Professional Documents
Culture Documents
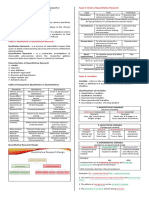
Qualitative and Quantitative Research
Qualitative and Quantitative Research
Uploaded by
Sayem Hossain0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views1 pageQualitative and quantitative research differ in their goals and methods. Qualitative research seeks to understand phenomena in context through interviews and observation, while quantitative research tests hypotheses about relationships between variables. Some topics are better suited to one approach over the other. It is important to understand the differences between qualitative and quantitative research to critically analyze research articles, as the advantages and limitations differ depending on the approach used.
Original Description:
about Qualitative and Quantitative Research
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentQualitative and quantitative research differ in their goals and methods. Qualitative research seeks to understand phenomena in context through interviews and observation, while quantitative research tests hypotheses about relationships between variables. Some topics are better suited to one approach over the other. It is important to understand the differences between qualitative and quantitative research to critically analyze research articles, as the advantages and limitations differ depending on the approach used.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views1 pageQualitative and Quantitative Research
Qualitative and Quantitative Research
Uploaded by
Sayem HossainQualitative and quantitative research differ in their goals and methods. Qualitative research seeks to understand phenomena in context through interviews and observation, while quantitative research tests hypotheses about relationships between variables. Some topics are better suited to one approach over the other. It is important to understand the differences between qualitative and quantitative research to critically analyze research articles, as the advantages and limitations differ depending on the approach used.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
Qualitative and Quantitative Research
Qualitative and Quantitative Research
In general, quantitative research seeks to understand the causal or correlational relationship between variables through
testing hypotheses, whereas qualitative research seeks to understand a phenomenon within a real-world context through the
use of interviews and observation. Both types of research are valid, and certain research topics are better suited to one
approach or the other. However, it is important to understand the differences between qualitative and quantitative research so
that you will be able to conduct an informed critique and analysis of any articles that you read, because you will understand
the different advantages, disadvantages, and influencing factors for each approach.
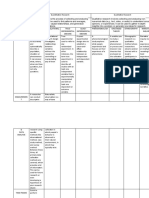
The table below illustrates the main differences between qualitative and quantitative research. Be aware that these are
generalizations, and that not every research study or article will fit neatly into these categories.
Qualitative Quantitative
Experiment, random assignment,
Complexity, contextual, inductive independent/dependent variable,
Keywords
logic, discovery, exploration causal/correlational, validity,
deductive logic
Discover causal relationships or
Purpose Understand a phenomenon
describe a phenomenon
Sample Purposive sample, small Random sample, large
Focus groups, interviews, field
Data Tests, surveys, questionnaires
observation
Experimental, quasi-experimental,
descriptive, methodological,
Phenomenological, grounded
exploratory, comparative,
theory, ethnographic, case study,
correlational, developmental (cross-
Methods/Design historical/narrative research,
sectional,
participatory research, clinical
longitudinal/prospective/cohort,
research
retrospective/ex post facto/case
control)
You might also like
- Definition of Organizational BehaviourDocument4 pagesDefinition of Organizational BehaviourSimran Kaur100% (2)
- Stevenson KeyWordsDocument1 pageStevenson KeyWordsmahanteshkuriNo ratings yet
- Qualitative and Quantitative ResearchDocument15 pagesQualitative and Quantitative ResearchAn ZalNo ratings yet
- Navia, Ma. Sharlyn - Activity 3Document2 pagesNavia, Ma. Sharlyn - Activity 3Ma Sharlyn Ariego NaviaNo ratings yet
- Qualitative Approach and EtcDocument26 pagesQualitative Approach and EtcCarl Jay Dag-umanNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER THREE-TemplateDocument3 pagesCHAPTER THREE-TemplateMohammed Al ArmaliNo ratings yet
- NON Experimental Study Designs in Pharmaceutical Services: Igar WidowatiDocument21 pagesNON Experimental Study Designs in Pharmaceutical Services: Igar Widowatiyer ikoNo ratings yet
- Selecting Scientific Procedures and Research MethodsDocument5 pagesSelecting Scientific Procedures and Research MethodsDoãn Phương LinhNo ratings yet
- Vanesch BusinessTheoryDocument31 pagesVanesch BusinessTheorypatriciaNo ratings yet
- NOTES of Your Mother Research TitleDocument9 pagesNOTES of Your Mother Research TitleBlessy MamangunNo ratings yet
- Nota Penyelidikan 2004Document38 pagesNota Penyelidikan 2004Along100% (10)
- 1introduction To Research1Document77 pages1introduction To Research1Reza HakimNo ratings yet
- Quantitative vs. Qualitative ResearchDocument10 pagesQuantitative vs. Qualitative ResearchAhmed AlkhaqaniNo ratings yet
- Final Save EdDocument36 pagesFinal Save Edtoro toroNo ratings yet
- 7 QUALITATIVE DATA COLLECTION AND ANALYSIS 26112020 100055am 22062021 042520pmDocument89 pages7 QUALITATIVE DATA COLLECTION AND ANALYSIS 26112020 100055am 22062021 042520pmthewarriorprincess02No ratings yet
- Characteristics of ResearchDocument4 pagesCharacteristics of ResearchAlthea Mae Cardenas PaatNo ratings yet
- 3-Research MethodologyDocument11 pages3-Research MethodologyInn Gyin KhineNo ratings yet
- Research Methodology: DR - RoyDocument100 pagesResearch Methodology: DR - RoyKumar BalramNo ratings yet
- Research Report Soft Copy (Qualitative and Quantitative)Document2 pagesResearch Report Soft Copy (Qualitative and Quantitative)Jean Gulleban100% (2)
- Research Methods EddieDocument91 pagesResearch Methods EddieNgonidzaishe DondofemaNo ratings yet
- Comparison TableDocument1 pageComparison TableFrancesca TabandaNo ratings yet
- Research Methodology 2022Document9 pagesResearch Methodology 2022Prodi Teknik Sipil UMSNo ratings yet
- QualitativeDocument2 pagesQualitativeWendy Marquez TababaNo ratings yet
- Quantitative ResearchDocument4 pagesQuantitative ResearchDiana Jalaynie S. SambolawanNo ratings yet
- 03 Practical Research 1 - Qualitative and Quantitative ResearchDocument2 pages03 Practical Research 1 - Qualitative and Quantitative Researchnievesarianne1No ratings yet
- Paradigm, Theory and MethodsDocument24 pagesParadigm, Theory and Methodsabrham abagedaNo ratings yet
- Research DesignsDocument13 pagesResearch DesignsAfaq AhmadNo ratings yet
- Xavier University - Qualitative V Quantitative Research, 2012Document1 pageXavier University - Qualitative V Quantitative Research, 2012Renchester AmoresNo ratings yet
- 4 - Research DesignsDocument16 pages4 - Research DesignsMarvin Sabesaje DaguploNo ratings yet
- Study Deisgn Part 1Document30 pagesStudy Deisgn Part 1Abdinasir Ahmed MohamedNo ratings yet
- Research DesignDocument37 pagesResearch DesignabachaNo ratings yet
- Research Paradigm: Paradigm Ontology: Epistemology: Axiology: Typical MethodsDocument5 pagesResearch Paradigm: Paradigm Ontology: Epistemology: Axiology: Typical MethodsMok Mun YeeNo ratings yet
- Practical Research 1 Quarter 1 LAS 1 GPDocument8 pagesPractical Research 1 Quarter 1 LAS 1 GPSamantha Cerado FloresNo ratings yet
- Dr. Yati Afiyanti, SKP., MN PresentDocument39 pagesDr. Yati Afiyanti, SKP., MN PresenttienNo ratings yet
- DIFFERENCES Quantitative Qualitative ResearchDocument1 pageDIFFERENCES Quantitative Qualitative ResearchFranz Vladimir Layme GonzaNo ratings yet
- Tugas 5Document20 pagesTugas 5kartigen19No ratings yet
- Research Design: Faculty of Public Health, Khon Kaen UniversityDocument32 pagesResearch Design: Faculty of Public Health, Khon Kaen UniversityWhatever UseeNo ratings yet
- Considerations in Conducting Research in The New Normal: Designs, Ethos, and PraxisDocument13 pagesConsiderations in Conducting Research in The New Normal: Designs, Ethos, and PraxissgswNo ratings yet
- Undestanding Quantitative Research MethodDocument84 pagesUndestanding Quantitative Research MethodPaula Inocando BernalNo ratings yet
- Qualitative Research by J.I. AniDocument23 pagesQualitative Research by J.I. Ani'Yemi AwofalaNo ratings yet
- Sistematika Penelitian: Wafi Nur MuslihatunDocument23 pagesSistematika Penelitian: Wafi Nur MuslihatunSiwi TrimulyaniNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Handout PR2 1st MasteryDocument3 pagesReviewer Handout PR2 1st MasteryKhalir SebastianNo ratings yet
- Metodologi PenelitianDocument25 pagesMetodologi PenelitianRaniah MardiantNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Qualitative Research and Quantitative ResearchDocument3 pagesDifference Between Qualitative Research and Quantitative ResearchAcharya Krishna100% (1)
- PR1Document4 pagesPR1Dona Valdez AgustinNo ratings yet
- Handouts PRACTICAL RESEARCHDocument3 pagesHandouts PRACTICAL RESEARCHSisley CanilloNo ratings yet
- August 23 NotesDocument5 pagesAugust 23 NotesCarmela BorresNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Qualitative Research MethodsDocument2 pagesIntroduction To Qualitative Research MethodsnehaNo ratings yet
- Qualitative Methods in ResearchDocument3 pagesQualitative Methods in ResearchLeslie Joy Edrosolo ColomaNo ratings yet
- Quantitative and Qualitative Research MethodsDocument7 pagesQuantitative and Qualitative Research MethodsAbdul Rehman ShahidNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Research Design 2.0Document3 pagesReviewer in Research Design 2.0Sobaihe BantuasNo ratings yet
- Study Designs in EpidemiologyDocument54 pagesStudy Designs in Epidemiologyriska yunitaNo ratings yet
- Qualitative vs. Quantitative ResearchDocument1 pageQualitative vs. Quantitative ResearchNouvie AguirreNo ratings yet
- Reserach Paradgms and Methods - QuantittiveDocument33 pagesReserach Paradgms and Methods - Quantittivessentume peterNo ratings yet
- 4 - Type of Epidemiology Studies Overall April 2019-2Document11 pages4 - Type of Epidemiology Studies Overall April 2019-2beakal mengistuNo ratings yet
- PR 1 AnswersDocument4 pagesPR 1 AnswersRaechelle Castro100% (2)
- Qualitative ResearchDocument37 pagesQualitative Researchsandhya67% (3)
- UNIT 2 Complete by PowerWithinDocument15 pagesUNIT 2 Complete by PowerWithinrerere100% (2)
- Practical Research Lesson 1Document2 pagesPractical Research Lesson 1Reinn DionisioNo ratings yet
- Research: Basic Research Applied ResearchDocument7 pagesResearch: Basic Research Applied ResearchMostafa ElghifaryNo ratings yet
- 6-WHLP-Week-6-Q2 (Jan 5 - 11, 2022)Document2 pages6-WHLP-Week-6-Q2 (Jan 5 - 11, 2022)Kenneth Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- Budget Participation and Budgetary Slack: A Review of LiteratureDocument24 pagesBudget Participation and Budgetary Slack: A Review of LiteratureYOGA DARMA100% (1)
- Homeroom Guidance Report Quarter 1 Grade-3-FaithDocument20 pagesHomeroom Guidance Report Quarter 1 Grade-3-FaithSeph TorresNo ratings yet
- Story Telling: Stories Around The WorldDocument2 pagesStory Telling: Stories Around The WorldMagali MadariagaNo ratings yet
- NLC23 - Grade 7 Foundational Mathematics Lesson Plan and Teachers Notes - FinalDocument191 pagesNLC23 - Grade 7 Foundational Mathematics Lesson Plan and Teachers Notes - FinalJohn Christopher Romero100% (1)
- The Depression BlueprintDocument67 pagesThe Depression Blueprintniku bonganayNo ratings yet
- The Amygdala Modulates The Consolidation of Memories of Emotionally Arousing ExpriencesDocument30 pagesThe Amygdala Modulates The Consolidation of Memories of Emotionally Arousing ExpriencesHéctor Enrique Hernández HinojianteNo ratings yet
- Workplace Wellbeing Questionnaire BlackDocument6 pagesWorkplace Wellbeing Questionnaire BlackBianca ElemNo ratings yet
- Interplay The Process of Interpersonal Communication 14th Edition Ebook PDFDocument42 pagesInterplay The Process of Interpersonal Communication 14th Edition Ebook PDFina.rogerson250100% (32)
- Psych p3Document8 pagesPsych p3Fatima MajidNo ratings yet
- Cot Filipino Q 2Document3 pagesCot Filipino Q 2Jane Bunuan SaludaresNo ratings yet
- The Research ProblemDocument6 pagesThe Research ProblemVictor John HermanoNo ratings yet
- Sharni Balamurugan - MC211015414Document3 pagesSharni Balamurugan - MC211015414sharni BalamuruganNo ratings yet
- Pelagio - Fs Module Lesson 2Document9 pagesPelagio - Fs Module Lesson 2api-613019400No ratings yet
- What Is A ParagraphDocument12 pagesWhat Is A ParagraphAlejandra SerranoNo ratings yet
- Emotion IdiomsDocument14 pagesEmotion IdiomsSofi FloresNo ratings yet
- Free Ratio Worksheets Grade 7Document3 pagesFree Ratio Worksheets Grade 7RosalindNo ratings yet
- Lesson 7Document20 pagesLesson 7Domer RegisNo ratings yet
- Barriers of CommunicationDocument5 pagesBarriers of CommunicationIVY YBAÑEZNo ratings yet
- QuantumSoundMiracleiQube Chapter 4 7 With M.S. ForewordDocument73 pagesQuantumSoundMiracleiQube Chapter 4 7 With M.S. Forewordmaggie100% (1)
- Fish Is Fish Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesFish Is Fish Lesson Planapi-230191738No ratings yet
- Nihms 830670Document23 pagesNihms 830670Pamela IndelliNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Psychological Capital On Work Engagement: Employee Well-Being As A MediatorDocument10 pagesThe Effect of Psychological Capital On Work Engagement: Employee Well-Being As A Mediatordewita andromedaNo ratings yet
- Guerin Behavior Analysis and The Social Construction of KnowledgeDocument10 pagesGuerin Behavior Analysis and The Social Construction of KnowledgeThiago CavalcanteNo ratings yet
- Pak Studies Environment of Pakistan 2059 2 WorkshopDocument22 pagesPak Studies Environment of Pakistan 2059 2 WorkshopTaha Yousaf100% (1)
- Practical Research RRLDocument6 pagesPractical Research RRLtriciaprivate000No ratings yet
- The Law of AttractionDocument1 pageThe Law of AttractionCatalina CirnatuNo ratings yet
- Anna Final Thesis - 03072023Document54 pagesAnna Final Thesis - 03072023akintweh231No ratings yet
- 10 Tips For Motivating Yourself - Russ HarrisDocument2 pages10 Tips For Motivating Yourself - Russ HarrisMargaritaMaríaNo ratings yet