument5 pagesReading and Writing Skills - Midterm ReviewerGerald BajadoNo ratings yet
- Topic Outline: - Transcribed By: Etcobanez, Hannah R. - Prof. Miles de Leon - 11 - RutherfordDocument5 pagesTopic Outline: - Transcribed By: Etcobanez, Hannah R. - Prof. Miles de Leon - 11 - RutherfordOlinaresNo ratings yet
- Hess Cognitive Rigor Matrix (Reading CRM)Document5 pagesHess Cognitive Rigor Matrix (Reading CRM)Raluca BobocNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2023-06-04 at 2.04.01 PMDocument6 pagesScreenshot 2023-06-04 at 2.04.01 PMZ.S.Z GamingNo ratings yet
- Eapp ReviewerDocument10 pagesEapp ReviewerHenry Lorenzo CruzNo ratings yet
- Language Functions and Forms: A Brief SummaryDocument2 pagesLanguage Functions and Forms: A Brief Summaryhbat saidNo ratings yet
- LanguageFunctionsForms PDFDocument2 pagesLanguageFunctionsForms PDFJJ PSNo ratings yet
- LanguageFunctionsForms PDFDocument2 pagesLanguageFunctionsForms PDFSandy Medyo GwapzNo ratings yet
- LanguageFunctionsForms PDFDocument2 pagesLanguageFunctionsForms PDFBoubaker GMNo ratings yet
- Language Functions and Forms: A Brief SummaryDocument2 pagesLanguage Functions and Forms: A Brief SummaryMitchNo ratings yet
- LanguageFunctionsForms PDFDocument2 pagesLanguageFunctionsForms PDFBe Creative - كن مبدعاNo ratings yet
- Language Functions and Forms: A Brief SummaryDocument2 pagesLanguage Functions and Forms: A Brief SummaryJujuNo ratings yet
- LanguageFunctionsForms PDFDocument2 pagesLanguageFunctionsForms PDFTariq AzizNo ratings yet
- LanguageFunctionsForms PDFDocument2 pagesLanguageFunctionsForms PDFSambarana EvanNo ratings yet
- Language Functions and Forms: A Brief SummaryDocument2 pagesLanguage Functions and Forms: A Brief SummaryJujuNo ratings yet
- LanguageFunctionsForms PDFDocument2 pagesLanguageFunctionsForms PDFKenali MaliNo ratings yet
- Latihan Soal BingDocument2 pagesLatihan Soal BingSambarana EvanNo ratings yet
- Language Functions and Forms: A Brief SummaryDocument2 pagesLanguage Functions and Forms: A Brief Summaryshaira alliah de castroNo ratings yet
- LanguageFunctionsForms PDFDocument2 pagesLanguageFunctionsForms PDFNamraNo ratings yet
- Reading and Writing NarrationDocument21 pagesReading and Writing NarrationisseylimboNo ratings yet
- Writing Revolution Pacing-Guide-Level-2-DetailedDocument2 pagesWriting Revolution Pacing-Guide-Level-2-DetailedStephen EdwaardsNo ratings yet
- Explanation Text: Literacy Curriculum - WritingDocument42 pagesExplanation Text: Literacy Curriculum - WritingFatwa KhairaNo ratings yet
- EAPP Transes Quarter 1Document5 pagesEAPP Transes Quarter 1Ma. Rhona Faye MedesNo ratings yet
- Flashcards PESDocument2 pagesFlashcards PESVishnumaya NNo ratings yet
- Dok Hess Cognitive RigorDocument1 pageDok Hess Cognitive Rigorapi-351081963No ratings yet
- Curriculum Links To ACARA and NESA - GrammarDocument2 pagesCurriculum Links To ACARA and NESA - Grammarlilnashty1No ratings yet
- TOEFL iBT StrategiesDocument10 pagesTOEFL iBT StrategiesMoon JiwonNo ratings yet
- Reading and Writing Reviewer First QuarterDocument2 pagesReading and Writing Reviewer First QuarterApricus BenciNo ratings yet
- EssayDocument11 pagesEssayAndreea CernatNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Skim Scan, Meaning, Topic, Main IdeaDocument11 pagesChapter 1 - Skim Scan, Meaning, Topic, Main IdeaHalim NordinNo ratings yet
- Template 2-English 10Document4 pagesTemplate 2-English 10Thelma R. VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Per101 - Study GuideDocument2 pagesPer101 - Study GuideCristina MarianoNo ratings yet
- TOEFL IBT Listening SectionDocument27 pagesTOEFL IBT Listening SectionTobias TobiasNo ratings yet
- ParaquoDocument2 pagesParaquoAli B. AlshehabNo ratings yet
- ELA Skills-7-12Document59 pagesELA Skills-7-12Jhanette De Los ReyesNo ratings yet
- Session Guide SampleDocument7 pagesSession Guide SampleJake Ryan Bince CambaNo ratings yet
- (1.1) HandsOn - CAP - (Long Term Plans)Document4 pages(1.1) HandsOn - CAP - (Long Term Plans)Vitória NevesNo ratings yet
- 5 Standards UnpackedDocument44 pages5 Standards UnpackedWasim DiabNo ratings yet
- Reading and WritingDocument3 pagesReading and WritingFrances Lorielyn TaborNo ratings yet
- R and W (Topic 5)Document2 pagesR and W (Topic 5)JEANNE G. LLAVENo ratings yet
- EAPP Modules 1Document95 pagesEAPP Modules 1Meschelle SeloveresNo ratings yet
- Reading and WritingDocument9 pagesReading and WritingEmziey ComendadorNo ratings yet
- Text TypesDocument3 pagesText TypessusannatomeltyNo ratings yet
- Cognitive Rigor MatrixDocument2 pagesCognitive Rigor MatrixJack Hayford IVNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1-Levels of Comprehension-Expository Text AnalysisDocument29 pagesLesson 1-Levels of Comprehension-Expository Text AnalysisTibetan FoxNo ratings yet
- Recount Assessment Rubric_Guide to Making JudgementDocument2 pagesRecount Assessment Rubric_Guide to Making Judgementsara ibrahimNo ratings yet
- Language-MatDocument2 pagesLanguage-MatlstewardNo ratings yet
- Writing Your Answer The AODocument2 pagesWriting Your Answer The AOSanuka PereraNo ratings yet
- 10 Concept PaperDocument20 pages10 Concept PaperGrantt ChristianNo ratings yet
- Text TypesDocument2 pagesText TypesTami GalarragaNo ratings yet
- Tips in Writing An Essay: ConjunctionDocument1 pageTips in Writing An Essay: ConjunctionJ-heart Basabas MalpalNo ratings yet
- Legal Technique Midterm NotesDocument7 pagesLegal Technique Midterm NotesChristia Sandee SuanNo ratings yet
- CAN DO Descriptors: Grade Level Cluster 1-2Document8 pagesCAN DO Descriptors: Grade Level Cluster 1-2Harry Jr.No ratings yet
- Student-Teacher Conference Portfolio FormDocument7 pagesStudent-Teacher Conference Portfolio Formapi-328194161No ratings yet
- Spectrum Reading for Main Ideas and Details in Informational TextFrom EverandSpectrum Reading for Main Ideas and Details in Informational TextRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- MEd TG G06 en 04-Oct DigitalDocument108 pagesMEd TG G06 en 04-Oct DigitalMuhammad AmmarNo ratings yet
- LightHouseLogiThink2 Eng 0601Document17 pagesLightHouseLogiThink2 Eng 0601api-3771376No ratings yet
- Public Administration Thesis TitleDocument4 pagesPublic Administration Thesis Titleafkngwetd100% (2)
- Tutor Marked Assignment B301 B: Making Sense of Strategy II SPRING Semester 2017 - 2018 Cut-Off Date 25/4/2018Document2 pagesTutor Marked Assignment B301 B: Making Sense of Strategy II SPRING Semester 2017 - 2018 Cut-Off Date 25/4/2018Elena AbdoNo ratings yet
- Emotional Intelligence and Critical ThinkingDocument17 pagesEmotional Intelligence and Critical ThinkingRichard WarrenNo ratings yet
- Clinical Decision Making Case Studies in Maternity and Womens Health Clinical Decision Making SeriesDocument6 pagesClinical Decision Making Case Studies in Maternity and Womens Health Clinical Decision Making SeriesClint NavarroNo ratings yet
- Filipino Psychology Thesis TopicsDocument8 pagesFilipino Psychology Thesis Topicsnicolestewartknoxville100% (2)
- Module - Technology in Language EducationDocument19 pagesModule - Technology in Language EducationFrancia LacruaNo ratings yet
- Euthenics 1 College LifeDocument25 pagesEuthenics 1 College Lifejosh arceoNo ratings yet
- Foundations of Education Part 1Document74 pagesFoundations of Education Part 1Gina BundaNo ratings yet
- 5-Crtical Reasoning 3Document21 pages5-Crtical Reasoning 3khaled NasrNo ratings yet
- Synthesis Essay English 102Document5 pagesSynthesis Essay English 102bkx3abyc100% (2)
- The Role of The Teacher ESSAY 1Document3 pagesThe Role of The Teacher ESSAY 1Timothy CNo ratings yet
- Thesis Statement About Communication TechnologyDocument8 pagesThesis Statement About Communication TechnologyWriteMyPaperInApaFormatCanada100% (1)
- Moot Court Clinical (Jurisdiction)Document15 pagesMoot Court Clinical (Jurisdiction)Heet DoshiNo ratings yet
- Oxford Companion To Childrens Literature ReviewDocument7 pagesOxford Companion To Childrens Literature Reviewea0bvc3sNo ratings yet
- Geography Forms 1-6 PDFDocument26 pagesGeography Forms 1-6 PDFbright mushori100% (1)
- Meaning of Literature Review in Project ReportDocument5 pagesMeaning of Literature Review in Project Reportafmaamehdbosuo100% (1)
- Teach Music SyllabusDocument8 pagesTeach Music SyllabusCherry lyn EnadNo ratings yet
- Q2 Module 1: I. The Brain and How It WorksDocument8 pagesQ2 Module 1: I. The Brain and How It WorksKristine MoresNo ratings yet
- Chapter ThreeDocument40 pagesChapter Threehinsene begnaNo ratings yet
- Syllabus in Biological SciDocument3 pagesSyllabus in Biological SciRodel Matulin Catajay100% (2)
- Tli Ai Misuse Rubric Guide Us 0223Document2 pagesTli Ai Misuse Rubric Guide Us 0223Koordinator Penelitian Puslitabmas STPBNo ratings yet
- ICT ReviewerDocument15 pagesICT ReviewerRay Lorenz OrtegaNo ratings yet
- One Pager On An Ethic of Excellence by Jamie ClarkDocument1 pageOne Pager On An Ethic of Excellence by Jamie ClarkMostafa YasserNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Case 2 - QuestionDocument7 pagesComprehensive Case 2 - QuestionPraveen RoshenNo ratings yet
- Newspaper Article CourseworkDocument5 pagesNewspaper Article Courseworkafjwofermaavkm100% (2)