Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views6 Delay Analysis Techniques
6 Delay Analysis Techniques
Uploaded by
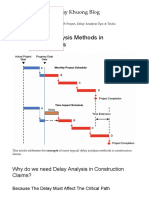
mangeshjoThis document describes six different methods for analyzing delays on construction projects:
1. As-Planned vs As-Built compares the original planned schedule to the actual completed schedule to determine causes of delays.
2. Updated As-Planned vs Updated As-Built also compares planned to actual schedules but considers schedule updates made during the project.
3. As-Planned Impacted adds delay events to the original baseline schedule to simulate their effects.
4. Time Impact Analysis similarly models delays but considers multiple schedule updates over time in windows or periods.
5. Collapsed As-Built subtracts delays from the final actual schedule to determine their impacts.
6. Collapsed As-Built
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- 1.3.2 Lenovo + Steeple AnalysisDocument3 pages1.3.2 Lenovo + Steeple Analysisdavid tsai100% (2)
- A320 Fuel SystemDocument7 pagesA320 Fuel SystemFadi Freiga100% (2)
- Memo+ISO+GPS+2018 Cetim ENDocument52 pagesMemo+ISO+GPS+2018 Cetim ENtoto.gmbh100% (1)
- Program Level SchedulingDocument7 pagesProgram Level SchedulingHatem HejaziNo ratings yet
- CM-PE-902 Procedure For Progress and Performance Measurement PDFDocument9 pagesCM-PE-902 Procedure For Progress and Performance Measurement PDFDavid PrastyanNo ratings yet
- Daily Windows Delay Analysis: Tarek Hegazy, M.ASCE, and Kehui ZhangDocument9 pagesDaily Windows Delay Analysis: Tarek Hegazy, M.ASCE, and Kehui ZhangAhed NabilNo ratings yet
- Critical Path MethodDocument3 pagesCritical Path MethodNeal CastilloNo ratings yet
- Critical Path MethodDocument11 pagesCritical Path Methodaryanboxer786No ratings yet
- Earned Value Project Management (Fourth Edition)From EverandEarned Value Project Management (Fourth Edition)Rating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (2)
- ABBF Analysis in P6Document11 pagesABBF Analysis in P6RenoMasrNo ratings yet
- Primavera - 06 GlossaryDocument17 pagesPrimavera - 06 GlossaryNaeem Uddin KolachiNo ratings yet
- How To Make As Built ProgramDocument15 pagesHow To Make As Built ProgramMem Nabil RamadanNo ratings yet
- Module 3 Project Scheduling, Monitoring & Risk ManagementDocument13 pagesModule 3 Project Scheduling, Monitoring & Risk Managementhanif malgundkarNo ratings yet
- Wjarr 2023 0231 PDFDocument10 pagesWjarr 2023 0231 PDFBeau NorNo ratings yet
- LBNL EVMS Reference Guide Final Rev0Document22 pagesLBNL EVMS Reference Guide Final Rev0orjuanNo ratings yet
- Implementing Time Impact Analyses and Update Impact Analyses On Large, Complex EPC ProjectsDocument45 pagesImplementing Time Impact Analyses and Update Impact Analyses On Large, Complex EPC ProjectsMiguel MarquesNo ratings yet
- Substantiation and Assessment of Claims For Extensions of TimeDocument12 pagesSubstantiation and Assessment of Claims For Extensions of Timeegglestona100% (2)
- Construction Scheduling Manual: Prepared by Construction ManagementDocument44 pagesConstruction Scheduling Manual: Prepared by Construction ManagementccemilovaNo ratings yet
- PAE Ch-5 Project-ExecutionDocument34 pagesPAE Ch-5 Project-ExecutionProf. Dr. Anbalagan ChinniahNo ratings yet
- CM-PE-902 Procedure For Progress and Performance MeasurementDocument7 pagesCM-PE-902 Procedure For Progress and Performance MeasurementSam_1_No ratings yet
- 2.0 Project Scheduling Terms That Every Planner Needs To KnowDocument12 pages2.0 Project Scheduling Terms That Every Planner Needs To Know01June2010No ratings yet
- Management of Software Development ProjectsDocument9 pagesManagement of Software Development Projectssaliya.gali21No ratings yet
- ScheduleDocument3 pagesSchedulenoriebel OlivaNo ratings yet
- Performance Intensity (PI)Document7 pagesPerformance Intensity (PI)Victoria Cynthia RebeccaNo ratings yet
- Project Engineer & Planning Interview QuestionsDocument7 pagesProject Engineer & Planning Interview QuestionsAnonymous E2oSW7No ratings yet
- ChapterDocument60 pagesChapterMa ThiNo ratings yet
- Baseling Schedule/Bar Charts/Gantt Charts/ Network Diagrams From Time PlanningDocument19 pagesBaseling Schedule/Bar Charts/Gantt Charts/ Network Diagrams From Time PlanningKendra TerryNo ratings yet
- Schedule Impact AnalysisDocument50 pagesSchedule Impact AnalysisFeNo ratings yet
- Schedule Impact AnalysisDocument47 pagesSchedule Impact AnalysisFeNo ratings yet
- Schedule Impact Analysis - Copy QW QDocument29 pagesSchedule Impact Analysis - Copy QW QFeNo ratings yet
- Schedule Impact AnalysisDocument44 pagesSchedule Impact AnalysisFeNo ratings yet
- Project Planning and Scheduling Glossary: The UltimateDocument14 pagesProject Planning and Scheduling Glossary: The UltimatesanthirajNo ratings yet
- Unit 15 Integrated Project Management Control System: ObjectivesDocument24 pagesUnit 15 Integrated Project Management Control System: ObjectivesSundaram SureshNo ratings yet
- 003 Converting Linear Schedules To CPM 27.10.12Document5 pages003 Converting Linear Schedules To CPM 27.10.12Sunil Varma DanthuluriNo ratings yet
- Software Engineering UNIT-2, Ayasha MalikDocument19 pagesSoftware Engineering UNIT-2, Ayasha MalikRisha SinghNo ratings yet
- Claim Digger Baseline Schedule VDocument28 pagesClaim Digger Baseline Schedule VDilip KumarNo ratings yet
- Is.15883.2.2013 - Copy (2) oDocument3 pagesIs.15883.2.2013 - Copy (2) oKendra TerryNo ratings yet
- Network ModelDocument69 pagesNetwork ModelAbdi NegassaNo ratings yet
- Critical Path MethodDocument4 pagesCritical Path MethodShin Min Rin100% (1)
- Typical Delay Analysis Methods in Construction Claims - Khuong Do BlogDocument7 pagesTypical Delay Analysis Methods in Construction Claims - Khuong Do BlogKhuong Do100% (2)
- Production Operations Management Module IIDocument249 pagesProduction Operations Management Module IIbaviskarvs123No ratings yet
- Ramskill Martin Programmes Progress Monitoring and ReportingDocument8 pagesRamskill Martin Programmes Progress Monitoring and ReportingmorrisioNo ratings yet
- Delay Analysis Methodologies. ICCP Industry Insights PDFDocument4 pagesDelay Analysis Methodologies. ICCP Industry Insights PDFWaheed ElbeihNo ratings yet
- Time Impact AnalysisDocument5 pagesTime Impact Analysisluisprieto100% (1)
- Network DiagramsDocument8 pagesNetwork Diagramscrystal50% (2)
- Project Time ManagementDocument10 pagesProject Time ManagementAli RazaNo ratings yet
- PM NotesDocument23 pagesPM Noteschandar70No ratings yet
- Schedule MGMT PlanDocument32 pagesSchedule MGMT PlanDrMohamed MustaqNo ratings yet
- Are We Moving in The Right Direction in Assessing Construction DelaysDocument34 pagesAre We Moving in The Right Direction in Assessing Construction DelaysAnonymous pGodzH4xLNo ratings yet
- Schedule Impact AnalysisDocument51 pagesSchedule Impact AnalysisFeNo ratings yet
- Schedule Impact AnalysisDocument30 pagesSchedule Impact AnalysisFeNo ratings yet
- 3.2 Work Breakdown StructureDocument4 pages3.2 Work Breakdown StructureNadeem AhmadNo ratings yet
- Typical Delay Analysis Methods in Construction ClaimsDocument8 pagesTypical Delay Analysis Methods in Construction ClaimsChakravarthy PujariNo ratings yet
- Unit-4 (SPM) Part - 1Document22 pagesUnit-4 (SPM) Part - 1rihanaparveen027No ratings yet
- Pickavance - Appendix 1 Glossary of Terms and DefinitionsDocument27 pagesPickavance - Appendix 1 Glossary of Terms and DefinitionsrishijaveriNo ratings yet
- Sen Unit 5 5 2Document11 pagesSen Unit 5 5 2Sarthak kadamNo ratings yet
- Source: - Downloaded: 2005-04-14T12:33Z Check The Source To Verify That This Is The Current Version Before UseDocument6 pagesSource: - Downloaded: 2005-04-14T12:33Z Check The Source To Verify That This Is The Current Version Before UsejmbourvenNo ratings yet
- 02 Handout 110Document5 pages02 Handout 110Eliza ColomaNo ratings yet
- Delay Analysis MethodDocument6 pagesDelay Analysis Methodvenkatesh_narayana_5No ratings yet
- Project Management PDFDocument123 pagesProject Management PDFJarosławIsiekAdamNo ratings yet
- CISA Exam-Testing Concept-PERT/CPM/Gantt Chart/FPA/EVA/Timebox (Chapter-3)From EverandCISA Exam-Testing Concept-PERT/CPM/Gantt Chart/FPA/EVA/Timebox (Chapter-3)Rating: 1.5 out of 5 stars1.5/5 (3)
- AACE Paper 2005 - Est08 - Controlling Non-ConstructionDocument7 pagesAACE Paper 2005 - Est08 - Controlling Non-ConstructionmangeshjoNo ratings yet
- Change Log - Schedule Log - 05-12-2019Document1 pageChange Log - Schedule Log - 05-12-2019mangeshjoNo ratings yet
- OD226766912640778000Document1 pageOD226766912640778000mangeshjoNo ratings yet
- Cleaning Work ExpenseDocument1 pageCleaning Work ExpensemangeshjoNo ratings yet
- 403 Security MS T1Document2 pages403 Security MS T1mangeshjoNo ratings yet
- Installment - Payment Plan: Name of Client Plot NumberDocument1 pageInstallment - Payment Plan: Name of Client Plot NumbermangeshjoNo ratings yet
- Engineer InstrumentationDocument4 pagesEngineer InstrumentationmangeshjoNo ratings yet
- Precision Plastic Industries PVT LTD.: Test Report Is: 3419Document2 pagesPrecision Plastic Industries PVT LTD.: Test Report Is: 3419mangeshjoNo ratings yet
- Electrical Wirings-Ground FloorDocument1 pageElectrical Wirings-Ground FloordrajkumarceNo ratings yet
- English Grade 3Document269 pagesEnglish Grade 3Berhanu AlemuNo ratings yet
- 2006 2008 Cbf1000 A 10 Clutch Starter ClutchDocument34 pages2006 2008 Cbf1000 A 10 Clutch Starter ClutchMurariu IonutNo ratings yet
- Inoculating Techniques LabDocument5 pagesInoculating Techniques LabJerome LisingNo ratings yet
- MRU3401-En-DS-P-003-A4 Process Datasheet For MRU Guard Bed - AFCDocument4 pagesMRU3401-En-DS-P-003-A4 Process Datasheet For MRU Guard Bed - AFCjoe oktaNo ratings yet
- Aquinas Summary PDFDocument3 pagesAquinas Summary PDFpaula AcostaNo ratings yet
- Pashu Prahari April To June MagzineDocument129 pagesPashu Prahari April To June MagzinesumNo ratings yet
- Delicious Egg Salad For Sandwiches: by Wifeyluvs2cookDocument1 pageDelicious Egg Salad For Sandwiches: by Wifeyluvs2cookAntigone Vasiliou MarkolefasNo ratings yet
- Cooling Load Calculation Through Transmission and ProductDocument4 pagesCooling Load Calculation Through Transmission and ProductKenneth CariñoNo ratings yet
- TM H628 V1.00 RA Amps Operation ManualDocument24 pagesTM H628 V1.00 RA Amps Operation ManualJErryNo ratings yet
- Product Catalogue - (SP-NEW)Document48 pagesProduct Catalogue - (SP-NEW)Turoy100% (1)
- Attendance ApplicationDocument1 pageAttendance Applicationgeniousbond007No ratings yet
- Format For Calculating Lagna (With Example) - (Courtesy - Prof. EDocument5 pagesFormat For Calculating Lagna (With Example) - (Courtesy - Prof. EsanthoshNo ratings yet
- Art Collector I105 07.09 2023Document236 pagesArt Collector I105 07.09 2023JjxpresidentNo ratings yet
- Word Problems Involving Negative Numbers - Unlocked PDFDocument3 pagesWord Problems Involving Negative Numbers - Unlocked PDFRuchika SachdevaNo ratings yet
- CRIMINALISTICS (QD PPT 3)Document102 pagesCRIMINALISTICS (QD PPT 3)JL Amora RamaNo ratings yet
- Girimananda SuttaDocument22 pagesGirimananda SuttaBuddhist Publication SocietyNo ratings yet
- Bhadbhut Barrage Project Across Naramada RiverDocument14 pagesBhadbhut Barrage Project Across Naramada RiverPalashXVNo ratings yet
- cfd1 IntroDocument6 pagescfd1 IntrowhateverNo ratings yet
- Brief History of BoholDocument12 pagesBrief History of BoholJimmy Makiling PamugasNo ratings yet
- TSH Conversion PDFDocument1 pageTSH Conversion PDFMarianNo ratings yet
- Laser Markable Label Material: Technical Data January 1, 1999Document3 pagesLaser Markable Label Material: Technical Data January 1, 1999jonathan6657No ratings yet
- Annex I - Svrvey, Investigation and Design ChecklistDocument12 pagesAnnex I - Svrvey, Investigation and Design ChecklistKidanemariam100% (1)
- Yoo Hyuk Sang Photo Cross Linkable and Thermo 2007Document13 pagesYoo Hyuk Sang Photo Cross Linkable and Thermo 2007FranciscoNo ratings yet
- How To Set Up The Dht11 Humidity Sensor On An ArduinoDocument9 pagesHow To Set Up The Dht11 Humidity Sensor On An Arduinogetnet100% (1)
- Exp#1 Diode Characteristics V2Document12 pagesExp#1 Diode Characteristics V2Shehda ZahdaNo ratings yet
- Las Science 9 Melc 7 q2 Week-7Document7 pagesLas Science 9 Melc 7 q2 Week-7LINDSY MAE SULA-SULANo ratings yet
6 Delay Analysis Techniques
6 Delay Analysis Techniques
Uploaded by
mangeshjo0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views6 pagesThis document describes six different methods for analyzing delays on construction projects:
1. As-Planned vs As-Built compares the original planned schedule to the actual completed schedule to determine causes of delays.
2. Updated As-Planned vs Updated As-Built also compares planned to actual schedules but considers schedule updates made during the project.
3. As-Planned Impacted adds delay events to the original baseline schedule to simulate their effects.
4. Time Impact Analysis similarly models delays but considers multiple schedule updates over time in windows or periods.
5. Collapsed As-Built subtracts delays from the final actual schedule to determine their impacts.
6. Collapsed As-Built
Original Description:
Tech
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document describes six different methods for analyzing delays on construction projects:
1. As-Planned vs As-Built compares the original planned schedule to the actual completed schedule to determine causes of delays.
2. Updated As-Planned vs Updated As-Built also compares planned to actual schedules but considers schedule updates made during the project.
3. As-Planned Impacted adds delay events to the original baseline schedule to simulate their effects.
4. Time Impact Analysis similarly models delays but considers multiple schedule updates over time in windows or periods.
5. Collapsed As-Built subtracts delays from the final actual schedule to determine their impacts.
6. Collapsed As-Built
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views6 pages6 Delay Analysis Techniques
6 Delay Analysis Techniques
Uploaded by
mangeshjoThis document describes six different methods for analyzing delays on construction projects:
1. As-Planned vs As-Built compares the original planned schedule to the actual completed schedule to determine causes of delays.
2. Updated As-Planned vs Updated As-Built also compares planned to actual schedules but considers schedule updates made during the project.
3. As-Planned Impacted adds delay events to the original baseline schedule to simulate their effects.
4. Time Impact Analysis similarly models delays but considers multiple schedule updates over time in windows or periods.
5. Collapsed As-Built subtracts delays from the final actual schedule to determine their impacts.
6. Collapsed As-Built
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 6
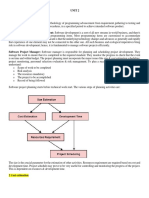
1. As‐Planned Vs.
As‐Built
It is one of the observational and static analysis.
It is the analysis of comparing the planned schedule as initially
envisaged to what actually happened as constructed, then
inferring/speculating from the differences between both, while
dividing the causes of delay, the resulting effects and then the
liability of each party.
2/18/2024 Annual Review 29
2. Updated As‐Planned Vs. Updated
As‐Built (As‐Planned Vs. As‐Built)
It is one of the observational and dynamic analysis.
This method considers project various schedule updates as works progressed such
as changes in sequence and critical path based on progress made.
It is the process of comparing the planned timing of activities on the first/former
planned schedule update to what actually happened as constructed as depicted
from the subsequent schedule update while comparing the critical path(s) of the
former update and the progressed update until developing a totally progressed
version of the first/former update from the successive schedule update up to the
successive update’s data date, then inferring from the differences between both,
while dividing the causes of delay, the resulting effects and then the liability of each
party.
This process is repeated between all consecutive schedule updates until the end of the project.
2/18/2024 Annual Review 35
3. As‐Planned Impacted (Single Base)
It is one of the modelled and static analysis.
It is the analysis of comparing the: i) original single baseline programme,
to ii) recalculated simulated programme,
whereby delay events/issues are added as discrete programme activities with
activity time‐duration and linked to other relevant activities (Predecessors/start
constraints and Successors), to calculate their effects on the baseline programme.
Then, the states before and after and the difference in completion date between
the original baseline programme and simulated programme represents the effect of
the inserted delay event(s).
2/18/2024 Annual Review 39
4. Time Impact Analysis (Windows
Analysis) (Recommended Method)
It is one of the modelled and dynamic analysis.
It is similar to aforementioned “As‐Planned Impacted (Single Base)” but carried out
in windows or watersheds’ analysis; so does consider the schedule updated
programmes as works progress not only the baseline programme, in addition to as‐
built data as well.
The additive simulation is carried out on various multiple CPM models representing
the baseline programme and all update schedules considering project
contemporaneous records.
Each model represents a window or a watershed for a defined period of the analysis
that confines the delay impact quantification in that period, whereby impact
events/fragnets are chronologically inserted into the proper updated programme.
2/18/2024 Annual Review 47
5. Collapsed As‐Built
It is one of the modelled and static analysis.
it is the analysis of comparing the: i) final As‐built programme, to
ii) recalculated simulated programme, whereby delay events/issues are subtracted
as discrete programme activities (fragnet or sub‐network) or as a calculated
duration that represents the delay event effect, to calculate their effects on the
final As‐built programme.
Then, the sates before and after and the difference in completion date between the
final As‐built programme and simulated programme represents the effect of the
delay event(s).
2/18/2024 Annual Review 50
6. Collapsed As‐Built (Multiple Base)
It is one of the modelled and dynamic analysis.
• It is similar to aforementioned “Collapsed As‐Built (Single Base)” but carried out
in windows or watersheds’ analysis; so does consider the schedule updated
programmes as works progress not only the final As‐built programme.
• The subtractive simulation is carried out on various multiple CPM models
representing the final As‐built programme and all update As‐built schedules
considering project contemporaneous records. Each model represents a window
or a watershed for a defined period of the analysis that confines the delay impact
quantification in that period, whereby impact events/fagnets are chronologically
subtracted from the proper As‐built updated programme.
2/18/2024 Annual Review 57
You might also like
- 1.3.2 Lenovo + Steeple AnalysisDocument3 pages1.3.2 Lenovo + Steeple Analysisdavid tsai100% (2)
- A320 Fuel SystemDocument7 pagesA320 Fuel SystemFadi Freiga100% (2)
- Memo+ISO+GPS+2018 Cetim ENDocument52 pagesMemo+ISO+GPS+2018 Cetim ENtoto.gmbh100% (1)
- Program Level SchedulingDocument7 pagesProgram Level SchedulingHatem HejaziNo ratings yet
- CM-PE-902 Procedure For Progress and Performance Measurement PDFDocument9 pagesCM-PE-902 Procedure For Progress and Performance Measurement PDFDavid PrastyanNo ratings yet
- Daily Windows Delay Analysis: Tarek Hegazy, M.ASCE, and Kehui ZhangDocument9 pagesDaily Windows Delay Analysis: Tarek Hegazy, M.ASCE, and Kehui ZhangAhed NabilNo ratings yet
- Critical Path MethodDocument3 pagesCritical Path MethodNeal CastilloNo ratings yet
- Critical Path MethodDocument11 pagesCritical Path Methodaryanboxer786No ratings yet
- Earned Value Project Management (Fourth Edition)From EverandEarned Value Project Management (Fourth Edition)Rating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (2)
- ABBF Analysis in P6Document11 pagesABBF Analysis in P6RenoMasrNo ratings yet
- Primavera - 06 GlossaryDocument17 pagesPrimavera - 06 GlossaryNaeem Uddin KolachiNo ratings yet
- How To Make As Built ProgramDocument15 pagesHow To Make As Built ProgramMem Nabil RamadanNo ratings yet
- Module 3 Project Scheduling, Monitoring & Risk ManagementDocument13 pagesModule 3 Project Scheduling, Monitoring & Risk Managementhanif malgundkarNo ratings yet
- Wjarr 2023 0231 PDFDocument10 pagesWjarr 2023 0231 PDFBeau NorNo ratings yet
- LBNL EVMS Reference Guide Final Rev0Document22 pagesLBNL EVMS Reference Guide Final Rev0orjuanNo ratings yet
- Implementing Time Impact Analyses and Update Impact Analyses On Large, Complex EPC ProjectsDocument45 pagesImplementing Time Impact Analyses and Update Impact Analyses On Large, Complex EPC ProjectsMiguel MarquesNo ratings yet
- Substantiation and Assessment of Claims For Extensions of TimeDocument12 pagesSubstantiation and Assessment of Claims For Extensions of Timeegglestona100% (2)
- Construction Scheduling Manual: Prepared by Construction ManagementDocument44 pagesConstruction Scheduling Manual: Prepared by Construction ManagementccemilovaNo ratings yet
- PAE Ch-5 Project-ExecutionDocument34 pagesPAE Ch-5 Project-ExecutionProf. Dr. Anbalagan ChinniahNo ratings yet
- CM-PE-902 Procedure For Progress and Performance MeasurementDocument7 pagesCM-PE-902 Procedure For Progress and Performance MeasurementSam_1_No ratings yet
- 2.0 Project Scheduling Terms That Every Planner Needs To KnowDocument12 pages2.0 Project Scheduling Terms That Every Planner Needs To Know01June2010No ratings yet
- Management of Software Development ProjectsDocument9 pagesManagement of Software Development Projectssaliya.gali21No ratings yet
- ScheduleDocument3 pagesSchedulenoriebel OlivaNo ratings yet
- Performance Intensity (PI)Document7 pagesPerformance Intensity (PI)Victoria Cynthia RebeccaNo ratings yet
- Project Engineer & Planning Interview QuestionsDocument7 pagesProject Engineer & Planning Interview QuestionsAnonymous E2oSW7No ratings yet
- ChapterDocument60 pagesChapterMa ThiNo ratings yet
- Baseling Schedule/Bar Charts/Gantt Charts/ Network Diagrams From Time PlanningDocument19 pagesBaseling Schedule/Bar Charts/Gantt Charts/ Network Diagrams From Time PlanningKendra TerryNo ratings yet
- Schedule Impact AnalysisDocument50 pagesSchedule Impact AnalysisFeNo ratings yet
- Schedule Impact AnalysisDocument47 pagesSchedule Impact AnalysisFeNo ratings yet
- Schedule Impact Analysis - Copy QW QDocument29 pagesSchedule Impact Analysis - Copy QW QFeNo ratings yet
- Schedule Impact AnalysisDocument44 pagesSchedule Impact AnalysisFeNo ratings yet
- Project Planning and Scheduling Glossary: The UltimateDocument14 pagesProject Planning and Scheduling Glossary: The UltimatesanthirajNo ratings yet
- Unit 15 Integrated Project Management Control System: ObjectivesDocument24 pagesUnit 15 Integrated Project Management Control System: ObjectivesSundaram SureshNo ratings yet
- 003 Converting Linear Schedules To CPM 27.10.12Document5 pages003 Converting Linear Schedules To CPM 27.10.12Sunil Varma DanthuluriNo ratings yet
- Software Engineering UNIT-2, Ayasha MalikDocument19 pagesSoftware Engineering UNIT-2, Ayasha MalikRisha SinghNo ratings yet
- Claim Digger Baseline Schedule VDocument28 pagesClaim Digger Baseline Schedule VDilip KumarNo ratings yet
- Is.15883.2.2013 - Copy (2) oDocument3 pagesIs.15883.2.2013 - Copy (2) oKendra TerryNo ratings yet
- Network ModelDocument69 pagesNetwork ModelAbdi NegassaNo ratings yet
- Critical Path MethodDocument4 pagesCritical Path MethodShin Min Rin100% (1)
- Typical Delay Analysis Methods in Construction Claims - Khuong Do BlogDocument7 pagesTypical Delay Analysis Methods in Construction Claims - Khuong Do BlogKhuong Do100% (2)
- Production Operations Management Module IIDocument249 pagesProduction Operations Management Module IIbaviskarvs123No ratings yet
- Ramskill Martin Programmes Progress Monitoring and ReportingDocument8 pagesRamskill Martin Programmes Progress Monitoring and ReportingmorrisioNo ratings yet
- Delay Analysis Methodologies. ICCP Industry Insights PDFDocument4 pagesDelay Analysis Methodologies. ICCP Industry Insights PDFWaheed ElbeihNo ratings yet
- Time Impact AnalysisDocument5 pagesTime Impact Analysisluisprieto100% (1)
- Network DiagramsDocument8 pagesNetwork Diagramscrystal50% (2)
- Project Time ManagementDocument10 pagesProject Time ManagementAli RazaNo ratings yet
- PM NotesDocument23 pagesPM Noteschandar70No ratings yet
- Schedule MGMT PlanDocument32 pagesSchedule MGMT PlanDrMohamed MustaqNo ratings yet
- Are We Moving in The Right Direction in Assessing Construction DelaysDocument34 pagesAre We Moving in The Right Direction in Assessing Construction DelaysAnonymous pGodzH4xLNo ratings yet
- Schedule Impact AnalysisDocument51 pagesSchedule Impact AnalysisFeNo ratings yet
- Schedule Impact AnalysisDocument30 pagesSchedule Impact AnalysisFeNo ratings yet
- 3.2 Work Breakdown StructureDocument4 pages3.2 Work Breakdown StructureNadeem AhmadNo ratings yet
- Typical Delay Analysis Methods in Construction ClaimsDocument8 pagesTypical Delay Analysis Methods in Construction ClaimsChakravarthy PujariNo ratings yet
- Unit-4 (SPM) Part - 1Document22 pagesUnit-4 (SPM) Part - 1rihanaparveen027No ratings yet
- Pickavance - Appendix 1 Glossary of Terms and DefinitionsDocument27 pagesPickavance - Appendix 1 Glossary of Terms and DefinitionsrishijaveriNo ratings yet
- Sen Unit 5 5 2Document11 pagesSen Unit 5 5 2Sarthak kadamNo ratings yet
- Source: - Downloaded: 2005-04-14T12:33Z Check The Source To Verify That This Is The Current Version Before UseDocument6 pagesSource: - Downloaded: 2005-04-14T12:33Z Check The Source To Verify That This Is The Current Version Before UsejmbourvenNo ratings yet
- 02 Handout 110Document5 pages02 Handout 110Eliza ColomaNo ratings yet
- Delay Analysis MethodDocument6 pagesDelay Analysis Methodvenkatesh_narayana_5No ratings yet
- Project Management PDFDocument123 pagesProject Management PDFJarosławIsiekAdamNo ratings yet
- CISA Exam-Testing Concept-PERT/CPM/Gantt Chart/FPA/EVA/Timebox (Chapter-3)From EverandCISA Exam-Testing Concept-PERT/CPM/Gantt Chart/FPA/EVA/Timebox (Chapter-3)Rating: 1.5 out of 5 stars1.5/5 (3)
- AACE Paper 2005 - Est08 - Controlling Non-ConstructionDocument7 pagesAACE Paper 2005 - Est08 - Controlling Non-ConstructionmangeshjoNo ratings yet
- Change Log - Schedule Log - 05-12-2019Document1 pageChange Log - Schedule Log - 05-12-2019mangeshjoNo ratings yet
- OD226766912640778000Document1 pageOD226766912640778000mangeshjoNo ratings yet
- Cleaning Work ExpenseDocument1 pageCleaning Work ExpensemangeshjoNo ratings yet
- 403 Security MS T1Document2 pages403 Security MS T1mangeshjoNo ratings yet
- Installment - Payment Plan: Name of Client Plot NumberDocument1 pageInstallment - Payment Plan: Name of Client Plot NumbermangeshjoNo ratings yet
- Engineer InstrumentationDocument4 pagesEngineer InstrumentationmangeshjoNo ratings yet
- Precision Plastic Industries PVT LTD.: Test Report Is: 3419Document2 pagesPrecision Plastic Industries PVT LTD.: Test Report Is: 3419mangeshjoNo ratings yet
- Electrical Wirings-Ground FloorDocument1 pageElectrical Wirings-Ground FloordrajkumarceNo ratings yet
- English Grade 3Document269 pagesEnglish Grade 3Berhanu AlemuNo ratings yet
- 2006 2008 Cbf1000 A 10 Clutch Starter ClutchDocument34 pages2006 2008 Cbf1000 A 10 Clutch Starter ClutchMurariu IonutNo ratings yet
- Inoculating Techniques LabDocument5 pagesInoculating Techniques LabJerome LisingNo ratings yet
- MRU3401-En-DS-P-003-A4 Process Datasheet For MRU Guard Bed - AFCDocument4 pagesMRU3401-En-DS-P-003-A4 Process Datasheet For MRU Guard Bed - AFCjoe oktaNo ratings yet
- Aquinas Summary PDFDocument3 pagesAquinas Summary PDFpaula AcostaNo ratings yet
- Pashu Prahari April To June MagzineDocument129 pagesPashu Prahari April To June MagzinesumNo ratings yet
- Delicious Egg Salad For Sandwiches: by Wifeyluvs2cookDocument1 pageDelicious Egg Salad For Sandwiches: by Wifeyluvs2cookAntigone Vasiliou MarkolefasNo ratings yet
- Cooling Load Calculation Through Transmission and ProductDocument4 pagesCooling Load Calculation Through Transmission and ProductKenneth CariñoNo ratings yet
- TM H628 V1.00 RA Amps Operation ManualDocument24 pagesTM H628 V1.00 RA Amps Operation ManualJErryNo ratings yet
- Product Catalogue - (SP-NEW)Document48 pagesProduct Catalogue - (SP-NEW)Turoy100% (1)
- Attendance ApplicationDocument1 pageAttendance Applicationgeniousbond007No ratings yet
- Format For Calculating Lagna (With Example) - (Courtesy - Prof. EDocument5 pagesFormat For Calculating Lagna (With Example) - (Courtesy - Prof. EsanthoshNo ratings yet
- Art Collector I105 07.09 2023Document236 pagesArt Collector I105 07.09 2023JjxpresidentNo ratings yet
- Word Problems Involving Negative Numbers - Unlocked PDFDocument3 pagesWord Problems Involving Negative Numbers - Unlocked PDFRuchika SachdevaNo ratings yet
- CRIMINALISTICS (QD PPT 3)Document102 pagesCRIMINALISTICS (QD PPT 3)JL Amora RamaNo ratings yet
- Girimananda SuttaDocument22 pagesGirimananda SuttaBuddhist Publication SocietyNo ratings yet
- Bhadbhut Barrage Project Across Naramada RiverDocument14 pagesBhadbhut Barrage Project Across Naramada RiverPalashXVNo ratings yet
- cfd1 IntroDocument6 pagescfd1 IntrowhateverNo ratings yet
- Brief History of BoholDocument12 pagesBrief History of BoholJimmy Makiling PamugasNo ratings yet
- TSH Conversion PDFDocument1 pageTSH Conversion PDFMarianNo ratings yet
- Laser Markable Label Material: Technical Data January 1, 1999Document3 pagesLaser Markable Label Material: Technical Data January 1, 1999jonathan6657No ratings yet
- Annex I - Svrvey, Investigation and Design ChecklistDocument12 pagesAnnex I - Svrvey, Investigation and Design ChecklistKidanemariam100% (1)
- Yoo Hyuk Sang Photo Cross Linkable and Thermo 2007Document13 pagesYoo Hyuk Sang Photo Cross Linkable and Thermo 2007FranciscoNo ratings yet
- How To Set Up The Dht11 Humidity Sensor On An ArduinoDocument9 pagesHow To Set Up The Dht11 Humidity Sensor On An Arduinogetnet100% (1)
- Exp#1 Diode Characteristics V2Document12 pagesExp#1 Diode Characteristics V2Shehda ZahdaNo ratings yet
- Las Science 9 Melc 7 q2 Week-7Document7 pagesLas Science 9 Melc 7 q2 Week-7LINDSY MAE SULA-SULANo ratings yet