Professional Documents
Culture Documents
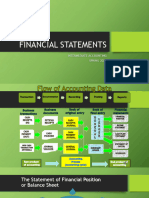
Account Titles
Account Titles
Uploaded by
Kristine JayOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Account Titles
Account Titles
Uploaded by
Kristine JayCopyright:
Available Formats
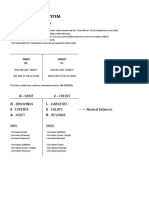
Account Titles
Account Titles:
• refers to the name given to a specific account in the general ledger, which represents a
particular asset, liability, equity, revenue, or expense.
• helps in identifying the nature and purpose of an account, and it is used to record,
classify, and summarize transactions in the financial records of a business.
Five Main Categories:
1. Assets
2. Expenses
3. Liabilities
4. Equity
5. Revenue (or income)
Assets
There are properties or rights to the property owned by the business with future economic
benefits. For an item to be classified as asset, it must satisfy the following requisites:
• Resources of the Business
• Controlled by the Enterprise
• Result of Past Transactions or Events
• Expected to Give Future Benefits
Classification of Assets:
1. Current Assets - an asset is classified as current when it satisfies any of the following
criteria:
• it is expected to be realized in, or is intended for sale or consumption in the entity's
normal operating cycle;
• it is held primarily for the purpose of being traded;
• it is expected to be realized within twelve months after balance sheet date; or
• it is cash or cash equivalent unless it is restricted from being exchanged or used to
settle liability for at least twelve months after balance sheet date
Classification of Current Assets:
1. Cash - account title that describes money, either in paper or coins.
2. Cash on Hand - coins, currency, checks, postal money orders and express
money orders.
3. Cash in Bank - cash deposited in savings and/or checking accounts. The
payments are made by checks.
4. Petty Cash Fund - represents money placed and set aside for "petty" or small
expenses. These are to be used for petty or small payments that cannot be
conveniently made with checks.
Date Developed: Jan 2022
Bookkeeping NCIII
Journalizing Transactions Developed by: Kristine Gonesto
5. Notes Receivables - represents collectibles from customers or clients arising
from sale of goods or services which are supported by promissory notes
executed by the customers.
6. Accounts receivables - represents collectibles from customers arising from
credit sale of goods or services, and not supported by promissory notes.
7. Allowance for Bad Debts - is an "asset offset" or "contra-asset" account which
provides for possible losses from uncollected accounts receivable. This
account title is also called Allowance for doubtful accounts.
8. Interest Receivables - represents the amount of interest earned on note
receivable.
9. Advances to Officers and Employees - represents the amounts collectible from
officers or employees within arising from cash advances.
10. Supplies or Supplies on Hand - represents the cost of stationery, paper, pencil,
ink and other related supplies purchased, and used, but still on hand at the
end of the accounting period. In other words, the account refers to Unused
Supplies.
11. Prepaid Expenses - represents expenses that are paid in advance but not yet
incurred or remain unexpired at the end of the period.
12. Inventories – the unsold goods at the end of the accounting period. This is
applicable only to merchandising business
2. Non-Current Assets - These are properties or resources, controlled by the business not
classified as current assets as a result of past events and from which economic benefits
are expected to flow to the entity
Classification of Non-Current Assets:
1. Property, Plant and Equipment - represents tangible assets which are held by
an enterprise for use in production or supply of goods and services, for rentals
to others or for administrative purposes and are expected to be used during
more than one period.
The following accounts are classified as property, plant and equipment.
• Land - the site where the administrative building, the store or the plant
is located. Building - physical structure on land. These are used in
business.
• Machinery - machines used by the business in the production process.
• Equipment - equipment used by the business for it to be able to perform
its main function or objective. It includes calculators, typewriters, adding
machines, computers, steel filing cabinet, cars used by the business in
its office, store and factory.
• Furniture and Fixture - this account title will include the chairs, tables,
counters, displays cases and be like.
• Accumulated Depreciation - refers to the sum of depreciation for
several years. Depreciation represents the expense portion of the asset
Date Developed: Jan 2022
Bookkeeping NCIII
Journalizing Transactions Developed by: Kristine Gonesto
because of the wear and tear. The decrease in the value of the asset is
technically called depreciation.
2. Long-term Investments - assets held by business entity for the purpose of
accumulating wealth through capital distribution such as interest, royalties,
dividends or rentals. Investments that is not readily marketable and intended
to be held for more than one year.
The following accounts are example of long-term investments:
• Investment in stocks
• Investment in bonds
• Investment in subsidiaries
• Investment in associated using equity method
• sinking fund
• plant expansion fund
3. Intangible Assets - identifiable non-monetary assets without physical
substances held for use in the production or supply of goods or services, for
rental to others, or for administrative purposes.
The typical examples of intangible assets are:
• Copyright
• Patent
• franchise
• trademark
• lease right
• Computer software
• Goodwill
Liabilities
There represent obligations of the enterprises arising from the past transactions or events, the
settlement of which is expected to result in an outflow from the enterprise of resources
embodying economic benefits.
Classification of Liabilities
1. Current Liabilities - A liability is classified as current liability when it satisfies any of the
following criteria:
• it is expected to be settled in the entity's normal operating cycle;
• it is held primarily for the purpose of being traded;
• it is due to be settled within twelve months after balance sheet date; or
• the entity does not have an unconditional right to defer settlement of the liability
for at least twelve months after the balance sheet date.
Classification of Current Liabilities
1. Accounts Payable - denotes obligations or debts of the business arising from
services received, merchandise, supplies or property, plant and equipment
acquired on account. It is amounts due to third parties for purchases on credit.
Date Developed: Jan 2022
Bookkeeping NCIII
Journalizing Transactions Developed by: Kristine Gonesto
2. Notes Payable - includes debts arising from the purchase of an asset or
acquisition of services on account evidenced by a promissory note.
3. Bank Payable or Loans Payable - financial obligations to banks and other
financial institutions arising from funds borrowed by the business from these
institutions; payable within twelve months or shorter.
4. Utilities Payable - an obligation to pay utility companies for services received
from them.
5. Salaries Payable - unpaid salaries of employees and workers for the services
rendered as a date of the financial statements.
6. Interest Payable - unpaid interest to the bank or other financing institutions
because of amounts borrowed.
7. SSS Premium Payable/ PhilHealth Premium Payable/PAG-IBIG Premium
Payable - the amount withheld from the salaries of employees and the
employer's unremitted share contribution to the Social Security System (SSS),
Philippine Health Insurance Corporation (PHIC) and Home Development
Mutual Fund (PAG-IBIG).
8. Unearned Income - income collected or received in advance, but it’s not yet
considered as earned
9. Withholding Tax Payable - amount of income tax withheld from the salaries of
employee.
2. Non-Current Liabilities - are the debts a business owes, but isn't due to pay for at least 12
months. They're also called long-term liabilities.
Classification of Non-current Liabilities:
1. Mortgage Payable - the amount of long-term liability that is supported or
backed up by collateral.
2. Long-Term Bank Loan - is used in presenting a bank loan with maturity period
or the term is beyond one year.
3. Non-current Portion of Long-term Debt - the portion of a debt or a loan that
will not mature within one year from the date of the statement of financial
position.
4. Finance Lease Liability - the liability portion of the asset acquired through
finance lease.
Equity or Capital
These represents the residual interest of the owner in the assets of the business after all its liabilities
Classification of Equity or Capital
1. Capital - the initial investment of the owner at the start of the operation or the beginning
capital of succeeding years.
Date Developed: Jan 2022
Bookkeeping NCIII
Journalizing Transactions Developed by: Kristine Gonesto
2. Withdrawal or Drawing - represents temporary withdrawal of capital by the owner from
the business for his personal use. This account is credited (increased) for business' net
profit and debited (decreased) for the net loss
Income
These increases in economic benefits during the accounting period in the form of inflows or
enhancements of assets or decreases of liabilities that result in increases in equity, other than
those relating to contributions from equity participants.
Classification of Income
1. Service or Sales Income - represents the income realized for all types of income derived
from service rendered and from sale of company.
2. Professional Income - represents the amount of income earned by professionals from the
practice of their professions.
3. Rental Income - the income earned from buildings, space and other properties rented or
leased out by the business.
4. Interest Income - amount of income realized arising from lending operations.
5. Miscellaneous Income - income earned that could not be classified properly on the
above income classifications. It should not represent the primary source of income of the
business
Expense
These decreases in economic benefits during the accounting period in the form of outflows or
depletions of assets or incurrence of liabilities that result in decreases in equity, other than those
relating to distributions to equity participants.
Classification of Expense
1. Salaries and Wages - payments of services rendered by workers and employees.
2. Rent Expense - amount paid for the use of office space, store space, or factory area.
3. Office Supplies Expense - the different materials used by the business in its office or offices,
but not limited to coupon bonds, carbon paper, worksheets, ledgers, ballpens, erasers,
or envelops. This account title is expired or used portion of the office supplies purchased
for office consumption.
4. Store Supplies Expense - store related materials used by the business in its day-to-day of
operations.
5. Insurance Expense - the expired portion of premiums paid on insurance coverage.
6. Interest Expense - the amount of interest paid or incurred during the accounting period.
7. Taxes and Licenses - the, payments for or incurrence of taxes licenses, government fees
and other similar fees.
8. Utilities Expense - the amount incurred or paid for the use of light, water, gas for the
business. Bad Debts Expense or Doubtful Accounts Expense - the amount of receivable
estimated to be doubtful of collection.
Date Developed: Jan 2022
Bookkeeping NCIII
Journalizing Transactions Developed by: Kristine Gonesto
9. Depreciation Expense - the expired portion of the cost of building, machinery,
equipment, store equipment, and other types of property, plant and equipment, except
land.
10. SSS Contribution/PhilHealth Contribution/PAG-IBIG Contribution - the share of the
employer in SSS, PhilHealth and PAG-IBIG for the welfare and benefit of the employees
as required by law.
11. Miscellaneous Expense - used for the amount paid or incurred where separate account
is not necessary because the expenses are immaterial, uncommon, and infrequent.
12. Cost of Sales or Cost of Services - the direct cost of the products sold or the services
rendered.
Date Developed: Jan 2022
Bookkeeping NCIII
Journalizing Transactions Developed by: Kristine Gonesto
You might also like
- CAPIFUND MCA Training Material 2022Document11 pagesCAPIFUND MCA Training Material 2022Carmelo PalaciosNo ratings yet
- Account Titles With DefinitionDocument5 pagesAccount Titles With DefinitionAngelo Miranda88% (8)
- Statement of Financial Position - PPT - Accounts TitlesDocument23 pagesStatement of Financial Position - PPT - Accounts TitlesMg GarciaNo ratings yet
- PropertyGuru 2020 Financial StatementDocument115 pagesPropertyGuru 2020 Financial StatementTerence LeeNo ratings yet
- Essential Elements of The Definition of AccountingDocument9 pagesEssential Elements of The Definition of AccountingPamela Diane Varilla AndalNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Basic Expanded Acctg. Equation Student VersionDocument29 pagesModule 2 Basic Expanded Acctg. Equation Student VersionRowena ReoloNo ratings yet
- ABM ReviewerDocument2 pagesABM Reviewermary christy mantalabaNo ratings yet
- FINACC1 Merged 1 MergedDocument34 pagesFINACC1 Merged 1 MergedTimone PurinoNo ratings yet
- Slides BookkeepingDocument82 pagesSlides BookkeepingErica FlorentinoNo ratings yet
- Account TitlesDocument9 pagesAccount TitlesFaelynnNo ratings yet
- UNIT II The Accounting Process Service and TradingDocument22 pagesUNIT II The Accounting Process Service and TradingAlezandra SantelicesNo ratings yet
- Accounting C2 Lesson 3 PDFDocument5 pagesAccounting C2 Lesson 3 PDFJake ShimNo ratings yet
- Accounting 1 - Module 7Document38 pagesAccounting 1 - Module 7CATHNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 SFPDocument14 pagesLesson 1 SFPLydia Rivera100% (3)
- CHAPTER 2-Accounting EquationDocument91 pagesCHAPTER 2-Accounting EquationHảo HuỳnhNo ratings yet
- HandoutDocument4 pagesHandoutZack CullenNo ratings yet
- Fabm1 Module-3Document14 pagesFabm1 Module-3Honey Shen100% (1)
- Types of Accounts and The Account TitlesDocument25 pagesTypes of Accounts and The Account TitlesSeung BatumbakalNo ratings yet
- Fa Module 2: Accounting Equation: LECTURE 1:the Accounting Equation Assets Liabilities + Owner's EquityDocument6 pagesFa Module 2: Accounting Equation: LECTURE 1:the Accounting Equation Assets Liabilities + Owner's EquitycheskaNo ratings yet
- FABM 1 Lec 2Document7 pagesFABM 1 Lec 2ariannekaryllemercadoNo ratings yet
- FABM1 Module C2Document11 pagesFABM1 Module C2Nathan CapsaNo ratings yet
- Accounting Equation and Double-Entry SystemDocument31 pagesAccounting Equation and Double-Entry SystemKendall JennerNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2: General Purpose Financial Statements: Business Resources Amount From Creditors + Amount From OwnersDocument5 pagesLesson 2: General Purpose Financial Statements: Business Resources Amount From Creditors + Amount From OwnersRomae DomagasNo ratings yet
- Types of Major AccountsDocument5 pagesTypes of Major AccountsJenny SaynoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 - Statement of Financial Position (Part 1)Document10 pagesLesson 5 - Statement of Financial Position (Part 1)yana jungNo ratings yet
- Accounting Terns and DefitionDocument10 pagesAccounting Terns and DefitionReign MontejoNo ratings yet
- FABM 1 Major AccountsDocument31 pagesFABM 1 Major AccountscatajannicolinNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Fabm 1Document4 pagesLesson 2 Fabm 1Janelle Grace PanizalesNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 Accounting ElementsDocument2 pagesLecture 2 Accounting ElementsSAROL, Gwen Alessandra V.No ratings yet
- Fabm 1Document8 pagesFabm 1zachie7770No ratings yet
- Five Major AccountsDocument25 pagesFive Major AccountsRhona Primne ServañezNo ratings yet
- CCD - Bookeeping Module, Lesson 3 & 4Document6 pagesCCD - Bookeeping Module, Lesson 3 & 4Jessa Eve LitangNo ratings yet
- MEFA - IV and V UnitsDocument30 pagesMEFA - IV and V UnitsMOHAMMAD AZEEMANo ratings yet
- CMBE 2 - Lesson 3 ModuleDocument12 pagesCMBE 2 - Lesson 3 ModuleEunice AmbrocioNo ratings yet
- Types of Major AccountsDocument25 pagesTypes of Major AccountsRain Sofia LoquinteNo ratings yet
- Financial ControlDocument9 pagesFinancial Controlima funtanaresNo ratings yet
- Las 3Document8 pagesLas 3Venus Abarico Banque-AbenionNo ratings yet
- A. Under Statement of Financial Position: Typical Account Titles UsedDocument6 pagesA. Under Statement of Financial Position: Typical Account Titles UsedAshlyn MaeNo ratings yet
- EntrepreneurshipDocument3 pagesEntrepreneurshipXty CtyiuNo ratings yet
- Lesson 8 Elements of FsDocument53 pagesLesson 8 Elements of FsSoothing BlendNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Accounting 1 CDocument6 pagesFundamentals of Accounting 1 CAle EalNo ratings yet
- Types of Major AccountsDocument4 pagesTypes of Major AccountsPortia AbestanoNo ratings yet
- Journal Entries 2Document13 pagesJournal Entries 2Kanan DasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Financial Statement Analysis Balance SheetDocument30 pagesChapter 6 Financial Statement Analysis Balance SheetKhadija YaqoobNo ratings yet
- Types of Accounts and The Account Titles: AssetsDocument90 pagesTypes of Accounts and The Account Titles: AssetsNichole Balao-asNo ratings yet
- Fabm Week 4 Study GuideDocument3 pagesFabm Week 4 Study GuideFERNANDO TAMZ2003No ratings yet
- MODULE 5-The Five Major AccountsDocument6 pagesMODULE 5-The Five Major Accountsgerlie gabrielNo ratings yet
- 1five Major AccountsDocument30 pages1five Major AccountsEaster LumangNo ratings yet
- Def of Assets and LiabilitiesDocument6 pagesDef of Assets and LiabilitieslancealcarazNo ratings yet
- C3A Balance SheetDocument3 pagesC3A Balance SheetSteeeeeeeephNo ratings yet
- The Accounting EquationDocument5 pagesThe Accounting EquationHuskyNo ratings yet
- Fabm 1 - Week 4Document3 pagesFabm 1 - Week 4FERNANDO TAMZ2003No ratings yet
- Fabm2 1Document17 pagesFabm2 1Jacel GadonNo ratings yet
- Accounting NotesDocument6 pagesAccounting NotesD AngelaNo ratings yet
- FABM2 - Statement of Financial PositionDocument36 pagesFABM2 - Statement of Financial PositionVron Blatz100% (6)
- Reviewer 2Document14 pagesReviewer 2micahellaise000No ratings yet
- Financial StatementsDocument32 pagesFinancial Statementspeterpark0903No ratings yet
- BFAR 09 - 09 - 2022 Double Entry SystemDocument5 pagesBFAR 09 - 09 - 2022 Double Entry SystemSheryl cornelNo ratings yet
- AE13 - FAR - Accounting Principles Generally Accepted Accounting PrinciplesDocument5 pagesAE13 - FAR - Accounting Principles Generally Accepted Accounting PrinciplesPun YeetahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8-Types of Major AccountsDocument2 pagesChapter 8-Types of Major AccountsRichael Ann Delubio ZapantaNo ratings yet
- "The Language of Business: How Accounting Tells Your Story" "A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding, Interpreting, and Leveraging Financial Statements for Personal and Professional Success"From Everand"The Language of Business: How Accounting Tells Your Story" "A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding, Interpreting, and Leveraging Financial Statements for Personal and Professional Success"No ratings yet
- Stamp Duty Act Amended To 2019-01Document58 pagesStamp Duty Act Amended To 2019-01Issa BoyNo ratings yet
- Pakam, Khiezna E. Bsac-1b Assignment 3-FarDocument5 pagesPakam, Khiezna E. Bsac-1b Assignment 3-FarKhiezna PakamNo ratings yet
- ICARE First Preboard AFARDocument17 pagesICARE First Preboard AFARaceNo ratings yet
- Financial Management: Chapter Three Time Value of MoneyDocument16 pagesFinancial Management: Chapter Three Time Value of MoneyLydiaNo ratings yet
- Blackstone 2 Q 22 Earnings Press ReleaseDocument41 pagesBlackstone 2 Q 22 Earnings Press ReleaseLinh Linh NguyenNo ratings yet
- Nazi War Finance and Banking (1944) PDFDocument105 pagesNazi War Finance and Banking (1944) PDFEmmanuel CookNo ratings yet
- Fabm 2: Quarter 3 - Module 6 Computing and Interpreting Financial RatiosDocument24 pagesFabm 2: Quarter 3 - Module 6 Computing and Interpreting Financial RatiosJunkyu Koala100% (1)
- CFS FormatDocument2 pagesCFS FormatAvanthikaNo ratings yet
- Banking Pricnciples and Practices Lecture Notes ch3Document17 pagesBanking Pricnciples and Practices Lecture Notes ch3ejigu nigussieNo ratings yet
- Business Unit 3 NotesDocument45 pagesBusiness Unit 3 Notesamir dargahiNo ratings yet
- The Cost of Higher Education in MalaysiaDocument12 pagesThe Cost of Higher Education in MalaysiaHAIKAL HAKIMI ABDUL MUIZNo ratings yet
- Dividend PolicyDocument16 pagesDividend PolicyDương Thuỳ TrangNo ratings yet
- Digest Central Bank V CADocument2 pagesDigest Central Bank V CAMeliza RenNo ratings yet
- Neck-Deep in Debt, Is Chenone and Its Parent Company About To Make A Comeback?Document10 pagesNeck-Deep in Debt, Is Chenone and Its Parent Company About To Make A Comeback?Maherban HaiderNo ratings yet
- Financial Sources of Reliance Industries: Chaubey Anandvardhan NagendraDocument9 pagesFinancial Sources of Reliance Industries: Chaubey Anandvardhan NagendraSUNNY GULATI-DM 21DM202No ratings yet
- Contract of Insurance A. Subject Matter of InsuranceDocument4 pagesContract of Insurance A. Subject Matter of InsuranceJim M. MagadanNo ratings yet
- 604f341e40d3960028590d84 1615803988 ACC 124 - Week 8 9 - ULOcDocument14 pages604f341e40d3960028590d84 1615803988 ACC 124 - Week 8 9 - ULOcFrancine Thea M. LantayaNo ratings yet
- Oblicon Chap 1 5 Lecture Notes 1Document27 pagesOblicon Chap 1 5 Lecture Notes 1darren chen100% (1)
- Topic: Partnershi P FormationDocument63 pagesTopic: Partnershi P FormationAllen Hendrick SantiagoNo ratings yet
- 3 Adjusting Entries HandoutsDocument10 pages3 Adjusting Entries HandoutsJuan Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Brief For Petitioner, Tyler v. Hennepin County, No. 22-166 (U.S. Feb. 27, 2023)Document65 pagesBrief For Petitioner, Tyler v. Hennepin County, No. 22-166 (U.S. Feb. 27, 2023)RHTNo ratings yet
- Accounting Theory and PractiseDocument9 pagesAccounting Theory and PractiseDiana And hakimNo ratings yet
- Rise Tax Mock QP With SolutionDocument18 pagesRise Tax Mock QP With SolutionEmperor YasuoNo ratings yet
- Negotiable InstrumentsDocument5 pagesNegotiable InstrumentsJinky MartinezNo ratings yet
- Bikila ResearchDocument57 pagesBikila ResearchBobasa S AhmedNo ratings yet
- Economics Pro Sem3Document23 pagesEconomics Pro Sem3Sumanth RoxtaNo ratings yet
- Analysing Working Capital of Kamps Ecotech PVT LTDDocument43 pagesAnalysing Working Capital of Kamps Ecotech PVT LTDxyzNo ratings yet
- PDF - 13-02-23 14-59-47Document2 pagesPDF - 13-02-23 14-59-47Miraculous IndiaNo ratings yet