Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Note For Combined Science Y7 Chapter 1
Note For Combined Science Y7 Chapter 1
Uploaded by
Felicia TTTOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Note For Combined Science Y7 Chapter 1
Note For Combined Science Y7 Chapter 1
Uploaded by
Felicia TTTCopyright:
Available Formats
Unit 1: Plants and humans as organisms
1. Why do organisms take food?
to grow their bodies
to take energy to carry out their life processes.
to build and maintain their bodies.
to repair the damaged parts of their bodies
2. Definition of chlorophyll
The chlorophyll contributes to the process of photosynthesis by absorbing the
sunlight.
3. Definition of photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is the process by which plants use sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide
to create oxygen and energy in the form of sugar.
4. Parts of plant
Flowers are reproductive organs. They produce
seeds, which can grow into new plants.
Leaves are the food factories of plant. They absorb
energy from sunlight and use it to make food.
Fruit is used to prevent the seeds from drying and
to disperse the seed.
Stem is used to hold the leaves and flowers
above the ground.
Roots is used to hold the plant firmly in the soil.
They absorb water and minerals from the soil.
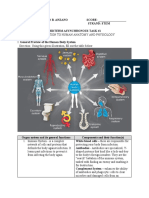
5. Definition of digestive system
Digestive system will break down and absorbs nutrients from the food and liquids you
consume to use for important things like energy, growth and repairing cells.
Parts Function
Liver Filtration. – filter the blood and breaks down the harmful substances
Digestion. – breaking down and absorbing nutrients from food
Metabolism and Detoxification.
Protein synthesis – the body’s cell makes proteins that are necessary
for cell structure and function
Storage of vitamins and minerals.
Stomach Temporary store food
Contact and relax to mix and break down food.
Produce enzymes and other specialized cells to digest food.
Acid in stomach – gastric acid (pH between 1-3)
Activating digestive enzymes together break down the long
change of amino acids of proteins
Pancreas Exocrine function- Produces substances (enzymes) that help with
digestion.
Endocrine function- Sends out hormones that control the amount of
sugar in your bloodstream.
Pancreatic juice – break down sugars, fats and starches.
It also helps digestive system by making hormones
Small intestine Break down food.
Absorb nutrients needed for the body.
Get rid of the unnecessary components from the body
Large intestine (Colon) Absorbing water and electrolytes
Producing and absorbing vitamins
Forming and propelling feces toward the rectum for elimination
Rectum The rectum stores feces until a person is ready to have a bowel
movement.
6. Definition of respiratory system
The respiratory system takes up oxygen from the air we breathe and expels the
unwanted carbon dioxide.
7. Definition of nervous system
Nervous system uses specialized cells called neurons to send signals, or messages, all
over your body.
These electrical signals travel between your brain, skin, organs, glands, and muscles.
The messages help you move your limbs and feel sensations, such as pain.
8. Function of human skeleton
Supports your body.
Helps to move.
Protect some of the soft organ inside the body.
9. Muscles and joints
10. Antagonistic muscles
Antagonistic Muscle is a muscle that opposes the action of another.
When an arm at the elbow is flexed, the muscle that lies above the upper
arm (biceps) is seen and felt bulging.
This muscle bulges due to contraction and becomes smaller in length, stiffer
and thicker.
Contraction of biceps draws the forearm towards the upper arm.
However, relaxation of biceps cannot push the forearm back to its original
position.
When the arm is extended or straightened, the muscle at the back of the
upper arm (triceps) contracts.
The two muscles work antagonistically or in opposite direction to bend or
flex and straighten the arm at the elbow.
You might also like
- Guidelines For Managing Substance Withdrawal in JailsDocument128 pagesGuidelines For Managing Substance Withdrawal in JailsepraetorianNo ratings yet
- Sugar Glider Care Guide PDFDocument2 pagesSugar Glider Care Guide PDFrizal0% (1)
- Hand Book of Poultry Farming and Feed FormulationsDocument3 pagesHand Book of Poultry Farming and Feed Formulationsေကာင္းကင္ တူးမဲ့သူNo ratings yet
- Review of Related Literature Term PaperDocument6 pagesReview of Related Literature Term PaperAllyana Julienne100% (6)
- NutritionDocument4 pagesNutritionAshley Nicole VillegasNo ratings yet
- Pedrano Page 8 BioDocument2 pagesPedrano Page 8 Bioian laurence pedranoNo ratings yet
- CLASS New SIX Science Subject 25-02 - 2024docxDocument14 pagesCLASS New SIX Science Subject 25-02 - 2024docxSaman AkramNo ratings yet
- Activity1 - Introduction To Human AnatomyDocument7 pagesActivity1 - Introduction To Human AnatomyAdrian AnzanoNo ratings yet
- Vegetative Propagation and Nutrient Procurement and Processing HandoutsDocument2 pagesVegetative Propagation and Nutrient Procurement and Processing Handoutsreyesenrique639No ratings yet
- MODULE 1 & 2 - General Biology 2Document12 pagesMODULE 1 & 2 - General Biology 2John Michael LopezNo ratings yet
- Science Elem BiologyDocument44 pagesScience Elem BiologyRicaJaneNatividadNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY NOTES Q4 RemasteredDocument11 pagesBIOLOGY NOTES Q4 RemasteredIfan SaavedraNo ratings yet
- Life ProcessesDocument15 pagesLife ProcessesShalom LogosNo ratings yet
- Circulatory+Digestive System 2Document20 pagesCirculatory+Digestive System 2madeleine.gaudissartNo ratings yet
- Pedrano Page 8Document2 pagesPedrano Page 8ian laurence pedranoNo ratings yet
- MMNK Bio Term 1 RevisionDocument6 pagesMMNK Bio Term 1 RevisionIngyin KhinNo ratings yet
- The Body OrgansDocument43 pagesThe Body OrgansNour YasserNo ratings yet
- HSB Section A Living OrganismDocument7 pagesHSB Section A Living OrganismliltrashNo ratings yet
- DigestiveDocument1 pageDigestiveadasdsadsafNo ratings yet
- All in One SCIENCE - 10 - Mid Map - CH 5aDocument1 pageAll in One SCIENCE - 10 - Mid Map - CH 5astoragenarunNo ratings yet
- Activity 3. Human Body CareDocument8 pagesActivity 3. Human Body CareARACELI DIAZ TERRIQUEZNo ratings yet
- Life Process 1Document4 pagesLife Process 1tanishqmalik20No ratings yet
- An. Sci. 121 Activity 4 Submitted by Hapinat Louie AnthonyDocument4 pagesAn. Sci. 121 Activity 4 Submitted by Hapinat Louie Anthonypaul andreyNo ratings yet
- Systems of The Body (5C, D, E)Document24 pagesSystems of The Body (5C, D, E)reneeNo ratings yet
- Digestive System Lesson PlanDocument6 pagesDigestive System Lesson PlanRosselle May JumayaoNo ratings yet
- ReportDocument20 pagesReportJeth JuradoNo ratings yet
- 5/ What Is The Relationship Between Structure of The Small Intestine and Its Function?Document3 pages5/ What Is The Relationship Between Structure of The Small Intestine and Its Function?just kimbooNo ratings yet
- Life Process Part 1Document49 pagesLife Process Part 1Jyoti AsatiNo ratings yet
- How Animals SurviveDocument4 pagesHow Animals SurviveAngelica Maeriz MindoroNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE 8 Q4 Weeks1to4 Binded Ver10-1Document41 pagesSCIENCE 8 Q4 Weeks1to4 Binded Ver10-1EFREN REYESNo ratings yet
- Content in Demo TeachingDocument6 pagesContent in Demo TeachingAgustines, Marie Char C.No ratings yet
- BiologyDocument7 pagesBiologyorla earnshawNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Study Sheet Nutrition and Digestion (21-22)Document6 pagesUnit 2 Study Sheet Nutrition and Digestion (21-22)PeacherinaEmmatullahNo ratings yet
- Digestive BookDocument11 pagesDigestive Bookpixelguardian94No ratings yet
- Cells, Tissues, Organs and Organ Systems: Summary SheetsDocument2 pagesCells, Tissues, Organs and Organ Systems: Summary SheetsmaarijzuhaNo ratings yet
- M8ENV9JLBR2WDocument2 pagesM8ENV9JLBR2Wminda.eslteacherNo ratings yet
- Cells, Tissues, Organs and Organ Systems: Summary SheetsDocument2 pagesCells, Tissues, Organs and Organ Systems: Summary SheetsmaarijzuhaNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Exercise 2A - SOQUITOSODocument4 pagesLaboratory Exercise 2A - SOQUITOSOShamaine J. SOQUITOSONo ratings yet
- Science ProjectDocument47 pagesScience ProjectArnav KadamNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science Week 13-14Document22 pagesEarth and Life Science Week 13-14Aleli Joy Profugo DalisayNo ratings yet
- Lifeprocesses 120620100700 Phpapp01 PDFDocument165 pagesLifeprocesses 120620100700 Phpapp01 PDFUtkarsh MahajanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - 1Document4 pagesChapter 6 - 1Prit mistryNo ratings yet
- Animal Organ SystemsDocument3 pagesAnimal Organ SystemsmaygracedigolNo ratings yet
- Workbook # Digestive System PDFDocument14 pagesWorkbook # Digestive System PDFDonna Jane Marcuap AlfonsoNo ratings yet
- 3 Human Digestive SystemDocument62 pages3 Human Digestive SystemKip SkipperNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Life ProcessesDocument10 pagesIntroduction To Life Processessaracastic123No ratings yet
- Introduction To Life ProcessesDocument9 pagesIntroduction To Life Processessaracastic123No ratings yet
- Animal Structure and Function Answer KeyDocument2 pagesAnimal Structure and Function Answer KeykpenalesNo ratings yet
- Plant and Animal SystemDocument6 pagesPlant and Animal Systemdwayne dixonNo ratings yet
- Group 3 Da Vinci Frog Dissection Formal Labolatory PaperDocument8 pagesGroup 3 Da Vinci Frog Dissection Formal Labolatory PapercudiamataidezhannesNo ratings yet
- Nutrition HandoutDocument5 pagesNutrition Handoutmiriam harriottNo ratings yet
- 2.best Insight Cardio Metabolic TeamDocument61 pages2.best Insight Cardio Metabolic TeamSaQlain BalochNo ratings yet
- Green Modern Ecology Ecosystem Presentation TemplateDocument55 pagesGreen Modern Ecology Ecosystem Presentation Templatelyka garciaNo ratings yet
- The Digestive SystemDocument5 pagesThe Digestive SystemSBNoadNo ratings yet
- HRM ReviewerDocument6 pagesHRM ReviewerChris AnnNo ratings yet
- AviandigestivesystemDocument68 pagesAviandigestivesystemahmad shoaibNo ratings yet
- Organisation of Living Things Study NotesDocument13 pagesOrganisation of Living Things Study NotesChamsNo ratings yet
- DigestiveeeeDocument8 pagesDigestiveeeejanepe47No ratings yet
- Campbell Biology - Chapters 1 Ans 2 SummaryDocument17 pagesCampbell Biology - Chapters 1 Ans 2 SummaryYana JohansonNo ratings yet
- Systems and Their ControlDocument38 pagesSystems and Their ControlsurainiNo ratings yet
- Nutrition: Nutritive RequirementsDocument7 pagesNutrition: Nutritive RequirementsMalkish RajkumarNo ratings yet
- Gen Biology ReviewerDocument53 pagesGen Biology ReviewerCecilia-Aint JaojocoNo ratings yet
- Autotrophic Nutrition Heterotrophic NutritionDocument1 pageAutotrophic Nutrition Heterotrophic NutritionAditya KediaNo ratings yet
- Sample HFL Gcse Grade 7 Revision Workbook PageDocument1 pageSample HFL Gcse Grade 7 Revision Workbook PageFelicia TTTNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Word Equation Exercise W AnsDocument4 pagesChemistry Word Equation Exercise W AnsFelicia TTTNo ratings yet
- 6789 1BDocument6 pages6789 1BFelicia TTTNo ratings yet
- Y5 Textbook VocabularyDocument1 pageY5 Textbook VocabularyFelicia TTTNo ratings yet
- Singular EXE2Document3 pagesSingular EXE2Felicia TTTNo ratings yet
- Maths Y7 Decimal Ratio Proportion and Percentage PracticeDocument19 pagesMaths Y7 Decimal Ratio Proportion and Percentage PracticeFelicia TTTNo ratings yet
- Past Tense ExerciseDocument3 pagesPast Tense ExerciseFelicia TTTNo ratings yet
- Final Note For Reaction N Acid Base N ElementDocument4 pagesFinal Note For Reaction N Acid Base N ElementFelicia TTTNo ratings yet
- Probability ExerciseDocument3 pagesProbability ExerciseFelicia TTTNo ratings yet
- Multiplication TableDocument1 pageMultiplication TableFelicia TTTNo ratings yet
- Revision Test 2 Y7 NoteDocument16 pagesRevision Test 2 Y7 NoteFelicia TTTNo ratings yet
- Chapter 22Document3 pagesChapter 22Felicia TTTNo ratings yet
- Stress ManagementDocument26 pagesStress Managementjune jaguarNo ratings yet
- One-on-One Coaching Template: Things To RememberDocument5 pagesOne-on-One Coaching Template: Things To RememberDeise Lopes100% (1)
- Udau M6.cia1Document2 pagesUdau M6.cia1Julianne ElbitNo ratings yet
- Ingilis Dili 4-Cü Sinif BSQ-1Document4 pagesIngilis Dili 4-Cü Sinif BSQ-1lalaNo ratings yet
- Physical Activity and ExerciseDocument5 pagesPhysical Activity and Exerciseaubrey rongcales100% (1)
- Knapik 2009Document7 pagesKnapik 2009Dr XNo ratings yet
- SPORTS: An Introduction: Modified Learning Materials/Modules Based On The Deped CurriculumDocument15 pagesSPORTS: An Introduction: Modified Learning Materials/Modules Based On The Deped Curriculumgemma marcitoNo ratings yet
- Breaking Bad News in InfertilityDocument10 pagesBreaking Bad News in InfertilityPaola ReeNo ratings yet
- How To Take Test Veritas 2Document2 pagesHow To Take Test Veritas 2Princess Jovelyn Gutierrez100% (1)
- IELTS Listening Test 3: Part 1: Questions 1-10 NUMBER For Each Answer Job InquiryDocument5 pagesIELTS Listening Test 3: Part 1: Questions 1-10 NUMBER For Each Answer Job InquiryAvinash SinghNo ratings yet
- Social Progress Index 2016Document147 pagesSocial Progress Index 2016Christian Tinoco Sánchez100% (1)
- Children's Rights and ResponsibilitiesDocument2 pagesChildren's Rights and Responsibilitiesrichardcycle92% (13)
- Perineal Lacerations and Episiotomy RepairDocument45 pagesPerineal Lacerations and Episiotomy Repairเฟรนด์ชิพ แก้วพลงามNo ratings yet
- Intravenous Fluid Therapy - Knowledge For Medical Students and PhysiciansDocument6 pagesIntravenous Fluid Therapy - Knowledge For Medical Students and PhysiciansNafiul IslamNo ratings yet
- The Simple Shredded SolutionDocument42 pagesThe Simple Shredded SolutionSamuel Dreiman100% (1)
- How To Design Test and Revise A SurveyDocument20 pagesHow To Design Test and Revise A SurveyAR SI100% (2)
- Chamberlain - 2012 - Do You Really Need A MethodologyDocument8 pagesChamberlain - 2012 - Do You Really Need A MethodologyIngrid noemi Gonzalez paltaNo ratings yet
- Dano - Rle CeraeDocument2 pagesDano - Rle CeraeEloisa DanoNo ratings yet
- Misery Transcript PDFDocument18 pagesMisery Transcript PDFapi-312453884No ratings yet
- How Long Has This Been in Here Resource GuideDocument2 pagesHow Long Has This Been in Here Resource Guideapi-534103975No ratings yet
- Physiologic Jaundice vs. Pathologic Jaundice I. Jaundice: Bilirubin - Is The Product Formed by The Breakdown ofDocument2 pagesPhysiologic Jaundice vs. Pathologic Jaundice I. Jaundice: Bilirubin - Is The Product Formed by The Breakdown ofIrene Grace BalcuevaNo ratings yet
- Running Head: An Orientation To Self-Forgiveness 1Document27 pagesRunning Head: An Orientation To Self-Forgiveness 1livius bolohanNo ratings yet
- Nursing Foundation: Unit Xi Infection Control in Clinicl SettingDocument45 pagesNursing Foundation: Unit Xi Infection Control in Clinicl Settingbemina jaNo ratings yet
- Epidemiologic MeasurementsDocument34 pagesEpidemiologic MeasurementsalaineaNo ratings yet
- AntihistaminesDocument2 pagesAntihistaminesdeepalisharma6No ratings yet
- Glasgow Modified Alcohol Withdrawal ScaleDocument5 pagesGlasgow Modified Alcohol Withdrawal ScaleRichard SymondsNo ratings yet