Professional Documents
Culture Documents
N Gen Math Algebra I.Unit 1.lesson 3.the Distributive Property
N Gen Math Algebra I.Unit 1.lesson 3.the Distributive Property
Uploaded by
arg456Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
N Gen Math Algebra I.Unit 1.lesson 3.the Distributive Property
N Gen Math Algebra I.Unit 1.lesson 3.the Distributive Property
Uploaded by
arg456Copyright:
Available Formats
Name: ____________________________________ Date: __________________
THE DISTRIBUTIVE PROPERTY
N-GEN MATH® ALGEBRA I
In the last lesson we saw two important properties of addition and multiplication: the commutative and
associative. The last of the three major properties combines addition and multiplication: the distributive property.
The first exercise will illustrate the idea.
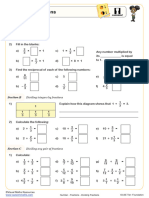
Exercise #1: Consider the product 4 15 .
(a) Evaluate using the standard algorithm. (b) Represent the equivalent product 4 10 5 as
repeated addition of 10 and 5. Find the product.
Exercise #1 shows the important property of being able to apply multiplication to all parts of a sum. In symbolic
form:
THE DISTRIBUTIVE PROPERTY (OF MULTIPLICATION OVER ADDITION AND SUBTRACTION)
If a, b, and c all represent real numbers then:
Exercise #2: Evaluate each product by using the distributive property to make it easier. On (b), express 18 as a
subtraction. Do not use a calculator.
(a) 7 23 (b) 9 18
Exercise #3: The distributive property can be used twice in order to multiply two-digit numbers. Find the product
12 28 by evaluating 10 2 20 8 . Show each step in your calculation. Do not use a calculator unless it
is to check.
® N-GEN MATH® ALGEBRA I – UNIT 1 – BUILDING BLOCKS OF ALGEBRA – LESSON 3 ®
eMATHinstruction, RED HOOK, NY 12571, © 2022
The distributive property can also be used on expressions that involve variables.
Exercise #4: Express the following products as binomial expressions. Show each step in your calculation.
(a) 5 2 x 3 (b) 4 5 x 8
(c) x x 4 (d) 5 x 2 7 x
Although not as commonly used, the distributive property also works for division. For division (represented in
fraction form), the property would be the following.
THE DISTRIBUTIVE PROPERTY (OF DIVISION OVER ADDITION AND SUBTRACTION)
If a, b, and c all represent real numbers then:
Exercise #5: Express each of the following quotients as binomials in simplest form. Show your calculations.
Some of your final answers will contain fractional coefficients.
8x 4 25 x 50
(a) (b)
2 5
2 x 16 9 x 18
(c) (d)
4 12
® N-GEN MATH® ALGEBRA I – UNIT 1 – BUILDING BLOCKS OF ALGEBRA – LESSON 3 ®
eMATHinstruction, RED HOOK, NY 12571, © 2022
Name: ____________________________________ Date: __________________
THE DISTRIBUTIVE PROPERTY
N-GEN MATH® ALGEBRA I HOMEWORK
FLUENCY
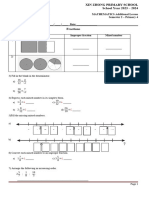
1. Using the equivalent expressions provided find the value of the expression on the left by evaluating the
expression on the right. Show your work.
96 90 6
(a) 5 42 5 40 2 (b) (c) 5 58 5 60 2
3 3 3
2. Which of the following is equivalent to the product 7 2 x 8 ?
(1) 14 x 56 (3) 9 x 16
(2) 14 x 8 (4) 9 x 8
4 x 40
3. The quotient can be rewritten in simplest form as
8
(1) 2 x 40 (3) 2 x 5
1 1
(2) x 40 (4) x5
2 2
4. Simplify the following expressions using the distributive property. Show your calculations.
(a) 5 8 x 3 (b) 4 3x 7 (c) 2 6 x 11
36 x 21 12 2 x 3 4 x 10
(d) (e) (f)
3 4 6
® N-GEN MATH® ALGEBRA I – UNIT 1 – BUILDING BLOCKS OF ALGEBRA – LESSON 3 ®
eMATHinstruction, RED HOOK, NY 12571, © 2022
5. Use the distributive property to rewrite each product below in its simplest form.
2
(a) 4 x 5 x 7 (b) 2 y 8 y 11 (c) n 9n 3
3
APPLICATIONS
6. The sum of an unknown number and 15 can be represented by the expression n 15 . Give a binomial
expression, in simplest form, that represents three times this quantity.
7. Eight times an unknown number which is then decreased by four is given by the expression 8 x 4 , where x
is the unknown number. Give an expression that represents one-fourth of this expression.
REASONING
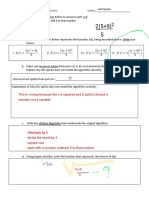
8. In the lesson we saw that we can multiply 2-digit numbers by using the distributive property twice. Use this
knowledge to multiply the following terms. Show the calculations that lead to you answers.
(a) 22 31 20 2 30 1 (b) 52 11 50 2 10 1
9. Which of the following is equivalent to 2 x 2 3 x 1 ? It may help to use problem #8(a) as a reference.
(1) 6 x 2 2 (3) 6 x 2 8 x 2
(2) 5 x 2 8 x 3 (4) 16x 3
® N-GEN MATH® ALGEBRA I – UNIT 1 – BUILDING BLOCKS OF ALGEBRA – LESSON 3 ®
eMATHinstruction, RED HOOK, NY 12571, © 2022
You might also like
- Digital Lab Manual 2023Document168 pagesDigital Lab Manual 2023isaacrajab17No ratings yet
- Lesson 6 - Solving Rational InequalitiesDocument2 pagesLesson 6 - Solving Rational InequalitiesGladys Degones GuillerNo ratings yet
- N Gen Math Algebra I.Unit 1.lesson 1.variables and ExpressionsDocument4 pagesN Gen Math Algebra I.Unit 1.lesson 1.variables and Expressionsarg456No ratings yet
- N Gen Math Algebra I.Unit 1.lesson 5.like TermsDocument4 pagesN Gen Math Algebra I.Unit 1.lesson 5.like Termsarg456No ratings yet
- Alg2Trig - Unit 3.lesson 6.5.factoring by GroupingDocument4 pagesAlg2Trig - Unit 3.lesson 6.5.factoring by GroupingDaeng Fatin Ummi Kalsom Abdul MalekNo ratings yet
- N Gen Math Algebra I.Unit 1.lesson 4.equivalent ExpressionsDocument4 pagesN Gen Math Algebra I.Unit 1.lesson 4.equivalent Expressionsarg456No ratings yet
- Yr 9 Advanced Indices Practice TestDocument12 pagesYr 9 Advanced Indices Practice TestPurple TelevisionNo ratings yet
- Properties of The Real Numbers: SectionDocument8 pagesProperties of The Real Numbers: SectionalexNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 InvestigationDocument5 pagesGrade 9 InvestigationThato TsaoaneNo ratings yet
- Math 101 - Supplemental Package FinalDocument83 pagesMath 101 - Supplemental Package Finalshaniya12thomas34No ratings yet
- Class8 Maths - WS1-Chapter 1 Rational Numbers Mumbai2Document4 pagesClass8 Maths - WS1-Chapter 1 Rational Numbers Mumbai2Yesha Shah CherubsNo ratings yet
- Ch.1 WSDocument2 pagesCh.1 WSSaumya MotianiNo ratings yet
- Cazoom Math. Fractions. Dividing FractionsDocument2 pagesCazoom Math. Fractions. Dividing FractionsFlora CoelieNo ratings yet
- 08 - Basic Rationals Review #2 PDFDocument5 pages08 - Basic Rationals Review #2 PDFMuskan HomeNo ratings yet
- Math-Summative-Test #4Document4 pagesMath-Summative-Test #4Salvacion RoqueNo ratings yet
- 7.05 Remarkable IdsDocument3 pages7.05 Remarkable Idsperezrealmadrid14No ratings yet
- Midterm Exam in Gen Math Sy 2022 2023Document4 pagesMidterm Exam in Gen Math Sy 2022 2023Portgas D. AceNo ratings yet
- Maths Year 10 Book 1Document98 pagesMaths Year 10 Book 1Hrishita PatelNo ratings yet
- Fractions Unit Assignment June2020Document3 pagesFractions Unit Assignment June2020ahsantaufique08No ratings yet
- Second Grading Exam 2023Document2 pagesSecond Grading Exam 2023Windy CarlesNo ratings yet
- Cazoom Maths. Fractions. Dividing FractionsDocument2 pagesCazoom Maths. Fractions. Dividing FractionsSalim HudheifaNo ratings yet
- Nsghs 2014 Yr 11 2u t1Document6 pagesNsghs 2014 Yr 11 2u t1Ye ZhangNo ratings yet
- M101Algebra Week 05Document4 pagesM101Algebra Week 05Jovelyn Deloria EspañolNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Inequalities and Absolute ValuesDocument4 pagesChapter 2: Inequalities and Absolute Valueszan2812No ratings yet
- Tutorial c2 Inequalities and Absolute Values 2021 IntakeDocument3 pagesTutorial c2 Inequalities and Absolute Values 2021 IntakeNur RafizahNo ratings yet
- L6-Linear InequalityDocument6 pagesL6-Linear Inequalityalan.zoylivingNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Kit (Mathematics-400 L) - Vol. 2Document68 pagesTutorial Kit (Mathematics-400 L) - Vol. 2Gebra TogunNo ratings yet
- Algebra 2Document13 pagesAlgebra 2Văn An NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Kami Export - W2 HW Intro To InversesDocument2 pagesKami Export - W2 HW Intro To InversesAlex NyokaNo ratings yet
- Chap9 3 PDFDocument6 pagesChap9 3 PDFStephen FloresNo ratings yet
- Midterm GenmathDocument4 pagesMidterm GenmathMerianne CanoneoNo ratings yet
- Add&Subtract RAEDocument23 pagesAdd&Subtract RAEJENNIELYN ABELLONo ratings yet
- Using Algebra Tiles From Polynomials To Factoring HandoutDocument13 pagesUsing Algebra Tiles From Polynomials To Factoring HandoutnoNo ratings yet
- Test Question 12-05-23Document5 pagesTest Question 12-05-23Sheena Tabaog GabuyoNo ratings yet
- Algebra 1 Review PacketDocument12 pagesAlgebra 1 Review Packetbesp63No ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Algebraic ExpressionsDocument15 pagesChapter 5 Algebraic ExpressionsSim Ping PingNo ratings yet
- MATH 5 PerformanceDocument6 pagesMATH 5 Performancepot poootNo ratings yet
- Bridging The Gap Between iGCSE and A Level Maths PDFDocument59 pagesBridging The Gap Between iGCSE and A Level Maths PDFSalmuel SmithNo ratings yet
- Maths Grade 7Document6 pagesMaths Grade 7Anonymous 3E1GVENo ratings yet
- LQ2 Gen MathDocument2 pagesLQ2 Gen MathJerom CanayongNo ratings yet
- LONG TEST 2 Oct.9Document3 pagesLONG TEST 2 Oct.9Sherry-Ann TulauanNo ratings yet
- NUM-K2-QPDocument5 pagesNUM-K2-QPSmartkidz International PreschoolNo ratings yet
- Math 7 QTR 2 Week 5Document9 pagesMath 7 QTR 2 Week 5Delos Santos, Jayson C.No ratings yet
- Review Exponentials 1Document3 pagesReview Exponentials 1730713No ratings yet
- GenMathQ1W2 - 03 ASDocument4 pagesGenMathQ1W2 - 03 ASgabosara298No ratings yet
- Grade 9 Math: UNIT 2: Powers and Exponent Laws - TEST NameDocument3 pagesGrade 9 Math: UNIT 2: Powers and Exponent Laws - TEST NameRadha RamineniNo ratings yet
- MPM1D Unit 1 Day 5 Diagnostic Test sg949fDocument7 pagesMPM1D Unit 1 Day 5 Diagnostic Test sg949fututoringunion1No ratings yet
- Math 8Document2 pagesMath 8Diane Iris AlbertoNo ratings yet
- Simplifying Rational Expressions: Algebra 2 9.1 NameDocument6 pagesSimplifying Rational Expressions: Algebra 2 9.1 Namedjvaughan01No ratings yet
- Math Additional Lesson FRACTION 2Document2 pagesMath Additional Lesson FRACTION 2aswinNo ratings yet
- Printed Activity Sheets Grade 8 - Mathematics Weeks 3 & 4Document4 pagesPrinted Activity Sheets Grade 8 - Mathematics Weeks 3 & 4Jeffrey ManligotNo ratings yet
- Module 3 Q1 WK 3Document22 pagesModule 3 Q1 WK 3Joel Hinay0% (1)
- Test Grade 7Document23 pagesTest Grade 7Nguyen DuyNo ratings yet
- April Assignment 2022-23Document3 pagesApril Assignment 2022-23Lit MasNo ratings yet
- Review Package - NguyenDocument8 pagesReview Package - Nguyenapi-310503032No ratings yet
- MPM2DZ CoursePack (2019)Document254 pagesMPM2DZ CoursePack (2019)Hope ZhangNo ratings yet
- g8 Mat PMT 1 Qp-set-ADocument3 pagesg8 Mat PMT 1 Qp-set-ABanupriya SNo ratings yet
- Maths Grade 7Document6 pagesMaths Grade 7Anonymous 3E1GVENo ratings yet
- Form 2 Mathematics Notes +exercise by Kelvin - Chapter 1Document5 pagesForm 2 Mathematics Notes +exercise by Kelvin - Chapter 1KelvinNo ratings yet
- Let's Practise: Maths Workbook Coursebook 7From EverandLet's Practise: Maths Workbook Coursebook 7No ratings yet
- PercentsQuizFREEBIE 1Document2 pagesPercentsQuizFREEBIE 1arg456No ratings yet
- Tortoise and The Hare: Very Slow FastDocument1 pageTortoise and The Hare: Very Slow Fastarg456No ratings yet
- HookesLawAPhetLab 1Document8 pagesHookesLawAPhetLab 1arg456No ratings yet
- ALG2 U1L3 Composition of FunctionsDocument4 pagesALG2 U1L3 Composition of Functionsarg456No ratings yet
- ALG2 U7L5 More Work With The Sine and Cosine FunctionsDocument4 pagesALG2 U7L5 More Work With The Sine and Cosine Functionsarg456No ratings yet
- ALG2 U7L4 The Definition of The Sine and Cosine FunctionsDocument4 pagesALG2 U7L4 The Definition of The Sine and Cosine Functionsarg456No ratings yet
- Prime and Composite Numbers ChartDocument1 pagePrime and Composite Numbers Chartarg456No ratings yet
- Grade 9 Math RubricsDocument5 pagesGrade 9 Math Rubricsarg456No ratings yet
- ALG2 U7L3 The Unit CircleDocument4 pagesALG2 U7L3 The Unit Circlearg456No ratings yet
- Ingles ThiagoDocument17 pagesIngles Thiagoarg456No ratings yet
- Mathematics 11 RubricsDocument2 pagesMathematics 11 Rubricsarg456No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 TestDocument11 pagesChapter 1 Testarg456No ratings yet
- Week Lesson Plan Original Style-LetterDocument9 pagesWeek Lesson Plan Original Style-Letterarg456No ratings yet
- Grade 8 MathDocument2 pagesGrade 8 Matharg456No ratings yet
- Math RB RL GR12 PreCalculus30Document4 pagesMath RB RL GR12 PreCalculus30arg456No ratings yet
- Grade 7Document3 pagesGrade 7arg456No ratings yet
- Lesson101OrderofOperations 1Document4 pagesLesson101OrderofOperations 1arg456No ratings yet
- Conversion WorksheetDocument2 pagesConversion WorksheetLouigene Tinao DonatoNo ratings yet
- EliminationDocument12 pagesEliminationMatthew JohnNo ratings yet
- Exponents and Order of Operations Exponents and Order of OperationsDocument15 pagesExponents and Order of Operations Exponents and Order of OperationsMye BeltranNo ratings yet
- 1st Grading Periodical Test in Math 7Document4 pages1st Grading Periodical Test in Math 7Mar Fred AroNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Datarepresentation PartA Bhanu ChanderDocument28 pagesModule 2 Datarepresentation PartA Bhanu ChanderAvv ReddyNo ratings yet
- Digital Electronic ComputerDocument179 pagesDigital Electronic ComputerromjeNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals in ALGEBRADocument8 pagesFundamentals in ALGEBRACarlo BiongNo ratings yet
- Math Quiz Final 8,9,10Document50 pagesMath Quiz Final 8,9,10Murali Krishna ShahNo ratings yet
- Reduction FormulaDocument2 pagesReduction FormulaKuldeep Lamba100% (1)
- UNIT-I (Operators)Document21 pagesUNIT-I (Operators)Prasanna PadmakarNo ratings yet
- FSM With DatapathDocument14 pagesFSM With DatapathQuoc Viet PhamNo ratings yet
- Basic-Math-Reviewer v2Document14 pagesBasic-Math-Reviewer v2Taoneki AdartseNo ratings yet
- Ward - Mayank Pandey RadziwillDocument13 pagesWard - Mayank Pandey RadziwillSwarup GhoshNo ratings yet
- Math Bcs 1,2,3 Finl BcsDocument8 pagesMath Bcs 1,2,3 Finl BcsHibha MoosaNo ratings yet
- Number TheoryDocument83 pagesNumber TheorySanat KamatNo ratings yet
- Class 10 MathsDocument376 pagesClass 10 Mathssaurabhpach100% (1)
- Year 3 Full Spring TermDocument108 pagesYear 3 Full Spring TermNavneet KaurNo ratings yet
- Singapore Math Curriculum (1676)Document10 pagesSingapore Math Curriculum (1676)Lalaine UrbinoNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 Ratio JournalDocument45 pagesGrade 8 Ratio JournalZunairah AdnanNo ratings yet
- Mathematics 7 Daily Lesson LogDocument15 pagesMathematics 7 Daily Lesson LogChelie Trangia100% (1)
- Write A Program in Java To Make Such A Pattern Like A Pyramid With A Number Which Will Repeat The Numbers in The Same RowDocument6 pagesWrite A Program in Java To Make Such A Pattern Like A Pyramid With A Number Which Will Repeat The Numbers in The Same RowNishan HamalNo ratings yet
- Induction Past HSC QuestionsDocument4 pagesInduction Past HSC QuestionsVictor GuanNo ratings yet
- SAT Math 1 NotesDocument47 pagesSAT Math 1 NotesSergioNo ratings yet
- Out of Order Floating Point Coprocessor For RISC V ISADocument7 pagesOut of Order Floating Point Coprocessor For RISC V ISAkiranNo ratings yet
- G10 T1 Mathematics Culminating Unit Assessment ReviewDocument9 pagesG10 T1 Mathematics Culminating Unit Assessment ReviewINigo Joaquin Velarde RoqueNo ratings yet
- Mathematics 10: Kauswagan National High SchoolDocument2 pagesMathematics 10: Kauswagan National High SchoolJunard CenizaNo ratings yet
- MATH Q1 Lesson 20 Estimating The Quotient of 3-To 4-Digit Dividends... MarvietblancoDocument21 pagesMATH Q1 Lesson 20 Estimating The Quotient of 3-To 4-Digit Dividends... MarvietblancoDuke Andrei C. Lincuna100% (1)
- Decimal To Binary (By Me)Document4 pagesDecimal To Binary (By Me)Raj Patel100% (1)
- Cambridge Primary Math Grade 6 Teacher Branka CurcicDocument6 pagesCambridge Primary Math Grade 6 Teacher Branka CurcicBranchi LitesNo ratings yet