Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Multiplication Division Progression Leaflet v3
Multiplication Division Progression Leaflet v3
Uploaded by
Josephine Beckford - Vista Heights PS (1560)0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views2 pagesThis document provides strategies for teaching multiplication and division to children. It recommends that children be able to use a variety of strategies confidently rather than relying on just one approach. Six strategies are described for teaching multiplication, including groups of, arrays, area models, grid methods, partitioning, and times tables. Four strategies are outlined for teaching division, such as grouping, arrays, area models, bar models, partitioning in different ways, and times tables. The document emphasizes developing a true understanding of these operations through flexible use of multiple representations and methods.
Original Description:
Original Title
Multiplication-Division-Progression-Leaflet-v3
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides strategies for teaching multiplication and division to children. It recommends that children be able to use a variety of strategies confidently rather than relying on just one approach. Six strategies are described for teaching multiplication, including groups of, arrays, area models, grid methods, partitioning, and times tables. Four strategies are outlined for teaching division, such as grouping, arrays, area models, bar models, partitioning in different ways, and times tables. The document emphasizes developing a true understanding of these operations through flexible use of multiple representations and methods.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views2 pagesMultiplication Division Progression Leaflet v3
Multiplication Division Progression Leaflet v3
Uploaded by
Josephine Beckford - Vista Heights PS (1560)This document provides strategies for teaching multiplication and division to children. It recommends that children be able to use a variety of strategies confidently rather than relying on just one approach. Six strategies are described for teaching multiplication, including groups of, arrays, area models, grid methods, partitioning, and times tables. Four strategies are outlined for teaching division, such as grouping, arrays, area models, bar models, partitioning in different ways, and times tables. The document emphasizes developing a true understanding of these operations through flexible use of multiple representations and methods.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 2
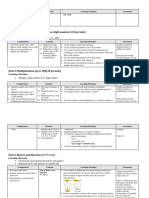
MULTIPLICATION STRATEGIES
To demonstrate a depth of understanding of multiplication children should be able to progress through and
confidently use a variety of strategies to solve problems and show working, and not be over reliant on one.
1. Groups Of 2. Arrays 3. Area Model
Use real items (sweets, counters, toys) Arrays are groups arranged 12 x 3
Breadth (row from array)
and drawings as representations. in rows and columns in the and length (column from
shape of a rectangle. array) multiply to find the
3 groups of 12 12 groups of 3 Always row x column. area of the rectangle
3 groups of 12 or 3 x 12
3 x 12
12 groups of 3 or 12 x 3
6. Formal Written 5. Partition 4. Grid
A true understanding Being able to partition a number to make them A progression from the Area model, and
of multiplication is easier to work with is very important, and can be an informal way of writing or recording
demonstrated by done throughout the progression of strategies. multiplication if a picture isn’t needed.
confidently using a
wide range of 3 x 12 12 x 3
strategies. The
formal written sum
should only be used
when confidence in
the use of others has
been achieved.
Skip Counting / Repeated Addition Times Tables
Count or add in jumps of multiple. Can be done orally or written. A good indicator for how well a child
remembers multiplication facts, but not
always how well they know how to
multiply. Ask how they know the answer.
DIVISION STRATEGIES
To demonstrate a depth of understanding of division children should be able to progress through and
confidently use a variety of strategies to solve problems and show working, and not be over reliant on one.
1. Grouping 2. Arrays 3. Area Model
Use real items (sweets, counters, toys) Arrays are groups arranged Rows (breadth) and total 15 ÷?=3
and drawings as representations. in rows and columns in the amount (area) divide to
Children should know the difference shape of a rectangle or find the answer of the
between groups and groups of. square. Row = dividing by rectangle or square.
Colum = Answer
15÷3 = ?
15 into 3 rows 15÷3=?
15 into rows of 3
15 into 5 groups 15 into groups of 5 15 ÷?=3
6. Formal Written 5. Partitioning in different ways 4. Bar Model
A true understanding Being able to partition or change a number to make them easier to Dividing the whole amount into equal
of division is work with is very important. It can be done throughout the parts. Use things to physically share or
demonstrated by progression of strategies and when working with different numbers. their knowledge of addition/multiplication
confidently using a amongst the parts to solve.
Multiplying Up 192÷8 / 72÷9
wide range of
strategies. The 72÷8
Multiply the divisor up to the
formal written calcu- number you’re dividing,
lation should only be continue until you reach the
used when confi- number dividing, then add the
dence in the use of total times divisor is multiplied.
others has been
achieved.
Skip Counting / Repeated Addition Times Tables
Count/subtract in jumps of multiple. Can be done orally or written.
72÷9=8
You might also like
- 1964-1986 OMC Sterndrive ManualDocument572 pages1964-1986 OMC Sterndrive ManualBarry Pieters80% (5)
- Lesson 9 Student WorkbookDocument16 pagesLesson 9 Student Workbookapi-470241815100% (1)
- Lesson 4 Student WorkbookDocument12 pagesLesson 4 Student Workbookapi-470241815No ratings yet
- Mathematics Interview Assessment Report and Lesson PlanDocument8 pagesMathematics Interview Assessment Report and Lesson Planapi-459495093No ratings yet
- Edma262 Mathematics Supp AssessmentDocument14 pagesEdma262 Mathematics Supp Assessmentapi-357915760No ratings yet
- Module 8 PDFDocument2 pagesModule 8 PDFapi-3769640700% (1)
- Mathematics 5: 21 Century MathletesDocument25 pagesMathematics 5: 21 Century MathletesAices Jasmin Melgar Bongao67% (3)
- Stress-Free Math: A Visual Guide to Acing Math in Grades 4-9From EverandStress-Free Math: A Visual Guide to Acing Math in Grades 4-9No ratings yet
- Year 11 Maths Ext 1 2019 Task 1Document9 pagesYear 11 Maths Ext 1 2019 Task 1bailey. sNo ratings yet
- Hexter - Fernand Braudel and The Monde Braudellien PDFDocument61 pagesHexter - Fernand Braudel and The Monde Braudellien PDFDarek SikorskiNo ratings yet
- Year 4 Unit 6Document68 pagesYear 4 Unit 6Mr GoldinNo ratings yet
- Calculation Policy - Multiplication & DivisionDocument54 pagesCalculation Policy - Multiplication & DivisionmheryantooNo ratings yet
- Website Math Lesson Plan 3 5Document2 pagesWebsite Math Lesson Plan 3 5api-545776066No ratings yet
- Multiplication Chart Printable Workbook PDFsDocument33 pagesMultiplication Chart Printable Workbook PDFsRenee MaloneyNo ratings yet
- Year 6 Week 6 Lesson 1 Main Focus Prior Knowledge Key Vocabulary Curriculum ObjectivesDocument17 pagesYear 6 Week 6 Lesson 1 Main Focus Prior Knowledge Key Vocabulary Curriculum Objectiveslenson kinyuaNo ratings yet
- Unitplank12 IhernandezDocument8 pagesUnitplank12 Ihernandezapi-378876175No ratings yet
- Vdoe FrameworkDocument9 pagesVdoe Frameworkapi-548452244No ratings yet
- Unit 2: Adding and Subtracting Three-Digit Numbers (34 Periods)Document2 pagesUnit 2: Adding and Subtracting Three-Digit Numbers (34 Periods)yitagesNo ratings yet
- Multiplication Facts UnitDocument9 pagesMultiplication Facts UnitMaria NasoneNo ratings yet
- Russian Peasant Multiplication Alternative Algorithm Sample LessonDocument3 pagesRussian Peasant Multiplication Alternative Algorithm Sample Lessonapi-400542088No ratings yet
- ICSE Class 7 Mathematics SyllabusDocument9 pagesICSE Class 7 Mathematics SyllabussivapraveenaNo ratings yet
- Grade 4 Unit 6 Scope and SequenceDocument8 pagesGrade 4 Unit 6 Scope and SequencereemaNo ratings yet
- Grade 4 Unit 3 Scope and SequenceDocument9 pagesGrade 4 Unit 3 Scope and SequencereemaNo ratings yet
- Fractions-Add and Subtract W/mixed Numbers: Grade Level: 5Document11 pagesFractions-Add and Subtract W/mixed Numbers: Grade Level: 5Eunice TrinidadNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document22 pagesAssignment 2api-485956198No ratings yet
- More Operations: Unit 6Document4 pagesMore Operations: Unit 6api-369620201No ratings yet
- Scope andDocument16 pagesScope andNurul AhmadNo ratings yet
- Freebie!Document5 pagesFreebie!Ariela Aguila Painen100% (1)
- Y3 Multiplying 2-Digit NumbersDocument15 pagesY3 Multiplying 2-Digit NumbersKatie ParkerNo ratings yet
- Coffee and Calculations: Workshop 4Document25 pagesCoffee and Calculations: Workshop 4Master NistroNo ratings yet
- 596 Assessment SlideDocument3 pages596 Assessment Slideapi-629245072No ratings yet
- MathDocument5 pagesMathapi-369628667No ratings yet
- Class 3 Maths SyllabusDocument8 pagesClass 3 Maths SyllabusKamal VermaNo ratings yet
- Calculation Policy - Addition & SubtractionDocument41 pagesCalculation Policy - Addition & SubtractionmheryantooNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Syllabus 7Document21 pagesMathematics Syllabus 7Ahmed SamahNo ratings yet
- Revised Division PolicyDocument11 pagesRevised Division PolicyRandall RhodesNo ratings yet
- ICSE Class 7 Maths Reduced Syllabus 2020 21Document10 pagesICSE Class 7 Maths Reduced Syllabus 2020 21AkashNo ratings yet
- Division & Decimals: Bridges in Mathematics Grade 5 Unit 7Document2 pagesDivision & Decimals: Bridges in Mathematics Grade 5 Unit 7api-289120259No ratings yet
- Grade 2 Unit 4 ParentletterDocument3 pagesGrade 2 Unit 4 Parentletterapi-294044622No ratings yet
- Ubd Unit - MathDocument3 pagesUbd Unit - Mathapi-610122953No ratings yet
- Filling A Ten When AddingDocument4 pagesFilling A Ten When AddingSive Veve QakanaNo ratings yet
- Adding and Subtracting Decimals To Hundredths Education Presentation in Blue Black White Simple Lined StyleDocument14 pagesAdding and Subtracting Decimals To Hundredths Education Presentation in Blue Black White Simple Lined Stylenadelyaa putriiNo ratings yet
- Landau Academy Syllabus Math Arzu H. (2020-2021)Document6 pagesLandau Academy Syllabus Math Arzu H. (2020-2021)Ulker AliyevaNo ratings yet
- Grade 4 Parent BrochureDocument2 pagesGrade 4 Parent Brochureapi-261342302No ratings yet
- 2016NJSLS-M Grade3Document17 pages2016NJSLS-M Grade3Gene HermanNo ratings yet
- Problem Solving StudentDocument73 pagesProblem Solving StudentVaneeta VijeyarasaNo ratings yet
- Math Unit 2 Q1 Multiplication of Whole NumbersDocument41 pagesMath Unit 2 Q1 Multiplication of Whole Numberswe.stan.enhypen12345No ratings yet
- Y6 Dividing Fractions by A Whole NumberDocument15 pagesY6 Dividing Fractions by A Whole NumberminamcfaulNo ratings yet
- Number Stories and Arrays: U Nit 2Document4 pagesNumber Stories and Arrays: U Nit 2api-369620201No ratings yet
- Base Ten ActivityDocument6 pagesBase Ten ActivitymrssouthernNo ratings yet
- Parent Overview Template-Es 3 Multiplication and Division 1Document2 pagesParent Overview Template-Es 3 Multiplication and Division 1api-266669871No ratings yet
- Unit 2-Big IdeasDocument3 pagesUnit 2-Big Ideasapi-233210734No ratings yet
- Teaching Skills APUDocument12 pagesTeaching Skills APUavikantbhardwajNo ratings yet
- Grade 5 Module 4 Parent LetterDocument4 pagesGrade 5 Module 4 Parent Letterapi-285755972No ratings yet
- 587 - Expanding A Single Bracket - LessonDocument36 pages587 - Expanding A Single Bracket - Lessonmanobilli30No ratings yet
- Problem Solving Maths 56Document73 pagesProblem Solving Maths 56Min WongNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Mathematics Curriculum in The Intermediate GradesDocument15 pagesLesson 2 Mathematics Curriculum in The Intermediate GradesRose Angel Manaog100% (1)
- Unit 3 Problem SolvingDocument21 pagesUnit 3 Problem SolvingRandolf Byron S. VirayNo ratings yet
- ICSE Class 6 Mathematics SyllabusDocument15 pagesICSE Class 6 Mathematics SyllabusTania BhaumikNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Mastery Project 2Document16 pagesUnit 4 Mastery Project 2api-583354474No ratings yet
- MultiplicationDocument3 pagesMultiplicationapi-283860704No ratings yet
- Divisibility Rules PDFDocument8 pagesDivisibility Rules PDFAlka KakkarNo ratings yet
- Palm Sunday: Matthew 21: 1-11 (NIV)Document4 pagesPalm Sunday: Matthew 21: 1-11 (NIV)Josephine Beckford - Vista Heights PS (1560)No ratings yet
- Palm Sunday: Story and Craftivity For Little KidsDocument15 pagesPalm Sunday: Story and Craftivity For Little KidsJosephine Beckford - Vista Heights PS (1560)No ratings yet
- How You Treat Others Is Who You AreDocument1 pageHow You Treat Others Is Who You AreJosephine Beckford - Vista Heights PS (1560)No ratings yet
- Ice Cream ScoopDocument1 pageIce Cream ScoopJosephine Beckford - Vista Heights PS (1560)No ratings yet
- Rez StoryDocument5 pagesRez StoryJosephine Beckford - Vista Heights PS (1560)No ratings yet
- 5 Light PagesDocument5 pages5 Light PagesJosephine Beckford - Vista Heights PS (1560)No ratings yet
- Dash Dot Across The CurriculumDocument23 pagesDash Dot Across The CurriculumJosephine Beckford - Vista Heights PS (1560)No ratings yet
- Risen CardstockDocument3 pagesRisen CardstockJosephine Beckford - Vista Heights PS (1560)No ratings yet
- Jesus Loves Me Worksheet - Twisty NoodleDocument1 pageJesus Loves Me Worksheet - Twisty NoodleJosephine Beckford - Vista Heights PS (1560)No ratings yet
- Joseph and His Coat AssemblyDocument5 pagesJoseph and His Coat AssemblyJosephine Beckford - Vista Heights PS (1560)No ratings yet
- Control and Optimization of Unit Operations: 8.1 Aeration and Do Controls 1484Document34 pagesControl and Optimization of Unit Operations: 8.1 Aeration and Do Controls 1484jigjigawNo ratings yet
- Makalah MorphologyDocument22 pagesMakalah Morphologyruly joanNo ratings yet
- A Novel Healthy and Time Aware Food Recommender Syst - 2023 - Expert Systems Wit PDFDocument22 pagesA Novel Healthy and Time Aware Food Recommender Syst - 2023 - Expert Systems Wit PDFARVIEL DELOS SANTOSNo ratings yet
- Python Classes: ClassDocument24 pagesPython Classes: Classns0447496No ratings yet
- Paper121 PDFDocument8 pagesPaper121 PDFjcvalenciaNo ratings yet
- Brochure FDP - EMDocument2 pagesBrochure FDP - EMAshlin AarthiNo ratings yet
- SAP Cash Cockpit ManualDocument41 pagesSAP Cash Cockpit ManualmikirichaNo ratings yet
- How To Download A Wikipedia Page As A PDF: 6 Steps (With Pictures)Document2 pagesHow To Download A Wikipedia Page As A PDF: 6 Steps (With Pictures)Grigoras CosminNo ratings yet
- Bentonite Trugel 100 2007-09Document1 pageBentonite Trugel 100 2007-09Tanadol PongsripachaNo ratings yet
- Innovations in Nursing EducationDocument18 pagesInnovations in Nursing EducationTapodhan VishuNo ratings yet
- Dasamsa by ShrikanthDocument23 pagesDasamsa by ShrikanthsasisekaranNo ratings yet
- 97050228-06 - Piezosteril 6 - Piezolight 6 - ENDocument9 pages97050228-06 - Piezosteril 6 - Piezolight 6 - ENRamona HarbuzNo ratings yet
- Sp-Uv1000 enDocument25 pagesSp-Uv1000 enPipomoNo ratings yet
- Centrifugal Compressor Pulsation-Vibration ProblemsDocument4 pagesCentrifugal Compressor Pulsation-Vibration ProblemszaidbismaNo ratings yet
- Personality DisordersDocument35 pagesPersonality DisordersEsraRamosNo ratings yet
- Defence Account CodeDocument41 pagesDefence Account Codem kNo ratings yet
- The Maharashtra Factories Rules 1963Document104 pagesThe Maharashtra Factories Rules 1963rasinv100% (1)
- PDC Lab Manual - Edited-1 PDFDocument55 pagesPDC Lab Manual - Edited-1 PDFArjun SankarNo ratings yet
- PDFDocument46 pagesPDFLidijaSpaseskaNo ratings yet
- Module 5 6 Week 5 6Document17 pagesModule 5 6 Week 5 6Jirah Joy PeañarNo ratings yet
- Fuel Injection SystemDocument24 pagesFuel Injection SystemDevendra Pratap SinghNo ratings yet
- Key External Factors: EFE MatrixDocument3 pagesKey External Factors: EFE MatrixAditya ChitaliyaNo ratings yet
- Ante Termite TreatmentDocument19 pagesAnte Termite TreatmentSoumya Sharma33% (3)
- Electrical Machine DesignDocument2 pagesElectrical Machine DesignAnonymous 1abQZINo ratings yet
- Module 8-c Sugar Manufacturing Process - Clarification Steps and CrystalisationDocument29 pagesModule 8-c Sugar Manufacturing Process - Clarification Steps and CrystalisationDaudNo ratings yet
- MGMT-631 Assignment 1Document2 pagesMGMT-631 Assignment 1Rehan HameedNo ratings yet
- SymgenicsTQ Automation Gas Start Up - SI UnitsDocument28 pagesSymgenicsTQ Automation Gas Start Up - SI UnitscahyaNo ratings yet