Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Reported Speech Theory
Reported Speech Theory
Uploaded by
Sergio Andrés Mendoza GómezOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Reported Speech Theory
Reported Speech Theory
Uploaded by
Sergio Andrés Mendoza GómezCopyright:
Available Formats
NAME:_____ TEACHER: SERGIO M.
A ___
DATE:_____________________ WHITE WEEK
Indirect Speech / Reported Speech
Indirect speech (sometimes called reported speech), doesn't use quotation marks to enclose what the person said and it doesn't
have to be word for word.
When reporting speech the tense usually changes. This is because when we use reported speech, we are usually talking about a
time in the past (because obviously the person who spoke originally spoke in the past). The verbs therefore usually have to be in
the past too.
For example:
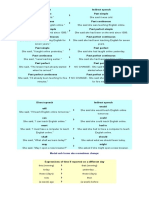
Direct speech Indirect speech
"I'm going to the cinema", he said. He said he was going to the cinema.
Tense change
As a rule when you report something someone has said you go back a tense: (the tense on the left changes to the tense on the
right):
Direct speech Indirect speech
Present simple Past simple
›
She said, "It's cold." She said it was cold.
Present continuous Past continuous
›
She said, "I'm teaching English online." She said she was teaching English online.
Present perfect simple Past perfect simple
›
She said, "I've been on the web since 1999." She said she had been on the web since 1999.
Present perfect continuous Past perfect continuous
›
She said, "I've been teaching English for seven years." She said she had been teaching English for seven years.
Past simple Past perfect
›
She said, "I taught online yesterday." She said she had taught online yesterday.
Past continuous Past perfect continuous
›
She said, "I was teaching earlier." She said she had been teaching earlier.
Past perfect Past perfect
She said, "The lesson had already started when he › NO CHANGE - She said the lesson had already started when he
arrived." arrived.
Past perfect continuous Past perfect continuous
›
She said, "I'd already been teaching for five minutes." NO CHANGE - She said she'd already been teaching for five minutes.
Modal verb forms also sometimes change:
Direct speech Indirect speech
will would
›
She said, "I'll teach English online tomorrow." She said she would teach English online tomorrow.
can could
›
She said, "I can teach English online." She said she could teach English online.
must had to
›
She said, "I must have a computer to teach English online." She said she had to have a computer to teach English online.
shall should
›
She said, "What shall we learn today?" She asked what we should learn today.
may might
›
She said, "May I open a new browser?" She asked if she might open a new browser.
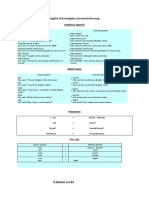
Time change
If the reported sentence contains an expression of time, you must change it to fit in with the time of reporting.
For example we need to change words like here and yesterday if they have different meanings at the time and place of reporting.
Now + 24 hours - Indirect speech
"Today's lesson is on presentations." She said yesterday's lesson was on presentations.
or
She said yesterday's lesson would be on presentations.
Expressions of time if reported on a different day
this (evening) › that (evening)
today › yesterday ...
these (days) › those (days)
now › then
(a week) ago › (a week) before
last weekend › the weekend before last / the previous weekend
here › there
next (week) › the following (week)
tomorrow › the next/following day
At work At home
"How long have you worked here?" She asked me how long I'd worked there.
Pronoun change In reported speech, the pronoun often changes. For example:
Me You
"I teach English online." Reported Speech
She said she teaches English online. or
She said she taught English online.
Reporting Verbs
Said, told and asked are the most common verbs used in indirect speech.
!Note - Here me is the object.
We use asked to report questions:-
We usually use said without an object.
For example: I asked Lynne what time the lesson started.
For example: Lynne said she was going to teach online.
We use told with an object.
If said is used with an object we must include to ;
For example: Lynne told me she felt tired.
For example: Lynne said to me that she'd never been to
!Note - We usually use told. China.
For example: Lynne told me (that) she'd never been to China.
There are many other verbs we can use apart from said, told and asked.
These include:-
accused, admitted, advised, alleged, agreed, apologised, begged, boasted, complained, denied, explained, implied,
invited, offered, ordered, promised, replied, suggested and thought.
Using them properly can make what you say much more interesting and informative.
For example: He invited me to the party.
He begged me to come to the party.
He asked me to come to the party:- He ordered me to come to the party.
He advised me to come to the party.
He suggested I should come to the party.
You might also like
- Secondary Syllabus Form 4 PDFDocument14 pagesSecondary Syllabus Form 4 PDFSyaifulHabibNo ratings yet
- CEFR LevelsDocument2 pagesCEFR LevelsLiterature92No ratings yet
- Indirect Speech / Reported Speech: For ExampleDocument5 pagesIndirect Speech / Reported Speech: For ExamplebeehornetNo ratings yet
- Direct Speech / Quoted Speech: For ExampleDocument6 pagesDirect Speech / Quoted Speech: For ExamplesaigovindarajanNo ratings yet
- English Grammar: Direct and Indirect SpeechDocument5 pagesEnglish Grammar: Direct and Indirect Speechhummingbird8606No ratings yet
- Direct Speech / Quoted Speech: For ExampleDocument3 pagesDirect Speech / Quoted Speech: For ExamplePacheking4No ratings yet
- DIRECT AND INDIRECT SPEECH-KLAS XI KurmerDocument10 pagesDIRECT AND INDIRECT SPEECH-KLAS XI KurmerVanesa Dwi FebriyantiNo ratings yet
- Cambios Estilo IndirectoDocument2 pagesCambios Estilo Indirectola ludotecaNo ratings yet
- Direct and IndirectDocument19 pagesDirect and IndirectSaqib ShahzadNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument3 pagesReported SpeechPleine LuneNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument3 pagesReported SpeechalexandraNo ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect Speech: Name: Hassan Ali Registration Number: EE133009Document11 pagesDirect and Indirect Speech: Name: Hassan Ali Registration Number: EE133009Helen HarlynNo ratings yet
- Active and PassiveDocument9 pagesActive and Passivevishu_86No ratings yet
- Further Explanation About Reported SpeechesDocument20 pagesFurther Explanation About Reported SpeechesGabriela GustiNo ratings yet
- Tense Change D and IDDocument4 pagesTense Change D and IDkunti robiyatunNo ratings yet
- Gómez Henao, J. I. (2019) - Reported Speech. University of Antioquia.Document18 pagesGómez Henao, J. I. (2019) - Reported Speech. University of Antioquia.Daniel ArenasNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument20 pagesReported Speechpocky-66100% (5)
- Indirect SpeechDocument12 pagesIndirect SpeechElaine OliveiraNo ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect SpeechDocument21 pagesDirect and Indirect Speechmarissaclaudia100% (1)
- Unit 10: Indirect Speech: (Reported Statements - Reported Questions)Document9 pagesUnit 10: Indirect Speech: (Reported Statements - Reported Questions)Trọng Nhân TrươngNo ratings yet
- GRAMMAR Reported SpeechDocument6 pagesGRAMMAR Reported SpeechLo les ruiz fabregatNo ratings yet
- Reported or Indirect Speech WorshopDocument6 pagesReported or Indirect Speech WorshopMARÍA FERNANDA VASQUEZ MOLINANo ratings yet
- Direct Speech Definition and ExamplesDocument14 pagesDirect Speech Definition and Examplesintiw_23No ratings yet
- Direct Indirect SpeechDocument9 pagesDirect Indirect SpeechmcrissyNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument3 pagesReported SpeechElisabet Deti KurniawatiNo ratings yet
- English Schulaufgabe ZusammenfassungDocument3 pagesEnglish Schulaufgabe ZusammenfassungTam_Tran_9818No ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect SpeechDocument5 pagesDirect and Indirect SpeechAqsal Alika putraNo ratings yet
- English GrammarDocument120 pagesEnglish GrammarSatria Baja Hitam RxNo ratings yet
- Direct and Reported SpeechDocument3 pagesDirect and Reported SpeechadrianNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument37 pagesReported SpeechFlying FriendsNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument16 pagesReported SpeechYassamine ChammouNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech DCDocument46 pagesReported Speech DCapi-252190418100% (4)
- M5-Ugtv - Ppt-Bahasa Inggris 1 Dan Tata Bahasa 1Document23 pagesM5-Ugtv - Ppt-Bahasa Inggris 1 Dan Tata Bahasa 1Aline TriciaNo ratings yet
- Inglês PPT - Integral - Aula de Direct X IndirectDocument22 pagesInglês PPT - Integral - Aula de Direct X IndirectEnglish Ingles Caderno100% (1)
- Indirect SpeechDocument37 pagesIndirect SpeechUmisadidaNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument32 pagesUntitledAsad RzayevNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech PPTDocument37 pagesReported Speech PPTJITENDRA YADAV0% (1)
- Reported Speech Ingles IiiDocument31 pagesReported Speech Ingles IiiOscar Andres Rojo CastilloNo ratings yet
- Dokumen PDFDocument27 pagesDokumen PDFKhairun NizamNo ratings yet
- Untuk Kelas 3Document5 pagesUntuk Kelas 3Dian OctavianiNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument3 pagesReported SpeechAlexandru LicaNo ratings yet
- Guía de Reported Speech Ingles 3ºmedioDocument5 pagesGuía de Reported Speech Ingles 3ºmedioLiceo Andrés Bello-ComunicacionesNo ratings yet
- Usually,, Didn'T Use To, Get Used To .Document73 pagesUsually,, Didn'T Use To, Get Used To .BoxviNo ratings yet
- KELOMPOK 18 Direct Indirect SpeechDocument23 pagesKELOMPOK 18 Direct Indirect SpeechsariNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech PPT 140311051942 Phpapp01Document34 pagesReported Speech PPT 140311051942 Phpapp01Liezel LebarnesNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument34 pagesReported SpeechRubicel Cordova0% (1)
- Direct Speech / Quoted Speech: For ExampleDocument4 pagesDirect Speech / Quoted Speech: For Examplemilagros curiNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 Q4 Week5 Direct Indirect Speech 2024Document2 pagesGrade 9 Q4 Week5 Direct Indirect Speech 2024Arteleih R. Ebar-MondejarNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech-1Document34 pagesReported Speech-1sanchisanchita9No ratings yet
- English-Grammar Reported SpeechDocument120 pagesEnglish-Grammar Reported SpeechMbagnick Diop100% (2)
- Inggris PPT Direct SpeechDocument10 pagesInggris PPT Direct SpeechTiara Putri PertiwiNo ratings yet
- Direct and Reported SpeechDocument4 pagesDirect and Reported Speechkravecp698No ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect SpeechDocument7 pagesDirect and Indirect Speechapi-3806123No ratings yet
- Curso de Ingles - English Lesson - Direct and Reported Speech (Lección de Inglés - El Estilo Directo y Indirecto)Document4 pagesCurso de Ingles - English Lesson - Direct and Reported Speech (Lección de Inglés - El Estilo Directo y Indirecto)David OrtizNo ratings yet
- DirectIndirect Speech PPT 1Document17 pagesDirectIndirect Speech PPT 1Puja RatanNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument2 pagesReported SpeechEDUARD MUÑOZ CENIZONo ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect SpeechDocument2 pagesDirect and Indirect SpeechDanielleOkNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech AND: Embedded QuestionsDocument18 pagesReported Speech AND: Embedded QuestionsEsdras EnríquezNo ratings yet
- Direct SpeechDocument4 pagesDirect SpeechPRINTDESK by DanNo ratings yet
- Narrations (Direct & Indirect) Rules For Direct & Indirect Tense To Tense Explanation With Examples PracticeDocument47 pagesNarrations (Direct & Indirect) Rules For Direct & Indirect Tense To Tense Explanation With Examples Practicekanwal hafeezNo ratings yet
- Passive Voice WorksheetDocument1 pagePassive Voice WorksheetSergio Andrés Mendoza GómezNo ratings yet
- The Causative Fun Activities Games 1086Document2 pagesThe Causative Fun Activities Games 1086lemonbusNo ratings yet
- Basic Phonetics Exam Production 1Document2 pagesBasic Phonetics Exam Production 1Sergio Andrés Mendoza GómezNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech Excercise - Stupid QuotesDocument1 pageReported Speech Excercise - Stupid QuotesSergio Andrés Mendoza GómezNo ratings yet
- Diptongos ProduccionDocument2 pagesDiptongos ProduccionSergio Andrés Mendoza GómezNo ratings yet
- QUANTIFIERSDocument1 pageQUANTIFIERSSergio Andrés Mendoza GómezNo ratings yet
- Pronouns - Theory + ExercisesDocument2 pagesPronouns - Theory + ExercisesSergio Andrés Mendoza GómezNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech ExcercisesDocument1 pageReported Speech ExcercisesSergio Andrés Mendoza GómezNo ratings yet
- Gerund and Infinitive SONG EXCERCISE - ETTA JAMESDocument1 pageGerund and Infinitive SONG EXCERCISE - ETTA JAMESSergio Andrés Mendoza GómezNo ratings yet
- Third Conditional WorksheetDocument1 pageThird Conditional WorksheetSergio Andrés Mendoza GómezNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech - Stupid Quotes - Anwer KeysDocument1 pageReported Speech - Stupid Quotes - Anwer KeysSergio Andrés Mendoza GómezNo ratings yet
- Prepositions of Time Lyrics Song CompleteDocument1 pagePrepositions of Time Lyrics Song CompleteSergio Andrés Mendoza GómezNo ratings yet
- Pronouns ExerxixxesDocument1 pagePronouns ExerxixxesSergio Andrés Mendoza GómezNo ratings yet
- Pluralization - Articles - Prepositions of Time (Theory)Document1 pagePluralization - Articles - Prepositions of Time (Theory)Sergio Andrés Mendoza GómezNo ratings yet
- Pronouns - Ayuda (Mi)Document1 pagePronouns - Ayuda (Mi)Sergio Andrés Mendoza GómezNo ratings yet
- Preposition of Time (Ayuda Mi)Document2 pagesPreposition of Time (Ayuda Mi)Sergio Andrés Mendoza GómezNo ratings yet
- КТП 8 34Document14 pagesКТП 8 34nzxqwNo ratings yet
- Pref - 5 - Grammar 3.5 - Revisión Del IntentoDocument5 pagesPref - 5 - Grammar 3.5 - Revisión Del IntentonaslyNo ratings yet
- GPR - C4 - 9i RazredDocument3 pagesGPR - C4 - 9i RazredFikreta ČoboNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech - Direct and Indirect Speech CONECTORS Are Words That Are Used To Join Words or SentencesDocument4 pagesReported Speech - Direct and Indirect Speech CONECTORS Are Words That Are Used To Join Words or SentencesHONGAN_ANHONG1No ratings yet
- Module4 - Text Connections - LMDocument29 pagesModule4 - Text Connections - LM9-GarnetSerencio, Khyla O.No ratings yet
- Course Code Course Title Course Planner Lectures Tutorials Practicals CreditsDocument7 pagesCourse Code Course Title Course Planner Lectures Tutorials Practicals CreditsAlisha AgarwalNo ratings yet
- A Latin Grammar ( (1900) ) PDFDocument294 pagesA Latin Grammar ( (1900) ) PDFkorrg1234No ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect SpeechDocument2 pagesDirect and Indirect Speechnawa alafiNo ratings yet
- TERM-2 Reported SpeechDocument3 pagesTERM-2 Reported SpeechMujtaba Ahmed SyedNo ratings yet
- Active and PassiveDocument9 pagesActive and Passivevishu_86No ratings yet
- Indirect Speech, Relative Clause, Passive VoiceDocument22 pagesIndirect Speech, Relative Clause, Passive VoiceFebby DwiNo ratings yet
- Cuadernillo Com EspecDocument52 pagesCuadernillo Com EspecAbrilNo ratings yet
- INDIRDocument3 pagesINDIRRaja RajNo ratings yet
- G7 English Term 2 Exam MEMODocument4 pagesG7 English Term 2 Exam MEMOKobashni Nair RamsamyNo ratings yet
- Rules For Reported SpeechDocument7 pagesRules For Reported SpeechPannaNo ratings yet
- Enjoying English GrammarDocument232 pagesEnjoying English GrammarSylvesterNo ratings yet
- Lista Aula 27 - Discurso Direto e IndiretoDocument4 pagesLista Aula 27 - Discurso Direto e IndiretoEmerson ASNo ratings yet
- Budget of Work SecondaryDocument6 pagesBudget of Work SecondaryMary Cris J. TabalanzaNo ratings yet
- Adverbs of FrequencyDocument12 pagesAdverbs of FrequencyRosário CangombaNo ratings yet
- 16 Narration E-BookDocument278 pages16 Narration E-BookSumit khanathia100% (2)
- Vince-LPFA - (13) Reported SpeechDocument7 pagesVince-LPFA - (13) Reported Speechangelica iribarrenNo ratings yet
- Embedded Question Información en Español: Sujeto+verbo, en Las 'Embedded Questions' Se Emplea El Orden NormalDocument3 pagesEmbedded Question Información en Español: Sujeto+verbo, en Las 'Embedded Questions' Se Emplea El Orden NormalErika LaraNo ratings yet
- ELT Catalog Secondary PDFDocument26 pagesELT Catalog Secondary PDFRafael Cruz IsidoroNo ratings yet
- Grammar S 2Document30 pagesGrammar S 2Najib نجيبNo ratings yet
- DLL January 2023Document2 pagesDLL January 2023Maryknoll PonceNo ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect SpeechDocument2 pagesDirect and Indirect SpeechumarNo ratings yet
- English Pre and Posttest Grade 9 FinalDocument2 pagesEnglish Pre and Posttest Grade 9 FinalJessamae AnasNo ratings yet
- B1 Intermediate Level PracticeDocument4 pagesB1 Intermediate Level PracticeYoniNo ratings yet