Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Internet of Things Master Class Notes
Internet of Things Master Class Notes
Uploaded by
vvip420.84.2Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Internet of Things Master Class Notes
Internet of Things Master Class Notes
Uploaded by
vvip420.84.2Copyright:
Available Formats
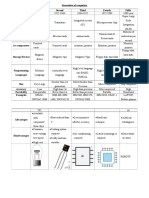
Hardware
Combination of + + TO DO SPECIFIC TASK
Mechanical Parts
#1 Embedded Systems Software
#1 Printer
#2 Mouse
Example #3 Washing Machine
It is a General Purpose Machine
Not COMPUTER / Mobile
Completes task in a specific time
#1 Real Time Embedded System Nuclear Reactors
Hard Realtime Ex
Air Bag - 4 Wheelers
Type
Soft Realtime Ex Game Controllers
Communicating other Embedded System
#2 Classification of Embedded System #2 Network Embedded System
IoT
Ex
Routers
Operated with a battery for a long time
#3 Mobile Embedded System
Ex Pacemakers
Details 12
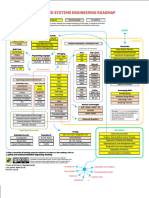
#1 Microprocessor
8085
Ex
8065
Details 9
#2 Microcontroller 8051
8 / 16 / 32 Bit
Ex ARM
PIC
Digital Signal Processor
#3 DSP Details 29
Ex TMS320C6000
Digital Signal Controller
#4 DSC Details
Ex TMS320C2000
Field Programmable Gate Array
#5 FPGA Details 5
#3 Types of Embedded System Zync Pynq Z2 2
Ex ZYNQ
Spartan
Complex Programmable Logic Device
#6 CPLD Details 4
Ex Xilinx Coolrunner
Application Specific Integrated Circuit
#7 ASIC Details
Intel Movidius
Ex
TGAM
System On Chip
#8 SOC Details 1
ESP-32
Ex
TI OMAP
#9 GPU
#10 TPU
Anything which is connected with Cloud via Internet
physical devices
vehicles
Things
Internet of Things buildings
Master Class and other items
#4 Internet of Things Revolution
1700s and early 1800s | optimized form of labor performed by people through the use of water and
INDUSTRY 1.0
steam-powered engines and other types of machine tools
Early part of the 20th century | The introduction of electricity enabled manufacturers to increase
INDUSTRY 2.0
efficiency and helped make factory machinery more mobile
Late 1950s |manufacturers began experiencing a shift that put less emphasis on analog and
Evolution of Industry INDUSTRY 3.0
mechanical technology and more on digital technology and automation software.
Interconnectivity through the Internet of Things (IoT), access to real-time data, and the
INDUSTRY 4.0
introduction of cyber-physical systems.
Industry 5.0 refers to robot and smart machines working alongside people with added resilience and
INDUSTRY 5.0 sustainability goals included. Where Industry 4.0 focused on technologies such as the Internet of
Things and big data, Industry 5.0 seeks to add human, environmental and social aspects back
into the equation.
Sensors/Devices Collect data from the surrounding environment
Connectivity Connect devices to the internet through various means (Wi-Fi, Cellular, Satellite)
#5 Key Components of IoT
Data Processing Process the collected data, either on the edge or in the cloud
Action Perform a task based on the processed data, such as sending an alert or adjusting settings
#6 4
#7 9
#8 9
#9 9
#10 7
#11 58
#12 25
#13 47
#14 16
#15 52
#16 24
#17 60
#18 58
You might also like
- Lisec Glass Cutting Table Machine Retrofit - Saint GobainDocument1 pageLisec Glass Cutting Table Machine Retrofit - Saint GobaineacondeNo ratings yet
- Allen-Bradley Stratix 5700™ Network Address Translation (NAT)Document20 pagesAllen-Bradley Stratix 5700™ Network Address Translation (NAT)Max100% (1)
- C - Documents and Settings - O - Local Settings - Application Data - Opera - Opera - Cache - G - 007D - opr011OHDocument2 pagesC - Documents and Settings - O - Local Settings - Application Data - Opera - Opera - Cache - G - 007D - opr011OHOleh PoNo ratings yet
- GP-Pro Ex-Basic TrainingDocument244 pagesGP-Pro Ex-Basic TrainingDAJIMMANZ TVNo ratings yet
- Embedded Engineer RoadMap 2022Document1 pageEmbedded Engineer RoadMap 2022CHEEDARA BHAVANI0% (1)
- Summer Training ON Embedded SystemsDocument26 pagesSummer Training ON Embedded SystemshimanicNo ratings yet
- Sargodha Institute of Technology: ProgramingDocument3 pagesSargodha Institute of Technology: ProgramingUsman UlHaqNo ratings yet
- Main Items BOQ Per SS: 4. Ethernet Switch 1. Control Panel & Panel Accessories 2. RTU System 5. Maintenance ToolsDocument1 pageMain Items BOQ Per SS: 4. Ethernet Switch 1. Control Panel & Panel Accessories 2. RTU System 5. Maintenance ToolsTarek KhafagaNo ratings yet
- Draft SylabbusDocument146 pagesDraft SylabbusKiambisNo ratings yet
- Generation First Second Third Fourth Fifth YearDocument2 pagesGeneration First Second Third Fourth Fifth Yearkeerthana vijayakumarNo ratings yet
- Group3 Tabulation IIOTDocument26 pagesGroup3 Tabulation IIOTdark knightNo ratings yet
- Dynatrace Introduction To TaspenDocument32 pagesDynatrace Introduction To TaspenANDIKA SUDARMANNo ratings yet
- Temas de ClaseDocument381 pagesTemas de ClaseterterNo ratings yet
- Microprogrammed ControlDocument30 pagesMicroprogrammed ControlRajdeep BiswasNo ratings yet
- Poster Schvar C Bacher RossiDocument1 pagePoster Schvar C Bacher RossiDraoui AhmedNo ratings yet
- Control and Modelling of Wireless RobotDocument4 pagesControl and Modelling of Wireless RobotPhaniendra KundetiNo ratings yet
- Wireless Data Aquisition System Sample2Document1 pageWireless Data Aquisition System Sample2Crescendo Solusi TamaNo ratings yet
- Ativa Slide Presentation - Infovista DetailDocument34 pagesAtiva Slide Presentation - Infovista Detailnhatnd88No ratings yet
- Faldic BDocument24 pagesFaldic BgsNo ratings yet
- Building Management - Monitor Building Power SupplyDocument1 pageBuilding Management - Monitor Building Power SupplyMusembiNo ratings yet
- Computer Science NotesDocument4 pagesComputer Science Notesemmastark2773No ratings yet
- Daikin SVM SG CatalogueDocument12 pagesDaikin SVM SG CatalogueChithravelu TamilkumaranNo ratings yet
- El Impacto en El Software de Las Arquitecturas MulticoreDocument48 pagesEl Impacto en El Software de Las Arquitecturas MulticoreXavier Gracia CervantesNo ratings yet
- Motionsuite Mp940 Machine Controller Hardware ManualDocument72 pagesMotionsuite Mp940 Machine Controller Hardware ManualJULIAN ANDRES ROJASNo ratings yet
- C4 EngineDocument1 pageC4 Engine姚飞No ratings yet
- Creative Computing v06 n12 1980 DecemberDocument232 pagesCreative Computing v06 n12 1980 Decemberdarkstar314No ratings yet
- Mind Map 01Document1 pageMind Map 01Dr. Suna PaanaNo ratings yet
- DENSO Robotics Online EXPO Catalog Set en 1Document15 pagesDENSO Robotics Online EXPO Catalog Set en 1docteur stringoNo ratings yet
- CTC 03Document53 pagesCTC 03BIBHISHAN MUNDENo ratings yet
- Euf Aut T2835 - EtasDocument28 pagesEuf Aut T2835 - EtaskuronoshirorespawnNo ratings yet
- DCOMP05R41 DIPC TS M Module 3 v.3BDocument90 pagesDCOMP05R41 DIPC TS M Module 3 v.3BThanh Kieu TienNo ratings yet
- Diagrama D6NDocument2 pagesDiagrama D6NPlstina Rams100% (1)
- ZONITH Dimetra Micro Fail Over SolutionDocument8 pagesZONITH Dimetra Micro Fail Over SolutionSohaib Omer SalihNo ratings yet
- Measurement and Automation Systems: The Iba SystemDocument11 pagesMeasurement and Automation Systems: The Iba Systemryan940No ratings yet
- FDM Printers Portfolio - EN A4 Quick Reference GuideDocument1 pageFDM Printers Portfolio - EN A4 Quick Reference GuideGokul SivaramanNo ratings yet
- Avrcam Code Commentary: JrobotDocument26 pagesAvrcam Code Commentary: JrobotAhmed Abd elmoneimNo ratings yet
- Visio AutomationDocument49 pagesVisio AutomationJAMNo ratings yet
- 2DRV YASKAWA ConM 124407 GB 2070-4Document13 pages2DRV YASKAWA ConM 124407 GB 2070-4jose luis mejia cortezNo ratings yet
- GI MicroElectronics Data Catalog 1978 Index PDFDocument22 pagesGI MicroElectronics Data Catalog 1978 Index PDFAnonymous KuTQvYTuNo ratings yet
- Isobus - The CAN-based Network System For Agriculture and Forestry MachinesDocument6 pagesIsobus - The CAN-based Network System For Agriculture and Forestry MachinesCARLA EMANOELE LABIAPARI NASCIMENTONo ratings yet
- Distributed Control SystemDocument15 pagesDistributed Control SystemLudwig MensahNo ratings yet
- Poster Presentation Prateek RastogiDocument1 pagePoster Presentation Prateek RastogiprateekNo ratings yet
- Embedded Engineering RoadmapDocument1 pageEmbedded Engineering Roadmapaksak4010No ratings yet
- Master 1Document1 pageMaster 1Quality Manager Jet ServeNo ratings yet
- Must KnowDocument1 pageMust KnowaeNo ratings yet
- Firmware Engineer Roadmap 2021 1632678252Document1 pageFirmware Engineer Roadmap 2021 1632678252Joao DuqueNo ratings yet
- CMW-Platform Bro en 5214-2833-12 v0500Document36 pagesCMW-Platform Bro en 5214-2833-12 v0500deve1986No ratings yet
- Memminger Networker Monitoring SystemDocument16 pagesMemminger Networker Monitoring SystemsentyNo ratings yet
- DecodeDocument79 pagesDecodeforfives2No ratings yet
- System Architecture - Fosber Master Cut Off Esursa EcuadorDocument1 pageSystem Architecture - Fosber Master Cut Off Esursa EcuadoreacondeNo ratings yet
- IPANema PDFDocument16 pagesIPANema PDFE. 17No ratings yet
- Home AutomationDocument9 pagesHome Automationvysnavi vrpNo ratings yet
- Welcome To Your Digital Edition Of: Tech Briefs, Photonics & Imaging Technology, and Sensor TechnologyDocument126 pagesWelcome To Your Digital Edition Of: Tech Briefs, Photonics & Imaging Technology, and Sensor TechnologyPetros TsenesNo ratings yet
- System Architecture - Fosber Compact Slitter Scorer Retrofit - Esursa EcuadorDocument1 pageSystem Architecture - Fosber Compact Slitter Scorer Retrofit - Esursa EcuadoreacondeNo ratings yet
- Intellisolar InsertDocument2 pagesIntellisolar Insertrahulasdfsharma1986No ratings yet
- MTConnect Information FlyerDocument2 pagesMTConnect Information FlyerMatheus SanderNo ratings yet
- Motion Smarter: Powerful Control Solutions For Demanding Multi-Axis MachineryDocument13 pagesMotion Smarter: Powerful Control Solutions For Demanding Multi-Axis MachineryTofel EmedNo ratings yet
- Spare Items BOM - Per SSDocument1 pageSpare Items BOM - Per SSTarek KhafagaNo ratings yet
- TP-Wireless-5.2.2-LRC-OSS Interface Developer Guide (Cellular)Document16 pagesTP-Wireless-5.2.2-LRC-OSS Interface Developer Guide (Cellular)Ofer KrausNo ratings yet
- IGS-6329 Series - LDocument14 pagesIGS-6329 Series - Lmayraelisa.salgadoNo ratings yet
- Wheatstone Bridge's Sensitivity, Resistors' Values Effect PDFDocument6 pagesWheatstone Bridge's Sensitivity, Resistors' Values Effect PDFMostafa KhaledNo ratings yet
- Problems Chptrs 19-30Document54 pagesProblems Chptrs 19-30Pawan NarayanNo ratings yet
- 2Q QuizDocument4 pages2Q QuizjcvoscribNo ratings yet
- SKii P83 AC12Document3 pagesSKii P83 AC12DYLAN JOSUE (SOLUCIONES TECNOLOGICA)No ratings yet
- 19EC516 - QR - HDL Programming APRIL 2024Document15 pages19EC516 - QR - HDL Programming APRIL 2024Nanda KishoreNo ratings yet
- ICA-UNIT-III - R19-CompleteDocument28 pagesICA-UNIT-III - R19-CompleteBhanu Kiran BKNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - Basic Computer OrganizationDocument17 pagesLesson 1 - Basic Computer OrganizationSteph Kier PonterasNo ratings yet
- ATP 250 Lyon 2023 Schematic 21 MayDocument1 pageATP 250 Lyon 2023 Schematic 21 MayHa Duc ThanhNo ratings yet
- A100K11013 Pulse - Getting - StartedDocument4 pagesA100K11013 Pulse - Getting - StartedMahran MastouriNo ratings yet
- College Name Course Name Closing Rank Category QuotaDocument31 pagesCollege Name Course Name Closing Rank Category QuotaLokesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Price List Royu Electrical November 2019 Issue PDFDocument16 pagesPrice List Royu Electrical November 2019 Issue PDFJeff CabusasNo ratings yet
- Basic Electronics and Electricity Assembly Kits - M-KITSDocument15 pagesBasic Electronics and Electricity Assembly Kits - M-KITSpfalencarNo ratings yet
- Interfacing The ADS8361 To The TMS320F2812 DSPDocument11 pagesInterfacing The ADS8361 To The TMS320F2812 DSPasokanenNo ratings yet
- A - V Sorround Receiver Avr-4806Document2 pagesA - V Sorround Receiver Avr-4806Jonathan NavasNo ratings yet
- AT89C5131 USB BootloaderDocument33 pagesAT89C5131 USB Bootloadercarlos augusto do carmo braiaNo ratings yet
- Design of A Smart Safety Device For Women Using Iot Design of A Smart Safety Device For Women Using IotDocument7 pagesDesign of A Smart Safety Device For Women Using Iot Design of A Smart Safety Device For Women Using Iotamta nadeemNo ratings yet
- 1986 NEC Linear ProductsDocument442 pages1986 NEC Linear ProductsJosé InácioNo ratings yet
- L3000A Manual de ServicioDocument44 pagesL3000A Manual de ServiciocarlosxxiNo ratings yet
- List of Top Polytechnic Colleges in Chennai and Their DetailsDocument6 pagesList of Top Polytechnic Colleges in Chennai and Their DetailsMahesh Divakar100% (1)
- Advantest R6243 PDFDocument12 pagesAdvantest R6243 PDFangelo_lopez1993No ratings yet
- Synopsis Mini ProjectDocument6 pagesSynopsis Mini ProjectMadan R HonnalagereNo ratings yet
- CH 6-q 1Document2 pagesCH 6-q 1মজুমদার অলিনNo ratings yet
- Ieee 1184Document37 pagesIeee 1184Jose Antonio EstofaneroNo ratings yet
- E-Ball Research PaperDocument4 pagesE-Ball Research PaperNarasimha LeViNo ratings yet
- Vestel DVB 4 - Sat 3600 - (ET)Document53 pagesVestel DVB 4 - Sat 3600 - (ET)peraja12No ratings yet
- LM629 Salida PWMDocument25 pagesLM629 Salida PWMLuis VarelaNo ratings yet
- UMCEE Presentation 06102015Document149 pagesUMCEE Presentation 06102015aryoNo ratings yet
- Se-330 Manual Neutral-Grounding-Resistor Monitor: All Rights ReservedDocument44 pagesSe-330 Manual Neutral-Grounding-Resistor Monitor: All Rights ReservedAlmir GarciaNo ratings yet
- Modeling and System-Level Performance Evaluation of Sub-Band Full Duplexing For 5G-AdvancedDocument15 pagesModeling and System-Level Performance Evaluation of Sub-Band Full Duplexing For 5G-AdvancedSimegnew ademeNo ratings yet