Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Amoeba Part 2 Notes
Amoeba Part 2 Notes
Uploaded by
jefftuazon010 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views8 pagesThis document discusses the pathogenic amoeba Entamoeba histolytica, which causes amoebiasis in humans. It has 5 stages in its life cycle: 1) cyst, 2) metacyst, 3) trophozoite, 4) precyst, and 5) cyst. The invasive trophozoite stage can invade tissues in the stomach and intestines, where it feeds. Mature cysts contain 4 nuclei and no cytoplasmic inclusions, making them resistant to the harsh stomach environment. There are 2 sizes of E. histolytica strains: large (>10 micrometers) and generally virulent, and small (5-10 micrometers) that are commensal and non-path
Original Description:
Amoeba Part 2 Notes
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses the pathogenic amoeba Entamoeba histolytica, which causes amoebiasis in humans. It has 5 stages in its life cycle: 1) cyst, 2) metacyst, 3) trophozoite, 4) precyst, and 5) cyst. The invasive trophozoite stage can invade tissues in the stomach and intestines, where it feeds. Mature cysts contain 4 nuclei and no cytoplasmic inclusions, making them resistant to the harsh stomach environment. There are 2 sizes of E. histolytica strains: large (>10 micrometers) and generally virulent, and small (5-10 micrometers) that are commensal and non-path
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views8 pagesAmoeba Part 2 Notes
Amoeba Part 2 Notes
Uploaded by
jefftuazon01This document discusses the pathogenic amoeba Entamoeba histolytica, which causes amoebiasis in humans. It has 5 stages in its life cycle: 1) cyst, 2) metacyst, 3) trophozoite, 4) precyst, and 5) cyst. The invasive trophozoite stage can invade tissues in the stomach and intestines, where it feeds. Mature cysts contain 4 nuclei and no cytoplasmic inclusions, making them resistant to the harsh stomach environment. There are 2 sizes of E. histolytica strains: large (>10 micrometers) and generally virulent, and small (5-10 micrometers) that are commensal and non-path
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 8
Amoeba Part 2 3.
Metacystic trophozoite/ like/broadly rounded pseudopodal
amoebulae extensions of the ectoplasm
Pathogenic Amoeba
4. Trophozoite o Shares motility of E.
- E. histolytica 5. Precyst gingivalis, but differ in
direction where the E.
Trophozoite
histolytica can go anywhere
E. histolytica - Invasive, growing, feeding stage of since it is unidirectional
the parasite o Direction changes rapidly in
- Tissue invading amoeba
- Invasive means the parasite is capable response to conditions of their
- Pathogenic amoeba of man
of invading tissues inside the stomach microclimate
Clinical manifestations - Invades the tissues wherein it will try - Cytoplasm is described as having a
to feed there ground glass appearance and is
- Amoebiasis
o Parasites are commensal; they differentiated into a clearer outer
- Amoebic dysentery
need a host to survive and feed ectoplasm and inner, finely granular
- Amoebic hepatitis (liver abscess)
off the host endoplasm in which food vacuoles
Synonyms - I&H Stain of containing ingested RBCs may be
Histolytica observed
- Amoeba coli o Same with E. coli except
trophozoite
- Amoeba dysenteriae different cytoplasm
- Entamoeba dysenteriae appearance, where E.
- Entamoeba tetragena histolytica has ground glass
- Entamoeba dispar appearance while E. coli is
- Endamoeba histolytica I. Living Trophozoite honeycomb shaped (dirty
- Endamoeba dysenteriae looking full of vacuoles of
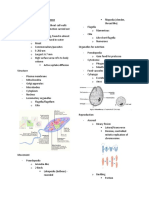
General Characteristics & Structure
Geographic Distribution ingested bacteria, not RBCs)
- Size: 10-60 micrometer in diameter - Nucleus can be occasionally seen in
- Same as non-pathogenic amoeba - Motility: Exhibits remarkable the center of the endoplasm
- Worldwide with high incidence in the locomotion which can be observed in - (I&H Preparation): Nucleus is
tropics and subtropics freshly passed dysenteric or diarrheic spherical; contains a small distinct
stools dotlike central karyosome surrounded
Morphology, Biology, Life Cycle
o Only the trophozoite stage is by an unstained halo and anchored by
- 5 Stages similar to E. coli motile numerous delicate, radiating
1. Cyst - Movement: Progressive achromatic fibrils to the inner surface
2. Metacyst unidirectional movement resulting of the nuclear membrane
from long, fingerlike/tongue-
Property of J. Tuazon © 2021
o The achromatic fibrils give is now able to penetrate the small B. Young Cyst
the nucleus the appearance of intestine.
- 1-2 nuclei
a spokes of a wheel or bull’s
A. Mature Cyst - Glycogen mass with hazy margins
eye
- Chromatoidal bodies, which are long
- 4 nuclei with centrally located
or short rods with rounded ends (cigar
karyosome, rarely 8 nuclei
or sausage-shaped) under the
o Characteristic of E. histolytica
microscope in a freshly-prepared
to have centrally located
slide
karyosome
II. Cyst - No cytoplasmic inclusions, making it
clear in appearance
General Characteristics & Structures - Nuclear structure: can be
uninucleated or quadrinucleated
o Uninucleated: contains
chromatid body and a large
glycogen mass/glycogen
vacuole
o Quadrinucleated: mature
cysts present only in the gut Recent evidence shows that there are 2
lumen, they NEVER invade significantly different sizes for strains:
the intestinal wall.
▪ Only the trophozoite 1. Large race
stage is invasive stage - Average cyst diameter is > 10
- Size: 10-20 micrometer, (average of micrometer
12-13 micrometer) - Generally virulent
- Spherical, may be subspherical or 2. Small race
ovoidal - Cyst
- Covered with smooth chitinous layer, o Size: 5-10 micrometer
making itself resistant to gastric acid o Commensal, non-pathogenic,
and other adverse conditions do not normally invade tissues
- Location of Cyst: inside the stomach; o Considered as a separate
with the chitinous layer, this parasite species: E. hartmanni
is capable of surviving the harsh o Life cycle, general
environment inside the stomach, and morphology, and overall
appearance are almost
Property of J. Tuazon © 2021
identical to E. histolytica, with linked Immunosorbent Assay cyst of E. histolytica. Later on, it will pass
the exception of size (closely (ELISA), and Isoeznyme analysis (or through the small intestine.
resembles E. nana) research techniques)
In the small intestine, the quadrinucleated
- Immature cyst
cyst will now be hydrolyzed by the enzyme
o Contains glycogen mass
trypsin inside the small intestine, dissolving
o Several to numerous
the chitinous layer/wall of the cyst. This
chromatoidals that are short
dissolution of the wall releases the
with tapered ends (rice grain-
quadrinucleated trophozoites.
shaped) or thin and bar-like E. histolytica Life Cycle
structure The quadrinucleated trophozoites will further
- Trophozoite divide into 8 metacystic trophozoites and will
o Size: 12-15 micrometer propagate in the small intestine environment.
o Do not ingest RBC Once they mature in the small intestine, they
o Motility is less vigorous will now pass through the colon.
(more sluggish) than E.
histolytica Multiplication
Metacystic trophozoites are carried by
peristaltic movements to the ileo-cecal region
Various reports indicate that there are 2 and divide by binary fission.
strains of E. histolytica differing in
pathogenicity There, they colonize the mucosal surfaces
and crypts of the large intestine.
E. histolytica has now been divided into 2
Encystation
species, the first species E. histolytica, the
other one being the noninvasive E. dispar Infective stage: Quadrinucleated mature cyst Encystation occurs in the small intestine and
- Although E. dispar is noninvasive, it of E. histolytica. is where the metacystic trophozoites are
is evidently capable of producing formed.
Ingestion
intestinal lesions in experimental Encystation occurs when there is food
animals (E. dispar is pathogenic in The first part of the life cycle is humans get
deprivation, crowding, desiccation, and
zoonotic cases so far) infected by the ingestion of quadrinucleated
accumulation of waste products.
cyst from the contaminated food and water.
Differentiation of the 2 species is not possible Later on will exit the excreta and get mixed
by light microscopy This mature cyst reaches the stomach once
with the food and water then the life cycle
ingested, and there, they resist the gastric acid
goes on.
- Only differentiated by Polymerase because of the chitinous wall of the mature
Chain Reaction (PCR), Enzyme-
Property of J. Tuazon © 2021
Contamination of food and water is only cockroaches and remain - May remain localized in the colon
possible when there is no proper sanitation. viable in feces and vomitus (where they colonize, feed, and grow)
When the community doesn’t have comfort for 48 hours and multiply in the crypts
rooms with septic tanks, E. histolytica will o Note: Filth flies (Musca - Attachment is mediated by an
most likely propagate. domestica) and cockroaches amoebal galactose or N-acetyl-d-
are important mechanical galactosamine adherence lectins
vectors of cysts. Their sticky, (Gal/GalNac lectin)
bristly appendages can easily - Inside the intestine, the parasites
carry cysts from fresh stool to ingest foodstuffs such as starch
Habitat the dinner table; their habit of granules (rice) that most humans are
- Cecum; make contact with mucosa or vomiting and defecating while eating
become lodged in the glandular crypts feeding is an important means - Probably utilize mucous secretions as
of transmission food
Modes of Transmission ▪ Even a second or - Metabolize anaerobically with certain
- Ingestion of food and drinks millisecond when the enteric bacteria, since they do not
contaminated with feces containing fly touches the food need O2 but more CO2
the quadrinucleated cysts (infective renders the entire food - Invasion of tissue
stage) contaminated with the
- Polluted water supply: cysts may parasite
remain viable in: - Use of human excreta in vegetable
o Damp soil = at least 8 days gardens
o In other moist cool conditions - Gross carelessness in personal
= for over 12 days hygiene in children’s asylums, mental
o Water (normal temperature) = hospitals, prisons, and other places
9-30 days - Sexually transmitted disease
o Water at 4 degrees Celsius = 3 - Human carriers or cyst passers
months
- Unclean handling of infected
individuals (hands, clothing, fomites) Pathogenicity
o Fomites like flies may carry E. When E. histolytica is capable of invading o Initiated when the trophozoite
histolytica and land on your is able to penetrate the mucus
tissue, it is now called Intestinal Amebiasis
food layer covering the colonic
- Droppings of flies and other insects - In the intestines epithelium
o Cysts are unchanged in the o Facilitated by the expression
intestine of flies and of virulence factors which
Property of J. Tuazon © 2021
have been extensively studied ▪The invasive form of false negative result may
and characterized up to the E. histolytica is the appear, so fixate the sample as
molecular level. These are: trophozoite, so it will needed
▪ Gal/GalNac lectin; not encyst or form o Wet mounts using Normal
▪ Amebapores; and back to cyst form Saline Solution (NSS)
▪ Cysteine proteinases o May affect other organs such o Preserve parasites if one
o They no longer depend on as the liver, brain, lungs, cannot examine directly or
bacteria but obtain their spleen immediately
nourishment through the ▪ Fix with MIF
absorption of dissolved (Merthiolate Iodine
tissue juices Diagnosis Formaldehyde
▪ They lyse mucosal fixative); or
1. Intestinal Amebiasis
cells by secreting ▪ PVA (Polyvinyl
lysosomal enzymes - Stool Examination (S/E) by direct Alcohol); or
forming flask-shaped smears and stained mounts ▪ Schaudinn’s fixative
ulcers (teardrop- o 3 or more specimens at 3- or for permanent staining
shaped) and 4-day intervals give more
Note: in lab practice, fixating stool samples
trophozoites are found positive (+) results than are uncommon because the fixatives are
in the wall of the examination of stool by expensive, and stool examinations cost only
abscess successive days because of the P90-P250, so it is recommended to examine
▪ Primary ulcers are random irregularity in the stool samples immediately after collection
found in the cecum, excretion of cyst and no longer fixate the specimen.
appendix, or - In diarrheic/dysenteric/watery stool,
adjacent portion of trophozoites are the parasite stage - In solid/formed stool, only cysts are
the ascending colon only seen, accompanied by blood and the parasite stage seen (usually seen
▪ Ulceration of the mucus in carriers or chronic patients,
intestinal wall may o Scrape a small portion of the amebiasis is worse)
give rise to amoebic sample where the blood and o Any part of the feces can be
dysentery mucus is located since that is scraped but should include a
o Encystation does not occur in where the cyst is most likely portion or any fleck of
the tissue or outside the located mucous adherent to feces or
intestinal lumen, therefore, o Should be examined as soon blood, get a sample where
specimens taken outside the as possibly preferably within there is mucous or blood like
lumen will contain the 30 minutes after voiding; if in formed stool
trophozoite stage only examined after 30 minutes a
Property of J. Tuazon © 2021
o Wet mounts using Normal o May be expressed from ulcers • Uncommon
Saline Solution (NSS) or by means of gentle pressure technique
Iodine Preparation (I2) from long-handled curette or - Culture
o If cysts are too few to be seen, loop o Commonly conducted in
do concentration technique o Obtaining specimens from the microbiology
(zinc sulfate [ZnSO4] tissues o Used in the study of its
centrifugal flotation method, o 1/3 of lesions are in the metabolism and
Formalin Ether Concentration sigmoidorectal area pathogenicity, and in the
Test [FECT] and the ▪ Insert instrument in production of antigens for
Merthiolate Iodine Formalin the anus serodiagnosis
Concentration [MIFC] Test) o Look for typical lesions (or o Trophozoite or cyst from
- Saline-purged specimens samad or lu-as) feces, material aspirated by
o Will provide material for o Scrapings or aspirates from sigmoidoscopy
positive (+) diagnosis when suspected sites of amebic ▪ After conducting
routine fecal examination has ulceration may be obtained or sigmoidoscopy,
been unrewarding/yield no punch biopsies secured conduct culture
result ▪ If previous test fails, immediately
o Sodium sulfate (Na2SO4 or aspiration can be used - Culture medium
Glauber salts) or phosphosoda ▪ Aspirated material o Dibasic medium of Boeck and
is preferred ingredient for this should be examined Drbohlav (egg slant base with
test microscopically for isotonic overlay = LES-Locke
o Following saline purgation, motile trophozoites egg serum)
earlier fecal evacuations are immediately (using o Diamond’s medium or TYI-
discarded. Sedimented Normal Saline S-33
elements of mucus and tissue Solution suspension) ▪ May reveal the
cells from the 2nd or 3rd bowel ▪ Punch biopsy – more presence of E.
movements are pipetted onto satisfactory to fix, histolytica when
the slide, placed in a cover section, and stain microscopic
slip, and examined for specimen before examination has
trophozoites (a complex attempting to examine failed, but they should
procedure, but this test is only it NEVER be used as a
conducted if the fecal exam • Conduct if S/E substitute for
has failed). and/or microscopic
- Sigmoidoscopy material aspiration fails examination
Property of J. Tuazon © 2021
▪ This type of test is or degenerated liver Note: Most common serologic tests
more expensive cells, RBC, occasional performed for amebiasis
compared to S/E and leukocytes are found
TAT for this test is ▪ Trophozoite recovered
around 3 days for in about 1/3 of cases, Table 1: Amebic vs Bacillary Dysentery
culture purposes best obtained from the
wall of the abscess
2. Hepatic amoebiasis and other
- X-Ray
extraintestinal lesions
o Cannot diagnose or identify a
- Results when trophozoites enter the particular amoeba
mesenteric venules and travel to the o Exhibit the extent of the
liver through the hepato-port system. damage in the colon, or small
This is where the amoeba is spreading intestine, or liver (if the
to the different parts of the body. The infection is systemic)
center of the abscess is filled with - Seroimmunologic tests
necrotic fluid, a median zone o When direct microscopic
consisting of liver stroma and the examination fails to reveal the
outer zone consisting of liver tissue presence of E. histolytica –
being attacked by amoebae, Antibody or Antigen
although it is bacterially sterile. detection
- Determine or establish the presence o Indirect hemagglutination test
of intestinal amoebiasis (IHAT)
o Clinical manifestations ▪ Detect Antibodies of Free-living Amoebae
include increased WBC and past infection
liver function test (elevated ▪ Not very useful since Free-living: because they don’t need a host in
BSP and ALP results) it only detects past order for them to survive or live.
o Aspiration of abscess – punch infection Taxonomical Classification
or needle biopsy, similar to o Agar gel Diffusion (AGD)
sigmoidoscopy o Counter-current Order: Schizopyrenida
▪ Characteristic Immunoelectrophoresis (CIE) Family: Valkamphidae
chocolate colored o Enzyme-linked
(anchovy sauce) Immunosorbent Assay Genus: Naegleria
content of abscess (ELISA)
▪ Mixture of sloughed o Indirect Fluorescent Antibody
liver tissue and blood Test (IFAT) Naegleria fowleri = Naegleria aerobia
Property of J. Tuazon © 2021
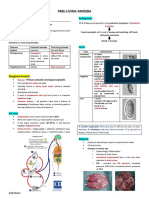
- Cause of Primary Amebic - Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) differentiated ectoplasm and a granular
Meningoencephalitis (PAM) and Enzyme-linked endoplasm.
- Amoebae proliferate rapidly in water Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) are
as temperature rises now used as specific N. fowleri tests
Parts of N. fowleri
1. Amoeboid Locally occurring species has been named
- Elongate with a broad anterior and Naegleria philippinensis
tapered posterior end
- Usually has a lobose
monopseudopodium Life Cycle of Naegleria fowleri
2. Flagellate
- 2 long flagella at the tip of a pear-
shaped body
o Amoeba to flagellate
transformation can take place
within a period of 2-3 hours or
up to 3-4 days
3. Nucleus
- Very prominent with a large centrally It starts with the penetration of the holes of
located karyosome the human (nose, ears, mouth, eyes).
o Might be confused with E.
histolytica The uninucleated cyst will pass through any
4. Conspicuous contractile vacuoles of the facial holes and will form several
5. Food vacuoles trophozoites, and these trophozoites are able
- Contain bacteria when free-living to multiply by binary fission, then several
- Host cell debris when parasitic trophozoites are produced and produce
6. Uninucleated cyst flagella to become motile, then excystation
- The free-living amoeba cyst form of occurs.
this parasite is uninucleated The pictures at the left side are the
uninucleated cyst, and the pictures at the right
side are the trophozoite form.
Diagnosis
In the stained picture (top right), the
trophozoite form of N. fowleri has a well-
Property of J. Tuazon © 2021
You might also like
- Tureks Orthopaedics - Principles and Their ApplicDocument1 pageTureks Orthopaedics - Principles and Their Applicqu402113No ratings yet
- ParasitologyDocument18 pagesParasitologyLudwig359100% (2)
- 2 Parasitology Parasitic AmoebasDocument8 pages2 Parasitology Parasitic AmoebasknkjnNo ratings yet
- Enperiment For Spotting-3Document18 pagesEnperiment For Spotting-3Debayan Bhattacharyya class:- 11-ANo ratings yet
- Supplemental Readings On ProtozoansDocument18 pagesSupplemental Readings On Protozoansferrerjericho300No ratings yet
- PARASITOLOGY (Quizlet)Document9 pagesPARASITOLOGY (Quizlet)Allyssa AniNo ratings yet
- Amoeba PrefinalsDocument5 pagesAmoeba PrefinalsKervy Jay AgraviadorNo ratings yet
- Para - Amoeba TabulatedDocument1 pagePara - Amoeba TabulatedKaoriMarieSembranoNo ratings yet
- AMOEBADocument11 pagesAMOEBAMicaella RemilloNo ratings yet
- Amoeba paraDocument9 pagesAmoeba paraHANNA CASANDRA GARCIANo ratings yet
- AMOEBADocument74 pagesAMOEBAhuyenthanh1807No ratings yet
- Free-Living Amoeba: General CharacteristicsDocument3 pagesFree-Living Amoeba: General CharacteristicsIrvin SamaniegoNo ratings yet
- Amoeba: Cytoplasm (Both in Cyst and Peripheral Chromatin (Both Trophozoite Cyst AmoebaDocument1 pageAmoeba: Cytoplasm (Both in Cyst and Peripheral Chromatin (Both Trophozoite Cyst AmoebapasambalyrradjohndarNo ratings yet
- Unit 7 ActivityDocument5 pagesUnit 7 ActivityLeah SembranoNo ratings yet
- Parasitic Amoebas by Dr. C. J. Castro PDFDocument4 pagesParasitic Amoebas by Dr. C. J. Castro PDFMiguel CuevasNo ratings yet
- ParasitologyDocument8 pagesParasitologyNonki VargasNo ratings yet
- Domain Eukarya Kingdom Fungi: Systematics LaboratoryDocument10 pagesDomain Eukarya Kingdom Fungi: Systematics LaboratorySIlverNo ratings yet
- Amoeba Notes 2015Document6 pagesAmoeba Notes 2015Ivy FlorentinoNo ratings yet
- Protista (Subdivision Protozoa) : Bütschlii), or Pathogenic (E. Histolytica)Document6 pagesProtista (Subdivision Protozoa) : Bütschlii), or Pathogenic (E. Histolytica)Primo GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Tabulated Review On AmoebaDocument1 pageTabulated Review On AmoebaKaoriMarieSembranoNo ratings yet
- Trematode SDocument16 pagesTrematode SSheine EspinoNo ratings yet
- Para Lec Lesson2Document9 pagesPara Lec Lesson2Tolentino, Edron E.No ratings yet
- Mindmap Bio320 Chapter 4 Protist ProtozoaDocument1 pageMindmap Bio320 Chapter 4 Protist Protozoanursuraya wahidaNo ratings yet
- XLSXDocument60 pagesXLSXLovely ReyesNo ratings yet
- Kingdoms Shortlisting PDFDocument28 pagesKingdoms Shortlisting PDFNoman KhanNo ratings yet
- Protozoa 1Document21 pagesProtozoa 1CDNo ratings yet
- 1.entamoeba Histolytica - Is The Major Pathogen in This GroupDocument14 pages1.entamoeba Histolytica - Is The Major Pathogen in This GroupJoseph De JoyaNo ratings yet
- 1.3 Hemoflagellates and Ciliates (Limpin)Document4 pages1.3 Hemoflagellates and Ciliates (Limpin)arvinkennethdelacruzNo ratings yet
- Parasitology-Lec 10 EntamoebaDocument7 pagesParasitology-Lec 10 Entamoebaapi-3743217100% (2)
- 2 Protista (15p)Document15 pages2 Protista (15p)Olanrewaju AgodirinNo ratings yet
- ProtozoaDocument28 pagesProtozoaFRANCESCA ALEXANDRIA PAREDESNo ratings yet
- Macabanding m5 Mt2h Subphylumsarcodina FlashcardsDocument56 pagesMacabanding m5 Mt2h Subphylumsarcodina FlashcardsNailah MacabandingNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity Part 2/2Document25 pagesBiodiversity Part 2/2Kim Say Chun / Sc.KIMNo ratings yet
- Amoeba: Ms. Helga SyDocument7 pagesAmoeba: Ms. Helga Syanti romantic txtNo ratings yet
- Disease Causing OrganismsDocument4 pagesDisease Causing OrganismsANKITA GAYENNo ratings yet
- (C-04) The AmoebasDocument24 pages(C-04) The AmoebasNick BatumbakalNo ratings yet
- P1 BSMLS Mycology IntroductionDocument86 pagesP1 BSMLS Mycology IntroductionpammcakeghzNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: Animal-Like ProtozoaDocument1 pageThis Study Resource Was: Animal-Like Protozoaayunna ayunniNo ratings yet
- Medical MycologyDocument10 pagesMedical MycologyNive KojNo ratings yet
- Intro Medical Mycology Part 1Document1 pageIntro Medical Mycology Part 1pammcakeghzNo ratings yet
- Protozoa-RevisionDocument6 pagesProtozoa-RevisionIssam HadiNo ratings yet
- Animalia ChartDocument8 pagesAnimalia CharthkNo ratings yet
- Plus 2 PracticalDocument16 pagesPlus 2 Practicaljayantaroy783360No ratings yet
- 4 - Introduction To FungiDocument54 pages4 - Introduction To FungiMohamed RabihNo ratings yet
- Tabular Parasitology MICROPARADocument19 pagesTabular Parasitology MICROPARAJerlyn FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Free Living AmoebaDocument5 pagesFree Living AmoebaEiveren Mae SutillezaNo ratings yet
- Parasitology (Lect #3) TransDocument6 pagesParasitology (Lect #3) TransSherlyn Giban InditaNo ratings yet
- Zoo 113 Module 3Document35 pagesZoo 113 Module 3Julienne LopezNo ratings yet
- Lower Invertebrates Comparative CharactersDocument5 pagesLower Invertebrates Comparative CharactersShadab HanafiNo ratings yet
- Gurumantra of Zoology Final File)Document65 pagesGurumantra of Zoology Final File)Shivam GuptaNo ratings yet
- 2a - Macabanding, Princess - Mtclinpara Lec - Module 7 AssignmentDocument57 pages2a - Macabanding, Princess - Mtclinpara Lec - Module 7 AssignmentNailah MacabandingNo ratings yet
- (MT 57) PARA - Pathogenic ProtozoaDocument5 pages(MT 57) PARA - Pathogenic ProtozoaLiana JeonNo ratings yet
- Nonpathogenic Amoebae - FlagellatesDocument20 pagesNonpathogenic Amoebae - FlagellatesHend AtijaniNo ratings yet
- protozoaDocument48 pagesprotozoaleoreynon19No ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: What Is Protista ?Document7 pagesThis Study Resource Was: What Is Protista ?ayunna ayunniNo ratings yet
- CnidariaDocument12 pagesCnidariaDave RapaconNo ratings yet
- PROTOZOA (Sarcodina) : ProtozoologyDocument7 pagesPROTOZOA (Sarcodina) : ProtozoologyReyven Niña DyNo ratings yet
- TrematodesDocument20 pagesTrematodesmiguel gaquitNo ratings yet
- 06b79542-41e3-4aaf-919d-66191e64aaa1Document14 pages06b79542-41e3-4aaf-919d-66191e64aaa1drsuryanshtripathiNo ratings yet
- Cestodes: Diphyllobothrium Latum, Broad or FishDocument2 pagesCestodes: Diphyllobothrium Latum, Broad or FishFrance Louie JutizNo ratings yet
- Camp's Zoology by the Numbers: A comprehensive study guide in outline form for advanced biology courses, including AP, IB, DE, and college courses.From EverandCamp's Zoology by the Numbers: A comprehensive study guide in outline form for advanced biology courses, including AP, IB, DE, and college courses.No ratings yet
- Jurnal 6 AgdesDocument21 pagesJurnal 6 AgdesBambang RinandiNo ratings yet
- 2020 Case Report Internasional Short Bowel Sindrom Dan BblserDocument6 pages2020 Case Report Internasional Short Bowel Sindrom Dan Bblserdayu mankNo ratings yet
- This Is A Bio-Attack AlertDocument20 pagesThis Is A Bio-Attack AlertJohn Burns100% (2)
- Test3-Med 1Document6 pagesTest3-Med 1Nguyễn Phước Bảo HưngNo ratings yet
- 3rd Sem SyllabusDocument23 pages3rd Sem SyllabusTopeshwar TpkNo ratings yet
- SANIFECT - High Level DisinfectantDocument3 pagesSANIFECT - High Level DisinfectantHa HoNo ratings yet
- HCDS KK (2023)Document123 pagesHCDS KK (2023)hrithiksankarNo ratings yet
- Msoga 1Document73 pagesMsoga 1gabrielNo ratings yet
- Eosinophilic Colitis and Colonic EosinophiliaDocument9 pagesEosinophilic Colitis and Colonic EosinophiliadkbritobNo ratings yet
- PED2 6.04 Evaluation of The Child With A LimpDocument15 pagesPED2 6.04 Evaluation of The Child With A LimprachelNo ratings yet
- Elecsys HIV Duo: Cobas e 801 English System InformationDocument6 pagesElecsys HIV Duo: Cobas e 801 English System InformationТатьяна ИсаеваNo ratings yet
- APACHE Scoring As An Indicator of Mortality Rate.9Document6 pagesAPACHE Scoring As An Indicator of Mortality Rate.9Mohamed TharwatNo ratings yet
- Hyperthyroidism in Sickle Cell AnaemiaDocument6 pagesHyperthyroidism in Sickle Cell AnaemiaKIU PUBLICATION AND EXTENSIONNo ratings yet
- Adult Orbital Rhabdomyosarcoma Case ReportDocument3 pagesAdult Orbital Rhabdomyosarcoma Case ReportInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- PathologyDocument28 pagesPathologyakkashamrishNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 - Q1 - W5 L1 - Compare and ContrastDocument7 pagesGrade 10 - Q1 - W5 L1 - Compare and ContrastAndre Marell Cacatian100% (1)
- Covid 19Document12 pagesCovid 19OmengMagcalasNo ratings yet
- Meningoencephalitis Caused by Mycoplasma EdwardiiDocument6 pagesMeningoencephalitis Caused by Mycoplasma EdwardiiLatifa Putri FajrNo ratings yet
- COVID-19 in Nigeria... Matters ArisingDocument3 pagesCOVID-19 in Nigeria... Matters ArisingGreater K. OYEJOBINo ratings yet
- PenisDocument4 pagesPenisckiely91No ratings yet
- 9 Extension: (6) (Admission: '1 Card: 0 Discharged: 0 Referral: 0 Transferred: 1 Expired: 0 HAMA: 0 Abscond: 0Document7 pages9 Extension: (6) (Admission: '1 Card: 0 Discharged: 0 Referral: 0 Transferred: 1 Expired: 0 HAMA: 0 Abscond: 0Patrick JohnNo ratings yet
- Azizi - Occupational Noise-Induced Hearing LossDocument8 pagesAzizi - Occupational Noise-Induced Hearing LossAna BrankovićNo ratings yet
- MisopaDocument2 pagesMisopaSaifur Rahman SuzonNo ratings yet
- Different Types of Medicines: List of Antibiotics and Their UsesDocument3 pagesDifferent Types of Medicines: List of Antibiotics and Their UsesAngelique BernardinoNo ratings yet
- Fourteen Home Remedies For Knee PainDocument12 pagesFourteen Home Remedies For Knee PainRatnaPrasadNalamNo ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal AssessmentDocument69 pagesMusculoskeletal AssessmentWorku Kifle100% (2)
- Homoeopathic & Biochemic Instant Prescriber PDFDocument689 pagesHomoeopathic & Biochemic Instant Prescriber PDFVetri Selvan100% (2)
- In Silico Validation of The Indigenous Knowledge of The Herbal Medicines Among Tribal Communities in Sathyamangalam Wildlife Sanctuary, IndiaDocument13 pagesIn Silico Validation of The Indigenous Knowledge of The Herbal Medicines Among Tribal Communities in Sathyamangalam Wildlife Sanctuary, IndiaJack WaltersNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Vitae: ProfileDocument6 pagesCurriculum Vitae: ProfileMohammed ZahedNo ratings yet