Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cell Cycle and Mitosis Worksheet
Cell Cycle and Mitosis Worksheet
Uploaded by
julia.dukeOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cell Cycle and Mitosis Worksheet
Cell Cycle and Mitosis Worksheet
Uploaded by
julia.dukeCopyright:
Available Formats
Name: _____________________________________________Date: _________________ Period: _____
Cell Cycle and Mitosis
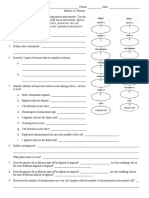
Using the labeled Cell Cycle diagram to the right do the following:
Left column: place the corresponding letter for the correct stage
Right column: Complete the description of the stage in the
1. A ____________________: Consists of G1, S and G2 phases
in the Cell Cycle.
Cytokinesis – division of the cytoplasm resulting in two
2. ___
identical d_______________ cells.
G1 – growth phase: Makes organelles and proteins needed for replication of DNA. Also contains a G 1
3. ___
checkpoint. If everything is correct, cell will proceed to S phase.
4. ___ S phase: DNA is replicated or synthesized.
5. D G2 - growth phase: Cell gets ready to undergo M_____________. Also contains a G2 checkpoint. If DNA
replication is correct, checkpoint allows cell to enter M phase.
Prophase: chromatin condenses to become chromatin, nuclear envelopes breaks down, and
6. ___
centrioles migrate to opposite poles in animal cells. Nucleolus disappears.
7. ___ M____________: sister chromatids line up along the metaphase plate in the middle. Spindle
apparatus attaches at the centromere of the chromosomes.
A______________: sister chromatids separate and move to opposite sides of the cell. The
8. G s___________ a______________ pulls them apart. This phase ends when the chromatids stop
moving.
Telophase: two nuclear envelopes begin reforming. Chromatids relax, uncoil & are now chromatin.
Cytokinesis is occurring during Telophase but it is NOT considered a part of mitosis because it does
9. ___
not involve the nucleus of the cell. In plant cells, a cell plate begins to form while a c_____________
f_____________ is visible in animal cells.
Mitosis: division of a cell’s nucleus. Occurs in this order: prophase, _________________,
10. ___
_______________, and telophase.
Label the phases of Mitosis below:
11. 12. 13. 14. 15.
Complete the table by checking the correct column for each statement.
Statement Interphase Mitosis
16. Cell growth occurs
17. Nuclear division occurs
18. Chromosomes are finishing moving into separate daughter cells.
19. Chromosomes are duplicated
20. DNA synthesis occurs
21. Where cells spend most of their life
22. Mitochondria and other organelles are made.
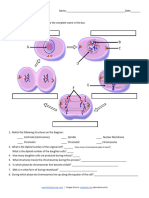
Use the following illustrations for questions 23 - 32
23. In cell A, what is the structure labeled X? ___________________
24. In cell F, what is the structure labeled Y? __________________
25. Which cell is not in a phase of mitosis? ______________________
26. New nuclear membranes are forming in B. What is this phase called? _____________________
27. Sequence the six diagrams in chronological order from first to last. ____, ____, ____, ____, ____, ____
28. Chromosomes move to the middle of the cell during? __________________________________________________
29. When do the sister chromatids separate? _____________________________________________________________
30. During which phase do chromosomes first become visible? ______________________________________________
31. During which phase does the cleavage furrow start forming on animal cells? _________________________________
32. If a cell has 46 chromosomes, how many chromosomes will each daughter cell have after mitosis? _____________
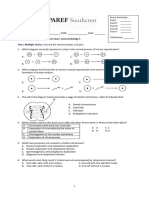
Identify the stage of mitosis each A E
lettered plant cell is in:
B
33. A
34. B
35. C D
C F
36. D
37. E
Regulation of the cell cycle
38. A mass of cancerous cells is called a t_____________________.
39. What is the purpose of checkpoints in the cell cycle?
40. What is a carcinogen? ___________________________________________________________________________
Give 2 examples of carcinogens: _________________________ and ____________________________
41. Cancer is defined as uncontrolled growth and division of cells due to a failure in the regulation of the cell cycle. Do
cancerous cells spend much of their time in Go, the resting period of the cell cycle? Explain why or why not.
Use the word box below to answer questions 42- 44
Apoptosis Chromosome Develop Grow
Daughter Chromatin Divide Repair
42. Programmed cell death is called _______________________ and is often trigged by cells that are damaged beyond
repair. This process can help protect against cancerous growth.
Big Ideas
43. What are reasons EUKARYOTIC cells divide?
a. To ____________& ___________________.
b. To ______________________ tissue.
44. What is the relationship between chromatin and chromosomes?
_____________ is thread-like DNA and is the form usually found in a cell that is not dividing. When a cell is
going to divide, chromatin coils up to form a(n) ___________________. Condensing and packaging DNA this way
makes it much more manageable and easier to ___________ DNA evenly among the 2 new IDENTICAL
________________ cells.
You might also like
- Practice Test ExplanationsDocument74 pagesPractice Test ExplanationsTar HajoNo ratings yet
- Mitosis WorksheetDocument3 pagesMitosis WorksheetAnicia Toscano100% (4)
- Mitosis Meiosis ComparedDocument1 pageMitosis Meiosis ComparedDURU ALTINKAYA100% (1)
- Meiosis-Webquest Answer KeyDocument4 pagesMeiosis-Webquest Answer KeyAshwin Raghuraman0% (1)
- 2017 OL Cell Cycle Exam ReviewDocument3 pages2017 OL Cell Cycle Exam ReviewAnne Romo50% (8)
- Mitosis Vs Meiosis WorksheetDocument2 pagesMitosis Vs Meiosis WorksheetFabian Andres Paez Velandia100% (1)
- Mitosis Meiosis ComparedDocument1 pageMitosis Meiosis ComparedDURU ALTINKAYANo ratings yet
- Snurfle Meiosis Another WSDocument2 pagesSnurfle Meiosis Another WSAdriana IzquierdoNo ratings yet
- Mitosis WorksheetDocument4 pagesMitosis WorksheetAmna Jamshed67% (3)
- Cell CycleDocument3 pagesCell Cycleapi-502781581No ratings yet
- Microbiology An Introduction: Thirteenth EditionDocument47 pagesMicrobiology An Introduction: Thirteenth EditionAnonymous r0fhYUnuNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle, Mitosis WorksheetDocument3 pagesCell Cycle, Mitosis Worksheetrosellevalerio2014No ratings yet
- Cell Cycle WorksheetDocument4 pagesCell Cycle Worksheet33 NICASA, DENDEN S.No ratings yet
- Cell Cycle WorksheetDocument3 pagesCell Cycle WorksheetBenay Çakaloğlu100% (2)
- The Cell Cycle Worksheet With AnswersDocument3 pagesThe Cell Cycle Worksheet With AnswersAngelic ZapantaNo ratings yet
- CH 12 The-Cell-Cycle-Worksheet With AnswersDocument4 pagesCH 12 The-Cell-Cycle-Worksheet With AnswersHavier EsparagueraNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle Review HomeworkDocument7 pagesCell Cycle Review HomeworkM.V.MatíasNo ratings yet
- Cell Replication AnswersDocument3 pagesCell Replication AnswersAlyssa JacobsNo ratings yet
- The Cell Cycle WorksheetDocument3 pagesThe Cell Cycle WorksheettrixieeeliaNo ratings yet
- RD ND: ML Bognalbal 1Document4 pagesRD ND: ML Bognalbal 1Dette Dominic BallanoNo ratings yet
- The-Cell-Cycle-Worksheet With AnswersDocument3 pagesThe-Cell-Cycle-Worksheet With AnswersHiezel Dapat100% (1)
- Class 11 Neet Cell Cycle and Cell DivisionDocument11 pagesClass 11 Neet Cell Cycle and Cell DivisionViswaNo ratings yet
- The Cell Cycle WorksheetDocument2 pagesThe Cell Cycle WorksheetLaarni Faye Sarmiento100% (1)
- Mitosis Worksheet 2Document5 pagesMitosis Worksheet 2Kaylee LewisNo ratings yet
- Act Sheet 2 4th Quarter Science 8Document3 pagesAct Sheet 2 4th Quarter Science 8Joseph Gabriel Genuino Cruz100% (1)
- The Cell's Life Cycle: Anatomy and Physiology Laboratory ManualDocument6 pagesThe Cell's Life Cycle: Anatomy and Physiology Laboratory ManualJan Edward Abarientos MandaniNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle Worksheet 2Document4 pagesCell Cycle Worksheet 2Rodolf Jones RaboNo ratings yet
- CH - 10 Dragonfly Mitosis Final EditDocument36 pagesCH - 10 Dragonfly Mitosis Final Edit639289117867 JesusmygodNo ratings yet
- Cell Division Work SheetDocument4 pagesCell Division Work SheetYvy Grace OjeñarNo ratings yet
- Untitled Document 2Document6 pagesUntitled Document 2Max TimbergerNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Unit 2.5 WorksheetDocument3 pagesChapter 2 Unit 2.5 Worksheetmaariamshamsi2No ratings yet
- Cell Division Homework 2Document2 pagesCell Division Homework 2runa yuraNo ratings yet
- General Biology Quiz Cell CycleDocument2 pagesGeneral Biology Quiz Cell CycleQueng ElediaNo ratings yet
- The Cell Cycle WorksheetDocument2 pagesThe Cell Cycle WorksheetHarold SagumNo ratings yet
- Student Exploration: Cell Division: Isabella Jacquin Rivas November 24, 2022Document5 pagesStudent Exploration: Cell Division: Isabella Jacquin Rivas November 24, 2022。Poki 。No ratings yet
- The Cell Cycle Worksheet: MatchingDocument2 pagesThe Cell Cycle Worksheet: MatchingElva chika Delia felatiNo ratings yet
- Homework HandoutDocument2 pagesHomework Handoutabdalla abdelhamidNo ratings yet
- Rajeem Outlaw Wright - Mitosis Vs Meiosis BiologyDocument2 pagesRajeem Outlaw Wright - Mitosis Vs Meiosis BiologyRajeem Outlaw WrightNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle Mitosis LectureDocument3 pagesCell Cycle Mitosis LectureFederico FernandezNo ratings yet
- MeiosisDocument5 pagesMeiosispenn hicksNo ratings yet
- The Cell Cycle WorksheetDocument3 pagesThe Cell Cycle WorksheetSelina LiNo ratings yet
- Final Exam For Modular in BiologyDocument3 pagesFinal Exam For Modular in BiologyMa.Janice GarciaNo ratings yet
- Student Exploration: Cell Division: Vocabulary: Cell Division, Centriole, Centromere, Chromatid, Chromatin, ChromosomeDocument5 pagesStudent Exploration: Cell Division: Vocabulary: Cell Division, Centriole, Centromere, Chromatid, Chromatin, ChromosomeBecka RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Mitosis - Worksheet KEYDocument4 pagesMitosis - Worksheet KEYGeorgia0% (1)
- PDFDocument4 pagesPDFYordan Gomez Capellan0% (1)
- Docsity Cell Division 29Document5 pagesDocsity Cell Division 29Jake KreidelNo ratings yet
- 5 1-5 2+St+Guide+23-24Document2 pages5 1-5 2+St+Guide+23-24kparsons938512No ratings yet
- Cell Cycle LabelingDocument1 pageCell Cycle LabelingMaybelle MadridNo ratings yet
- CellcylcereviewDocument2 pagesCellcylcereviewMacKenzieNo ratings yet
- MGS M07 2011 Na CHT A 02Document4 pagesMGS M07 2011 Na CHT A 02rofi modiNo ratings yet
- C and H Practice TestDocument6 pagesC and H Practice Testahmedmustefa773No ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument15 pagesCell DivisionShin3 KimNo ratings yet
- Las in Science 12Document3 pagesLas in Science 12Richez VillaranNo ratings yet
- Biology 1 Q1 Periodical ExaminationDocument4 pagesBiology 1 Q1 Periodical ExaminationJessie PeraltaNo ratings yet
- Mitosis Worksheet - 9ADocument4 pagesMitosis Worksheet - 9Amezna432No ratings yet
- Biology Review 1Document4 pagesBiology Review 1Mehakpreet GillNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Cell DivisionDocument5 pagesChapter 3 Cell DivisionNurul FasihahNo ratings yet
- Midterm Exam - MitosisDocument6 pagesMidterm Exam - MitosisSherefel RosalejosNo ratings yet
- Mitosis QuizDocument2 pagesMitosis Quizkarim karakiraNo ratings yet
- Science 8 2nd Quarter ReviewerDocument5 pagesScience 8 2nd Quarter ReviewerMartin AlvinNo ratings yet
- Cell Division Assignment#2 .123Document3 pagesCell Division Assignment#2 .123jaeminsoftboiNo ratings yet
- High School Biology: Questions & Explanations for Cell & Molecular BiologyFrom EverandHigh School Biology: Questions & Explanations for Cell & Molecular BiologyNo ratings yet
- Deepanshu ReportDocument17 pagesDeepanshu Reportpulkit mishraNo ratings yet
- Herpes LabialisDocument3 pagesHerpes LabialisSuganya MurugaiahNo ratings yet
- Dengue Fever EngDocument17 pagesDengue Fever EngRia Tustina HendrayaniNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 6 DNA RecombinationDocument68 pagesChapter - 6 DNA RecombinationSai HarshNo ratings yet
- Thesis VirusDocument4 pagesThesis Virushan0fus1gij2100% (2)
- DUMMYS026 : LPL - Production Test Collection Centre Sector - 18, Block-E Rohini DELHI 110085Document2 pagesDUMMYS026 : LPL - Production Test Collection Centre Sector - 18, Block-E Rohini DELHI 110085shakh ismailNo ratings yet
- Bovine Papilloma VirusDocument39 pagesBovine Papilloma VirusXoshy A TofiqNo ratings yet
- 7 - The Biliary TractDocument48 pages7 - The Biliary TractKim RamosNo ratings yet
- Mod2 PDFDocument30 pagesMod2 PDFمحمود عامرNo ratings yet
- June 2017 MSDocument20 pagesJune 2017 MSEefaNo ratings yet
- Notes 2019 (Repaired)Document145 pagesNotes 2019 (Repaired)prashant kumarNo ratings yet
- Presentation Sue McConnellDocument112 pagesPresentation Sue McConnellRonald ChevalierNo ratings yet
- Sequencing Technologies - The Next Generation: Michael L. MetzkerDocument16 pagesSequencing Technologies - The Next Generation: Michael L. MetzkerWayne JiaoNo ratings yet
- Epigenetic and Cancer Therapy, 2019Document12 pagesEpigenetic and Cancer Therapy, 2019AbsjeyNo ratings yet
- Mycology McqsDocument6 pagesMycology McqsmryamNo ratings yet
- COVID MutationDocument17 pagesCOVID MutationdhairyasheelNo ratings yet
- Ficha Técnica - Agar NutritivoDocument1 pageFicha Técnica - Agar NutritivoJherson Santamaria EstevesNo ratings yet
- Cokwe 54Document100 pagesCokwe 54maurocadoshNo ratings yet
- Igenetics A Mendelian Approach 1st Edition Russell Test BankDocument9 pagesIgenetics A Mendelian Approach 1st Edition Russell Test Bankesperanzatrinhybziv100% (36)
- Lesson 1 - The Characteristics of CellsDocument12 pagesLesson 1 - The Characteristics of CellsJohny Cristian Mamani ContrerasNo ratings yet
- Tecnicas y Metodos de Laboratorio Clínico 3a EdicionDocument9 pagesTecnicas y Metodos de Laboratorio Clínico 3a EdicionJosé Neftalí Márquez HernándezNo ratings yet
- India The Emerging Hub For Biologics and BiosimilarsDocument22 pagesIndia The Emerging Hub For Biologics and BiosimilarssanjitlNo ratings yet
- Medicine: Primary Testicular T-Lymphoblastic Lymphoma in A ChildDocument5 pagesMedicine: Primary Testicular T-Lymphoblastic Lymphoma in A ChildgalalNo ratings yet
- Bacteriophages and Their Applications PDFDocument12 pagesBacteriophages and Their Applications PDFLuis AlcarazNo ratings yet
- Chapter 08 - Transport in HumansDocument84 pagesChapter 08 - Transport in Humanshussaini polackNo ratings yet
- Xam Idea Biology 12th - PDF QuestionsDocument69 pagesXam Idea Biology 12th - PDF QuestionsDeepa SinghNo ratings yet
- Tiger Milk Mushroom (: Lignosus Rhinocerotis (Cooke) Ryvarden)Document4 pagesTiger Milk Mushroom (: Lignosus Rhinocerotis (Cooke) Ryvarden)Babyruth BalderamaNo ratings yet
- Over DominanceDocument11 pagesOver DominanceJeniNo ratings yet