Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ChatPDF-WMN QUESTION BANK
ChatPDF-WMN QUESTION BANK
Uploaded by
varadahumaneCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Chapter 5 - Analyzing Ethernet Lan SwitchingDocument79 pagesChapter 5 - Analyzing Ethernet Lan Switchingchris topherNo ratings yet
- 320 - Computer Security - R - 2021Document12 pages320 - Computer Security - R - 2021avfg gfavd100% (1)
- GSM System OverviewDocument12 pagesGSM System Overviewvemala vandanaNo ratings yet
- 19CBS1003 - Mobile Computing - LabDocument6 pages19CBS1003 - Mobile Computing - LabYala yoloNo ratings yet
- 1 - Introduction and Motivation: Evolving of Technology To 4G WirelessDocument13 pages1 - Introduction and Motivation: Evolving of Technology To 4G WirelessSalma SwaidanNo ratings yet
- Assignment No 1Document13 pagesAssignment No 1game palNo ratings yet
- GSM Cellular Network: 1 Principles of GSM Mobile Communication TechnologyDocument17 pagesGSM Cellular Network: 1 Principles of GSM Mobile Communication TechnologyTuan-Anh BuiNo ratings yet
- Global System For Mobile Communication (GSM)Document65 pagesGlobal System For Mobile Communication (GSM)Svv KarthikNo ratings yet
- Overview of The Global System For Mobile CommunicationsDocument25 pagesOverview of The Global System For Mobile Communicationszaid_asiaNo ratings yet
- Unit-4 (Wireless Communication)Document15 pagesUnit-4 (Wireless Communication)Anonymous EjQbY1CNo ratings yet
- Overview of The GSM CommunicationsDocument18 pagesOverview of The GSM CommunicationsronyiutNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of GSMDocument16 pagesFundamentals of GSMKalai SelvanNo ratings yet
- Name-Suvajit Mondal. Stream-E.C.E. Roll No.-3047. Semester-8 - Subject-3G PresentationDocument21 pagesName-Suvajit Mondal. Stream-E.C.E. Roll No.-3047. Semester-8 - Subject-3G PresentationSubir MaityNo ratings yet
- CN Module4 PDFDocument19 pagesCN Module4 PDFRakshith AcchuNo ratings yet
- Mobile TechnologyDocument18 pagesMobile TechnologyLady BugNo ratings yet
- Unit-5: GSM (Global System For Mobile Communication) What Is GSM?Document23 pagesUnit-5: GSM (Global System For Mobile Communication) What Is GSM?AkankshaguptaNo ratings yet
- Wireless and Mobile CommunicationDocument10 pagesWireless and Mobile CommunicationAkash Sankar ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Overview of The Global System For Mobile CommunicationsDocument25 pagesOverview of The Global System For Mobile Communicationsaytacerd0% (1)
- Files 1 2020 September NotesHubDocument 1600957714Document12 pagesFiles 1 2020 September NotesHubDocument 1600957714bapoorv5No ratings yet
- Call Setup in A GSM NetworkDocument6 pagesCall Setup in A GSM NetworkluvdembadNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document12 pagesChapter 4Nandhini PNo ratings yet
- Telecommunication: GSM (Global System For Mobile Communication)Document7 pagesTelecommunication: GSM (Global System For Mobile Communication)Simum100% (1)
- Mobile Computing-Question With Answers SHORT NOTES MCDocument46 pagesMobile Computing-Question With Answers SHORT NOTES MCTauseef khan100% (2)
- Global System For Mobile CommunicationDocument20 pagesGlobal System For Mobile CommunicationGaurav PuriNo ratings yet
- 3.3) Basics of GSMDocument13 pages3.3) Basics of GSMRobin SinghNo ratings yet
- GSM Architecture INGGRISDocument6 pagesGSM Architecture INGGRISJesika Oktavia1110No ratings yet
- GPRSDocument14 pagesGPRSRuhisha AnandNo ratings yet
- John Scourias: A Brief Overview of GSM, byDocument14 pagesJohn Scourias: A Brief Overview of GSM, bymohsinakram1No ratings yet
- GSM OverviewDocument18 pagesGSM Overviewchandunandamuri8940No ratings yet
- Digit AnalysisDocument50 pagesDigit Analysisesther_kakani2029100% (1)
- GSM Technologies ArchitectureDocument18 pagesGSM Technologies ArchitectureHasan HadidiNo ratings yet
- LTE White PaperDocument0 pagesLTE White PaperkidreckNo ratings yet
- WMNDocument25 pagesWMNfracasstoneNo ratings yet
- 8th Semester QuestionsDocument17 pages8th Semester QuestionsArkadeep RoyNo ratings yet
- BSNL 20 PagesDocument16 pagesBSNL 20 PagesJaspreet KaurNo ratings yet
- WMC Lab 3Document12 pagesWMC Lab 3Sandeep RaoNo ratings yet
- 3G & 4G Standards: 1. Explain About Global System For Mobile (GSM)Document8 pages3G & 4G Standards: 1. Explain About Global System For Mobile (GSM)vinod3457No ratings yet
- CSP Unit 4Document12 pagesCSP Unit 4m.revathiNo ratings yet
- GprsDocument24 pagesGprsSalahuddin HusseinNo ratings yet
- Future Developments in Non-Repudiation in GSM WAP ApplicationsDocument12 pagesFuture Developments in Non-Repudiation in GSM WAP ApplicationsJournal of Mobile, Embedded and Distributed Systems (JMEDS)No ratings yet
- Cs9251 Mobile Computing 2marks 16marks Question PapersDocument11 pagesCs9251 Mobile Computing 2marks 16marks Question PapersValar MathiNo ratings yet
- Report On 3g and 4g TechnologyDocument29 pagesReport On 3g and 4g Technologyshujathullas100% (1)
- Cellular ConceptsDocument342 pagesCellular ConceptsTulipNo ratings yet
- UMTS Network Architecture: Wireless Principles and CommunicationDocument11 pagesUMTS Network Architecture: Wireless Principles and CommunicationNuces LahoreNo ratings yet
- DCC Chapter 3Document5 pagesDCC Chapter 3Khan Rahil AhmedNo ratings yet
- Monthly Report 2Document22 pagesMonthly Report 2khalid hussenNo ratings yet
- E4-E5 CM (3G Network Overview)Document11 pagesE4-E5 CM (3G Network Overview)VIKAS NIGAMNo ratings yet
- M.SC Computer Science: Mother Teresa Women'S UniversityDocument96 pagesM.SC Computer Science: Mother Teresa Women'S UniversityRAJESHNo ratings yet
- Rappaport GSMDocument18 pagesRappaport GSMUsman100% (1)
- 4 G Mobile Network ArchitectureDocument13 pages4 G Mobile Network ArchitectureNaeem IslamNo ratings yet
- Ece Department: Associated Minds With This SeminarDocument40 pagesEce Department: Associated Minds With This SeminarSankha MullickNo ratings yet
- Wireless Communication Unit 4Document10 pagesWireless Communication Unit 4Lavanya R GowdaNo ratings yet
- BSNL 20 PagesDocument16 pagesBSNL 20 PagesJaspreet KaurNo ratings yet
- What Is IUBDocument17 pagesWhat Is IUBtuyambaze jean claudeNo ratings yet
- E2 SEM 4 Wireless Communication-1Document15 pagesE2 SEM 4 Wireless Communication-1King of SuccessNo ratings yet
- Program: B.E Subject Name: Mobile Computing Subject Code: EC-8003 Semester: 8thDocument17 pagesProgram: B.E Subject Name: Mobile Computing Subject Code: EC-8003 Semester: 8thNidhi ChavanNo ratings yet
- GPRS NotesDocument15 pagesGPRS NotesAkankshaNo ratings yet
- 502 MC Tut 1Document5 pages502 MC Tut 1Vaibhav AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Cs 72 Mobile Computing 2 Mark Questions Unit I 1) What Are The Categories of Mobile Services?Document20 pagesCs 72 Mobile Computing 2 Mark Questions Unit I 1) What Are The Categories of Mobile Services?Rama SubramanianNo ratings yet
- Q1 Explain Base Station Server Concept in Mobile EnvironmentDocument46 pagesQ1 Explain Base Station Server Concept in Mobile Environmentpurushottam singhNo ratings yet
- UMTS - WCDMA TechnologyDocument10 pagesUMTS - WCDMA TechnologysurvivalofthepolyNo ratings yet
- Software-Defined Networking (SDN) : The Security Review: Journal of Cyber Security TechnologyDocument67 pagesSoftware-Defined Networking (SDN) : The Security Review: Journal of Cyber Security TechnologyPradeep KhaitanNo ratings yet
- Template 4Document2 pagesTemplate 4Rudrali HitechNo ratings yet
- Cisco Catalyst 9200 Series MantenimientoDocument16 pagesCisco Catalyst 9200 Series MantenimientoChamberlain AraujoNo ratings yet
- CMTS - Software - Config - Guide - 2 - 7 - 13 - ToRelease - 6.1.3, 1GDocument678 pagesCMTS - Software - Config - Guide - 2 - 7 - 13 - ToRelease - 6.1.3, 1GGene DrydenNo ratings yet
- Network Infrastructure Upgrade SOWDocument16 pagesNetwork Infrastructure Upgrade SOWobee1234No ratings yet
- Ims Registration OverviewDocument1 pageIms Registration OverviewwriteshekharNo ratings yet
- ITC LAB 3 - NetworkingDocument10 pagesITC LAB 3 - NetworkingpathwayNo ratings yet
- Quick Start Guide: 1. Unpack The Switch and Check Contents 2. Attach The BracketsDocument9 pagesQuick Start Guide: 1. Unpack The Switch and Check Contents 2. Attach The BracketsJohn JacobNo ratings yet
- Ccna Pocket Guide PDFDocument2 pagesCcna Pocket Guide PDFnoerxNo ratings yet
- MPLS Segment RoutingDocument347 pagesMPLS Segment RoutingDúber PérezNo ratings yet
- Super Flexible, Super Fast, Super Value: Gigabit PTMP Client and PTP With Modular AntennasDocument5 pagesSuper Flexible, Super Fast, Super Value: Gigabit PTMP Client and PTP With Modular AntennasAbdallaNo ratings yet
- GT v7 0 X Performance Element User ManualDocument406 pagesGT v7 0 X Performance Element User Manualburrows0050% (2)
- DG WLAN Secure Guest Access ArubaOS25Document43 pagesDG WLAN Secure Guest Access ArubaOS25luisNo ratings yet
- All About ARPDocument15 pagesAll About ARPazrul asreeNo ratings yet
- Assessment 1 (Wireless Network Solved)Document23 pagesAssessment 1 (Wireless Network Solved)Amna QayyumNo ratings yet
- PC Worx Function Blocks Rev 18Document63 pagesPC Worx Function Blocks Rev 18Centrala MetalaNo ratings yet
- OpenLAB CDS RequirementsDocument74 pagesOpenLAB CDS Requirementskhawar.nehalNo ratings yet
- Cisco Aci Avi Vantage Design GuideDocument23 pagesCisco Aci Avi Vantage Design GuidemervisNo ratings yet
- Seminar ReportDocument22 pagesSeminar ReportSyed Ahmed HussainiNo ratings yet
- KEVIN STEWART ResumeDocument3 pagesKEVIN STEWART ResumeaaravaNo ratings yet
- Era Day3 Part1Document129 pagesEra Day3 Part1Jitendra AsatiNo ratings yet
- Full Download Ebook PDF A Practical Guide To Advanced Networking 3rd Edition PDFDocument41 pagesFull Download Ebook PDF A Practical Guide To Advanced Networking 3rd Edition PDFlydia.hawkins293100% (35)
- Rail Metro Brochure Critical Networks Services ENG WDocument4 pagesRail Metro Brochure Critical Networks Services ENG Wdrrpubli3309No ratings yet
- Assignment: Software Defined Networking (SDN)Document12 pagesAssignment: Software Defined Networking (SDN)Rosemelyne WartdeNo ratings yet
- Ethernet PDF TutorialDocument2 pagesEthernet PDF TutorialNickNo ratings yet
- Ports and Protocols 2022Document1 pagePorts and Protocols 2022Raelene GarzaNo ratings yet
- Monograph Wasima Habib AutoDocument99 pagesMonograph Wasima Habib AutoheliNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Transport LayerDocument57 pagesIntroduction To Transport LayerkjhofboaNo ratings yet
ChatPDF-WMN QUESTION BANK
ChatPDF-WMN QUESTION BANK
Uploaded by
varadahumaneOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
ChatPDF-WMN QUESTION BANK
ChatPDF-WMN QUESTION BANK
Uploaded by
varadahumaneCopyright:
Available Formats
PDF: Welcome to the WMN Question Bank PDF file!
This document contains a
comprehensive list of questions related to GPRS, GSM, Bluetooth, WIFI, and other
wireless communication technologies. Whether you are a student studying these
topics or a professional looking to refresh your knowledge, this PDF file is here
to help you.
Example questions:
1. Can you explain the function of a temporary identity subscriber in GSM?
2. How does GPRS architecture differ from GSM architecture?
3. What are the services offered in GSM?
Me: give me answers to all the questions asked in this pdf
PDF: I can provide answers to the questions listed in the PDF file. Here are the
answers:
1. List any two GPRS services:
- Two GPRS services are:
1. Packet-Switched Data Service
2. Multimedia Messaging Service
2. Write the function of a temporary identity subscriber:
- The temporary identity subscriber is used to provide a temporary identity to
the subscriber when they are roaming in a different network. It helps in
maintaining the subscriber's identity and ensuring seamless connectivity.
3. List services offered in GSM:
- Services offered in GSM include:
- Voice services
- Short Message Service (SMS)
- Data services
- Supplementary services like call forwarding, call waiting, etc.
4. Write the IEEE standard for Bluetooth WIFI:
- The IEEE standard for Bluetooth is IEEE 802.15.1, and for WIFI, it is IEEE
802.11.
5. Write two functions of HLR & VLR:
- Home Location Register (HLR):
1. Stores subscriber information and location data.
2. Manages subscriber authentication and call routing.
- Visitor Location Register (VLR):
1. Stores temporary subscriber information when they are in a visiting
network.
2. Handles call setup and mobility management for roaming subscribers.
6. Write the function of EUC & EIR:
- Equipment Identity Check (EUC):
- Verifies the identity of mobile equipment to prevent theft and fraud.
- Equipment Identity Register (EIR):
- Stores a list of valid mobile equipment identities to check against
unauthorized devices.
Please let me know if you need answers to more questions from the PDF file.
Me: give me all 24 answers
PDF: I can provide answers to all 24 questions listed in the PDF file. Here are the
answers:
1. List any two GPRS services:
- Two GPRS services are:
1. Packet-Switched Data Service
2. Multimedia Messaging Service
2. Write the function of a temporary identity subscriber:
- The temporary identity subscriber is used to provide a temporary identity to
the subscriber when they are roaming in a different network. It helps in
maintaining the subscriber's identity and ensuring seamless connectivity.
3. List services offered in GSM:
- Services offered in GSM include:
- Voice services
- Short Message Service (SMS)
- Data services
- Supplementary services like call forwarding, call waiting, etc.
4. Write the IEEE standard for Bluetooth WIFI:
- The IEEE standard for Bluetooth is IEEE 802.15.1, and for WIFI, it is IEEE
802.11.
5. Write two functions of HLR & VLR:
- Home Location Register (HLR):
1. Stores subscriber information and location data.
2. Manages subscriber authentication and call routing.
- Visitor Location Register (VLR):
1. Stores temporary subscriber information when they are in a visiting
network.
2. Handles call setup and mobility management for roaming subscribers.
6. Write the function of EUC & EIR:
- Equipment Identity Check (EUC):
- Verifies the identity of mobile equipment to prevent theft and fraud.
- Equipment Identity Register (EIR):
- Stores a list of valid mobile equipment identities to check against
unauthorized devices.
7. Describe call processing in GSM:
- Call processing in GSM involves various steps such as call setup,
authentication, encryption, routing, and handover to ensure seamless voice
communication between mobile devices.
8. What is the Wireless Application Protocol (WAP):
- The Wireless Application Protocol is a standard for accessing information over
a mobile wireless network. It enables mobile devices to access web content and
services tailored for small screens and limited bandwidth.
9. Describe Wireless Markup Language (WML):
- Wireless Markup Language is a markup language used to create content for WAP-
enabled devices. It is similar to HTML but optimized for mobile browsing with
features like card-based navigation and limited graphics support.
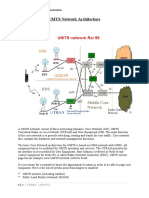
10. Explain GPRS architecture with a neat diagram:
- The GPRS architecture consists of elements like SGSN, GGSN, BSC, and BTS
interconnected to provide packet-switched data services over GSM networks. Refer to
a diagram for a detailed illustration.
11. Explain Home Agent & Foreign Agent:
- Home Agent is a router on the home network that maintains the permanent
address of a mobile node in Mobile IP. Foreign Agent is a router on a foreign
network that assists in routing packets to and from the mobile node when it is away
from its home network.
12. Explain Personal Communication Service (PCS):
- Personal Communication Service refers to wireless communication services that
offer a combination of voice, data, and multimedia services to individual users. It
provides enhanced features and mobility compared to traditional landline services.
13. Explain GPRS services:
- GPRS services include packet-switched data services, multimedia messaging,
internet browsing, email access, and mobile VPN services. These services enable
efficient data transmission over GSM networks.
14. Explain how GPRS architecture differs from GSM architecture:
- GPRS architecture introduces additional elements like SGSN and GGSN to
support packet-switched data services, while GSM architecture focuses on circuit-
switched voice services. GPRS enables faster data transmission and efficient use of
network resources compared to GSM.
15. Distinguish between Bluetooth & WIFI based on range, bandwidth, modulation
technique, number of devices connected:
- Bluetooth:
- Range: Short-range communication (typically up to 10 meters).
- Bandwidth: Lower bandwidth suitable for voice and data transfer.
- Modulation Technique: Frequency-hopping spread spectrum.
- Number of Devices Connected: Supports connecting multiple devices
simultaneously.
- WIFI:
- Range: Longer-range communication (up to hundreds of meters).
- Bandwidth: Higher bandwidth suitable for high-speed data transfer.
- Modulation Technique: Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM).
- Number of Devices Connected: Supports connecting multiple devices to a
single access point.
16. Explain the principle of Mobile IP:
- Mobile IP is a protocol that enables mobile devices to maintain continuous
connectivity while moving between different networks. It assigns a unique IP
address to the mobile device, allowing seamless communication without changing the
device's IP address.
17. Explain GSM Traffic Channel:
- GSM Traffic Channels are used for carrying voice and data traffic between
mobile devices and the base station. They are divided into Full Rate, Half Rate,
and Enhanced Full Rate channels to optimize bandwidth usage and call quality.
18. Explain the architecture of GSM:
- The GSM architecture consists of elements like Mobile Station (MS), Base
Station Subsystem (BSS), Network Switching Subsystem (NSS), and Operation Support
Subsystem (OSS) interconnected to provide mobile communication services.
19. Explain GSM Frequency Spectrum:
- GSM operates in the 900 MHz and 1800 MHz frequency bands, divided into uplink
and downlink channels for communication between mobile devices and base stations.
The frequency spectrum is allocated to different operators to avoid interference.
20. Explain the mobility of the database:
- The mobility of the database refers to the ability of subscriber information
to move between different network elements like HLR and VLR as subscribers roam
between different networks. This ensures seamless connectivity and service
availability.
21. Explain features of GPRS architecture:
- GPRS architecture features elements like SGSN, GGSN, BSC, and BTS
interconnected to provide packet-switched data services with features like IP
connectivity, efficient resource allocation, and support for multimedia
applications.
22. Explain Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) with a neat diagram:
- Radio Frequency Identification is a technology that uses radio waves to
identify and track objects or individuals. It consists of tags (transponders)
attached to objects, readers to communicate with tags, and a backend system for
data processing. Refer to a diagram for a detailed illustration.
23. Explain in detail SGSM & GGSM:
- SGSM (Simultaneous GSM) and GGSM (GPRS over GSM) are technologies that enable
simultaneous voice and data services over GSM networks. SGSM allows voice and data
transmission concurrently, while GGSM enhances GSM networks to support GPRS data
services.
24. Explain the concept of Mobile IP with a neat diagram:
- Mobile IP is a protocol that enables mobile devices to maintain connectivity
while moving between networks by assigning a unique IP address. The concept
involves home agents, foreign agents, and mobile nodes to facilitate seamless
communication. Refer to a diagram for a detailed illustration.
These answers provide a comprehensive overview of the topics covered in the WMN
Question Bank PDF file. If you need further clarification or additional
information, feel free to ask.
Me: elgonate these answers so that i can use them to study for my test
PDF: Certainly! Here are the elaborated answers for each question to help you study
for your test:
1. **List any two GPRS services:**
- GPRS (General Packet Radio Service) offers various services to mobile users.
Two key services are:
- **Packet-Switched Data Service:** GPRS enables the transmission of data in
packets, allowing users to access the internet, send/receive emails, and use
various data applications.
- **Multimedia Messaging Service (MMS):** GPRS supports MMS, allowing users to
send multimedia content such as images, videos, and audio files over the mobile
network.
2. **Write the function of a temporary identity subscriber:**
- The temporary identity subscriber function is crucial for maintaining user
identity during roaming. It provides a temporary identity to the subscriber when
they are in a different network, ensuring seamless connectivity and service
availability while roaming.
3. **List services offered in GSM:**
- GSM (Global System for Mobile Communications) provides a range of services,
including:
- **Voice services:** Basic voice calls between mobile users.
- **Short Message Service (SMS):** Text messaging service for sending short
messages.
- **Data services:** Basic data transmission services for accessing the
internet and basic data applications.
- **Supplementary services:** Additional services like call forwarding, call
waiting, and conference calling to enhance user experience.
4. **Write the IEEE standard for Bluetooth WIFI:**
- The IEEE standards for wireless technologies are:
- **Bluetooth:** IEEE 802.15.1
- **WIFI:** IEEE 802.11
5. **Write two functions of HLR & VLR:**
- **Home Location Register (HLR):**
- **Stores subscriber information:** HLR stores subscriber data, including
user profiles, services subscribed, and location information.
- **Manages subscriber authentication:** HLR authenticates subscribers and
authorizes network access.
- **Visitor Location Register (VLR):**
- **Stores temporary subscriber information:** VLR stores temporary data of
roaming subscribers for efficient call routing.
- **Handles call setup and mobility management:** VLR manages call setup and
facilitates seamless mobility for roaming subscribers.
6. **Write the function of EUC & EIR:**
- **Equipment Identity Check (EUC):**
- EUC verifies the identity of mobile equipment to prevent theft and fraud by
checking the equipment's identity against a list of authorized devices.
- **Equipment Identity Register (EIR):**
- EIR maintains a database of valid mobile equipment identities to verify the
authenticity of devices connecting to the network and prevent unauthorized access.
7. **Describe call processing in GSM:**
- Call processing in GSM involves several steps, including call setup,
authentication, encryption, routing, and handover. These processes ensure seamless
voice communication between mobile devices within the GSM network.
8. **What is the Wireless Application Protocol (WAP):**
- The Wireless Application Protocol (WAP) is a standard for accessing
information over mobile wireless networks. It enables mobile devices to access web
content and services optimized for small screens and limited bandwidth, enhancing
the mobile browsing experience.
9. **Describe Wireless Markup Language (WML):**
- Wireless Markup Language (WML) is a markup language used to create content for
WAP-enabled devices. It is similar to HTML but tailored for mobile browsing,
featuring card-based navigation and limited graphics support to optimize content
delivery on mobile devices.
10. **Explain GPRS architecture with a neat diagram:**
- The GPRS architecture comprises elements like Serving GPRS Support Node
(SGSN), Gateway GPRS Support Node (GGSN), Base Station Controller (BSC), and Base
Transceiver Station (BTS) interconnected to provide packet-switched data services
over GSM networks. Refer to a diagram for a visual representation of the
architecture.
11. **Explain Home Agent & Foreign Agent:**
- **Home Agent:** Home Agent is a router on the home network that maintains the
permanent address of a mobile node in Mobile IP, ensuring seamless communication
and mobility management.
- **Foreign Agent:** Foreign Agent is a router on a foreign network that
assists in routing packets to and from the mobile node when it is away from its
home network, facilitating communication during roaming.
12. **Explain Personal Communication Service (PCS):**
- Personal Communication Service (PCS) offers a comprehensive range of wireless
communication services, including voice, data, and multimedia services tailored to
individual users. PCS provides enhanced features, mobility, and connectivity
compared to traditional landline services, catering to diverse communication needs.
13. **Explain GPRS services:**
- GPRS services encompass packet-switched data services, multimedia messaging,
internet browsing, email access, and mobile VPN services. These services enable
efficient data transmission over GSM networks, enhancing user connectivity and data
access capabilities.
14. **Explain how GPRS architecture differs from GSM architecture:**
- GPRS architecture introduces additional elements like SGSN and GGSN to
support packet-switched data services, enhancing data transmission efficiency
compared to the circuit-switched voice-centric GSM architecture. GPRS enables
faster data transfer and optimized network resource utilization, distinguishing it
from traditional GSM architecture.
15. **Distinguish between Bluetooth & WIFI based on range, bandwidth, modulation
technique, number of devices connected:**
- **Bluetooth:**
- **Range:** Short-range communication (up to 10 meters).
- **Bandwidth:** Lower bandwidth suitable for voice and data transfer.
- **Modulation Technique:** Frequency-hopping spread spectrum.
- **Number of Devices Connected:** Supports connecting multiple devices
simultaneously.
- **WIFI:**
- **Range:** Longer-range communication (up to hundreds of meters).
- **Bandwidth:** Higher bandwidth suitable for high-speed data transfer.
- **Modulation Technique:** Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing
(OFDM).
- **Number of Devices Connected:** Supports connecting multiple devices to a
single access point.
16. **Explain the principle of Mobile IP:**
- Mobile IP is a protocol that enables mobile devices to maintain continuous
connectivity while moving between different networks by assigning a unique IP
address to the mobile device. This allows seamless communication without changing
the device's IP address, ensuring uninterrupted connectivity during mobility.
17. **Explain GSM Traffic Channel:**
- GSM Traffic Channels facilitate voice and data traffic between mobile devices
and base stations. These channels are categorized into Full Rate, Half Rate, and
Enhanced Full Rate channels to optimize bandwidth usage and ensure high-quality
voice communication within the GSM network.
18. **Explain the architecture of GSM:**
- The GSM architecture comprises essential elements like Mobile Station (MS),
Base Station Subsystem (BSS), Network Switching Subsystem (NSS), and Operation
Support Subsystem (OSS) interconnected to provide mobile communication services.
Each component plays a vital role in ensuring seamless voice and data connectivity
for GSM users.
19. **Explain GSM Frequency Spectrum:**
- GSM operates within the 900 MHz and 1800 MHz frequency bands, divided into
uplink and downlink channels for communication between mobile devices and base
stations. The frequency spectrum is allocated to different operators to prevent
interference and ensure efficient communication within the GSM network.
20. **Explain the mobility of the database:**
- The mobility of the database refers to the seamless transfer of subscriber
information between network elements like HLR and VLR as subscribers move between
different networks. This mobility ensures continuous connectivity and service
availability for roaming subscribers, enhancing user experience and network
efficiency.
21. **Explain features of GPRS architecture:**
- GPRS architecture incorporates elements like SGSN, GGSN, BSC, and BTS
interconnected to provide packet-switched data services with features such as IP
connectivity, efficient resource allocation, and support for multimedia
applications. These features enhance data transmission efficiency and user
experience within the GPRS network.
22. **Explain Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) with a neat diagram:**
- Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) is a technology that uses radio waves
to identify and track objects or individuals. It comprises tags (transponders),
readers, and a backend system for data processing. Refer to a diagram for a visual
representation of RFID technology and its components.
23. **Explain in detail SGSM & GGSM:**
- **SGSM (Simultaneous GSM):** SGSM enables simultaneous voice and data
services over GSM networks, allowing users to engage in voice calls and data
transmission concurrently.
- **GGSM (GPRS over GSM):** GGSM enhances GSM networks to support GPRS data
services, enabling users to access packet-switched data services over existing GSM
infrastructure. GGSM optimizes data transmission and enhances network capabilities
for data-centric applications.
24. **Explain the concept of Mobile IP with a neat diagram:**
- Mobile IP is a protocol that facilitates continuous connectivity for mobile
devices as they move between networks by assigning a unique IP address. The concept
involves home agents, foreign agents, and mobile nodes to ensure seamless
communication during mobility. Refer to a diagram for a visual representation of
Mobile IP architecture and its components.
These elaborated answers provide in-depth explanations of the topics covered in the
WMN Question Bank PDF file. Feel free to review and study these answers for your
test preparation. If you have any further questions or need additional
clarification, please let me know. Good luck with your studies and your test!
You might also like
- Chapter 5 - Analyzing Ethernet Lan SwitchingDocument79 pagesChapter 5 - Analyzing Ethernet Lan Switchingchris topherNo ratings yet
- 320 - Computer Security - R - 2021Document12 pages320 - Computer Security - R - 2021avfg gfavd100% (1)
- GSM System OverviewDocument12 pagesGSM System Overviewvemala vandanaNo ratings yet
- 19CBS1003 - Mobile Computing - LabDocument6 pages19CBS1003 - Mobile Computing - LabYala yoloNo ratings yet
- 1 - Introduction and Motivation: Evolving of Technology To 4G WirelessDocument13 pages1 - Introduction and Motivation: Evolving of Technology To 4G WirelessSalma SwaidanNo ratings yet
- Assignment No 1Document13 pagesAssignment No 1game palNo ratings yet
- GSM Cellular Network: 1 Principles of GSM Mobile Communication TechnologyDocument17 pagesGSM Cellular Network: 1 Principles of GSM Mobile Communication TechnologyTuan-Anh BuiNo ratings yet
- Global System For Mobile Communication (GSM)Document65 pagesGlobal System For Mobile Communication (GSM)Svv KarthikNo ratings yet
- Overview of The Global System For Mobile CommunicationsDocument25 pagesOverview of The Global System For Mobile Communicationszaid_asiaNo ratings yet
- Unit-4 (Wireless Communication)Document15 pagesUnit-4 (Wireless Communication)Anonymous EjQbY1CNo ratings yet
- Overview of The GSM CommunicationsDocument18 pagesOverview of The GSM CommunicationsronyiutNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of GSMDocument16 pagesFundamentals of GSMKalai SelvanNo ratings yet
- Name-Suvajit Mondal. Stream-E.C.E. Roll No.-3047. Semester-8 - Subject-3G PresentationDocument21 pagesName-Suvajit Mondal. Stream-E.C.E. Roll No.-3047. Semester-8 - Subject-3G PresentationSubir MaityNo ratings yet
- CN Module4 PDFDocument19 pagesCN Module4 PDFRakshith AcchuNo ratings yet
- Mobile TechnologyDocument18 pagesMobile TechnologyLady BugNo ratings yet
- Unit-5: GSM (Global System For Mobile Communication) What Is GSM?Document23 pagesUnit-5: GSM (Global System For Mobile Communication) What Is GSM?AkankshaguptaNo ratings yet
- Wireless and Mobile CommunicationDocument10 pagesWireless and Mobile CommunicationAkash Sankar ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Overview of The Global System For Mobile CommunicationsDocument25 pagesOverview of The Global System For Mobile Communicationsaytacerd0% (1)
- Files 1 2020 September NotesHubDocument 1600957714Document12 pagesFiles 1 2020 September NotesHubDocument 1600957714bapoorv5No ratings yet
- Call Setup in A GSM NetworkDocument6 pagesCall Setup in A GSM NetworkluvdembadNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document12 pagesChapter 4Nandhini PNo ratings yet
- Telecommunication: GSM (Global System For Mobile Communication)Document7 pagesTelecommunication: GSM (Global System For Mobile Communication)Simum100% (1)
- Mobile Computing-Question With Answers SHORT NOTES MCDocument46 pagesMobile Computing-Question With Answers SHORT NOTES MCTauseef khan100% (2)
- Global System For Mobile CommunicationDocument20 pagesGlobal System For Mobile CommunicationGaurav PuriNo ratings yet
- 3.3) Basics of GSMDocument13 pages3.3) Basics of GSMRobin SinghNo ratings yet
- GSM Architecture INGGRISDocument6 pagesGSM Architecture INGGRISJesika Oktavia1110No ratings yet
- GPRSDocument14 pagesGPRSRuhisha AnandNo ratings yet
- John Scourias: A Brief Overview of GSM, byDocument14 pagesJohn Scourias: A Brief Overview of GSM, bymohsinakram1No ratings yet
- GSM OverviewDocument18 pagesGSM Overviewchandunandamuri8940No ratings yet
- Digit AnalysisDocument50 pagesDigit Analysisesther_kakani2029100% (1)
- GSM Technologies ArchitectureDocument18 pagesGSM Technologies ArchitectureHasan HadidiNo ratings yet
- LTE White PaperDocument0 pagesLTE White PaperkidreckNo ratings yet
- WMNDocument25 pagesWMNfracasstoneNo ratings yet
- 8th Semester QuestionsDocument17 pages8th Semester QuestionsArkadeep RoyNo ratings yet
- BSNL 20 PagesDocument16 pagesBSNL 20 PagesJaspreet KaurNo ratings yet
- WMC Lab 3Document12 pagesWMC Lab 3Sandeep RaoNo ratings yet
- 3G & 4G Standards: 1. Explain About Global System For Mobile (GSM)Document8 pages3G & 4G Standards: 1. Explain About Global System For Mobile (GSM)vinod3457No ratings yet
- CSP Unit 4Document12 pagesCSP Unit 4m.revathiNo ratings yet
- GprsDocument24 pagesGprsSalahuddin HusseinNo ratings yet
- Future Developments in Non-Repudiation in GSM WAP ApplicationsDocument12 pagesFuture Developments in Non-Repudiation in GSM WAP ApplicationsJournal of Mobile, Embedded and Distributed Systems (JMEDS)No ratings yet
- Cs9251 Mobile Computing 2marks 16marks Question PapersDocument11 pagesCs9251 Mobile Computing 2marks 16marks Question PapersValar MathiNo ratings yet
- Report On 3g and 4g TechnologyDocument29 pagesReport On 3g and 4g Technologyshujathullas100% (1)
- Cellular ConceptsDocument342 pagesCellular ConceptsTulipNo ratings yet
- UMTS Network Architecture: Wireless Principles and CommunicationDocument11 pagesUMTS Network Architecture: Wireless Principles and CommunicationNuces LahoreNo ratings yet
- DCC Chapter 3Document5 pagesDCC Chapter 3Khan Rahil AhmedNo ratings yet
- Monthly Report 2Document22 pagesMonthly Report 2khalid hussenNo ratings yet
- E4-E5 CM (3G Network Overview)Document11 pagesE4-E5 CM (3G Network Overview)VIKAS NIGAMNo ratings yet
- M.SC Computer Science: Mother Teresa Women'S UniversityDocument96 pagesM.SC Computer Science: Mother Teresa Women'S UniversityRAJESHNo ratings yet
- Rappaport GSMDocument18 pagesRappaport GSMUsman100% (1)
- 4 G Mobile Network ArchitectureDocument13 pages4 G Mobile Network ArchitectureNaeem IslamNo ratings yet
- Ece Department: Associated Minds With This SeminarDocument40 pagesEce Department: Associated Minds With This SeminarSankha MullickNo ratings yet
- Wireless Communication Unit 4Document10 pagesWireless Communication Unit 4Lavanya R GowdaNo ratings yet
- BSNL 20 PagesDocument16 pagesBSNL 20 PagesJaspreet KaurNo ratings yet
- What Is IUBDocument17 pagesWhat Is IUBtuyambaze jean claudeNo ratings yet
- E2 SEM 4 Wireless Communication-1Document15 pagesE2 SEM 4 Wireless Communication-1King of SuccessNo ratings yet
- Program: B.E Subject Name: Mobile Computing Subject Code: EC-8003 Semester: 8thDocument17 pagesProgram: B.E Subject Name: Mobile Computing Subject Code: EC-8003 Semester: 8thNidhi ChavanNo ratings yet
- GPRS NotesDocument15 pagesGPRS NotesAkankshaNo ratings yet
- 502 MC Tut 1Document5 pages502 MC Tut 1Vaibhav AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Cs 72 Mobile Computing 2 Mark Questions Unit I 1) What Are The Categories of Mobile Services?Document20 pagesCs 72 Mobile Computing 2 Mark Questions Unit I 1) What Are The Categories of Mobile Services?Rama SubramanianNo ratings yet
- Q1 Explain Base Station Server Concept in Mobile EnvironmentDocument46 pagesQ1 Explain Base Station Server Concept in Mobile Environmentpurushottam singhNo ratings yet
- UMTS - WCDMA TechnologyDocument10 pagesUMTS - WCDMA TechnologysurvivalofthepolyNo ratings yet
- Software-Defined Networking (SDN) : The Security Review: Journal of Cyber Security TechnologyDocument67 pagesSoftware-Defined Networking (SDN) : The Security Review: Journal of Cyber Security TechnologyPradeep KhaitanNo ratings yet
- Template 4Document2 pagesTemplate 4Rudrali HitechNo ratings yet
- Cisco Catalyst 9200 Series MantenimientoDocument16 pagesCisco Catalyst 9200 Series MantenimientoChamberlain AraujoNo ratings yet
- CMTS - Software - Config - Guide - 2 - 7 - 13 - ToRelease - 6.1.3, 1GDocument678 pagesCMTS - Software - Config - Guide - 2 - 7 - 13 - ToRelease - 6.1.3, 1GGene DrydenNo ratings yet
- Network Infrastructure Upgrade SOWDocument16 pagesNetwork Infrastructure Upgrade SOWobee1234No ratings yet
- Ims Registration OverviewDocument1 pageIms Registration OverviewwriteshekharNo ratings yet
- ITC LAB 3 - NetworkingDocument10 pagesITC LAB 3 - NetworkingpathwayNo ratings yet
- Quick Start Guide: 1. Unpack The Switch and Check Contents 2. Attach The BracketsDocument9 pagesQuick Start Guide: 1. Unpack The Switch and Check Contents 2. Attach The BracketsJohn JacobNo ratings yet
- Ccna Pocket Guide PDFDocument2 pagesCcna Pocket Guide PDFnoerxNo ratings yet
- MPLS Segment RoutingDocument347 pagesMPLS Segment RoutingDúber PérezNo ratings yet
- Super Flexible, Super Fast, Super Value: Gigabit PTMP Client and PTP With Modular AntennasDocument5 pagesSuper Flexible, Super Fast, Super Value: Gigabit PTMP Client and PTP With Modular AntennasAbdallaNo ratings yet
- GT v7 0 X Performance Element User ManualDocument406 pagesGT v7 0 X Performance Element User Manualburrows0050% (2)
- DG WLAN Secure Guest Access ArubaOS25Document43 pagesDG WLAN Secure Guest Access ArubaOS25luisNo ratings yet
- All About ARPDocument15 pagesAll About ARPazrul asreeNo ratings yet
- Assessment 1 (Wireless Network Solved)Document23 pagesAssessment 1 (Wireless Network Solved)Amna QayyumNo ratings yet
- PC Worx Function Blocks Rev 18Document63 pagesPC Worx Function Blocks Rev 18Centrala MetalaNo ratings yet
- OpenLAB CDS RequirementsDocument74 pagesOpenLAB CDS Requirementskhawar.nehalNo ratings yet
- Cisco Aci Avi Vantage Design GuideDocument23 pagesCisco Aci Avi Vantage Design GuidemervisNo ratings yet
- Seminar ReportDocument22 pagesSeminar ReportSyed Ahmed HussainiNo ratings yet
- KEVIN STEWART ResumeDocument3 pagesKEVIN STEWART ResumeaaravaNo ratings yet
- Era Day3 Part1Document129 pagesEra Day3 Part1Jitendra AsatiNo ratings yet
- Full Download Ebook PDF A Practical Guide To Advanced Networking 3rd Edition PDFDocument41 pagesFull Download Ebook PDF A Practical Guide To Advanced Networking 3rd Edition PDFlydia.hawkins293100% (35)
- Rail Metro Brochure Critical Networks Services ENG WDocument4 pagesRail Metro Brochure Critical Networks Services ENG Wdrrpubli3309No ratings yet
- Assignment: Software Defined Networking (SDN)Document12 pagesAssignment: Software Defined Networking (SDN)Rosemelyne WartdeNo ratings yet
- Ethernet PDF TutorialDocument2 pagesEthernet PDF TutorialNickNo ratings yet
- Ports and Protocols 2022Document1 pagePorts and Protocols 2022Raelene GarzaNo ratings yet
- Monograph Wasima Habib AutoDocument99 pagesMonograph Wasima Habib AutoheliNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Transport LayerDocument57 pagesIntroduction To Transport LayerkjhofboaNo ratings yet