Professional Documents
Culture Documents
سيتو اسأله الكتاب
سيتو اسأله الكتاب
Uploaded by
M.Ahmed0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views12 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views12 pagesسيتو اسأله الكتاب
سيتو اسأله الكتاب
Uploaded by
M.AhmedCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf
You are on page 1of 12
D. The nonpolar tails are
hydrophobic.
E. The phospholipids form a
bilayer.
4A
Particular molecule or ion to freely
protein allows a
cross the plasma membrane as it
enters or exits the cell.
A. cell-recognition
B. carrier
C. receptor
D. enzymatic
E. channel
5) A protein combines with a
substance and helps to move it across
the membrane.
A. carrier
B. channel
C. _cell-recognition
D. receptor
E. enzymatic
6) A protein has a specific
shape such that only a particular
molecule can bind to it.
A. enzymatic
B. receptor
C. __cell-recognition
D. channel
E. cartier
1) Which of the following statements
is NOT correct regarding the plasma
membrane structure?
A. Protein molecules may be
partially or wholly embedded.
B. Protein molecules are
localized toward one side of the
cell.
C. Phospholipids form a
bilayer.
D. Phospholipids have a fluid
consistency.
E. The head of the
phospholipid molecule is attracted
toward water.
2) Which of the following molecules
would NOT be found in animal plasma
membranes?
A. proteins
phospholipids
glycolipids
cholesterols
moO®D
nucleic acids
3) Which of the following statements
is NOT correct about the phospholipid
‘molecules in the plasma membrane?
A. The polar heads face
outward.
B. The nonpolar tails face
inward.
C. The polar heads are
hydrophobic.
CamScanner 2 92 4>g.uaall
D. Molecules move from higher
to lower concentration.
11)Diffusion does not necessarily
require a membraneliifLipid-soluble
molecules and gases enter the cell by
A. diffusion through the
channel proteins
B. osmosis through the channel
proteins
c. diffusion through the lipid
bilayer
D. osmosis through the lipid
bilayer
E. active transport through the
lipid bilayer
12)The diffusion of water across a
differentially permeable membrane is
called
A. simple diffusion
facilitated diffusion
osmosis
exocytosis
endocytosis
moop
13)Which type of solution will cause
cells to swell, or even to burst?
‘A. isotonic solution
B. hypotonic solution
C. hypertonic solution
D. _hygrotonic solution
7) Which statement best describes
the plasma membrane?
A. It is freely permeable to all
substances.
B. tis selectively permeable to
certain substances,
C. It is nonpermeable to all
substances.
8) Which of the following is NOT an
active method where molecules pass
across the plasma membrane?
A. simple diffusion
B. active transport
C. endocytosis
D. exocytosis
9) Pinocytosis is a type of
A. endocytosis
exocytosis
active transport
simple diffusion
facilitated diffusion
moo®
10)Which of the following conditions
does NOT apply to diffusion?
A. Diffusion continues even
after the molecules are distributed
equally.
B. Diffusion is a physical
process.
C. Diffusion is a passive
process.
CamScanner 2 92 4>g.uaall
17)Which of the following transport
processes will form a vesicle?
A diffusion
facilitated diffusion
osmosis
active transport
phagocytosis
moop
18)Which of the following transport
processes will utilize the Golgi
apparatus?
A. osmosis
B. pinocytosis
C. phagocytosis
D. exocytosis
19)Pinocytotic vesicles or phagocytotic
vesicles often fuse with a
inside the cell for digestion.
A. mitochondrion
B. lysosome
C. — Golgi apparatus
D. rough endoplasmic reticulum
E. smooth endoplasmic
reticulum
20)The carriers for the electron
transport system are located _
A. within the cytoplasm of a cell
B. on the cristae of
mitochondria
C. within the — matrix of
mitochondria
D. within the Golgi apparatus
14)Which type of solution has a lower
percentage of solute than the cell?
A. isotonic solution
B. _ hypotonic solution
C. hypertonic solution
15)Which of the following conditions
does NOT apply to facilitated
transport?
A requires specific carrier
proteins
B. transports molecules down
the concentration gradient
C. requires the expenditure of
energy
D. transports molecules from
one side of the membrane to the
other side
E. transports molecules
through the membrane much faster
than simple diffusion
16)Which process will transport
sodium ions to the outside of the cell
and potassium ions to the inside of the
cell?
A. simple diffusion
B. facilitated diffusion
C. osmosis
D. active transport
E. pinocytosis
CamScanner 2 92 4>g.uaall
C. surrounds the cell
D. helps make proteins
25) Which organelle. makes
proteins using coded instructions that
come from the nucleus?
A. — Golgi apparatus
B. mitochondrion
C. vacuole
D. ribosome
26)What part of the cell serves as the
intracellular highway?
endoplasmic reticulum
golgi apparatus
cell membrane
mitochondria
pom>
27)Which statement —_correctly
characterizes bound ribosomes?
A. Bound ribosomes are
enclosed in their own membrane.
B. Bound and free ribosomes
are structurally different.
C. Bound ribosomes generally
synthesize membrane proteins and
secretory proteins.
D. The most common location
for bound ribosomes is the
cytoplasmic surface of the plasma
membrane.
. within the stroma of
chloroplasts
21)Which of the following pathways
will use coenzyme A during aerobic
cellular respiration?
A. glycolysis
B. transition reaction
C. Krebs cycle
D. electron transport system
E. fermentation
22)Based on chemiosmosis, hydrogen
ions accumulate in the of the
mitochondrion to create a large
electrochemical gradient for aerobic
cellular respiration.
A intermembrane space
B. cristae
Cc. matrix
D. stroma
23)The acts as a
packaging and processing center in
the cell to process proteins,
A, Smooth E.R.
B. Rough E.R.
C. Golgi Body
D. Nucleus
24)Which of the following is a function
of the cytoskeleton?
‘A. helps a cell keep its shape
B. contains DNA
CamScanner 2 92 4>g.uaall
A. The intestinal cells are fused
together into one giant cell.
B. The intestinal cells are
bound together by plasmodesmata.
C. The intestinal cells are
bound together by tight junctions.
D. The intestinal cells are
bound together by gap junctions.
E. The intestinal cells are
bound together by the extracellular
matrix.
32)The primary role of ___ is to bind
animal cells together.
A. plasmodesmata
B. gap (communicating)
junctions
C. the cytoskeleton
D. desmosomes
E. tight junctions
33) aid in the coordination of the
activities of adjacent animal cells.
A. Gap (communicating)
junctions
B, Tight junctions
C. Keratin fibers
D. Plasmodesmata
E. Desmosomes
34)Ribosomal subunits are
manufactured by the __.
‘A. lysosome
B. nucleolus
28)Which cell would be best for
A.
B.
Cc.
Db.
Ey
‘studying lysosomes?
muscle cell
nerve cell
phagocytic white blood cell
leaf cell of a plant
bacterial cell
29)In eukaryotic cells the first step in
protein synthesis is the-
A. translation of an RNA nucleotide
sequence into a sequence of amino
acids
B. linking of nucleotides to form a
polypeptide
C. translation of a DNA nucleotide
sequence into a sequence of amino
acids
D. transferring of information
DNA to messenger RNA
E. removal of introns from RNA and
the stitching together of exons
from
30)The cilia and flagella of eukaryotic
cells are composed of _.
A. microtubules
B. intermediate filaments
C. microfilaments
D. tonofilaments
31)Your intestine is lined with individual
cells. No fluids leak between these
cells from the gut into your body. Why?
CamScanner 2 92 4>g.uaall
‘A. Only eukaryotic cells can
synthesize proteins but prokaryotic
cells cannot.
B. Only eukaryotic cells have
DNA.
C. — Compartmentalization of the
cytoplasm by membrane-bounded
organelles only occurs in
eukaryotic cells.
D. Eukaryotic cells have a
plasma membrane and prokaryotic
cells do not.
E. Eukaryotic cells are larger
than prokaryotic cells.
39)What is the functional connection
between the nucleolus, nuclear pores,
and the nuclear membrane?
A. Subunits of ribosomes are
assembled in the nucleolus and
pass through the _—nuclear
membrane via the nuclear pores.
B, The nuclear pores are
connections between the nuclear
membrane and the endoplasmic
reticulum that permit ribosomes to
assemble on the surface of the ER.
C. The nucleolus contains
messenger RNA (mRNA), which
crosses the nuclear envelope
through the nuclear pores.
D. Endoplasmic reticulum
membrane is produced in the
C. peroxisome
D. rough endoplasmic reticulum
E. smooth endoplasmic
reticulum
35)Which of these are hollow rods that
shape and support the cell?
A. plasma membrane
B. microtubules
C. chloroplasts
D. microfilaments
E. peroxisomes
36)Where is calcium stored?
A. mitochondria
B. smooth endoplasmic
reticulum
C. centrioles
D. rough endoplasmic reticulum
E. microtubules
37)Which of these —_ organelles
produces H202 as a by-product?
A. mitochondrion
B. nucleus
C. centrioles
D. flagellum
E. peroxisome
38)In terms of cellular function, what is
the most important difference between
prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
CamScanner 2 92 4>g.uaall
A. ER — Golgi — vesicles that
fuse with plasma membrane
B. Golgi ER — lysosome
C. nucleus + ER — Golgi
D. ER — lysosomes — vesicles
that fuse with plasma membrane
E. ER — Golgi — nucleus
44)You would expect a cell with an
extensive Golgi apparatus to__. ()
store large quantities of ions
secrete a lot of protein
move rapidly
absorb nutrients in the Gl
tract
E. make a lot of ATP
p:om>
45)The smooth ER is especially
abundant in cells that synthesize
extensive amounts of
A. toxins
B. proteins
C. enzymes
D. lipids
E. nucleic acids
46)Intermediate Filaments (IFs) use
the motor protein:
A. Dynein
B. Myosin
C. Actin
D. None
nucleolus and leaves the nucleus
through the nuclear pores.
E. none of the above
40)You would expect a cell with an
extensive Golgi apparatus to ‘
A. make a lot of ATP
secrete a lot of protein
move rapidly
perform photosynthesis
‘store large quantities of ions
moo
41)Cilia and flagella move due to the
interaction of the cytoskeleton with
Which of the following?
A. actin
pseudopodia
mitochondria
‘tubulin
moog
Motor proteins
42)Basal bodies are most closely
associated with which one of the
following cell components?
nucleus
A. mitochondria
B. cilia
C. the central vacuole
D. Golgi apparatus
43)What is the most likely pathway
taken by a newly synthesized protein
that will be secreted by a cell?
CamScanner 2 92 4>g.uaall
50)A major function of glycoproteins
and glycolipids in the cell membrane is
to
A. allow the cells to recognize
each other.
B. help the cell retain its shape.
C. help the cell resist swelling.
D. glue cells together to form
tissues,
E. attach the cell membrane to
the cytoskeleton
51)A bacterial cell's DNA is found in its
A. nucleoid region.
ribosomes.
peroxisome.
capsule.
Nucleus
moo
52) facilitate the diffusion of
water in plant cells and in animal cells.
carrier protein
channel protein
aquaporin
ion channel
all of previous
mOO@>
53)A stimulus causes channels to
open or close.
A. lon Channels
B. gated channels
47)Who's dynamic?
A. Microtubules
B. Intermediate filaments
C. Microfilaments
48)The membranous
compartmentalization of a cell
A. allows different metabolic
processes to occur
simultaneously.
B. divides the cell into two
equal-sized halves.
C. requires the presence of a
cell wall,
D. is common in prokaryotes
and eukaryotes.
E. requires the presence of a
large central vacuole.
49)Which of the following functions
could be assigned to the cytoskeleton?
A chromosome
movement during mitosis.
B. change in shape of
an amoeba.
C. movement
(streaming) of cytoplasm in
plant cells
Do A&B
E. A,B&C
We / VY
CamScanner 2 92 4>g.uaall
D. Passive transport
E. Diffusion
57)Bulk transport across the plasma
membrane occurs by.
A. Simple diffusion
8. _ Exocytose and Endocytosis
C. Water channels
D. be
E. _ none of previous
58)Large molecules (e.g. proteins and
polysaccharides) cross membranes
by.
A. Bulk transport
B. Active transport
Cc. Passive transport
D. Facilitated transport
59)Phagocytes, pinocytosis. and
receptor-mediated endocytosis are
three types of.
A. Exocytosis
B. Endocytosis
C. bulk transport
C. type of facilitated diffusion
D. type of channels protein
E. all of previous
84). undergo a subtle
change in shape that to translocation
the solute-binding site across the
membrane.
A. carrier protein
active transport
passive transport
channel protein
moog
none of previous
55)One of the following is non-living
organism
A. bacteria
B. fungi
Cc. virus
D. algae
56)In certain inherited diseases, such
as Cystinuria, specific transport
systems are either defective or
missing
A. Channel protein
8. Cartier proteins
\v- / \¥o
C. Active transport
CamScanner 2 92 4>g.uaall
legends to receptors on the cell's
surface.
A. Bulk transport
B. simple diffusion
C. receptor-mediated endocytosis
D. cell-signaling
E. cell recognition
63)Cholesterol enters the cells by
A. endocytosis
B. exocytosis
C. protein carrier
D. receptor-mediated endocytosis
E. protein channels
64)The cell adhesion proteins of the
desmosome are members of the
“ family of cell
molecules.
adhesion
A. cadherins
B. reticulin
C. collagen
D. albumin
60)Membranous organelles
localization are specific character
A. Viruses
B. Prokaryotes
C. Eukaryotes
D. ac
E. none of previous
61) Endocytosis of fluid droplets is
A. phagocytosis
B. pinocytosis
C. receptor-mediated endocytosis
9
. cell Vaculation
E. cell recognition
62)The process of importing specific
macromolecules into the cell by the
inward budding of vesicles occurs in
fesponse to the binding of specific
CamScanner 2 92 4>g.uaall
E. Be made up of ionic particles in even
balance
67)They are short hair-like structures
that protrude from the surface of some
eukaryotic cells. They can propel the
cell through water, but are also found
in the respiratory system of humans.
A. Flagella
B. Chloroplasts
C. Lysosomes
D. Ribosomes
E. Cilia
68)It is a dark structure found in the
nucleus that produces parts of the
ribosomes.
A. Nuclear Pore
B. Cytoskeleton
C. Organelles
D. Nucleolus
£. Cell Membrane
69)Tay-Sachs disease results from the
absence of a particular enzyme found
inthe
‘A. endoplasmic reticulum.
B. mitochondria.
C. lysosomes.
-10-
65)Nuclear membranes contain pores
that:
A. Allow only water to pass into the
nucleus
B. Allow only nonpolar molecules to
pass through the membrane
C. Connect the inner and outer
nuclear membranes, _ allowing
mRNA and some ions to pass
D. Are among the smallest structures
in the cell, allowing no ions to pass
through
E. Are always open so that materials
can enter or exit the nucleus
66)A major function of cellular
membranes is to block the passage of
water-soluble ions and polar
molecules. To do this, the membrane
should:
. Contain many protein pores
. Contain a nonpolar barrier made up of
hydrocarbon tails of phospholipid
molecules
. Have a polar barrier in the interior of
the membrane
Be made up primarily of water-soluble
molecules
CamScanner +
D. Golgi bodies.
70)Secretion involves _ information
transfer from the DNA to
A.mRNA which directs manufacture
of proteins.
B.tRNA which directs manufacture of
proteins.
C.tRNA which directs manufacture of
mRNA.
D.mRNA which directs manufacture
of tRNA.
CamScanner 2 92 4>g.uaall
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5824)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (903)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (541)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (823)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (403)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- CRA77Document279 pagesCRA77M.AhmedNo ratings yet
- CamScanner ٠٣-١٤-٢٠٢٢ ٠١.٣٣Document10 pagesCamScanner ٠٣-١٤-٢٠٢٢ ٠١.٣٣M.AhmedNo ratings yet
- CRA27Document25 pagesCRA27M.AhmedNo ratings yet
- CameraScan 26-Mar-2022 19.56Document5 pagesCameraScan 26-Mar-2022 19.56M.AhmedNo ratings yet
- الدليل الوطني لتصنيف الأنشطة الاقتصاديةDocument110 pagesالدليل الوطني لتصنيف الأنشطة الاقتصاديةM.AhmedNo ratings yet
- Newsletter March 2018Document28 pagesNewsletter March 2018M.AhmedNo ratings yet
- NorganicDocument7 pagesNorganicM.AhmedNo ratings yet
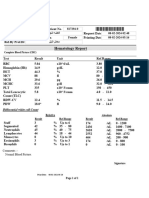
- Hematology Report: Test Result Ref - Range UnitDocument1 pageHematology Report: Test Result Ref - Range UnitM.AhmedNo ratings yet
- Skin 1Document16 pagesSkin 1M.AhmedNo ratings yet
- Histo LabDocument7 pagesHisto LabM.AhmedNo ratings yet
- Analytical Alaa Omar + 2024Document6 pagesAnalytical Alaa Omar + 2024M.AhmedNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrate Lect - OkkkkkDocument51 pagesCarbohydrate Lect - OkkkkkM.AhmedNo ratings yet
- Ethology LecturesDocument33 pagesEthology LecturesM.AhmedNo ratings yet
- Nervous Sys Except Reflex ArcDocument23 pagesNervous Sys Except Reflex ArcM.AhmedNo ratings yet
- CamScanner ٠٧-١٢-٢٠٢٣ ١٣.٤٤Document1 pageCamScanner ٠٧-١٢-٢٠٢٣ ١٣.٤٤M.AhmedNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrate Lect - OkkkkkDocument6 pagesCarbohydrate Lect - OkkkkkM.AhmedNo ratings yet
- Ans. Exam 2024Document8 pagesAns. Exam 2024M.AhmedNo ratings yet
- مقرر د عمر الروضي.pdf · Version 1Document68 pagesمقرر د عمر الروضي.pdf · Version 1M.AhmedNo ratings yet
- Molecular Spectroscopy Adel + 2024Document35 pagesMolecular Spectroscopy Adel + 2024M.AhmedNo ratings yet
- Cytology DrawingsDocument52 pagesCytology DrawingsM.AhmedNo ratings yet
- 5- رابعات توضيح للنهائىDocument1 page5- رابعات توضيح للنهائىM.AhmedNo ratings yet
- Sponsor Ship Letter AledMed 2024Document2 pagesSponsor Ship Letter AledMed 2024M.AhmedNo ratings yet
- BehaviorDocument15 pagesBehaviorM.AhmedNo ratings yet
- Endo جزء الميدDocument29 pagesEndo جزء الميدM.AhmedNo ratings yet
- 1-Principles of Probability Ended222Document31 pages1-Principles of Probability Ended222M.AhmedNo ratings yet
- 13 1 2024محمد طاهرDocument1 page13 1 2024محمد طاهرM.AhmedNo ratings yet
- MusclesDocument8 pagesMusclesM.AhmedNo ratings yet
- 3-Method of CountDocument8 pages3-Method of CountM.AhmedNo ratings yet
- 2 - Random Variable222222222Document45 pages2 - Random Variable222222222M.AhmedNo ratings yet
- 5 - Test of HypothesisDocument34 pages5 - Test of HypothesisM.AhmedNo ratings yet