Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Brand Positioning
Brand Positioning
Uploaded by
bhaveshjain8800 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views5 pagesThis document discusses the concept of positioning in marketing. It provides three key points:
1. Positioning refers to how a brand is perceived by customers in their minds relative to competitors. It is defined by customer perceptions rather than by objective product attributes.
2. A brand's position should reflect the benefits it offers customers and be unique, credible, and sustainable. Positioning aims to occupy a distinctive place in customers' consideration sets.
3. The example of Cadbury's Dairy Milk brand positioning shows it aims to be an indulgence for people of all ages at any time and place, without reference to any competitors. Customers respond based on their perceptions of brands rather than just the real product attributes
Original Description:
About brand positing
Original Title
brand positioning
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses the concept of positioning in marketing. It provides three key points:
1. Positioning refers to how a brand is perceived by customers in their minds relative to competitors. It is defined by customer perceptions rather than by objective product attributes.
2. A brand's position should reflect the benefits it offers customers and be unique, credible, and sustainable. Positioning aims to occupy a distinctive place in customers' consideration sets.
3. The example of Cadbury's Dairy Milk brand positioning shows it aims to be an indulgence for people of all ages at any time and place, without reference to any competitors. Customers respond based on their perceptions of brands rather than just the real product attributes
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views5 pagesBrand Positioning
Brand Positioning
Uploaded by
bhaveshjain880This document discusses the concept of positioning in marketing. It provides three key points:
1. Positioning refers to how a brand is perceived by customers in their minds relative to competitors. It is defined by customer perceptions rather than by objective product attributes.
2. A brand's position should reflect the benefits it offers customers and be unique, credible, and sustainable. Positioning aims to occupy a distinctive place in customers' consideration sets.
3. The example of Cadbury's Dairy Milk brand positioning shows it aims to be an indulgence for people of all ages at any time and place, without reference to any competitors. Customers respond based on their perceptions of brands rather than just the real product attributes
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 5
positioning: rThe
) productsConsumers' andconsumer". competitive
Thebrands.Definitions -their extensively. nosition
atwas intention
the The Chapter
dimension
theorder customer much
Positioning Given "Positioning non-functional This position discovered
keycustomer's
A suppliers'
positioning actual
in perception concept
refers
to
is below the minds aspect of
demonstrate
to the Modernsecure
side, position ofa
implies used would category. creates mind. end. by
are for brand the
to of
benefits
reflects marketing Success. a
of quantity it
is the th e a marketers A physical
position
Cadbury's making embody position
brand need
essential of
brand" a is
features a unique, the
superiority product in the arose Llke
the perception is
direct andcustomer essence during akin is space of
Dary why to which refers credible, judgment for warfare, military
resolve
WARAKAO0SS Go
or is is suppliers1970s. to or
Milk. andindirect the of warfare. location
and may to th e it the in
distinction. brand who its
sustainable of brings way Positioning
Brand origin.
competitive be thatbrand Markets marketing,
reference objective to The CHENNA 106
tothe noted about it own a LIBRARY
be
consume. is soldier
target in perceived importance
were In OVEAOMA00sS
used. terms a military VAIS#
in place and in distinctive position
Figure to dimensions. the
thcustomer
e The relation becoming occupies
vis-a-vis valued of mind
rival its in engagements,
7.1.
competitive of is
to functional ofa relation positioning
position
depictsbrands is; On place crowdedemployed with
how the brand other target
in in to in an
7.2 Brand Management
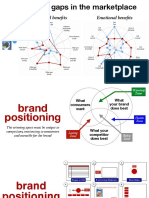
No competitive reference For whom: Age no bar
against anyone Adults (focused)
Children included
Cadbury's
Dairy
Milk
When: Any time
Why: The indulgence,
the taste of life Where: Any place
Figure: 7.1l - Brand Positioning of
Cadbury 's Dairy Milk
(2) Customers do not respond to offerings on the basis of the real products.
They respond to products or brands as they are perceived. Abrandina
customer's perception is more than a product. It is a perceptual entity.
(3) Positioning is linked to the concept of image. It is the act of designing the
company's brandsto occupy a distinct place in the target market's mind.
(4) The position can be of two types: the actual position and perceived
position. The actual position of a product refers to its objective place
vis-a-vis other products in the category. Perceived position means customers
respond to brands, as they are perceived.
(5) Alltools like product, packaging, pricing, distribution, endorsement,
publicity etc., help in positioning a brand.
(6) The essence of brand positioning is the achievement of valued distinction
or differentiation in aprospect's mind.
(T) Whether a brand owns a position or not couldeasily be found by asimple
word association. Some wellpositioned brands are as follows:
Brand Positioning
(1) Vatika 7.3
Hair oil with natural ingredients
2) Fair and Lovely Fairness
(3) Dettol- antiseptic
(4) Bisleri - safe
(5) Pepsi fun,
excitement, younger generation
(6) Close up - fresh
breath, confidence
(T) Babool -
(8) Raymond-
economy
complete man
Positioning errors
In Kotler's view, a
errors:
brand may suffer because of the following
()) Under positioning
understanding positioning:
about the Under positioning occurs when
brand. buyers lack
The brand does not enjoy a They seem to
clear association. have a vague idea of the bránd.
(2) Over
brand, a brandpositioning: Over positioning is due to a very
isperceived to have a narrow narrow image of the.
Customer perceives Casio as only a digital limiting association. For example, a
range of watches. watch. But in reality it may offer awide
(3) Confused
Positioning:
may ultimately result in a
When a brand tries to
associate many
when a brand makes manyconfusion. Generally, confusion occurs in things, it
over positioning
claims and changes them
(4) Doubtful
positioning: frequently time.
The brand manager Customers oubt the
shoulddetermine exactly whatclaims made by the
customer's mind. What is its position? Is it the brand stands forbrand.
in a
rival brands positioned? distinctive? Is it valued? How are
(5)Brand
position. Thererepositioning:
are two typesRepositioning involves changing the brand's current
of repositioning
) Effecting a change in the strategies:
brand in order to distance that brand
existing associations and attach a new set of from its
underwent repositioning from the 'Pure' to 'safe'associations. Bisleri brand
() Repositioning the platform.
0çcupy the mind. competition becomes
This includes sayingnecessary when too much ofbrands
Change customer's, mind about the rival something about rival brands to
Savlon brand triedto reposition its rival, product. Johnson and Johnson's
Dettol.
7.4
Follow up: Hasty conclusions may lead Brand Management
errors: brand managers to committhe
following
1. Incorporating changes in brand structure where they are actually not
2. Omitting the brand elements where changes are needed.
needed.
BRAND CHECKS
To safeguard against
positioning errors, the brand managers must perform
regular brand checks. Brand
as it develops over time. checks would reveal the correct picture of the brand
When
would be taken. Brand check istrouble spots are discovered, necessary actions
directed at surveying (1) Brand Awareness;
(2) Brand image; and (3) Brand positioning errors.
(1)Brand Awareness
Brand awareness is the essential condition for
customer is aware of the brand being sold in the achieving
market.
brand success. The
reflected in brand recognition and brand recall. Brand awareness is
In abrand recognition test, the ability of the
elements is tested. Upon seeing brand elementscustomers
like
to identify the brand
brand symbol etc. Customersare able to confirm thepriorbrand name, packaging,
exposure to th¡t brand.
The brand recognition check may involve
direct measures or indirect
measures. A high response to indirect (disguised) measures would, reveal the
great strength of brand recognition.
Brand recall: Brand recall is the rigorous test of brand
stands for the
awareness. Recall
ability of the customer or prospect to retrieve the brand from
memory. Both aided recallor unaided recall may be used to test brand recall. In
unaided recall a respondent is asked to mention the brands in the particular
product category (for example, brand names in the cell phone market),. The
respondent may recall various brands (Nokia, Samsung, Motorola, etc). The
investigators should note the brand which is first recalled. Among those recalled,
the first recalled brand is assumed to have a strong position. It also signifies the
top of the mind avwareness. Investigators use aided recall tests when the brands
may not be recalled. Variety of aids used in this regard may include product
attributes, usage quantity, poduct form, etc.
(2) Brand Image
Brand image is decoded identity in the customer's mind. Image refers to the
associations that are linked to the brand name. While checking primary
associations, a respondent is asked to utter the first word that comes to his mind
when a brand name is sounded to him. Sometimes, marketers endeavour to
uncover whatever is associated with the brand name. However, the brand
associations revealed by thisexercise is not always real.
RrandPositioning 7.5
)Brandppositioningerrors
positioninganalysis reveals problems with a brand's positioning. The
The maybeinthe
problems
form of under positioning, over positioning, confused
positioning,doubtfulpositioning etc. Under positioning reflects astate of buyer's
understandingaboutthe brand. Over positioning reflects a very narrow
lackof
inage ofthebrand. Sometimes, a brand may try to asSociate with many things
inconfusion. Doubtful positioning occurs when customers find it hard
esulting
vethe claims made bythe brand.
belie
1o
Positioningstrategies
Positioningstrategyaims.at building brand differentiationint1thetarget market.
productororganization may existinthe perception of customer inthe form of
Aassociation set. This is what creates an overall
an
impression. So, brand
positioninginvolves deciding aboutthe kind of associations that are to be created.
Broadly, there are five positioning strategies
1 Attribute positioning: Customers find a unique benefit or attribute in
brands. Such an attribute, associated with brand tempts purchases. For
example, car buying motives include economy, speed, luxury, esteem and
safety. Anew brand of car becomes successful when it is superior to existing
brands.
2.Price or Quality positioning: Abrand may be positioned as high price and
high quality while others may take the low price and low quality position. At the
bottom end it means an economy position while at the top end it means
premium positions. It appeals to the price or quality conscious customers. For
example, HLL's Wheel detergent was positioned on the economy front while
Surf Excel was positioned as apremium brand. Madura Garments had the Peter
England at the lower end and Louis Philippe at the higher end.
3. Use or application positioning: Abrand is positioned on the basis of its
isage time on application. Abath cream is positioned for application after the
bath. Maggi Noodles for long promoted itself as aquick snack for kids when they
return from school.
4. User positioning: User positioning focuses on establishing a connection
between the brand and the user. For example, Johnson and Johnson soap is
POSItioned for kids. Developing strong, favourable and unique associations
Wth users of the brand is fundamental to user positioning. The class of people
WhO are associated with the brand differentiate brands powerfully.
5. Product
for its class positioning: Brandrepresents value that a marketer packs
taarget customer. Marketers position their brands with respect to a
uuctclass by developing class related associations. Nescafe is positioned as
instant coffee (product class). Bru brand is related with filter coffee.
You might also like
- Principles of Marketing Ebook An Asian Perspective - (Marketing Managing Profitable Customer Relationships)Document36 pagesPrinciples of Marketing Ebook An Asian Perspective - (Marketing Managing Profitable Customer Relationships)Phạm Yến NhiNo ratings yet
- Value Proposition CanvasDocument5 pagesValue Proposition CanvasHafizszul FeyzulNo ratings yet
- Building on Whole Leadership: Energizing and Strengthening Your Early Childhood ProgramFrom EverandBuilding on Whole Leadership: Energizing and Strengthening Your Early Childhood ProgramNo ratings yet
- Advertisement in Insurance SectorDocument63 pagesAdvertisement in Insurance Sectorharrykhera0% (1)
- New Collar Apprenticeship Program OverviewDocument9 pagesNew Collar Apprenticeship Program OverviewDao MingleberryNo ratings yet
- 2021 Session 1 StrategyDocument127 pages2021 Session 1 StrategyftelenaNo ratings yet
- RAVI Private LabelsDocument3 pagesRAVI Private LabelsrdkoolNo ratings yet
- Product Related StrategyDocument13 pagesProduct Related StrategyPragathi NarasimmanNo ratings yet
- HRMDocument21 pagesHRMLakshita NegiNo ratings yet
- Functions of MarketingDocument1 pageFunctions of MarketingmariNo ratings yet
- Case Study Chapter 1Document2 pagesCase Study Chapter 1demongamin2006No ratings yet
- Resumes: HobbiesDocument1 pageResumes: HobbiesDina SaberNo ratings yet
- Oswal OrganisingDocument16 pagesOswal OrganisingMuskan LohariwalNo ratings yet
- Workshop On Prepositions and VocabularyDocument7 pagesWorkshop On Prepositions and VocabularyCharityn FrancoNo ratings yet
- Customer-Based Brand Equity or The Kellers Brand Equity ModelDocument19 pagesCustomer-Based Brand Equity or The Kellers Brand Equity ModelHuNtEr GamerYTNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneur Summit - Aaron SansoniDocument11 pagesEntrepreneur Summit - Aaron SansoniAnna Murakawa100% (1)
- Business Organization Management Sem 1Document5 pagesBusiness Organization Management Sem 1BhushanNo ratings yet
- Creating Brand EquityDocument1 pageCreating Brand EquitymarttriadhiNo ratings yet
- DownloadfileDocument4 pagesDownloadfileJayesh MandhyanNo ratings yet
- Sphere FaceDocument9 pagesSphere FaceSkarica En RedNo ratings yet
- Brand Identity Prism Paco RabanneDocument1 pageBrand Identity Prism Paco RabanneEstefanía Giraldo OsorioNo ratings yet
- C7.International PositioningDocument1 pageC7.International PositioningKhánh Nguyễn ĐìnhNo ratings yet
- Business CH 1Document24 pagesBusiness CH 1Archit JainNo ratings yet
- Project Management Fundamentals: Working With TeamsDocument11 pagesProject Management Fundamentals: Working With TeamsFrankNo ratings yet
- T-IEET001 - Business-Model-Canvas - Ta-Ay, Jay L. - MEE31Document1 pageT-IEET001 - Business-Model-Canvas - Ta-Ay, Jay L. - MEE31JayNo ratings yet
- Taller 7.odtDocument6 pagesTaller 7.odtjeisonNo ratings yet
- Performance Drilling Reservoir Contact Tour BRDocument5 pagesPerformance Drilling Reservoir Contact Tour BRhagh1234No ratings yet
- Attributes of Entrepreneurs:: Report of Jesse Wilvic JacildoDocument19 pagesAttributes of Entrepreneurs:: Report of Jesse Wilvic JacildoShinjiNo ratings yet
- Businessstandard PDFDocument1 pageBusinessstandard PDFParita BhattNo ratings yet
- Sphereface: Deep Hypersphere Embedding For Face RecognitionDocument9 pagesSphereface: Deep Hypersphere Embedding For Face RecognitionCẩm Tú CầuNo ratings yet
- Design Principles and Elements: Emphasis AppropriatenessDocument1 pageDesign Principles and Elements: Emphasis AppropriatenessDexter CaroNo ratings yet
- Experian Decisioning Messaging FrameworkDocument16 pagesExperian Decisioning Messaging FrameworkBayCreativeNo ratings yet
- Simu GuidelinesDocument54 pagesSimu Guidelinesniket mehtaNo ratings yet
- Module 4 - Capstone Project 2 - The Dessert AffairDocument1 pageModule 4 - Capstone Project 2 - The Dessert Affairar.hinayasminNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 07-Nov-2023Document17 pagesAdobe Scan 07-Nov-2023Shekharvan HazarikaNo ratings yet
- Week 1 BDocument19 pagesWeek 1 BLifeStacksNo ratings yet
- Contractual Relationship: Business Organisation StakeholdersDocument1 pageContractual Relationship: Business Organisation StakeholdersMinhh KhanggNo ratings yet
- BM Chapter 2Document12 pagesBM Chapter 2Usman AzizNo ratings yet
- Patrones Estructurales: Decorator FacadeDocument1 pagePatrones Estructurales: Decorator FacadeDiego GarciaNo ratings yet
- Brand Analysis Quick Guide Part IDocument1 pageBrand Analysis Quick Guide Part IVăn Thắng MaiNo ratings yet
- HRDCS - V-Leader - Management Competency Model-8-20-09Document2 pagesHRDCS - V-Leader - Management Competency Model-8-20-09cjhicksNo ratings yet
- Grow - Thoughts - Issue 20 - On Cultural BrandingDocument7 pagesGrow - Thoughts - Issue 20 - On Cultural BrandingAnthonyNo ratings yet
- Generative AI in Banking and Financial Services by Accubits CompressedDocument34 pagesGenerative AI in Banking and Financial Services by Accubits CompresseddivyanshuNo ratings yet
- Agile PO Poster 2017 Ver10 DandyDocument1 pageAgile PO Poster 2017 Ver10 DandyTheone TrukingNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument3 pagesIntroductionSaad ShahNo ratings yet
- Sphereface: Deep Hypersphere Embedding For Face RecognitionDocument9 pagesSphereface: Deep Hypersphere Embedding For Face RecognitionMoxlyNo ratings yet
- WillowDocument2 pagesWillowChitharanjan VishnukripalNo ratings yet
- What Is Brand?Document19 pagesWhat Is Brand?sadia_2189No ratings yet
- Yordanos MulugetaDocument2 pagesYordanos MulugetaKaleab AlemayehuNo ratings yet
- Funtional Benefits Emotional Benefits: Identifying Gaps in The MarketplaceDocument21 pagesFuntional Benefits Emotional Benefits: Identifying Gaps in The MarketplaceAllilah ANo ratings yet
- Key Note Address BITMDocument17 pagesKey Note Address BITMArup BaksiNo ratings yet
- Tuning Your Resume To The Right KeywordsDocument5 pagesTuning Your Resume To The Right KeywordsRahul YodhNo ratings yet
- 20 Reserch Papers Relevant To The Intended Area of StudyDocument3 pages20 Reserch Papers Relevant To The Intended Area of StudyAiman BaigNo ratings yet
- Is My Driver Observation Model Overconfident? Input-Guided Calibration Networks For Reliable and Interpretable Confidence EstimatesDocument15 pagesIs My Driver Observation Model Overconfident? Input-Guided Calibration Networks For Reliable and Interpretable Confidence Estimatesreaver voidNo ratings yet
- Branding PDFDocument9 pagesBranding PDFNana RosdianaNo ratings yet
- Constraints To Consider: Expected New Uses of MetaverseDocument1 pageConstraints To Consider: Expected New Uses of MetaverseRamapriyaNo ratings yet
- CIDAM in ENGLISH 7Document2 pagesCIDAM in ENGLISH 7Charry AltamiaNo ratings yet
- Region Driving Remote Sensing Image CaptioningDocument9 pagesRegion Driving Remote Sensing Image Captioninghemalatha7No ratings yet
- PDF Kajaria Report Final - CompressDocument40 pagesPDF Kajaria Report Final - CompressMd Borhan Uddin 2035097660No ratings yet
- Chris Hammond Joins Donnelly Timmons & AssociatesDocument2 pagesChris Hammond Joins Donnelly Timmons & AssociatesPR.comNo ratings yet
- Digital Marketing Agency in MelbourneDocument10 pagesDigital Marketing Agency in MelbourneGrownomics AuNo ratings yet
- Creating BRAND Equity: Dr. Ashutosh Kumar Asia Pacific Institute of ManagementDocument24 pagesCreating BRAND Equity: Dr. Ashutosh Kumar Asia Pacific Institute of ManagementPriyanka MazumderNo ratings yet
- 06 Chapter 1Document28 pages06 Chapter 1Janhssen Agusan BeterboNo ratings yet
- Creating Internet Marketing Strategies (Budget Allocation)Document3 pagesCreating Internet Marketing Strategies (Budget Allocation)NishantNo ratings yet
- Haribo CatalogDocument88 pagesHaribo CatalogHuzeyfe IslamogluNo ratings yet
- Affiliate MarketingDocument13 pagesAffiliate MarketingMainak RanjanNo ratings yet
- End Term IMC 2021Document6 pagesEnd Term IMC 2021Satyam RajNo ratings yet
- RohanChawda Mumbai 13.08 YrsDocument2 pagesRohanChawda Mumbai 13.08 YrsChinmay VaradkarNo ratings yet
- (External MY) Shopee Collaborative Ads (CPAS) Setup Guide - v2021Document59 pages(External MY) Shopee Collaborative Ads (CPAS) Setup Guide - v2021Robert De niroNo ratings yet
- Kathmandu University School of Management (KUSOM) Course Plan (BBA-Hons) Digital Marketing Spring 2019Document4 pagesKathmandu University School of Management (KUSOM) Course Plan (BBA-Hons) Digital Marketing Spring 2019Ashley WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Gisella Cindy 115180047 JADocument32 pagesGisella Cindy 115180047 JAYuyun AnitaNo ratings yet
- Masters of Conversion Sales LetterDocument20 pagesMasters of Conversion Sales LettertlskiNo ratings yet
- Business StrategiesDocument2 pagesBusiness Strategiesthristanlexter694No ratings yet
- Article Review - NUR AKMAL AHMAD TAJUDDIN - AA7014A (2019449782)Document4 pagesArticle Review - NUR AKMAL AHMAD TAJUDDIN - AA7014A (2019449782)AKMALNo ratings yet
- Amex Blue Case StudyDocument4 pagesAmex Blue Case Studyvincent.andrettaNo ratings yet
- GetCRAFT - Indonesia Native Advertising Influencer Marketing Report 2018Document25 pagesGetCRAFT - Indonesia Native Advertising Influencer Marketing Report 2018Clara LilaNo ratings yet
- Basnet - Strategi Pemsaran Digital Media (2022)Document14 pagesBasnet - Strategi Pemsaran Digital Media (2022)Rizki MeilizaNo ratings yet
- Apex Footwear Marketing Plan OkDocument2 pagesApex Footwear Marketing Plan Okঅদেখা ভুবনNo ratings yet
- Proposal For Edumate: (SEO: Search Engine OptimizerDocument14 pagesProposal For Edumate: (SEO: Search Engine Optimizerseoservices singaporeNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Sponsored Ad TypesDocument125 pagesIntroduction To Sponsored Ad TypesNazim AltafNo ratings yet
- Billabong Building A Digital Marketing StrategyDocument2 pagesBillabong Building A Digital Marketing StrategyJYOTI MAURYANo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Promo 1st Edition OguinnDocument14 pagesTest Bank For Promo 1st Edition Oguinnkieraorianavstz4No ratings yet
- 4 P's SurveyDocument3 pages4 P's SurveychariseNo ratings yet
- Advertising Programmes ComponentsDocument18 pagesAdvertising Programmes ComponentsakshaypahalwanNo ratings yet
- Nivea: Managing An Umbrella BrandDocument28 pagesNivea: Managing An Umbrella BrandGaurav Nagar100% (3)
- Target ImcDocument8 pagesTarget Imcginish12100% (1)
- Academy Lesson Slides - Amanda Bond Facebook Ads PDFDocument44 pagesAcademy Lesson Slides - Amanda Bond Facebook Ads PDFDona KalitNo ratings yet
- Marketing - Promotional ToolsDocument14 pagesMarketing - Promotional ToolsRhea May PeducaNo ratings yet