Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Y10 January Assessment Revision List
Y10 January Assessment Revision List
Uploaded by
RiztremeOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Y10 January Assessment Revision List
Y10 January Assessment Revision List
Uploaded by
RiztremeCopyright:
Available Formats
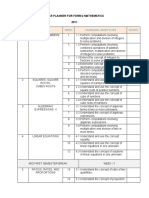
Unit and Title Specification Reference Links to teaching resources
Edexcel Student books 1 (units 1 to 5) and
2 (units 6 to 10)
Collins Edexcel International GCSE
convert recurring decimals into fractions Unit 7, page 103 2.3
round to a given number of significant figures or Unit 1, Page 13 8.2
decimal places
1 Decimals use estimation to evaluate approximations to Unit 5, page 301 8.4
numerical calculations
use a scientific electronic calculator to determine Unit 7, page 105 10.6
numerical results
express integers as product of powers of prime Unit 3, page 175 1.5
factors
find highest common factors (HCF) and Unit 3, page 177 1.6
lowest common multiples (LCM)
Special numbers understand the meaning of surds Unit 10, page 350 5.3
2
and powers
manipulate surds, including rationalising a Unit 10, page 356 5.3
denominator
use index laws to simplify and evaluate numerical Unit 6, page 12 18.1, 18.2, 18.3, 18.4
expressions involving integer, fractional and negative
powers
9 Algebraic use index notation involving fractional, negative and Unit 6, page 35 18.1, 18.2, 18.3, 18.4
manipulation zero powers
use index laws in simple cases Unit 2, page 118 18.1, 18.2, 18.3, 18.4
collect like terms Unit 1, page 20 12.1
multiply a single term over a bracket Unit 1, page 22 12.2
take out common factors Unit 3, page 185 12.3
expand the product of two or more linear expressions Unit 5, page 311 12.4, 12.5
understand the concept of a quadratic expression Unit 5, page 316 12.6, 12.7
and be able to factorise such expressions
manipulate algebraic fractions where the numerator Unit 2, page 113
and/or the denominator can be numeric, linear or
quadratic Unit 3, page 186
Unit 10, page 362 12.8
complete the square for a given quadratic expression Unit 7, page 114 (13.6)
use algebra to support and construct proofs
substitute positive and negative integers, decimals Unit 4, page 247
and fractions for words and letters in expressions and
formulae 11.2
use formulae from mathematics and other real-life 13.2
contexts expressed initially in words or diagrammatic
form and convert to letters and symbols
Expressions,
formulae and derive a formula or expression 11.1
10
rearranging
formulae understand the process of manipulating formulae or Unit 4, page 249
equations to change the subject, to include cases
where the subject may appear twice or a power of 11.3, 11.4
the subject occurs
set up problems involving direct or inverse proportion Unit 6 page 21
and relate algebraic solutions to graphical
representation of the equations 19.1, 19.2
11 Linear solve linear equations, with integer or fractional Unit 1, page 22
coefficients, in one unknown in which the unknown
appears on either side or both sides of the equation
Unit 2, page 116
equations and Unit 3,page 187, 13.1, 13.3
inequalities set up simple linear equations from given data Unit 1, page 26, 13.2
solve simple linear inequalities in one variable and Unit 2, page 119
represent the solution set on a number line
20.1
understand and use common difference (d) and first Unit 6, page 43
term (a) in an arithmetic sequence
17.1, 17.2
12 Sequences know and use nth term = a + (n – 1)d Unit 6, page 53 17.3
find the sum of the first n terms of an arithmetic Unit 6, page 56
series (Sn)
17.4
construct and interpret histograms Unit 9, page 333, 31.5
Graphical construct cumulative frequency diagrams from Unit 4, page 285
30 representation tabulated data
of data 32.9
use cumulative frequency diagrams Unit 4, page 290, 32.9
31 Statistical understand the concept of average
measures
calculate the mean, median, mode and range for a Unit 2, page 162
discrete data set
32.1, 32.2, 32.3, 32.4
calculate an estimate for the mean for grouped data Unit 3, page 225 32.6, 32.7
identify the modal class for grouped data Unit 3, page 225, 32.7
estimate the median from a cumulative frequency Unit 4, page 285
diagram 32.9
understand the concept of a measure of spread Unit 4, page 285, 32.8
find the interquartile range from a discrete data set Unit 4, page 286 32.8
estimate the interquartile range from a cumulative Unit 4, page 290 32.9
frequency diagram
order fractions and calculate a given fraction Unit 1, page 3
of a given quantity 2.1
express a given number as a fraction of another 2.7
number
convert a fraction to a decimal or percentage 2.2, 2.4
3 Fractions
use common denominators to add and subtract 3.4
fractions and mixed numbers
understand and use fractions as multiplicative 3.3
inverses
multiply and divide fractions and mixed numbers 3.5
4 Percentages express a given number as a percentage of another Unit 2, page 103
number;
2.7
express a percentage as a fraction and as a decimal 2.4
understand the multiplicative nature of percentages 2.5,
as operators
solve simple percentage problems, including 2.6
percentage increase and decrease
use reverse percentages Unit 4, page 241 2.8
use compound interest and depreciation Unit 4, page 237 2.9, 2.10
use repeated percentage change 2.11
solve compound interest problems 2.10
You might also like
- RPT Form 1 Maths DLPDocument38 pagesRPT Form 1 Maths DLPdaharizuraida0% (1)
- Add Maths Year 9Document12 pagesAdd Maths Year 9Yenny TigaNo ratings yet
- Scheme of Work Mathematics Form 1Document16 pagesScheme of Work Mathematics Form 1Cikgu SaripahNo ratings yet
- Mitel Call Paths and PortsDocument18 pagesMitel Call Paths and PortsChris McAndrewNo ratings yet
- Table of Specifications: Second Periodical Test in Mathematics IvDocument6 pagesTable of Specifications: Second Periodical Test in Mathematics IvJaharaSalbayani100% (1)
- MathematicsDocument15 pagesMathematicsLuis VasquezNo ratings yet
- Year 9 & 10 Igcse MathematicsDocument7 pagesYear 9 & 10 Igcse MathematicsinniNo ratings yet
- DCSBME604Document5 pagesDCSBME604bariNo ratings yet
- Math I-Can 5thDocument2 pagesMath I-Can 5thapi-235722069No ratings yet
- Maths Year 10 EOS1 LO BookletDocument46 pagesMaths Year 10 EOS1 LO Booklet29x4rk8pgfNo ratings yet
- SOW F1 KBSM MathematicsDocument11 pagesSOW F1 KBSM MathematicsHuiYingNo ratings yet
- Table of Specifications: Second Periodical Test in Mathematics IvDocument6 pagesTable of Specifications: Second Periodical Test in Mathematics IvJoi EresehtNo ratings yet
- 2ND Periodical Test Math 4Document6 pages2ND Periodical Test Math 4Cecilyn Santiago - TantiongcoNo ratings yet
- Grade 6 4th Math Learning CompetenciesDocument3 pagesGrade 6 4th Math Learning CompetenciesMelinda RafaelNo ratings yet
- Ontario Math Curriculum Expectations Checklist - Grade 5Document6 pagesOntario Math Curriculum Expectations Checklist - Grade 5LEE SIEW FANGNo ratings yet
- PT MathematicsDocument6 pagesPT MathematicsKendisNo ratings yet
- For: Second Engineer 3000kW Class 1 Fishing Engineer Yacht 2 Chief Engineer (Y2)Document19 pagesFor: Second Engineer 3000kW Class 1 Fishing Engineer Yacht 2 Chief Engineer (Y2)Rakesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Rational Numbers: SMK Sentosa Kampar, Perak Yearly Teaching Plan FORM 1 2018Document29 pagesChapter 1: Rational Numbers: SMK Sentosa Kampar, Perak Yearly Teaching Plan FORM 1 2018harshana rajagopalNo ratings yet
- Igcse Accelerated Mathematics 0580 (Extended 2 Years) Scheme of Work For Year 9 (2011)Document74 pagesIgcse Accelerated Mathematics 0580 (Extended 2 Years) Scheme of Work For Year 9 (2011)Steve JonzieNo ratings yet
- OASMATH7 THDocument3 pagesOASMATH7 THkalebg100No ratings yet
- RPT (Ting 1 BM & DLP)Document38 pagesRPT (Ting 1 BM & DLP)Noor Amira RosliNo ratings yet
- Budget of Work Math5 EDITEDDocument4 pagesBudget of Work Math5 EDITEDSassa IndominationNo ratings yet
- Mathematics 4 - Q2 - PTDocument6 pagesMathematics 4 - Q2 - PTMarlon CorpuzNo ratings yet
- ALC MasterDocument113 pagesALC MasterShubhamNo ratings yet
- Math7-Diagnostic Test TOS Q1Document9 pagesMath7-Diagnostic Test TOS Q1Jdrew BautistaNo ratings yet
- 16th Sep - Pure MathematicsDocument133 pages16th Sep - Pure Mathematicssalem05alnuaimiNo ratings yet
- Math1081 Syllabus Problems 2019T3Document55 pagesMath1081 Syllabus Problems 2019T3Neel PatelNo ratings yet
- Lesson Outline Grade 9 and 10 SY 2022-23Document12 pagesLesson Outline Grade 9 and 10 SY 2022-23Hassan AliNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Second Periodical Wo KeyDocument9 pagesMathematics Second Periodical Wo KeyROBERTO FLORESNo ratings yet
- MATH P1 GR11 NOV2013 QP (Eng)Document9 pagesMATH P1 GR11 NOV2013 QP (Eng)Kgalema KgomoNo ratings yet
- ATAR Mathematics Applications Revision Booklet 2022Document48 pagesATAR Mathematics Applications Revision Booklet 2022benjobrian3No ratings yet
- MathDocument5 pagesMathapi-369628667No ratings yet
- Budget of Work in Mathematics 5: Fortuna Elementary SchoolDocument2 pagesBudget of Work in Mathematics 5: Fortuna Elementary SchoolFortuna ES (R III - Pampanga)No ratings yet
- (DLP) RPT Modular MT KSSR SemakanDocument13 pages(DLP) RPT Modular MT KSSR SemakanScNo ratings yet
- Original Linear Algebra-@ RichieDocument111 pagesOriginal Linear Algebra-@ RichieIbrahim LatifNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2024-02-12 at 8.50.54 AMDocument3 pagesScreenshot 2024-02-12 at 8.50.54 AMzkqgwtjvfhNo ratings yet
- MT101 ماثDocument208 pagesMT101 ماثqq qNo ratings yet
- READ FIRST Year 3 Assessment GuidanceDocument2 pagesREAD FIRST Year 3 Assessment Guidancekhadijahesham00No ratings yet
- (DLP) RPT MODULAR MT KSSR SEMAKAN Year 3Document14 pages(DLP) RPT MODULAR MT KSSR SEMAKAN Year 3Tamilarrasi RajamoneyNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 MathematicsDocument11 pagesGrade 8 Mathematicsmoona imranNo ratings yet
- Y8 TBAT by UnitDocument5 pagesY8 TBAT by UnitHana JuiceNo ratings yet
- RPT Math F4 2013Document34 pagesRPT Math F4 2013ummuinsyirahNo ratings yet
- (DLP) RPT MODULAR MT KSSR SEMAKAN Year 3Document21 pages(DLP) RPT MODULAR MT KSSR SEMAKAN Year 3Vijayan KasturiNo ratings yet
- Math LOs For 3 YearsDocument51 pagesMath LOs For 3 Yearsahmedelmelegy850No ratings yet
- PT Mathematics 4 q2Document6 pagesPT Mathematics 4 q2Emman Pataray CudalNo ratings yet
- Mathematics 2019-2020 Scheme of Work/term Wise Syllabus Breakup Class 11Document3 pagesMathematics 2019-2020 Scheme of Work/term Wise Syllabus Breakup Class 11Stella ElytraNo ratings yet
- I BBS Business Statistics MathematicsDocument5 pagesI BBS Business Statistics Mathematicsalostguy1No ratings yet
- School Ytd by Strand and SkillDocument70 pagesSchool Ytd by Strand and Skillapi-236897542No ratings yet
- Assignment 11 Fall17Document4 pagesAssignment 11 Fall17ahmedNo ratings yet
- 2nd Math OasDocument2 pages2nd Math Oasapi-411338120No ratings yet
- 21-22 Algebra I-StandardsDocument6 pages21-22 Algebra I-Standardsapi-471242393No ratings yet
- CH3 Fundamentals For Finite Element Method - v2Document8 pagesCH3 Fundamentals For Finite Element Method - v2Eng.Hesham AL-Helalee100% (1)
- Math 103 Integral Calculus 2nd Sem-2021-2022Document34 pagesMath 103 Integral Calculus 2nd Sem-2021-2022Fremon RamosNo ratings yet
- BW Mathematics 5Document2 pagesBW Mathematics 5Jayson MendozaNo ratings yet
- Year Planner For Form 2Document3 pagesYear Planner For Form 2Muhammad Yusof AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Evaluasi Diri Kelas 7Document10 pagesEvaluasi Diri Kelas 7kristianasillyNo ratings yet
- MsthsDocument89 pagesMsthsDimitrios KoulianosNo ratings yet
- Math (Grade 1, Semester 1) : Right Triangle TrigonometryDocument51 pagesMath (Grade 1, Semester 1) : Right Triangle TrigonometryhenryNo ratings yet
- G6 Core MathsDocument2 pagesG6 Core MathsKabi MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Practical Finite Element Modeling in Earth Science using MatlabFrom EverandPractical Finite Element Modeling in Earth Science using MatlabNo ratings yet
- Mikrotik FundamentalDocument126 pagesMikrotik Fundamentalkurikulum smk tel sidoarjo100% (1)
- AST Carrier Log Report1Document50 pagesAST Carrier Log Report1Juan Carlitos xyNo ratings yet
- Customer Churn PredictionDocument3 pagesCustomer Churn PredictionmbibachrisNo ratings yet
- Ncert Solutions Class 8 Math Chapter 11 Ex 11 4Document9 pagesNcert Solutions Class 8 Math Chapter 11 Ex 11 4Divyanshu JhaNo ratings yet
- Sharp 37gt-27s - Chassis - Squad-TDocument44 pagesSharp 37gt-27s - Chassis - Squad-TGeorge MerisiotisNo ratings yet
- Android Hacking: by Kyle B3nacDocument24 pagesAndroid Hacking: by Kyle B3nacElite Sack100% (2)
- Protocolo Comunicacion EnvoyDocument12 pagesProtocolo Comunicacion Envoyfmaestre76No ratings yet
- U900 2nd Carrier 4 Sectors Rev - ADocument8 pagesU900 2nd Carrier 4 Sectors Rev - AEhtesham KhanNo ratings yet
- Keyboard Shortcuts Everyone Should KnowDocument2 pagesKeyboard Shortcuts Everyone Should KnowMIk AzizNo ratings yet
- SAP Product Costing NotesDocument37 pagesSAP Product Costing NotesMuhammad Javed Iqbal100% (1)
- L9 Logistical Regression Models UpdatedDocument10 pagesL9 Logistical Regression Models UpdatedMahmudul hasanNo ratings yet
- Charles H. Hapgood Earths Shifting Crust 1 110Document110 pagesCharles H. Hapgood Earths Shifting Crust 1 110Cesar Ruiz100% (1)
- Sel Relay Trip CurveDocument8 pagesSel Relay Trip CurveAhmed Magdy100% (1)
- Texto 1: The Digital AgeDocument6 pagesTexto 1: The Digital AgeMaria Cristina LourenconiNo ratings yet
- UART ArchitectureDocument23 pagesUART ArchitectureEdgar Mugabi Tusuubira100% (4)
- AMS4016MDocument5 pagesAMS4016M黄当甲No ratings yet
- Day 4 - Session 4 - Local Reference FieldsDocument43 pagesDay 4 - Session 4 - Local Reference FieldsEmmanuel Uchenna ChukwuNo ratings yet
- Ch14 ZKH3 Multiple RegressionDocument45 pagesCh14 ZKH3 Multiple RegressionAhanaf RasheedNo ratings yet
- Pneumatic Sand Filtering MachineDocument35 pagesPneumatic Sand Filtering MachineAMEY GHADIGAONKAR194014100% (1)
- Oran 2Document263 pagesOran 2KerimberdiNo ratings yet
- MachineDocument13 pagesMachineashu0990% (2)
- NFS 320 PDFDocument8 pagesNFS 320 PDFjosueNo ratings yet
- Ef I K Language 00 Una FrichDocument78 pagesEf I K Language 00 Una FrichPich78100% (1)
- Glasnik ŠF - 6Document111 pagesGlasnik ŠF - 6ajagodicaNo ratings yet
- 12-Plinth & Damp Proof CourseDocument8 pages12-Plinth & Damp Proof CourseAzkah MaheenNo ratings yet
- First Summative Test ElectromagnetismDocument24 pagesFirst Summative Test ElectromagnetismJr CapanangNo ratings yet
- Rak For Shitte BecDocument12 pagesRak For Shitte BecAsh YehiaNo ratings yet
- Influence of Cultural Environment Factors in Creating Employee Experience and Its Impact On Employee Engagement - An Employee PerspectiveDocument7 pagesInfluence of Cultural Environment Factors in Creating Employee Experience and Its Impact On Employee Engagement - An Employee PerspectiveKamaljit Kaur GrewalNo ratings yet
- My Add Maths NotesDocument21 pagesMy Add Maths NotesliveelaughloveNo ratings yet