Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lamberte, Joshua Paul - Exercise 4
Lamberte, Joshua Paul - Exercise 4
Uploaded by
lambertejoshuapaulOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lamberte, Joshua Paul - Exercise 4
Lamberte, Joshua Paul - Exercise 4
Uploaded by
lambertejoshuapaulCopyright:
Available Formats
Department of Agronomy
College of Agriculture and Science
Visayas State University
Visca, Baybay City, Leyte
Name: Joshua Paul G. Lamberte Course Number: Agro21
Laboratory Instructor: Ms. Lovely Vasquez Paderes Offering Number: C234
Exercise No.4
“Cultural Management Practices in Field Crop Production”
Introduction:
In crop production there are practices or management need to adopt to make the crop
grow favorable to their growth and development. It includes the techniques which can utilize
by the farmers to maximize the crop productivity. It is important to understand the cultural
management as well as its type. Cultural management are the activities or operations
performed by a farmer in the field before, during and after crops have been planted. Including
the decision on the crops to be grown, time, manner of planting, crop sanitation and tillage,
fertilizer application, irrigation up to the harvesting time. In this activity we will find out the
different method or cultural management practices applied to their crop production from land
preparation to harvesting.
Objective:
1. Acquaint yourself with the different cultural practices employed by the farmer on a
specific crop and the reasons(s) for using them.
Methodology:
In this exercise using the materials provided such as ballpen, paper and also cellphone
for documentation, I had visited 2 Farmers in our locality, one is growing a rice and the other
is growing a peanut. As I approached to them, I asked several question regarding to the
cultural management practices applied to their crop production from land preparation to
harvesting. All the gathered information was tabulated. (See table 1)
Results and Discussion
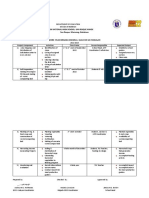
Table 1. Cultural Management Practices in field crop Production.
Cultural How Is It When Is It Why Is It
Farmer Crop
Management Done? Done? Done?
To determine
the suitable
18 kilos hybrid
quality seeds
SEED seeds provided Before land
to be utilized
SELECTION by Department preparation
in the crop
of Agriculture.
production
process.
To improve
soil
By
granulation
Discing
and to have a
uniform soil.
LAND
DATCHE RICE To pulverize
FULACHE Oryza sativa PREPARATION
Month of soil and to
By APRIL break crop
and
harrowing residues and
(1-month to uproot
SEED BED
Preparation) weeds.
MAKING
By To level the
leveling soil
SEED Expose to the To determine
After land
preparation
sun
(Expose for
2hrs) unwanted
seeds.
24 hours
after
Soak in water
exposing
under the sun
When it is
already
drained.
Sacking /
(16 hours
packing
PREPARATION inside the
sack/
cellophane)
For easy
After 16 germination
hours of seeds
Soak again in
Soak for
water
about 24
hours
2-3 days
Final sacking
Before
/ packing
planting
Use complete
fertilizer and To improve
After 15
other fertilizer and maintain
days after
contain with the nutrient
FERTILIZER planting
sulphate. content in the
APPLICATION
soil needed
After 45 for the crop
Top dressing days after production.
planting
PEST No specific To keep away
Bait traps
CONTROL date from any
Apply
rodenticides
(when the attacking pest
pest and that can harm
Apply rodents the crop.
Pesticides attack)
Cultural How Is It When Is It Why Is It
Farmer Crop
Management Done? Done? Done?
To break any
Between the
crusted soil.
SEED BED / month of
By
LAND May & June
Tilling Easy
PREPARATION (summer
controlling
time)
the weeds.
To attain the
desired plant
To leave 16
1 week after population
THINNING plants per
sowing and minimize
linear meter
competition
among plants.
Before the
RAYMOND MUNGBEAN branch To know the
IJOLEN Vigna radiata (L.)
FERTILIZER By develop. appropriate
APPLICATION Soil testing. (Early fertilizer to
Growth apply.
stage)
Proper Early
storing and germination
To keep away
PEST applying period.
from any
CONTROL some non-
attacking pest.
toxic Storing
chemical period.
The table shows that the cultural management employed by the farmers are mostly
similar but only differ in ways or process of doing it.
Answer to Question:
1. Can you enumerate the different cultural management practices employed by
the farmer before planting?
For cereal production (rice) it was done by Seed Selection, Land
Preparation, Seed Preparation, Fertilizer Application, and pest control.
On the other hand, for Legumes production (mungbean) it was done same to
the cereal but differ in methods or process.
2. Can you give reason why they are doing this?
The reason why they are doing this in order for their crop grow a favorable
and a good crop productivity. And also, the consumer will love and be
satisfied to their product.
3. Do cultural management practices employed to corn or rice production differ
from the mungbean or peanut or any legumes?
Not so, actually they are the same, they only differ in the process of land
preparation and fertilizer application.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, there are a lot of cultural management we can do to have a good and
favorable growth development of our crop. Most of them are similar practices whatever crop
you planted but they only differ is in a way how it was done.
References:
“Agricultural Cultural Practices (meaning of Cultural Practices)” retrieved on
December 8, 2021 from https://classnotes.com.ng.
Documentation:
A. Mr. Datche Fulache (Rice Production)
B. Mr. Raymond Ijolen (Mungbean Production)
You might also like
- Answer To Previous Board Exam QuestionsDocument595 pagesAnswer To Previous Board Exam QuestionsPhebe Villaganas100% (12)
- Farmers Friendly Handbook PDFDocument106 pagesFarmers Friendly Handbook PDFRameshNo ratings yet
- Exercise 4Document6 pagesExercise 4lambertejoshuapaulNo ratings yet
- CpSc21 LaboratoryExerciseNo.2 Dautil C255Document6 pagesCpSc21 LaboratoryExerciseNo.2 Dautil C255Jastine Managbanag DautilNo ratings yet
- Wa0009.Document14 pagesWa0009.Pradeep SinghNo ratings yet
- Null 2Document3 pagesNull 2Obakeng TlouNo ratings yet
- PISTAKASAN 2020 - Action PlanDocument1 pagePISTAKASAN 2020 - Action Plannhel gutierrezNo ratings yet
- Ch-1 Crops Production and ManagementDocument7 pagesCh-1 Crops Production and ManagementAryan RoyNo ratings yet
- NCERT Solution For Crop Production and Management: Kharif CropsDocument8 pagesNCERT Solution For Crop Production and Management: Kharif CropsRam Prasad BismilNo ratings yet
- Agronomy Organic CompostDocument2 pagesAgronomy Organic Compostpfdc GuwahatiNo ratings yet
- Chap7 Agriculture PDFDocument19 pagesChap7 Agriculture PDFFortnite with hadi7qNo ratings yet
- PoP (Organic) 2021Document58 pagesPoP (Organic) 2021PritomDuttaNo ratings yet
- Upland Rice Cultivation Guide: AromaDocument5 pagesUpland Rice Cultivation Guide: AromaMA DapNo ratings yet
- 62 85Document3 pages62 85Dana PerdanaNo ratings yet
- Gossypium: From The Pathological of The Bureau of Animal Industry, United States Department of AgricultureDocument30 pagesGossypium: From The Pathological of The Bureau of Animal Industry, United States Department of AgricultureAlexNo ratings yet
- Review in Allied Subjects Crop Science (Agronomy)Document18 pagesReview in Allied Subjects Crop Science (Agronomy)Jordan YapNo ratings yet
- Gulayan Sa Paaralan Accomplishment ReportDocument3 pagesGulayan Sa Paaralan Accomplishment ReportRomar Santos100% (1)
- Ntse 9Document9 pagesNtse 9MUZEER PASHANo ratings yet
- 2022 Gulayan Work PlanDocument2 pages2022 Gulayan Work PlanLove MaribaoNo ratings yet
- Planting DistanceDocument4 pagesPlanting DistanceJONATHAN CACAYURINNo ratings yet
- Soil Fertility ManagementDocument5 pagesSoil Fertility Managementmauricio calderonNo ratings yet
- PQH SPDocument4 pagesPQH SPmishellNo ratings yet
- Tle AgricultureDocument32 pagesTle Agriculturehazel ann lazaro100% (1)
- Promotional-Booklet 035024Document12 pagesPromotional-Booklet 035024Raselle NicolasNo ratings yet
- A Review of Iron-Coating Technology To Stabilize RDocument12 pagesA Review of Iron-Coating Technology To Stabilize RkkkNo ratings yet
- ECHO Development Notes: New Uses of Moringa Studied in NicaraguaDocument8 pagesECHO Development Notes: New Uses of Moringa Studied in Nicaraguantv2000No ratings yet
- Frappe Customization Problem StatementDocument3 pagesFrappe Customization Problem Statementganesh.cerpdataNo ratings yet
- Effect of Seed Priming On Seed Germination and Seedling Growth of Modern Rice (Oryza Sativa L.) VarietiesDocument10 pagesEffect of Seed Priming On Seed Germination and Seedling Growth of Modern Rice (Oryza Sativa L.) VarietiesLaurence MagistradoNo ratings yet
- Pengaruh Kompos Tandan Kosong Kelapa SawDocument15 pagesPengaruh Kompos Tandan Kosong Kelapa Sawjaka djNo ratings yet
- David Karran CPDocument13 pagesDavid Karran CPnilNo ratings yet
- Agro - PK Post - New - Vol 68 APR 2023 - D 006 FINAL - PDFDocument4 pagesAgro - PK Post - New - Vol 68 APR 2023 - D 006 FINAL - PDFAtman PatelNo ratings yet
- Pengaruh Alelopati Padi Terhadap Pertumbuhan Dan Hasil Kedelai Pada Sistem Tanam Berurutan Padi-KedelaiDocument9 pagesPengaruh Alelopati Padi Terhadap Pertumbuhan Dan Hasil Kedelai Pada Sistem Tanam Berurutan Padi-KedelaiFiqihNo ratings yet
- Exp SC 8 - Chapter 01Document18 pagesExp SC 8 - Chapter 01megamind publicationNo ratings yet
- Green Manures PDFDocument13 pagesGreen Manures PDFSUBRAMANIAM CNo ratings yet
- ArticleDocument7 pagesArticleM. Riyo Rizki RidwanNo ratings yet
- Ess Bee AyeDocument18 pagesEss Bee AyeMalikiNo ratings yet
- ICAR Stressed On Climate Resilient Cropping System - FinalDocument6 pagesICAR Stressed On Climate Resilient Cropping System - Finalbeeram.indNo ratings yet
- Annamalai University Faculty of Agriculture Department of Agronomy Rawe Agr 411 Agronomy Interventions (0+3) Rawe Program - 2021Document25 pagesAnnamalai University Faculty of Agriculture Department of Agronomy Rawe Agr 411 Agronomy Interventions (0+3) Rawe Program - 2021Kish oreNo ratings yet
- Crop Production and Management-Exercises PDFDocument3 pagesCrop Production and Management-Exercises PDFShrey DNo ratings yet
- Pechay Production For Urban Gardening LeafletDocument2 pagesPechay Production For Urban Gardening LeafletCharles Joseph MaldiaNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Potting Media For The Production of Rough Lemon Nursery StockDocument8 pagesEvaluation of Potting Media For The Production of Rough Lemon Nursery StockVansala GanesanNo ratings yet
- 109am - 5.EPRA JOURNALS-5089Document8 pages109am - 5.EPRA JOURNALS-5089meriam.nool002No ratings yet
- Guide Technique Pour La Production de Plants en PepiniereDocument108 pagesGuide Technique Pour La Production de Plants en PepiniereNicolas Wilson Mandyer PIERRENo ratings yet
- Topics To Be Covered AFO-2019Document5 pagesTopics To Be Covered AFO-2019deepakNo ratings yet
- 9 Basic Steps Towards A Bountiful Corn HarvestDocument2 pages9 Basic Steps Towards A Bountiful Corn HarvestMay an CarbonelNo ratings yet
- Blackberry Production in The Home GardenDocument3 pagesBlackberry Production in The Home GardenrapipenNo ratings yet
- Complete Agriculture For Prelims 2024 - IAS PCS PathshalaDocument11 pagesComplete Agriculture For Prelims 2024 - IAS PCS PathshalaHarshrajeNo ratings yet
- Agriculture Best Handwritten Notes Padhai Ak Mazza 2024Document7 pagesAgriculture Best Handwritten Notes Padhai Ak Mazza 2024keshavkrishna20007100% (1)
- Abm CornDocument5 pagesAbm CornJohnmark OtacanNo ratings yet
- Administration of Azolla Compost Fertilizer On The Growth of Cocoa Seeds (Theobroma Cacao L) With Different DosagesDocument4 pagesAdministration of Azolla Compost Fertilizer On The Growth of Cocoa Seeds (Theobroma Cacao L) With Different DosagesInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Agricultural Science Kimberly CornwallDocument50 pagesAgricultural Science Kimberly CornwallkimberlycornwallNo ratings yet
- Production Manual of Carrots (Daucus Carota L.)Document2 pagesProduction Manual of Carrots (Daucus Carota L.)Mwala100% (1)
- No-Till Case Study, Bauer Farm: Cover Crop Cocktails On Former CRP LandDocument8 pagesNo-Till Case Study, Bauer Farm: Cover Crop Cocktails On Former CRP LandGlen YNo ratings yet
- Malting Barley StoryDocument8 pagesMalting Barley StoryeduenglerNo ratings yet
- Effect of Four Different Tillage Practices On Maize Performance UnderDocument6 pagesEffect of Four Different Tillage Practices On Maize Performance UnderAspirant MNo ratings yet
- Feasibility Study of Mat-Type Paddy SeedlingsDocument6 pagesFeasibility Study of Mat-Type Paddy SeedlingsSapuniiNo ratings yet
- Aditya Dixit2223bag16gt002 Module 2 Org..Document18 pagesAditya Dixit2223bag16gt002 Module 2 Org..DADADADGGGNo ratings yet
- Devbio Rania1Document3 pagesDevbio Rania1KAREN GRACE VILLAMONNo ratings yet
- Intercropping Cereals and Grain Legumes - A Farmers PerspectiveDocument2 pagesIntercropping Cereals and Grain Legumes - A Farmers PerspectivesedianpoNo ratings yet
- Soil PreparationFrom EverandSoil PreparationNo ratings yet
- Crop Production and Soil Management Techniques for the TropicsFrom EverandCrop Production and Soil Management Techniques for the TropicsNo ratings yet
- Heat Stress and Marijuana PlantsDocument12 pagesHeat Stress and Marijuana PlantsGeorge PotoleaNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 - (Tainos) The Indigenous People of The AmericasDocument23 pagesGrade 9 - (Tainos) The Indigenous People of The Americasjohn greenNo ratings yet
- The Middle AgesDocument38 pagesThe Middle Agesapi-40256386No ratings yet
- Pawankar KN, Samanta R, Ghosh N, Bera S, Channa GR and Ramteke SSDocument6 pagesPawankar KN, Samanta R, Ghosh N, Bera S, Channa GR and Ramteke SSKarnsai PawankarNo ratings yet
- Green Investments Required in The Forest Products Industry in NigeriaDocument14 pagesGreen Investments Required in The Forest Products Industry in NigeriaAlexander DeckerNo ratings yet
- Swedish-English Vocabulary PDFDocument18 pagesSwedish-English Vocabulary PDFArthur von ArthurNo ratings yet
- The Livestock Production & ManagementDocument237 pagesThe Livestock Production & ManagementtrukuniNo ratings yet
- CSP's Strategy 2010 - 2014:: Building Synergy For Sustainable Cocoa IndustryDocument31 pagesCSP's Strategy 2010 - 2014:: Building Synergy For Sustainable Cocoa IndustryDewi Dwi Puspitasari Sutejo100% (1)
- Supply Chain Management of Food Grains in South TamilnaduDocument37 pagesSupply Chain Management of Food Grains in South TamilnaduSreejith NairNo ratings yet
- Integrated Strategy On Fundamental Principles and Rights at Work 2017-2023Document24 pagesIntegrated Strategy On Fundamental Principles and Rights at Work 2017-2023MohdshariqNo ratings yet
- Cupressus Lusitanica: Managing PlantationDocument29 pagesCupressus Lusitanica: Managing PlantationZelalem TadeleNo ratings yet
- Recent Analysis of Sewage Treatment Plan (STP) Using Blue-Green AlgaeDocument10 pagesRecent Analysis of Sewage Treatment Plan (STP) Using Blue-Green AlgaeIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- University of Caloocan City - : An Analysis Paper OnDocument9 pagesUniversity of Caloocan City - : An Analysis Paper OnKylieNo ratings yet
- Botkins Environmental Science Notes Chapter 8-16Document16 pagesBotkins Environmental Science Notes Chapter 8-16Ella CardenasNo ratings yet
- PotatoDocument145 pagesPotatoOmprakash Kumar Singh100% (1)
- "Alfalfa: The Thirstiest Crop" - Natural Defenses Resource CouncilDocument5 pages"Alfalfa: The Thirstiest Crop" - Natural Defenses Resource CouncildocdumpsterNo ratings yet
- B.ed 4th Semester SyllabusDocument14 pagesB.ed 4th Semester Syllabusnawanisimran961No ratings yet
- Vocabulary List - Extreme VersionDocument24 pagesVocabulary List - Extreme Versionthuy94575No ratings yet
- Allocation of Business RulesDocument181 pagesAllocation of Business RulesJassi SinghNo ratings yet
- Poster SwamiDocument1 pagePoster SwamiShaik MunnaNo ratings yet
- ATO Industry ClassificationDocument47 pagesATO Industry ClassificationCraig ThomlerNo ratings yet
- Evolution of Dentition in Cattle LifeDocument7 pagesEvolution of Dentition in Cattle LifeDragos MisteryoNo ratings yet
- Mango Farming HandbookDocument37 pagesMango Farming HandbookMiminimtu100% (1)
- KPI Dictionary Vol2 PreviewDocument12 pagesKPI Dictionary Vol2 PreviewJahja Aja100% (1)
- 03b-Factors Affecting Duty & Its ImprovementDocument19 pages03b-Factors Affecting Duty & Its Improvementinam ullahNo ratings yet
- MACHINES TESTED August, 2022Document2 pagesMACHINES TESTED August, 2022Anurag SharmaNo ratings yet
- Review of Session 2007-2008Document417 pagesReview of Session 2007-2008The Royal Society of EdinburghNo ratings yet
- Assignment IIDocument6 pagesAssignment IIjosNo ratings yet