Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views13 Identify Componenet of EFI
13 Identify Componenet of EFI
Uploaded by
maliksawan376116The document outlines a daily lesson plan about fuel injection and carburetion systems. The 120-minute class will teach 1st year auto and diesel students about the components of an electronic fuel injection (EFI) system and the working principle of EFI systems. The lesson will focus on the working of EFI systems through hands-on activities inspecting and troubleshooting an EFI system. The 15 main components of an EFI system are described in detail, including the fuel injector, engine control unit, various sensors, fuel pump, fuel rail, and more. Students will be assessed on their understanding of EFI systems through questions and explaining what they learned.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Al Maths Pure Unit 6 MsDocument8 pagesAl Maths Pure Unit 6 MsHacjer EiNSTi3NNo ratings yet
- Introduction to the simulation of power plants for EBSILON®Professional Version 15From EverandIntroduction to the simulation of power plants for EBSILON®Professional Version 15No ratings yet
- Diesel Common Rail Injection Electronic Components ExplainedFrom EverandDiesel Common Rail Injection Electronic Components ExplainedRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (7)
- Experiment No 08: Electronic Injection System in S.I. EngineDocument6 pagesExperiment No 08: Electronic Injection System in S.I. EngineSIDDHARTH JAINNo ratings yet
- EFI (Electronic Fuel Injectionnbmn)Document4 pagesEFI (Electronic Fuel Injectionnbmn)Saladin NominorNo ratings yet
- Submitted by P.Nagaraju 160113735159: Electronic Fuel InjectorDocument20 pagesSubmitted by P.Nagaraju 160113735159: Electronic Fuel InjectorvamshiNo ratings yet
- Electronic Fuel Management in I.C Engines G Nagarajan Professor Department of Mechanical Engg. Anna University Chennai 60025Document5 pagesElectronic Fuel Management in I.C Engines G Nagarajan Professor Department of Mechanical Engg. Anna University Chennai 60025alagarg137691No ratings yet
- 1) Efi Inf 1 IntroDocument14 pages1) Efi Inf 1 IntroNahwera IvanNo ratings yet
- Ic Engine AssignmentDocument7 pagesIc Engine AssignmentMuhammad Fahad Khan 51-FET/BSCMET/F19No ratings yet
- Automotive: Describe EFI Engine Working ProcedureDocument19 pagesAutomotive: Describe EFI Engine Working ProcedureJ Naveen KumarNo ratings yet
- Multi Point Fuel Injection SystemDocument12 pagesMulti Point Fuel Injection Systemashwini yewaleNo ratings yet
- Multi Port Fuel Injection SystemDocument4 pagesMulti Port Fuel Injection SystemVarsha SreekumarNo ratings yet
- Ae 1 Module PDFDocument113 pagesAe 1 Module PDFUnni HaridasNo ratings yet
- Electronic Fuel Injection System: Damian CastelinoDocument23 pagesElectronic Fuel Injection System: Damian CastelinoRamjiNo ratings yet
- Mat Unit-1 Part-2Document14 pagesMat Unit-1 Part-2Md zakirNo ratings yet
- MR SolomonDocument6 pagesMR SolomonMarcusNo ratings yet
- Spark IgnitionDocument23 pagesSpark IgnitionRoshaan RoshanNo ratings yet
- Electronics Fuel InjectionDocument6 pagesElectronics Fuel Injectionsorin grecuNo ratings yet
- Engine Management MechatronicsDocument18 pagesEngine Management MechatronicsTanuj Kumar67% (3)
- Basic Overview of Electronic Fuel InjectionDocument23 pagesBasic Overview of Electronic Fuel InjectionAndhieAbrahamNo ratings yet
- UNIT7L1 - 2S - Electronically Controlled Fuel SystemsDocument10 pagesUNIT7L1 - 2S - Electronically Controlled Fuel SystemsEbied Yousif AlyNo ratings yet
- AE&ES Lab Front Page Merged Pages 2 22Document4 pagesAE&ES Lab Front Page Merged Pages 2 22VIVEK KUMAR DASNo ratings yet
- Multi Point Fuel InjectionDocument15 pagesMulti Point Fuel InjectionHemanth MagantiNo ratings yet
- Fuel Injection SystemDocument9 pagesFuel Injection SystemJM PraveenNo ratings yet
- Automotive ElectronicsDocument44 pagesAutomotive ElectronicsRohit Kumar100% (1)
- Soochna 2012 FinalDocument140 pagesSoochna 2012 FinalHanuma Reddy100% (1)
- Electronic Assignment 2Document5 pagesElectronic Assignment 2MarcusNo ratings yet
- AE - Unit III - Lect 4Document14 pagesAE - Unit III - Lect 4Hh HhNo ratings yet
- Electronic Fuel Injection OverviewDocument9 pagesElectronic Fuel Injection Overviewalllhass97No ratings yet
- Electronic Fuel Injection System ELECTRODocument6 pagesElectronic Fuel Injection System ELECTRODIGITAL DAILY DEALSNo ratings yet
- Lexus Es300 Technical TrainingDocument20 pagesLexus Es300 Technical Trainingkelly100% (50)
- Unit 7: Electronically Controlled Fuel SystemsDocument8 pagesUnit 7: Electronically Controlled Fuel SystemsArmando HenríquezNo ratings yet
- Multipoint Fuel Injection SystemDocument6 pagesMultipoint Fuel Injection Systemalan kurniawanNo ratings yet
- Mixture Preparation SIDocument42 pagesMixture Preparation SIMekonnen AyalNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document49 pagesUnit 2Ramanathan DuraiNo ratings yet
- Electronic Fuel Injection System: Contributions and Challenges For Light VehiclesDocument22 pagesElectronic Fuel Injection System: Contributions and Challenges For Light VehiclesRoba FikaduNo ratings yet
- Fuel System: Systems OperationDocument7 pagesFuel System: Systems OperationbejoythomasNo ratings yet
- 1 Mechanical Engineering Dept. CEME NUSTDocument34 pages1 Mechanical Engineering Dept. CEME NUSTAhsan AliNo ratings yet
- Fuel Injection EvolutionDocument9 pagesFuel Injection EvolutioncarechimbacomemierdaNo ratings yet
- Fuel System C27Document7 pagesFuel System C27insano008No ratings yet
- Electronic Diesel ControlDocument31 pagesElectronic Diesel ControlAnteneh MesfinNo ratings yet
- Electronics Final ProjectDocument13 pagesElectronics Final ProjectScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Report-Multi Point Fuel Injection-MpfiDocument16 pagesReport-Multi Point Fuel Injection-MpfiIshan Rastogi100% (4)
- What Is Fuel Injection System?Document20 pagesWhat Is Fuel Injection System?gelo an binbi nonNo ratings yet
- FUEL SYSTEM OF C18 and C6.6Document135 pagesFUEL SYSTEM OF C18 and C6.6Sahr, Cyprian Fillie100% (2)
- Lecture-9-Electronic Engine Management SystemDocument102 pagesLecture-9-Electronic Engine Management SystemPiyush BidwaiNo ratings yet
- 4 Engine: 4.1 General DescriptionDocument63 pages4 Engine: 4.1 General DescriptionGabriel Balcazar100% (1)
- CHAPTER - 8 Electronic Fuel Injection and Ignition SystemsDocument30 pagesCHAPTER - 8 Electronic Fuel Injection and Ignition SystemsAbubeker Arebo0% (1)
- Explain Function of Mass Air Flow Sensor.: The Leaner FuelDocument15 pagesExplain Function of Mass Air Flow Sensor.: The Leaner FuelAbubaker MuzayinNo ratings yet
- Fuel Injection SystemDocument26 pagesFuel Injection Systemjayant pathakNo ratings yet
- Electronic Multipoint Fuel Injection SystemDocument15 pagesElectronic Multipoint Fuel Injection SystemDIPAK VINAYAK SHIRBHATE100% (1)
- MPFI Vs Carburetor Technology For Multi Cylinder EnginesDocument14 pagesMPFI Vs Carburetor Technology For Multi Cylinder EnginesDipak Kumar100% (1)
- GDIDocument7 pagesGDIlinhda561No ratings yet
- Knock SensorDocument15 pagesKnock SensorSurya IrawanNo ratings yet
- Report-Multi Point Fuel Injection-MpfiDocument19 pagesReport-Multi Point Fuel Injection-MpfiHemant PatraNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document25 pagesLecture 3ShzllNo ratings yet
- Electronic Fuel Injection in VehiclesDocument46 pagesElectronic Fuel Injection in Vehicleskelvinthuita877No ratings yet
- Computer Control SystemDocument67 pagesComputer Control SystemToua YajNo ratings yet
- AUTOTRONICADocument3 pagesAUTOTRONICAJhon Arreaga AguilarNo ratings yet
- Naval Diesel Engineering: The Fundamentals of Operation, Performance and EfficiencyFrom EverandNaval Diesel Engineering: The Fundamentals of Operation, Performance and EfficiencyNo ratings yet
- 5 Identify Parts of Exhaust SystemDocument3 pages5 Identify Parts of Exhaust Systemmaliksawan376116No ratings yet
- 18 Dismental and Assemble Distributer Type Diesel Fuel PumpDocument3 pages18 Dismental and Assemble Distributer Type Diesel Fuel Pumpmaliksawan376116No ratings yet
- 3 Dismble Assemble Oil Bath FilterDocument2 pages3 Dismble Assemble Oil Bath Filtermaliksawan376116No ratings yet
- 24 Identify Component of Vehicle Cruistronic SystemDocument2 pages24 Identify Component of Vehicle Cruistronic Systemmaliksawan376116No ratings yet
- 14 Fault Finding by Coding and Decoding of EFI by ManuallyDocument3 pages14 Fault Finding by Coding and Decoding of EFI by Manuallymaliksawan376116No ratings yet
- A Z of Simple Living BookDocument68 pagesA Z of Simple Living Bookdrsubramanian100% (4)
- Test - Environmental Eng. - DRAFTDocument7 pagesTest - Environmental Eng. - DRAFTDesire IsaiahNo ratings yet
- SJP Catalogue Speed and GrowthDocument12 pagesSJP Catalogue Speed and GrowthSharmishta AngreNo ratings yet
- Resume - Jacob WellsDocument2 pagesResume - Jacob Wellsapi-647095294No ratings yet
- Chemistry Project On Presence of Insecticides & Pesticides in FDocument8 pagesChemistry Project On Presence of Insecticides & Pesticides in FShaila BhandaryNo ratings yet
- IIAS 1.0.21 - Columnar Incremental Schema Backup and Restore Feature - 1Document12 pagesIIAS 1.0.21 - Columnar Incremental Schema Backup and Restore Feature - 1HS UFNo ratings yet
- LRS Trading StrategyDocument24 pagesLRS Trading Strategybharatbaba363No ratings yet
- Darft Pas Xii GasalDocument11 pagesDarft Pas Xii GasalMutia ChimoetNo ratings yet
- MQ Series: Do Not Have To Be Executing at The Same TimeDocument10 pagesMQ Series: Do Not Have To Be Executing at The Same TimeSanjay DasNo ratings yet
- As Pure Unit 8 Exponentials and Logarithms QPDocument2 pagesAs Pure Unit 8 Exponentials and Logarithms QPrebecca.frohockNo ratings yet
- Business ProposalDocument35 pagesBusiness ProposalMJ MacapagalNo ratings yet
- Twelve Principles SMC2017 2Document65 pagesTwelve Principles SMC2017 2Fadel PratamaNo ratings yet
- Transmission - 700R4 General InfoDocument1 pageTransmission - 700R4 General Infotambache69No ratings yet
- Writing Analysis OfficialDocument5 pagesWriting Analysis OfficialAva KaiserNo ratings yet
- LESSON 3: Talk About Your Weekend or Holiday Plan Using VerbsDocument3 pagesLESSON 3: Talk About Your Weekend or Holiday Plan Using VerbsjoannaNo ratings yet
- WGST 3809A - Feminist ThoughtDocument12 pagesWGST 3809A - Feminist ThoughtIonaNo ratings yet
- 2410014738242451Document2 pages2410014738242451abdul wahabNo ratings yet
- 2019 2020 AEB Expression of InterestDocument1 page2019 2020 AEB Expression of InterestCentre AdministratorNo ratings yet
- Software Quality Assurance: Lecture # 6Document37 pagesSoftware Quality Assurance: Lecture # 6rabiaNo ratings yet
- Question Bank AR VRDocument17 pagesQuestion Bank AR VRarambamranajsingh04No ratings yet
- Himalayan Group of Professional Institutions Kala Amb, Sirmaur, H.PDocument16 pagesHimalayan Group of Professional Institutions Kala Amb, Sirmaur, H.PSanjeevKumarNo ratings yet
- Surya Resume PDFDocument1 pageSurya Resume PDFBEST MOVIES DHAMAKANo ratings yet
- MCQ IadDocument23 pagesMCQ Iads soyaNo ratings yet
- Hampleton Partners M&A 1H2022 Report - Digital CommerceDocument18 pagesHampleton Partners M&A 1H2022 Report - Digital CommerceMiroNo ratings yet
- 5.00 FD An1 s1 CE Chemistry 23-24Document4 pages5.00 FD An1 s1 CE Chemistry 23-24imsNo ratings yet
- Ñas, Crizelle S. BSHM 1-2Document3 pagesÑas, Crizelle S. BSHM 1-2Jophet Banabana MagalonaNo ratings yet
- Mix 2Document4 pagesMix 2yebexa3845No ratings yet
- TartaryDocument3 pagesTartaryImran Shahzad50% (2)
- CBSE Class 10 English Assignment - OzymandiasDocument5 pagesCBSE Class 10 English Assignment - OzymandiasParthiva SinhaNo ratings yet
13 Identify Componenet of EFI
13 Identify Componenet of EFI
Uploaded by
maliksawan3761160 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views3 pagesThe document outlines a daily lesson plan about fuel injection and carburetion systems. The 120-minute class will teach 1st year auto and diesel students about the components of an electronic fuel injection (EFI) system and the working principle of EFI systems. The lesson will focus on the working of EFI systems through hands-on activities inspecting and troubleshooting an EFI system. The 15 main components of an EFI system are described in detail, including the fuel injector, engine control unit, various sensors, fuel pump, fuel rail, and more. Students will be assessed on their understanding of EFI systems through questions and explaining what they learned.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document outlines a daily lesson plan about fuel injection and carburetion systems. The 120-minute class will teach 1st year auto and diesel students about the components of an electronic fuel injection (EFI) system and the working principle of EFI systems. The lesson will focus on the working of EFI systems through hands-on activities inspecting and troubleshooting an EFI system. The 15 main components of an EFI system are described in detail, including the fuel injector, engine control unit, various sensors, fuel pump, fuel rail, and more. Students will be assessed on their understanding of EFI systems through questions and explaining what they learned.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views3 pages13 Identify Componenet of EFI
13 Identify Componenet of EFI
Uploaded by
maliksawan376116The document outlines a daily lesson plan about fuel injection and carburetion systems. The 120-minute class will teach 1st year auto and diesel students about the components of an electronic fuel injection (EFI) system and the working principle of EFI systems. The lesson will focus on the working of EFI systems through hands-on activities inspecting and troubleshooting an EFI system. The 15 main components of an EFI system are described in detail, including the fuel injector, engine control unit, various sensors, fuel pump, fuel rail, and more. Students will be assessed on their understanding of EFI systems through questions and explaining what they learned.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 3
DAILY LESSON PLAN
WEEK: Taught by: Trade Instr Asad Ali
Date: Practical
Subject: Fuel injection and carburation Class: 1st year
Auto & Diesel Dept. Time: 120 minutes
Topic: Component of EFI system
Objectives: Student will be able to:
Importance of EFI system
Working principal of EFI system
Skill focused on: Working of EFI system work
Resources :
Hand tools, spanner, plier, battery, wiring.
Methodology:
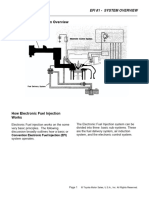
An Electronic Fuel Injection (EFI) system is a complex system used in modern vehicles
to manage and deliver fuel to the engine's combustion chambers. Various components
make up an EFI system, each playing a crucial role in its operation. Here are some of
the key components of an EFI system:
1. Fuel Injector: Fuel injectors are responsible for spraying a precise amount of
fuel into the engine's intake manifold or directly into the combustion chamber.
The number of injectors depends on the engine's design.
2. ECU (Engine Control Unit): The ECU is the brain of the EFI system. It receives
data from various sensors and makes real-time adjustments to control fuel
injection, ignition timing, and other engine functions.
3. Sensors:
MAF (Mass Airflow Sensor): Measures the mass of incoming air to
determine the appropriate air-fuel mixture.
MAP (Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor): Measures intake manifold
pressure to calculate engine load.
ECT (Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor): Monitors engine temperature
to adjust fuel delivery and ignition timing.
IAT (Intake Air Temperature Sensor): Measures the temperature of the
incoming air.
Oxygen (O2) Sensor: Monitors the amount of oxygen in the exhaust
gases, providing feedback for fuel trim adjustments.
TPS (Throttle Position Sensor): Detects the position of the throttle to
adjust fuel and air delivery.
Crankshaft Position Sensor: Determines the position and speed of the
crankshaft for precise ignition timing and fuel injection.
Camshaft Position Sensor: Monitors the position of the camshaft for
precise fuel injection timing (in some systems).
4. Fuel Pump: The fuel pump is responsible for delivering pressurized fuel from the
fuel tank to the fuel injectors.
5. Fuel Rail: This component distributes pressurized fuel to individual fuel injectors.
6. Fuel Pressure Regulator: Maintains a constant fuel pressure in the fuel rail by
regulating excess fuel back to the fuel tank.
7. Throttle Body: Controls the amount of air entering the engine and, in some
cases, houses the fuel injectors.
8. Idle Air Control Valve (IACV): Regulates the engine's idle speed by controlling
the amount of air bypassing the throttle plate.
9. Ignition System: While not directly related to fuel injection, the EFI system often
integrates ignition control, including components like the ignition coil, distributor
(in older systems), and spark plugs.
10. Wiring Harness: Connects all the EFI components, sensors, and the ECU
together, allowing them to communicate and function as a system.
11. Fuel Pressure Sensor: Monitors the fuel pressure in the fuel rail and provides
feedback to the ECU for fuel delivery adjustments.
12. Fuel Tank and Lines: Store and transport fuel from the tank to the engine.
13. Evaporative Emissions System: Manages and controls fuel vapor emissions,
including the charcoal canister, purge valve, and related components.
14. Electronic Throttle Control (ETC): In modern systems, the throttle may be
electronically controlled rather than mechanically operated.
15. Crankcase Ventilation System: Manages the venting of gases from the
engine's crankcase to the intake for emission control.
These components work together to ensure precise fuel delivery and engine
performance in EFI systems. The ECU continuously monitors sensor data to make real-
time adjustments to optimize combustion and emissions while maintaining efficient
engine operation
Activity-2: Inspection of EFI system
Activity-3: Troubleshooting of EFI system
Success Criteria
Inspection procedure of EFI system
Assemble / Disassemble of EFI system
Students are able to find out and resolve the problems in EFI system
Assessment Plan
A couple of questions ask from the student to clarify the understanding of the whole
class for example
According to each of one definition
Everybody will explain what we have learned today in his own view.
C.W: Types of EFI system
HW: Write a detail note on working of EFI system
HOD ( A&D) _________________ Date:________________
You might also like
- Al Maths Pure Unit 6 MsDocument8 pagesAl Maths Pure Unit 6 MsHacjer EiNSTi3NNo ratings yet
- Introduction to the simulation of power plants for EBSILON®Professional Version 15From EverandIntroduction to the simulation of power plants for EBSILON®Professional Version 15No ratings yet
- Diesel Common Rail Injection Electronic Components ExplainedFrom EverandDiesel Common Rail Injection Electronic Components ExplainedRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (7)
- Experiment No 08: Electronic Injection System in S.I. EngineDocument6 pagesExperiment No 08: Electronic Injection System in S.I. EngineSIDDHARTH JAINNo ratings yet
- EFI (Electronic Fuel Injectionnbmn)Document4 pagesEFI (Electronic Fuel Injectionnbmn)Saladin NominorNo ratings yet
- Submitted by P.Nagaraju 160113735159: Electronic Fuel InjectorDocument20 pagesSubmitted by P.Nagaraju 160113735159: Electronic Fuel InjectorvamshiNo ratings yet
- Electronic Fuel Management in I.C Engines G Nagarajan Professor Department of Mechanical Engg. Anna University Chennai 60025Document5 pagesElectronic Fuel Management in I.C Engines G Nagarajan Professor Department of Mechanical Engg. Anna University Chennai 60025alagarg137691No ratings yet
- 1) Efi Inf 1 IntroDocument14 pages1) Efi Inf 1 IntroNahwera IvanNo ratings yet
- Ic Engine AssignmentDocument7 pagesIc Engine AssignmentMuhammad Fahad Khan 51-FET/BSCMET/F19No ratings yet
- Automotive: Describe EFI Engine Working ProcedureDocument19 pagesAutomotive: Describe EFI Engine Working ProcedureJ Naveen KumarNo ratings yet
- Multi Point Fuel Injection SystemDocument12 pagesMulti Point Fuel Injection Systemashwini yewaleNo ratings yet
- Multi Port Fuel Injection SystemDocument4 pagesMulti Port Fuel Injection SystemVarsha SreekumarNo ratings yet
- Ae 1 Module PDFDocument113 pagesAe 1 Module PDFUnni HaridasNo ratings yet
- Electronic Fuel Injection System: Damian CastelinoDocument23 pagesElectronic Fuel Injection System: Damian CastelinoRamjiNo ratings yet
- Mat Unit-1 Part-2Document14 pagesMat Unit-1 Part-2Md zakirNo ratings yet
- MR SolomonDocument6 pagesMR SolomonMarcusNo ratings yet
- Spark IgnitionDocument23 pagesSpark IgnitionRoshaan RoshanNo ratings yet
- Electronics Fuel InjectionDocument6 pagesElectronics Fuel Injectionsorin grecuNo ratings yet
- Engine Management MechatronicsDocument18 pagesEngine Management MechatronicsTanuj Kumar67% (3)
- Basic Overview of Electronic Fuel InjectionDocument23 pagesBasic Overview of Electronic Fuel InjectionAndhieAbrahamNo ratings yet
- UNIT7L1 - 2S - Electronically Controlled Fuel SystemsDocument10 pagesUNIT7L1 - 2S - Electronically Controlled Fuel SystemsEbied Yousif AlyNo ratings yet
- AE&ES Lab Front Page Merged Pages 2 22Document4 pagesAE&ES Lab Front Page Merged Pages 2 22VIVEK KUMAR DASNo ratings yet
- Multi Point Fuel InjectionDocument15 pagesMulti Point Fuel InjectionHemanth MagantiNo ratings yet
- Fuel Injection SystemDocument9 pagesFuel Injection SystemJM PraveenNo ratings yet
- Automotive ElectronicsDocument44 pagesAutomotive ElectronicsRohit Kumar100% (1)
- Soochna 2012 FinalDocument140 pagesSoochna 2012 FinalHanuma Reddy100% (1)
- Electronic Assignment 2Document5 pagesElectronic Assignment 2MarcusNo ratings yet
- AE - Unit III - Lect 4Document14 pagesAE - Unit III - Lect 4Hh HhNo ratings yet
- Electronic Fuel Injection OverviewDocument9 pagesElectronic Fuel Injection Overviewalllhass97No ratings yet
- Electronic Fuel Injection System ELECTRODocument6 pagesElectronic Fuel Injection System ELECTRODIGITAL DAILY DEALSNo ratings yet
- Lexus Es300 Technical TrainingDocument20 pagesLexus Es300 Technical Trainingkelly100% (50)
- Unit 7: Electronically Controlled Fuel SystemsDocument8 pagesUnit 7: Electronically Controlled Fuel SystemsArmando HenríquezNo ratings yet
- Multipoint Fuel Injection SystemDocument6 pagesMultipoint Fuel Injection Systemalan kurniawanNo ratings yet
- Mixture Preparation SIDocument42 pagesMixture Preparation SIMekonnen AyalNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document49 pagesUnit 2Ramanathan DuraiNo ratings yet
- Electronic Fuel Injection System: Contributions and Challenges For Light VehiclesDocument22 pagesElectronic Fuel Injection System: Contributions and Challenges For Light VehiclesRoba FikaduNo ratings yet
- Fuel System: Systems OperationDocument7 pagesFuel System: Systems OperationbejoythomasNo ratings yet
- 1 Mechanical Engineering Dept. CEME NUSTDocument34 pages1 Mechanical Engineering Dept. CEME NUSTAhsan AliNo ratings yet
- Fuel Injection EvolutionDocument9 pagesFuel Injection EvolutioncarechimbacomemierdaNo ratings yet
- Fuel System C27Document7 pagesFuel System C27insano008No ratings yet
- Electronic Diesel ControlDocument31 pagesElectronic Diesel ControlAnteneh MesfinNo ratings yet
- Electronics Final ProjectDocument13 pagesElectronics Final ProjectScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Report-Multi Point Fuel Injection-MpfiDocument16 pagesReport-Multi Point Fuel Injection-MpfiIshan Rastogi100% (4)
- What Is Fuel Injection System?Document20 pagesWhat Is Fuel Injection System?gelo an binbi nonNo ratings yet
- FUEL SYSTEM OF C18 and C6.6Document135 pagesFUEL SYSTEM OF C18 and C6.6Sahr, Cyprian Fillie100% (2)
- Lecture-9-Electronic Engine Management SystemDocument102 pagesLecture-9-Electronic Engine Management SystemPiyush BidwaiNo ratings yet
- 4 Engine: 4.1 General DescriptionDocument63 pages4 Engine: 4.1 General DescriptionGabriel Balcazar100% (1)
- CHAPTER - 8 Electronic Fuel Injection and Ignition SystemsDocument30 pagesCHAPTER - 8 Electronic Fuel Injection and Ignition SystemsAbubeker Arebo0% (1)
- Explain Function of Mass Air Flow Sensor.: The Leaner FuelDocument15 pagesExplain Function of Mass Air Flow Sensor.: The Leaner FuelAbubaker MuzayinNo ratings yet
- Fuel Injection SystemDocument26 pagesFuel Injection Systemjayant pathakNo ratings yet
- Electronic Multipoint Fuel Injection SystemDocument15 pagesElectronic Multipoint Fuel Injection SystemDIPAK VINAYAK SHIRBHATE100% (1)
- MPFI Vs Carburetor Technology For Multi Cylinder EnginesDocument14 pagesMPFI Vs Carburetor Technology For Multi Cylinder EnginesDipak Kumar100% (1)
- GDIDocument7 pagesGDIlinhda561No ratings yet
- Knock SensorDocument15 pagesKnock SensorSurya IrawanNo ratings yet
- Report-Multi Point Fuel Injection-MpfiDocument19 pagesReport-Multi Point Fuel Injection-MpfiHemant PatraNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document25 pagesLecture 3ShzllNo ratings yet
- Electronic Fuel Injection in VehiclesDocument46 pagesElectronic Fuel Injection in Vehicleskelvinthuita877No ratings yet
- Computer Control SystemDocument67 pagesComputer Control SystemToua YajNo ratings yet
- AUTOTRONICADocument3 pagesAUTOTRONICAJhon Arreaga AguilarNo ratings yet
- Naval Diesel Engineering: The Fundamentals of Operation, Performance and EfficiencyFrom EverandNaval Diesel Engineering: The Fundamentals of Operation, Performance and EfficiencyNo ratings yet
- 5 Identify Parts of Exhaust SystemDocument3 pages5 Identify Parts of Exhaust Systemmaliksawan376116No ratings yet
- 18 Dismental and Assemble Distributer Type Diesel Fuel PumpDocument3 pages18 Dismental and Assemble Distributer Type Diesel Fuel Pumpmaliksawan376116No ratings yet
- 3 Dismble Assemble Oil Bath FilterDocument2 pages3 Dismble Assemble Oil Bath Filtermaliksawan376116No ratings yet
- 24 Identify Component of Vehicle Cruistronic SystemDocument2 pages24 Identify Component of Vehicle Cruistronic Systemmaliksawan376116No ratings yet
- 14 Fault Finding by Coding and Decoding of EFI by ManuallyDocument3 pages14 Fault Finding by Coding and Decoding of EFI by Manuallymaliksawan376116No ratings yet
- A Z of Simple Living BookDocument68 pagesA Z of Simple Living Bookdrsubramanian100% (4)
- Test - Environmental Eng. - DRAFTDocument7 pagesTest - Environmental Eng. - DRAFTDesire IsaiahNo ratings yet
- SJP Catalogue Speed and GrowthDocument12 pagesSJP Catalogue Speed and GrowthSharmishta AngreNo ratings yet
- Resume - Jacob WellsDocument2 pagesResume - Jacob Wellsapi-647095294No ratings yet
- Chemistry Project On Presence of Insecticides & Pesticides in FDocument8 pagesChemistry Project On Presence of Insecticides & Pesticides in FShaila BhandaryNo ratings yet
- IIAS 1.0.21 - Columnar Incremental Schema Backup and Restore Feature - 1Document12 pagesIIAS 1.0.21 - Columnar Incremental Schema Backup and Restore Feature - 1HS UFNo ratings yet
- LRS Trading StrategyDocument24 pagesLRS Trading Strategybharatbaba363No ratings yet
- Darft Pas Xii GasalDocument11 pagesDarft Pas Xii GasalMutia ChimoetNo ratings yet
- MQ Series: Do Not Have To Be Executing at The Same TimeDocument10 pagesMQ Series: Do Not Have To Be Executing at The Same TimeSanjay DasNo ratings yet
- As Pure Unit 8 Exponentials and Logarithms QPDocument2 pagesAs Pure Unit 8 Exponentials and Logarithms QPrebecca.frohockNo ratings yet
- Business ProposalDocument35 pagesBusiness ProposalMJ MacapagalNo ratings yet
- Twelve Principles SMC2017 2Document65 pagesTwelve Principles SMC2017 2Fadel PratamaNo ratings yet
- Transmission - 700R4 General InfoDocument1 pageTransmission - 700R4 General Infotambache69No ratings yet
- Writing Analysis OfficialDocument5 pagesWriting Analysis OfficialAva KaiserNo ratings yet
- LESSON 3: Talk About Your Weekend or Holiday Plan Using VerbsDocument3 pagesLESSON 3: Talk About Your Weekend or Holiday Plan Using VerbsjoannaNo ratings yet
- WGST 3809A - Feminist ThoughtDocument12 pagesWGST 3809A - Feminist ThoughtIonaNo ratings yet
- 2410014738242451Document2 pages2410014738242451abdul wahabNo ratings yet
- 2019 2020 AEB Expression of InterestDocument1 page2019 2020 AEB Expression of InterestCentre AdministratorNo ratings yet
- Software Quality Assurance: Lecture # 6Document37 pagesSoftware Quality Assurance: Lecture # 6rabiaNo ratings yet
- Question Bank AR VRDocument17 pagesQuestion Bank AR VRarambamranajsingh04No ratings yet
- Himalayan Group of Professional Institutions Kala Amb, Sirmaur, H.PDocument16 pagesHimalayan Group of Professional Institutions Kala Amb, Sirmaur, H.PSanjeevKumarNo ratings yet
- Surya Resume PDFDocument1 pageSurya Resume PDFBEST MOVIES DHAMAKANo ratings yet
- MCQ IadDocument23 pagesMCQ Iads soyaNo ratings yet
- Hampleton Partners M&A 1H2022 Report - Digital CommerceDocument18 pagesHampleton Partners M&A 1H2022 Report - Digital CommerceMiroNo ratings yet
- 5.00 FD An1 s1 CE Chemistry 23-24Document4 pages5.00 FD An1 s1 CE Chemistry 23-24imsNo ratings yet
- Ñas, Crizelle S. BSHM 1-2Document3 pagesÑas, Crizelle S. BSHM 1-2Jophet Banabana MagalonaNo ratings yet
- Mix 2Document4 pagesMix 2yebexa3845No ratings yet
- TartaryDocument3 pagesTartaryImran Shahzad50% (2)
- CBSE Class 10 English Assignment - OzymandiasDocument5 pagesCBSE Class 10 English Assignment - OzymandiasParthiva SinhaNo ratings yet