Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lab06b RIPv2 Routing
Lab06b RIPv2 Routing
Uploaded by
alialyazedi2403Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lab06b RIPv2 Routing
Lab06b RIPv2 Routing
Uploaded by
alialyazedi2403Copyright:
Available Formats
Lab 6.
B Verifying RIP v2 Configuration
Objective
Configure RIP v1 and v2 on routers.
Use show commands to verify RIP v2 operation.
Background/Preparation
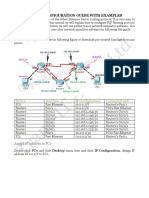
Cable a network similar to the one shown in the diagram. Any router that meets the interface
requirements displayed on the above diagram may be used. For example, router series 800, 1600,
1700, 2500, and 2600 or any such combination can be used. Please refer to the chart at the end of
the lab to correctly identify the interface identifiers to be used based on the equipment in the lab. The
configuration output used in this lab is produced from 1721 series routers. Any other router used may
produce slightly different output. Perform the following steps on each router unless specifically
instructed otherwise.
Step 1 Configure the routers
On the routers, configure the hostnames. Next configure the serial interface IP address and the Fast
Ethernet interface IP address. Be sure to save the configurations just created.
Step 2 Configure the routing protocol on the Gadsden router
Go to the correct command mode and configure RIP routing on the Gadsden router according to the
chart.
GAD>enable
GAD(config)#configure terminal
GAD(config-router)#router rip
GAD(config-router)#no auto-summary
GAD(config-router)#passive-interface F0/0
GAD(config-router)#network 172.16.0.0
GAD(config-router)#network 172.17.0.0
Step 3 Save the Gadsden router configuration
Any time that changes are correctly made to the running configuration, they should be saved to
the startup configuration. Otherwise, if the router is reloaded or power cycled, the changes that
are not saved in the startup configuration will be lost.
Step 4 Configure the routing protocol on the Birmingham router
Go to the correct command mode and configure RIP routing on the Birmingham router according
to the chart. (similar to Step 2 but with different networks)
Step 5 Save the Birmingham router configuration
Step 6 Configure the hosts with the proper IP address, subnet mask, and default gateway
Step 7 Verify that the internetwork is functioning by pinging the FastEthernet interface of
the other router
a. From the host attached to the GAD, ping the other host attached to the BHM router. Was
the ping successful?
b. From the host attached to the BHM, ping the other host attached to the GAD router. Was
the ping successful?
c. If the answer is no for either question, troubleshoot the router configurations to find the
error. Then do the pings again until the answer to both questions is yes.
Step 8 Show the routing tables for each router
a. From the enable privileged EXEC mode, examine the routing table entries using command
show ip route command on each router.
b. What are the entries in the GAD routing table?
[Answer here]
c. What are the entries in the BHM routing table?
[Answer here]
Step 9 Enable RIP v2 routing
Enable version 2 of the RIP routing protocol on both of the routers, Gadsden and Birmingham.
GAD(config)#router rip
GAD(config-router)#version 2
GAD(config-router)#exit
GAD(config)#exit
BHM(config)#router rip
BHM(config-router)#version 2
BHM(config-router)#exit
BHM(config)#exit
Step 10 Show the routing tables
a. Show the routing tables on both routers again.
b. Have they changed now that RIP v2 is now being used instead of RIP v1? [Answer here]
c. What is the difference between RIP v2 and RIP v1? [Answer here]
d. What must be done in order to see a difference between RIP v2 and RIP v1?
[Answer here]
Step 11 Change the Fast Ethernet IP subnet mask on the Gadsden router
a. Change the subnet mask on router GAD from a class B (255.255.0.0) to a Class
C (255.255.255.0). Use the same IP address.
GAD(config)#interface fastethernet 0/0
GAD(config-if)#ip address 172.16.0.1 255.255.255.0
GAD(config-if)#exit
b. How does this change affect the address for the FastEthernet interface?
[Answer here]
Step 12 Show the GAD routing table
a. Show the GAD routing table.
b. Has the output changed with the addition of a subnetted IP address? [Answer here]
c. How has it changed? [Answer here]
Step 13 Show the BHM routing table
a. Show the BHM routing table.
b. Has the output changed with the addition of a subnetted IP address? [Answer here]
Step 14 Change the network addressing scheme
Change the addressing scheme of the network to a single class B network with a class C subnet (8-
bits of subnetting).
a. On the BHM router:
BHM(config)#interface serial 0/1/0
BHM(config-if)#ip address 172.16.1.2 255.255.255.0
BHM(config-if)#exit
BHM(config)#interface fastethernet 0/0
BHM(config-if)#ip address 172.16.3.1 255.255.255.0
BHM(config-if)#exit
BHM (config)#router rip
BHM (config-router)#network 172.16.1.0
BHM (config-router)#network 172.16.3.0
b. On the GAD router:
GAD(config)#interface serial 0/1/0
GAD(config-if)#ip address 172.16.1.1 255.255.255.0
GAD(config-if)#exit
GAD(config)#router rip
GAD(config-router)#network 172.16.1.0
GAD(config-router)#network 172.16.0.0
Step 15 Show the routing table
a. Show the GAD routing table.
b. Has the output changed with the addition of subnetted IP addresses? [Answer here]
c. How has it changed? [Answer here]
Step 16 Show the routing table
a. Show the BHM routing table.
b. Has the output changed with the addition of a subnetted IP address? [Answer here]
Step 17 Change the host configurations
Change the host configuration to reflect the new IP addressing scheme of the network
Step 18 Ping all of the interfaces on the network from each host
a. Were all of the interfaces still able to be pinged? [Answer here]
b. If not, troubleshoot the network and ping again.
Step 19 Use show ip route to see different routes by type
a. Enter show ip route connected on the GAD router.
b. What networks are displayed? [Answer here]
c. What interface is directly connected? [Answer here]
d. Enter show ip route rip
e. List the routes listed in the routing table? [Answer here]
f. What is the administrative distance? [Answer here]
g. Enter show ip route connected on the BHM router.
h. What networks are displayed? [Answer here]
i. What interface is directly connected? [Answer here]
j. Enter show ip route rip
k. List the routes listed in the routing table? [Answer here]
Step 20 Use the show IP protocol command
a. Enter show ip protocol on the GAD router.
b. When will the routes be flushed? [Answer here]
c. What is the default distance listed for RIP? [Answer here]
Erasing and reloading the router
Enter into the privileged EXEC mode by typing enable.
If prompted for a password, enter class. If that does not work, ask the instructor for assistance.
Router>enable
At the privileged EXEC mode, enter the command erase startup-config.
Router#erase startup-config
The responding line prompt will be:
Erasing the nvram filesystem will remove all files! Continue? [confirm]
Press Enter to confirm. The
response should be:
Erase of nvram: complete
Now at the privileged EXEC mode, enter the command reload.
Router(config)#reload
The responding line prompt will be:
System configuration has been modified. Save? [yes/no]:
Type n and then press Enter.
The responding line prompt will be:
Proceed with reload? [confirm]
Press Enter to confirm.
In the first line of the response will be:
Reload requested by console.
After the router has reloaded the line prompt will be:
Would you like to enter the initial configuration dialog? [yes/no]:
Type n and then press Enter.
The responding line prompt will be:
Press RETURN to get started!
Press Enter.
Now the router is ready for the assigned lab to be performed.
Router Interface Summary for Lab 6B
Ethernet Ethernet Serial Serial
Router Model
Interface #1 Interface #2 Interface #1 Interface #2
800 (806) Ethernet 0 (E0) Ethernet 1 (E1)
1600 Ethernet 0 (E0) Ethernet 1 (E1) Serial 0 (S0) Serial 1 (S1)
1700 FastEthernet 0 (FA0) FastEthernet 1 (FA1) Serial 0 (S0) Serial 1 (S1)
2500 Ethernet 0 (E0) Ethernet 1 (E1) Serial 0 (S0) Serial 1 (S1)
FastEthernet 0/0
2600 FastEthernet 0/1 (FA0/1) Serial 0/0 (S0/0) Serial 0/1 (S0/1)
(FA0/0)
In order to find out exactly how the router is configured, look at the interfaces. This will identify what type and
how many interfaces the router has. There is no way to effectively list all of the combinations of configurations
for each router class. What is provided are the identifiers for the possible combinations of interfaces in the
device.
This interface chart does not include any other type of interface even though a specific router may contain one.
An example of this might be an ISDN BRI interface. The string in parenthesis is the legal abbreviation that can
be used in IOS command to represent the interface.
You might also like
- Sisko 3.2.1.8Document6 pagesSisko 3.2.1.8GinanjarNawawi100% (1)
- Cisco CCNA Command Guide: An Introductory Guide for CCNA & Computer Networking Beginners: Computer Networking, #3From EverandCisco CCNA Command Guide: An Introductory Guide for CCNA & Computer Networking Beginners: Computer Networking, #3No ratings yet
- Packet Tracer - Connect A Router To A LAN: Addressing TableDocument4 pagesPacket Tracer - Connect A Router To A LAN: Addressing TableBenj MendozaNo ratings yet
- Lab 7.2.2 Configuring RIP - Instructor Version 2500: ObjectiveDocument14 pagesLab 7.2.2 Configuring RIP - Instructor Version 2500: ObjectivesafaNo ratings yet
- CCNA2 Lab 7 2 7 enDocument6 pagesCCNA2 Lab 7 2 7 enapi-3809703No ratings yet
- CCNA2 Lab Inst 3 1 5 enDocument18 pagesCCNA2 Lab Inst 3 1 5 enblahblah2331No ratings yet
- Lab 3 1 6Document5 pagesLab 3 1 6HamzaSpahijaNo ratings yet
- Basic Router ConfigDocument8 pagesBasic Router ConfigKaka MuhammadNo ratings yet
- A Lab1acceslistDocument5 pagesA Lab1acceslistveracespedesNo ratings yet
- Lab 6-1-6Document6 pagesLab 6-1-6Chullachat_Chu_1486No ratings yet
- Lab 1.2.5 Verifying RIP v2 Configuration: ObjectiveDocument7 pagesLab 1.2.5 Verifying RIP v2 Configuration: ObjectiveHà TrầnNo ratings yet
- Basic Two Router LabDocument10 pagesBasic Two Router LabsannuscribdNo ratings yet
- Lab 3.1.7 Troubleshooting A Serial InterfaceDocument6 pagesLab 3.1.7 Troubleshooting A Serial InterfaceDany CanulNo ratings yet
- Lab 3.1.3 Configuring Router Passwords - Instructor Version 2500Document14 pagesLab 3.1.3 Configuring Router Passwords - Instructor Version 2500Andra RyandaNo ratings yet
- 2 Router Basic Configuration Lab: ObjectiveDocument13 pages2 Router Basic Configuration Lab: Objectivesamsingh12345000No ratings yet
- Eigrp Configuration Step by Step GuideDocument19 pagesEigrp Configuration Step by Step GuideDiego MartinezNo ratings yet
- Lab 5.3.5 Configuring Basic Router Settings With The Cisco IOS CLIDocument5 pagesLab 5.3.5 Configuring Basic Router Settings With The Cisco IOS CLIPunita VasuNo ratings yet
- CCNA4 Lab 1 2 6Document6 pagesCCNA4 Lab 1 2 6Alexandra AlmeidaNo ratings yet
- Lab Experiment 1 One Router 2 Switches and 4 PCS: Pc0 Ip ConfigurationDocument24 pagesLab Experiment 1 One Router 2 Switches and 4 PCS: Pc0 Ip ConfigurationRabiulAlamNo ratings yet
- Router CommandsDocument9 pagesRouter Commandsanon-640566100% (2)
- 6.4.3.3 Packet Tracer - Connect A Router To A LAN Instructions IGDocument5 pages6.4.3.3 Packet Tracer - Connect A Router To A LAN Instructions IGopiNo ratings yet
- Lab 7.2.9 Load Balancing Across Multiple Paths: ObjectiveDocument5 pagesLab 7.2.9 Load Balancing Across Multiple Paths: Objectivesahil4INDNo ratings yet
- Lab 3.2.1 Configuring EIGRP Routing: ObjectiveDocument5 pagesLab 3.2.1 Configuring EIGRP Routing: ObjectiveguijjouNo ratings yet
- Take Assessment - Erouting Chapter 5 - Ccna Exploration: Routing Protocols and Concepts (Version 4.0) - Answers - 2012 - 2013Document8 pagesTake Assessment - Erouting Chapter 5 - Ccna Exploration: Routing Protocols and Concepts (Version 4.0) - Answers - 2012 - 2013Dzevad MakotaNo ratings yet
- Router Configuration Using Setup: Start Programs Accessories Communications Hyper TerminalDocument5 pagesRouter Configuration Using Setup: Start Programs Accessories Communications Hyper TerminalabduasdfNo ratings yet
- Lab 3.1.7 Troubleshooting A Serial Interface: ObjectiveDocument5 pagesLab 3.1.7 Troubleshooting A Serial Interface: ObjectiveVo Ngoc HoangNo ratings yet
- Lab 3.1.2 Command Modes and Router Identification: Background/PreparationDocument5 pagesLab 3.1.2 Command Modes and Router Identification: Background/PreparationNawaz Ali100% (2)
- Lab 5.2.2 Configuring Frame Relay PVC: ObjectiveDocument13 pagesLab 5.2.2 Configuring Frame Relay PVC: Objectivemustehsan2009No ratings yet
- Basic Router ConfigurationDocument26 pagesBasic Router ConfigurationNajeeb KhanNo ratings yet
- Lab 4 Static Default RouteDocument8 pagesLab 4 Static Default RouteLipp00 M0MANo ratings yet
- CiscoDocument37 pagesCiscoTomCat1989No ratings yet
- How To Configure Routing Information Protocol RIP Routing Information Protocol Version 2 RIPv2 Lab PRDocument7 pagesHow To Configure Routing Information Protocol RIP Routing Information Protocol Version 2 RIPv2 Lab PRshinde_jayesh2005No ratings yet
- Laboratory 1Document2 pagesLaboratory 1dkhanNo ratings yet
- Lab 1Document10 pagesLab 1Israel EliasNo ratings yet
- CCNA 2 Chapter 5Document5 pagesCCNA 2 Chapter 5marek_202No ratings yet
- Rip-Protocol-Configuration-Guide-With-Examples COMPLILEDDocument24 pagesRip-Protocol-Configuration-Guide-With-Examples COMPLILEDPerbz JayNo ratings yet
- 10.3.4 Packet Tracer - Connect A Router To A LanDocument8 pages10.3.4 Packet Tracer - Connect A Router To A LanMarinela BrânzeanuNo ratings yet
- Lab Basic Router Configuration (Example) : Topology DiagramDocument8 pagesLab Basic Router Configuration (Example) : Topology Diagrambluesupra1kNo ratings yet
- Cisco CCNA Exploration V 4.0, Module 2, Chapter 5 ExamDocument7 pagesCisco CCNA Exploration V 4.0, Module 2, Chapter 5 ExamAdryana EnacheNo ratings yet
- 10.3.4 Packet Tracer - Connect A Router To A LANDocument4 pages10.3.4 Packet Tracer - Connect A Router To A LANDan jonesNo ratings yet
- Lab 3.2.5 Configuring Message-of-the-Day (MOTD) : Background/PreparationDocument4 pagesLab 3.2.5 Configuring Message-of-the-Day (MOTD) : Background/PreparationNawaz Ali100% (2)
- Router: Router1 (Config-Router) # Passive-Interface Fastethernet 0/0Document13 pagesRouter: Router1 (Config-Router) # Passive-Interface Fastethernet 0/0copley50No ratings yet
- 10.3.4 Packet Tracer - Connect A Router To A LANDocument4 pages10.3.4 Packet Tracer - Connect A Router To A LANkds20850No ratings yet
- Module 11 - Answered (100%)Document7 pagesModule 11 - Answered (100%)Vantung DangNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 - Routing Information ProtocolDocument10 pagesLecture 5 - Routing Information ProtocolDervpolo VansNo ratings yet
- Lab 1 - Static RoutesDocument9 pagesLab 1 - Static RoutesAndrew MaverickNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Exam AnswersDocument5 pagesChapter 11 Exam Answerskapilvastutaulihawa100% (2)
- Add Devices and Connect Cables Configure Pcs Configure R1 Configure R2 Save The Packet Tracer FileDocument12 pagesAdd Devices and Connect Cables Configure Pcs Configure R1 Configure R2 Save The Packet Tracer FileMeme222No ratings yet
- Lab 3: OSPF With Three RoutersDocument6 pagesLab 3: OSPF With Three RoutersAmjad hassanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 - Static and Default RoutingDocument14 pagesLecture 5 - Static and Default RoutingOge EstherNo ratings yet
- Lab6 - Connect A Router To A LANDocument4 pagesLab6 - Connect A Router To A LANkaisbarboura99No ratings yet
- 200-125 V21.02Document205 pages200-125 V21.02AntonioNo ratings yet
- CCNA 2 Chapter 5 V4.0 Answers: Admin Leave A CommentDocument9 pagesCCNA 2 Chapter 5 V4.0 Answers: Admin Leave A Commentsathesh005No ratings yet
- CCNA 2 Practice Final ExamDocument19 pagesCCNA 2 Practice Final ExamDebbie M. LazoNo ratings yet
- 10.3.4 Packet Tracer Connect A Router To A LanDocument4 pages10.3.4 Packet Tracer Connect A Router To A LanVince Mitchell LinaNo ratings yet
- DCCN All Labs 2nd Year 1st SemesterDocument9 pagesDCCN All Labs 2nd Year 1st SemesterSupun MannapperumaNo ratings yet
- Network with Practical Labs Configuration: Step by Step configuration of Router and Switch configurationFrom EverandNetwork with Practical Labs Configuration: Step by Step configuration of Router and Switch configurationNo ratings yet
- CISCO PACKET TRACER LABS: Best practice of configuring or troubleshooting NetworkFrom EverandCISCO PACKET TRACER LABS: Best practice of configuring or troubleshooting NetworkNo ratings yet