Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 viewsABEL 321 (1M) 313 Airline Marketing (Traffic & Sales Procedures)
ABEL 321 (1M) 313 Airline Marketing (Traffic & Sales Procedures)
Uploaded by
Francesca Nichole VergaraThis document provides an overview of airline marketing principles and techniques. It discusses key concepts like defining marketing, different corporate strategies like production and sales orientations, and the marketing mix elements of product, price, place, and promotion. It also outlines techniques for market investigation and segmentation of different passenger and freight markets. Demand forecasting methods are presented, like growth factor analysis and regression analysis. Factors affecting future demand like price, market trends, and service provision are also summarized. The document uses acronyms and mnemonics to help recall the various concepts.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Corporate and Division Level Strategic PlanningDocument7 pagesCorporate and Division Level Strategic PlanningMOHAMMED ALI CHOWDHURY100% (8)
- Tourism and Hospitality Marketing Reviewer-1Document6 pagesTourism and Hospitality Marketing Reviewer-1aira mikaela ruazolNo ratings yet
- Marketing Management Notes Unit 1Document34 pagesMarketing Management Notes Unit 1Neha Hittoo100% (1)
- Asset SwapsDocument5 pagesAsset Swaps15dumplings100% (1)
- FIN331-101 2010 Fall Exam2 AnswersDocument7 pagesFIN331-101 2010 Fall Exam2 Answersdaliaol100% (1)
- Marketing ManagementDocument29 pagesMarketing Managementapi-3708369100% (1)
- Full Download Small Business Management Longenecker 17Th Edition Solutions Manual PDFDocument41 pagesFull Download Small Business Management Longenecker 17Th Edition Solutions Manual PDFmaryann.spiller922100% (21)
- Marketing Plan OutlineDocument2 pagesMarketing Plan OutlineChristian ReambonanzaNo ratings yet
- Developing Marketing Strategies and PlansDocument5 pagesDeveloping Marketing Strategies and PlansPragati100% (1)
- Marketing ReviewerDocument6 pagesMarketing ReviewerLara BalangiaoNo ratings yet
- DocxDocument18 pagesDocx朱潇妤No ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document6 pagesChapter 2rico enteroneNo ratings yet
- Marketing 1 6 SGDocument12 pagesMarketing 1 6 SGImtiaz SultanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document36 pagesChapter 6oakleyhouNo ratings yet
- Marketing Concept Consumer Behavior B.com V Sem HonsDocument38 pagesMarketing Concept Consumer Behavior B.com V Sem HonsgauravNo ratings yet
- Agri REVIEWERDocument11 pagesAgri REVIEWERLeila Jane TorresNo ratings yet
- Winning Markets Through Market-Oriented Strategic PlanningDocument8 pagesWinning Markets Through Market-Oriented Strategic PlanningRashid AliNo ratings yet
- MKTG Plan OutlineDocument4 pagesMKTG Plan Outlineadriane aquinoNo ratings yet
- Introduction of Marketing Management: Chapter - 1Document5 pagesIntroduction of Marketing Management: Chapter - 1Rajat PalNo ratings yet
- MKTG FunctionDocument44 pagesMKTG FunctionTanvi DeshmukhNo ratings yet
- MK 323 Final Study GuideDocument20 pagesMK 323 Final Study GuidePutt SiripakornNo ratings yet
- Marketingmanagement 1Document8 pagesMarketingmanagement 1Nithyashree MNo ratings yet
- Advertising Campaign Format I. Executive SummaryDocument4 pagesAdvertising Campaign Format I. Executive SummaryAui PauNo ratings yet
- MarketingReviewer 4thQDocument6 pagesMarketingReviewer 4thQmancao813474No ratings yet
- Market?: MarketingDocument15 pagesMarket?: Marketingmurshidaman3No ratings yet
- GROUP 2 BMHDocument2 pagesGROUP 2 BMHPearl RagasajoNo ratings yet
- Sales BudgetsDocument34 pagesSales BudgetsRaman KulkarniNo ratings yet
- Marketing Management Quiz Questions - CompiledDocument16 pagesMarketing Management Quiz Questions - Compiledsanpreet.kaur531No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Developing Marketing Strategies and Plans: The Value ChainDocument9 pagesChapter 2 Developing Marketing Strategies and Plans: The Value ChainJunaid AhmedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Fesibility StudyDocument43 pagesChapter 2 - Fesibility StudyDaniella A. LazaroNo ratings yet
- (Inglés Téc.) EVALUACIÓN (Resuelto) - Taller Modales PasivosDocument3 pages(Inglés Téc.) EVALUACIÓN (Resuelto) - Taller Modales PasivosPachaNo ratings yet
- Overview of Strategic MarketingDocument5 pagesOverview of Strategic Marketingglrosaaa cNo ratings yet
- Terms of Reference - Final Work Prof. Andrés Venegas PiedrahitaDocument6 pagesTerms of Reference - Final Work Prof. Andrés Venegas PiedrahitaLaura CelisNo ratings yet
- Assignment SCMDocument2 pagesAssignment SCMBOL AKETCHNo ratings yet
- ABE 426 Lesson 2 of Module 1 02062024Document10 pagesABE 426 Lesson 2 of Module 1 02062024ruthieann542No ratings yet
- Marketing ManagementDocument39 pagesMarketing ManagementPranay ManwarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Developing Marketing Strategies and Plans I. Marketing and Customer Value The Value Delivery ProcessDocument7 pagesChapter 2: Developing Marketing Strategies and Plans I. Marketing and Customer Value The Value Delivery ProcessNicole OngNo ratings yet
- Sales ForecastingDocument4 pagesSales ForecastingNishtha GuptaNo ratings yet
- General Parts of Business PlanDocument6 pagesGeneral Parts of Business PlanGabriel MartinNo ratings yet
- Marketing ManagementDocument38 pagesMarketing ManagementKhubaib AkNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document5 pagesChapter 5Kaleab TessemaNo ratings yet
- Strategic Marketing Plan StructureDocument7 pagesStrategic Marketing Plan StructureOana GorneaNo ratings yet
- CH 3 Marketing Management Bba 2020Document70 pagesCH 3 Marketing Management Bba 2020shoaibNo ratings yet
- MM - Unit 1Document15 pagesMM - Unit 184.PREMNATH ENo ratings yet
- Second Semester Principles of Marketing PDFDocument8 pagesSecond Semester Principles of Marketing PDFIvan NuescaNo ratings yet
- MKM 302: Product Management: Unit 6: Developing Product StrategyDocument3 pagesMKM 302: Product Management: Unit 6: Developing Product StrategyPlatero RolandNo ratings yet
- Core Strategy: I. Objective & PrioitiesDocument7 pagesCore Strategy: I. Objective & PrioitiesDietmar LengauerNo ratings yet
- Marketing 1Document16 pagesMarketing 1tamilarasu.r11No ratings yet
- EnglezaDocument18 pagesEnglezaLucian MaicanNo ratings yet
- Assignment03 AE-CP2 Sinag Karylle Lindsay D BSA IIDocument10 pagesAssignment03 AE-CP2 Sinag Karylle Lindsay D BSA IILinrylle LesinNo ratings yet
- 1 Sem Bcom - Marketing and Service Management CH 1-5 PDFDocument52 pages1 Sem Bcom - Marketing and Service Management CH 1-5 PDFAkashNo ratings yet
- StrategicDocument44 pagesStrategicMichael LucasNo ratings yet
- Assignment of Marketing ManagementDocument27 pagesAssignment of Marketing ManagementPrabhat PatelNo ratings yet
- MM-V BBM 2017 SyDocument59 pagesMM-V BBM 2017 Sykhubaib AkramNo ratings yet
- Sales and Distibution - Maha CementDocument101 pagesSales and Distibution - Maha CementVenkatesh100% (1)
- Chapter 1: Defining Marketing For New RealitiesDocument52 pagesChapter 1: Defining Marketing For New RealitiesAmit JhaNo ratings yet
- POMDocument64 pagesPOMvignesh. viswanathanNo ratings yet
- Cheat Sheet MarketingDocument3 pagesCheat Sheet MarketingCharlotte GillandersNo ratings yet
- Innovation Management GlobalDocument2 pagesInnovation Management Globalvaksoo vaiNo ratings yet
- Marketing in ITDocument11 pagesMarketing in ITMenesKhidaAngelicaNo ratings yet
- Portfolio in Marketing MGTDocument48 pagesPortfolio in Marketing MGTNerizza TiraoNo ratings yet
- Stocks and BondsDocument46 pagesStocks and BondsAlaissaNo ratings yet
- MMPC 014Document6 pagesMMPC 014Pawan ShokeenNo ratings yet
- Financial Statement AnalysisDocument9 pagesFinancial Statement AnalysisJamil SalibioNo ratings yet
- Managing Bank CapitalDocument24 pagesManaging Bank CapitalHenry So E DiarkoNo ratings yet
- RIL-RPL ValuationReportDocument11 pagesRIL-RPL ValuationReportjpalkarNo ratings yet
- Determinants of Portfolio Performance: A Framework For AnalysisDocument6 pagesDeterminants of Portfolio Performance: A Framework For AnalysisVicky SajnaniNo ratings yet
- Treasury BondsDocument5 pagesTreasury BondsDivya Raja ManickamNo ratings yet
- Evaluating The External EnvironmentDocument40 pagesEvaluating The External EnvironmentPaulus FanggidaeNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 Tutorial ProblemsDocument4 pagesTopic 2 Tutorial Problemsda.arts.ttNo ratings yet
- Credit Policy For Tam EnterprisesDocument3 pagesCredit Policy For Tam Enterprises04Ronita MitraNo ratings yet
- Research CryptocurrencyDocument19 pagesResearch Cryptocurrencymayhem happening100% (1)
- Long Term Sources of FundsDocument63 pagesLong Term Sources of FundsAnonymous 9YyCbPANo ratings yet
- Bse and NseDocument5 pagesBse and Nse29.Kritika SinghNo ratings yet
- Forex Factory Forex MarketsDocument1 pageForex Factory Forex MarketsMohammad RamezaniNo ratings yet
- Black Book Project PalakDocument93 pagesBlack Book Project PalakJoel CyrusNo ratings yet
- Mini CaseDocument15 pagesMini CaseSammir Malhotra0% (1)
- Foro 2 Carlos MongeDocument3 pagesForo 2 Carlos MongeCARLOSNo ratings yet
- Arbitrage Pricing ModelDocument11 pagesArbitrage Pricing ModelAmit SinhaNo ratings yet
- Interview With Pierre Gabris, Alpenrose Wealth ManagementDocument3 pagesInterview With Pierre Gabris, Alpenrose Wealth ManagementWorldwide finance newsNo ratings yet
- Banking and Finance QuestionsDocument22 pagesBanking and Finance Questionsatul mishraNo ratings yet
- Who Really Owns Your Stocks and BondsDocument13 pagesWho Really Owns Your Stocks and BondsMuffy Dobbs0% (1)
- Financial Times Europe - 07-11-2020Document124 pagesFinancial Times Europe - 07-11-2020HoangNo ratings yet
- What Accounts For The Difference in Price of Bubble Teas in Bangkok?Document32 pagesWhat Accounts For The Difference in Price of Bubble Teas in Bangkok?teerakarn.tangNo ratings yet
- Exam #1 ReviewDocument5 pagesExam #1 ReviewThùy DươngNo ratings yet
- Forex & DerivativesDocument6 pagesForex & Derivativessarahbee100% (1)
- FOREXDocument7 pagesFOREXpoppy2890No ratings yet
- Jays Momentum Setup With Bar CountDocument22 pagesJays Momentum Setup With Bar CountlowtarhkNo ratings yet
ABEL 321 (1M) 313 Airline Marketing (Traffic & Sales Procedures)
ABEL 321 (1M) 313 Airline Marketing (Traffic & Sales Procedures)
Uploaded by
Francesca Nichole Vergara0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views3 pagesThis document provides an overview of airline marketing principles and techniques. It discusses key concepts like defining marketing, different corporate strategies like production and sales orientations, and the marketing mix elements of product, price, place, and promotion. It also outlines techniques for market investigation and segmentation of different passenger and freight markets. Demand forecasting methods are presented, like growth factor analysis and regression analysis. Factors affecting future demand like price, market trends, and service provision are also summarized. The document uses acronyms and mnemonics to help recall the various concepts.
Original Description:
Original Title
ACFrOgBGdj7xQQ8mJ8lcIIMcAhhUAD64gkj2PWdqmZ-7efjT0lk4_pR1RlSp9DjK5tT2257H0RANbDZjNMI7fRS3Fn5Mv3tRbTHQvMWqKsWRGMhN_Uta81LAAHAAdKT788W404HNo8uBiiX1pDZE
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides an overview of airline marketing principles and techniques. It discusses key concepts like defining marketing, different corporate strategies like production and sales orientations, and the marketing mix elements of product, price, place, and promotion. It also outlines techniques for market investigation and segmentation of different passenger and freight markets. Demand forecasting methods are presented, like growth factor analysis and regression analysis. Factors affecting future demand like price, market trends, and service provision are also summarized. The document uses acronyms and mnemonics to help recall the various concepts.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views3 pagesABEL 321 (1M) 313 Airline Marketing (Traffic & Sales Procedures)
ABEL 321 (1M) 313 Airline Marketing (Traffic & Sales Procedures)
Uploaded by
Francesca Nichole VergaraThis document provides an overview of airline marketing principles and techniques. It discusses key concepts like defining marketing, different corporate strategies like production and sales orientations, and the marketing mix elements of product, price, place, and promotion. It also outlines techniques for market investigation and segmentation of different passenger and freight markets. Demand forecasting methods are presented, like growth factor analysis and regression analysis. Factors affecting future demand like price, market trends, and service provision are also summarized. The document uses acronyms and mnemonics to help recall the various concepts.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 3
ABEL 321 (1M) 313
Airline Marketing (Traffic & Sales Procedures)
Reference: Air Transport – A Marketing Perspective (1982) by Stephen Shaw
I. General Provisions (Prelims) (Week 1)
A. Fundamentals of Marketing
a. Marketing Defined – two definitions:
i. (Remember MP-IAS-CRP) The Management Process responsible for Identifying, Anticipating and Satisfying Customer Requirement Profitably (UK
Institute of Marketing, quoted in Wilmshurst, 1978)
ii.(Remember HADS-NW-EP) Is Human Activity Directed at Satisfying Needs and Wants through Exchange Processes (Kotler, 1976)
b. The Application of Marketing Theory
i. Market Investigation – a business may employ three (3) different philosophies: (Remember PSM)
1. Production Orientation – corporate effort is directed to the manufacture of high-quality products
2. Sales Orientation – costly expenditure on advertising, trade promotions through inducements or price cuts, or high-pressure selling by a
large sales force.
3. Marketing Orientation – research is conducted to gain a thorough knowledge of the structure of [the] markets.
ii.Definition of Corporate Strategy – the following are the phases: (Remember OMP)
1. Objective
a. profit maximization;
b. minimization of environmental nuisance;
c. other social goals, e.g., to help increase employment during rising structural unemployment
2. Mission – statement of the broad area of activity with which the firm is concerned
3. Plan – aims to use market gap which can exploit the strengths of the firm whilst reducing or eliminating its weaknesses
iii. Organizing for Marketing (Remember IE)
1. Internal Organization – deployment of own (human) resources, e.g., definition of a corporate management structure, or application of
appropriate personnel recruitment and training policies
2. External Organization – defines the role to be played by outsiders in marketing and who these outsiders should be, i.e., outsourcing
iv. Designing the Product – (Remember M-GRUN)
the ideal of product development is a phase whereby products are made of a type, and in a sufficient quantity, to allow a launch that will Meet
Genuinely Understood and Researched consumer Needs
v.Pricing the Product – decisions must be made about
(Remember GR)
1. the General level of prices of products, and also
2. about any Readjustments
[Purpose] is to give psychologically appealing and convenient prices
vi. Selling the Product
– not a synonym for ‘marketing;’
- (Remember OBC) culmination of the marketing process, where products planned on the basis of detailed market investigation are Offered
to and Bought by Consumers
Divided into two (2) parts: (Remember CpAo)
1. Communication with potential customers
2. Administration of the order through suitable procedures
vii. Distributing the Product – often takes place in advance of sale, due to customer demands for an immediate availability of goods through
point-of-sale stockholding
viii. Product Strategy (diversification) and Life Cycles (never-ending because a product moves to maturity and eventual decline, and then
introduction of a new product)
c. Marketing and Airlines – the theory of marketing can indeed indicate a logical process for airline decision-making
B. Marketing in the Air Transport Services (Week 2)
a. Techniques of Market Investigation (Remember RC-TUD)
i. Desk Research – collection of statistics
ii.Consumer Surveys – defining reaction of customers
iii. Test Marketing – mounting a campaign over only a small market area he hopes eventually to penetrate
iv. Use of Consumer Groups – setting up of committees to represent views of air travellers
v.Deduction (from easily available data)
b. Air Passenger Market Segmentation (Remember BLAP)
i. Business Travel Market
ii.Leisure Travel Market
iii. Personal Travel Market
iv. Air Freight Market
1. Air Freight Market Segmentation (Remember pEn)
a. Emergency Traffic
b. Routine Perishable Traffic
c. Routine Non-Perishable Traffic
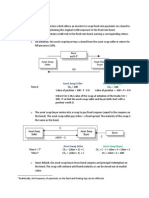
c. Demand Forecasting Techniques – (Remember GCM)
i. Growth Factor Method- attempts to derive a time-series of past traffic data covering a period of years prior to the forecasting base
ii.Category Analysis – divides the population of the market area into a number of categories according to socioeconomic characteristics
iii. Multiple Regression Analysis – relates changes in demand to those factors which are believed to cause such changes to arise
d. Factors Affecting Future Demand Levels (Remember PTP)
i. Price of Air Travel
ii.Trends in Air Travel Market Potential
iii. Provision of Air Transport Services
You might also like
- Corporate and Division Level Strategic PlanningDocument7 pagesCorporate and Division Level Strategic PlanningMOHAMMED ALI CHOWDHURY100% (8)
- Tourism and Hospitality Marketing Reviewer-1Document6 pagesTourism and Hospitality Marketing Reviewer-1aira mikaela ruazolNo ratings yet
- Marketing Management Notes Unit 1Document34 pagesMarketing Management Notes Unit 1Neha Hittoo100% (1)
- Asset SwapsDocument5 pagesAsset Swaps15dumplings100% (1)
- FIN331-101 2010 Fall Exam2 AnswersDocument7 pagesFIN331-101 2010 Fall Exam2 Answersdaliaol100% (1)
- Marketing ManagementDocument29 pagesMarketing Managementapi-3708369100% (1)
- Full Download Small Business Management Longenecker 17Th Edition Solutions Manual PDFDocument41 pagesFull Download Small Business Management Longenecker 17Th Edition Solutions Manual PDFmaryann.spiller922100% (21)
- Marketing Plan OutlineDocument2 pagesMarketing Plan OutlineChristian ReambonanzaNo ratings yet
- Developing Marketing Strategies and PlansDocument5 pagesDeveloping Marketing Strategies and PlansPragati100% (1)
- Marketing ReviewerDocument6 pagesMarketing ReviewerLara BalangiaoNo ratings yet
- DocxDocument18 pagesDocx朱潇妤No ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document6 pagesChapter 2rico enteroneNo ratings yet
- Marketing 1 6 SGDocument12 pagesMarketing 1 6 SGImtiaz SultanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document36 pagesChapter 6oakleyhouNo ratings yet
- Marketing Concept Consumer Behavior B.com V Sem HonsDocument38 pagesMarketing Concept Consumer Behavior B.com V Sem HonsgauravNo ratings yet
- Agri REVIEWERDocument11 pagesAgri REVIEWERLeila Jane TorresNo ratings yet
- Winning Markets Through Market-Oriented Strategic PlanningDocument8 pagesWinning Markets Through Market-Oriented Strategic PlanningRashid AliNo ratings yet
- MKTG Plan OutlineDocument4 pagesMKTG Plan Outlineadriane aquinoNo ratings yet
- Introduction of Marketing Management: Chapter - 1Document5 pagesIntroduction of Marketing Management: Chapter - 1Rajat PalNo ratings yet
- MKTG FunctionDocument44 pagesMKTG FunctionTanvi DeshmukhNo ratings yet
- MK 323 Final Study GuideDocument20 pagesMK 323 Final Study GuidePutt SiripakornNo ratings yet
- Marketingmanagement 1Document8 pagesMarketingmanagement 1Nithyashree MNo ratings yet
- Advertising Campaign Format I. Executive SummaryDocument4 pagesAdvertising Campaign Format I. Executive SummaryAui PauNo ratings yet
- MarketingReviewer 4thQDocument6 pagesMarketingReviewer 4thQmancao813474No ratings yet
- Market?: MarketingDocument15 pagesMarket?: Marketingmurshidaman3No ratings yet
- GROUP 2 BMHDocument2 pagesGROUP 2 BMHPearl RagasajoNo ratings yet
- Sales BudgetsDocument34 pagesSales BudgetsRaman KulkarniNo ratings yet
- Marketing Management Quiz Questions - CompiledDocument16 pagesMarketing Management Quiz Questions - Compiledsanpreet.kaur531No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Developing Marketing Strategies and Plans: The Value ChainDocument9 pagesChapter 2 Developing Marketing Strategies and Plans: The Value ChainJunaid AhmedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Fesibility StudyDocument43 pagesChapter 2 - Fesibility StudyDaniella A. LazaroNo ratings yet
- (Inglés Téc.) EVALUACIÓN (Resuelto) - Taller Modales PasivosDocument3 pages(Inglés Téc.) EVALUACIÓN (Resuelto) - Taller Modales PasivosPachaNo ratings yet
- Overview of Strategic MarketingDocument5 pagesOverview of Strategic Marketingglrosaaa cNo ratings yet
- Terms of Reference - Final Work Prof. Andrés Venegas PiedrahitaDocument6 pagesTerms of Reference - Final Work Prof. Andrés Venegas PiedrahitaLaura CelisNo ratings yet
- Assignment SCMDocument2 pagesAssignment SCMBOL AKETCHNo ratings yet
- ABE 426 Lesson 2 of Module 1 02062024Document10 pagesABE 426 Lesson 2 of Module 1 02062024ruthieann542No ratings yet
- Marketing ManagementDocument39 pagesMarketing ManagementPranay ManwarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Developing Marketing Strategies and Plans I. Marketing and Customer Value The Value Delivery ProcessDocument7 pagesChapter 2: Developing Marketing Strategies and Plans I. Marketing and Customer Value The Value Delivery ProcessNicole OngNo ratings yet
- Sales ForecastingDocument4 pagesSales ForecastingNishtha GuptaNo ratings yet
- General Parts of Business PlanDocument6 pagesGeneral Parts of Business PlanGabriel MartinNo ratings yet
- Marketing ManagementDocument38 pagesMarketing ManagementKhubaib AkNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document5 pagesChapter 5Kaleab TessemaNo ratings yet
- Strategic Marketing Plan StructureDocument7 pagesStrategic Marketing Plan StructureOana GorneaNo ratings yet
- CH 3 Marketing Management Bba 2020Document70 pagesCH 3 Marketing Management Bba 2020shoaibNo ratings yet
- MM - Unit 1Document15 pagesMM - Unit 184.PREMNATH ENo ratings yet
- Second Semester Principles of Marketing PDFDocument8 pagesSecond Semester Principles of Marketing PDFIvan NuescaNo ratings yet
- MKM 302: Product Management: Unit 6: Developing Product StrategyDocument3 pagesMKM 302: Product Management: Unit 6: Developing Product StrategyPlatero RolandNo ratings yet
- Core Strategy: I. Objective & PrioitiesDocument7 pagesCore Strategy: I. Objective & PrioitiesDietmar LengauerNo ratings yet
- Marketing 1Document16 pagesMarketing 1tamilarasu.r11No ratings yet
- EnglezaDocument18 pagesEnglezaLucian MaicanNo ratings yet
- Assignment03 AE-CP2 Sinag Karylle Lindsay D BSA IIDocument10 pagesAssignment03 AE-CP2 Sinag Karylle Lindsay D BSA IILinrylle LesinNo ratings yet
- 1 Sem Bcom - Marketing and Service Management CH 1-5 PDFDocument52 pages1 Sem Bcom - Marketing and Service Management CH 1-5 PDFAkashNo ratings yet
- StrategicDocument44 pagesStrategicMichael LucasNo ratings yet
- Assignment of Marketing ManagementDocument27 pagesAssignment of Marketing ManagementPrabhat PatelNo ratings yet
- MM-V BBM 2017 SyDocument59 pagesMM-V BBM 2017 Sykhubaib AkramNo ratings yet
- Sales and Distibution - Maha CementDocument101 pagesSales and Distibution - Maha CementVenkatesh100% (1)
- Chapter 1: Defining Marketing For New RealitiesDocument52 pagesChapter 1: Defining Marketing For New RealitiesAmit JhaNo ratings yet
- POMDocument64 pagesPOMvignesh. viswanathanNo ratings yet
- Cheat Sheet MarketingDocument3 pagesCheat Sheet MarketingCharlotte GillandersNo ratings yet
- Innovation Management GlobalDocument2 pagesInnovation Management Globalvaksoo vaiNo ratings yet
- Marketing in ITDocument11 pagesMarketing in ITMenesKhidaAngelicaNo ratings yet
- Portfolio in Marketing MGTDocument48 pagesPortfolio in Marketing MGTNerizza TiraoNo ratings yet
- Stocks and BondsDocument46 pagesStocks and BondsAlaissaNo ratings yet
- MMPC 014Document6 pagesMMPC 014Pawan ShokeenNo ratings yet
- Financial Statement AnalysisDocument9 pagesFinancial Statement AnalysisJamil SalibioNo ratings yet
- Managing Bank CapitalDocument24 pagesManaging Bank CapitalHenry So E DiarkoNo ratings yet
- RIL-RPL ValuationReportDocument11 pagesRIL-RPL ValuationReportjpalkarNo ratings yet
- Determinants of Portfolio Performance: A Framework For AnalysisDocument6 pagesDeterminants of Portfolio Performance: A Framework For AnalysisVicky SajnaniNo ratings yet
- Treasury BondsDocument5 pagesTreasury BondsDivya Raja ManickamNo ratings yet
- Evaluating The External EnvironmentDocument40 pagesEvaluating The External EnvironmentPaulus FanggidaeNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 Tutorial ProblemsDocument4 pagesTopic 2 Tutorial Problemsda.arts.ttNo ratings yet
- Credit Policy For Tam EnterprisesDocument3 pagesCredit Policy For Tam Enterprises04Ronita MitraNo ratings yet
- Research CryptocurrencyDocument19 pagesResearch Cryptocurrencymayhem happening100% (1)
- Long Term Sources of FundsDocument63 pagesLong Term Sources of FundsAnonymous 9YyCbPANo ratings yet
- Bse and NseDocument5 pagesBse and Nse29.Kritika SinghNo ratings yet
- Forex Factory Forex MarketsDocument1 pageForex Factory Forex MarketsMohammad RamezaniNo ratings yet
- Black Book Project PalakDocument93 pagesBlack Book Project PalakJoel CyrusNo ratings yet
- Mini CaseDocument15 pagesMini CaseSammir Malhotra0% (1)
- Foro 2 Carlos MongeDocument3 pagesForo 2 Carlos MongeCARLOSNo ratings yet
- Arbitrage Pricing ModelDocument11 pagesArbitrage Pricing ModelAmit SinhaNo ratings yet
- Interview With Pierre Gabris, Alpenrose Wealth ManagementDocument3 pagesInterview With Pierre Gabris, Alpenrose Wealth ManagementWorldwide finance newsNo ratings yet
- Banking and Finance QuestionsDocument22 pagesBanking and Finance Questionsatul mishraNo ratings yet
- Who Really Owns Your Stocks and BondsDocument13 pagesWho Really Owns Your Stocks and BondsMuffy Dobbs0% (1)
- Financial Times Europe - 07-11-2020Document124 pagesFinancial Times Europe - 07-11-2020HoangNo ratings yet
- What Accounts For The Difference in Price of Bubble Teas in Bangkok?Document32 pagesWhat Accounts For The Difference in Price of Bubble Teas in Bangkok?teerakarn.tangNo ratings yet
- Exam #1 ReviewDocument5 pagesExam #1 ReviewThùy DươngNo ratings yet
- Forex & DerivativesDocument6 pagesForex & Derivativessarahbee100% (1)
- FOREXDocument7 pagesFOREXpoppy2890No ratings yet
- Jays Momentum Setup With Bar CountDocument22 pagesJays Momentum Setup With Bar CountlowtarhkNo ratings yet