Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Structures Lec Mod1 1
Structures Lec Mod1 1
Uploaded by
Alexandrea RavecheOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Structures Lec Mod1 1
Structures Lec Mod1 1
Uploaded by
Alexandrea RavecheCopyright:
Available Formats
I.
For your activity you have to articulate the advantage and disadvantages of
using Tail wheel Gear Type and Tricycle gear Type of Landing gear.
Tail Wheel Gear Type
Advantages Disadvantages
Less expensive to manufacture Generally suffer from poorer forward visibility
on the ground
Less expensive to maintain More difficult to taxi during high wind
conditions
weigh less and cause less drag Due to pilot’s error on handling the breaks,
"nose-over" accidents
Advantageous when operating in and out of
non-paved runways.
Tricycle Gear Type
Advantages Disadvantages
better visibility from the flight deck The nose gear of a few aircraft with
tricycle-type landing gear is not controllable.
More forceful application of breaks Harder to handle on the ground
Prevents ground looping Not as good for rough fields as nose gear can
easily break off because of only one landing
gear in the front
Tricycle gear Type
Advantage Disadvantage
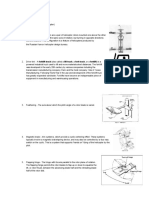
II. Landing Gears Nomenclature:
Base on the given figure in this module for the Landing Gear Nomenclature give the
function and description of each nomenclature.
Landing Gear Nomenclature Function & Description
1. Beam Hanger Is generally a deep timber beam located
perpendicular at right angles or 90º to ceiling
joists and directly above them. Reduce the
span of the ceiling joists.
2. Main Gear Actuator It is the component in any machine that
enables movement. An actuator is a device
that converts energy, which may be electric,
hydraulic, pneumatic, etc., to mechanical in
such a way that it can be controlled.
3. Ground Speed Brake Cable (Right
Gear Only)
4. Trunnion Link
5. Drag Strut is a structural element (could be a truss)
installed parallel to an applied load that
collects and transfers diaphragm shear forces
to the vertical-force-resisting element or
distributes forces within the diaphragm or
shear wall.
6. Universal Side Strut Fitting
7. Damper Hydraulic Line A damper is a valve or plate that stops or
regulates the flow of air
8. Main Gear Damper
9. Torsion Links The hinged link between the piston and
cylinder of an oleo-type landing gear shock
absorber. The torque links allow the piston to
move freely in and out of the landing gear
cylinder, but prevent it rotating
10. Axie
11. Gravel Deflector Its purpose is to deflect gravel from daging
the parts of landing gear or the
12. Uplock Roller
13. Shock Strut The main objective of the shock absorber is
to absorb and damp the impact energy or
shocks during impact landing or taxiing over
bumps so that minimum gets transmitted to
other airframe parts and the passengers get
utmost comfort
14. Side Strut This is also called a side strut. An overcenter
link is used to apply pressure to the center
pivot joint in a drag or side brace link. This
prevents the link from pivoting at this joint
except when the gear is retracted, thus
preventing a collapse of the gear during
ground operation
15. Downlock used to lock the nose gear in the down
position whilst the aircraft is on the ground.
This prevents the downlock struct from
folding and in turn, prevent landing gear from
being unlocked from this position.
16. Uplock Spring Bungeer
17. Uplock Actuator
18. Reaction Link
19. Downlock Actuator forces the downlock linkage out of the
overcenter condition, allowing the nose
landing gear to move. The pressure to the
side brace actuator is used to release the
internal downlock, allowing the actuator to
move.
20. Downlock Spring Bungee
21. Walking Beam is conventionally provided for the purpose of
providing mechanical advantage to a
retraction actuator
III. Guided Question
Some of the early aircraft designs use a skid rather than a tail wheel type of landing
gears, why do you think most manufacturers prefer to use skids and what is it that
the tail wheel type has to offer for them to switch with this type of landing gear.
You might also like
- Conventional, Tricycle and Tandem (Landing Gears)Document3 pagesConventional, Tricycle and Tandem (Landing Gears)Sergio Pingol100% (1)
- Aircraft Design Project 2 PDFDocument76 pagesAircraft Design Project 2 PDFUma shree100% (4)
- B767 - Hydraulic SystemDocument37 pagesB767 - Hydraulic SystemTarik Benzineb100% (6)
- A330 ATA Chap 51 StructuresDocument408 pagesA330 ATA Chap 51 StructuresJohn Woods100% (9)
- Aircraft Landing Gear PresentationDocument340 pagesAircraft Landing Gear PresentationSThaneasMurNo ratings yet
- Module 11 CompleteDocument1,227 pagesModule 11 CompleteHADNASIRI91% (44)
- Mel Boeing 767Document818 pagesMel Boeing 767javier pizarro100% (1)
- Liebherr R904C Litronic Crawler Excavator Service Repair Manual SN23072 PDFDocument70 pagesLiebherr R904C Litronic Crawler Excavator Service Repair Manual SN23072 PDFjfjkskemmdm0% (4)
- Someone Might KnowDocument4 pagesSomeone Might Knowkp140629No ratings yet
- Landing Gear StructureDocument12 pagesLanding Gear StructureRayhan AlfaridziNo ratings yet
- Landing GearDocument25 pagesLanding GearHari65050% (2)
- Landing Gear Slide Chapter 1Document34 pagesLanding Gear Slide Chapter 1mellon3duwenNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Landing Gear SystemsDocument120 pagesAircraft Landing Gear SystemsAldwin Ipac Naguiat100% (2)
- 15 Afh ch13 PDFDocument8 pages15 Afh ch13 PDFAyrton NobileNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Landing Gear SystemsDocument120 pagesAircraft Landing Gear SystemsJoshua Christopher RamirezNo ratings yet
- Kalmar DRF 450 Drive AxleDocument8 pagesKalmar DRF 450 Drive Axletuấn anh nguyễnNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Landing Gear System 1 PDFDocument52 pagesAircraft Landing Gear System 1 PDFNaveen NaveenNo ratings yet
- TOPIC No 3. LANDING GEAR UPDATEDDocument8 pagesTOPIC No 3. LANDING GEAR UPDATEDSamarth SNo ratings yet
- Week 1 Intro Trunnion Sequence ValveDocument7 pagesWeek 1 Intro Trunnion Sequence ValveAnonymous pxy22mwps5No ratings yet
- Week 1 Intro Trunnion Sequence ValveDocument7 pagesWeek 1 Intro Trunnion Sequence ValveAnonymous pxy22mwps5No ratings yet
- Amte 132 - NotesDocument12 pagesAmte 132 - NotesMaybelyn ConsignadoNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Landing Gear System FinalDocument111 pagesAircraft Landing Gear System FinalCeacer Julio SsekatawaNo ratings yet
- Ground Handling and Servicing 13-21: Start EnginesDocument11 pagesGround Handling and Servicing 13-21: Start EnginesPSImMeroNo ratings yet
- Cap 13 Landing Gear System-15-16Document2 pagesCap 13 Landing Gear System-15-16Fidel Molina RojasNo ratings yet
- Landing Gear (ATA 32) - B1Document134 pagesLanding Gear (ATA 32) - B1Ayyub AchilevNo ratings yet
- Chapter Thirteen: Nose Wheel Steering SystemsDocument5 pagesChapter Thirteen: Nose Wheel Steering SystemsAnonymous pxy22mwps5No ratings yet
- Landing Gear SystemDocument16 pagesLanding Gear SystemLeanne SisonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Aircraft Landing Gear SystemsDocument52 pagesChapter 9 Aircraft Landing Gear Systemsjeremyallan.ligeroNo ratings yet
- PB Tyre Handling Equipment LR 20200324ADocument6 pagesPB Tyre Handling Equipment LR 20200324AYanis Ramírez LagosNo ratings yet
- Gyroplane SafetyDocument13 pagesGyroplane Safetyrpr01No ratings yet
- Steering Gear From Marineengg Uk Site PDFDocument32 pagesSteering Gear From Marineengg Uk Site PDFPratham SinghNo ratings yet
- AMT214 A (Helicopter Design)Document2 pagesAMT214 A (Helicopter Design)ricky fluor50No ratings yet
- 1986-1988 SuzukiSamurai Clutch ManualDocument10 pages1986-1988 SuzukiSamurai Clutch ManualHatnean CristianNo ratings yet
- Aircraftlandinggearpresentation2 140524181007 Phpapp01Document320 pagesAircraftlandinggearpresentation2 140524181007 Phpapp01Anonymous QcGwuYXYTkNo ratings yet
- Landing Gear SystemDocument5 pagesLanding Gear SystemDania BaniyounesNo ratings yet
- Aircraft UndercarriageDocument5 pagesAircraft UndercarriageSNL tvNo ratings yet
- International P S Series Front Air Suspension and Axle AssemblyDocument36 pagesInternational P S Series Front Air Suspension and Axle AssemblyTran PhuocNo ratings yet
- GIW Technical Series: Impeller Removal TechniquesDocument2 pagesGIW Technical Series: Impeller Removal TechniquesTravis SkinnerNo ratings yet
- Unit 14Document58 pagesUnit 14Parul SinghNo ratings yet
- Brake: 1 BackgroundDocument6 pagesBrake: 1 BackgroundTomislav OctenjakNo ratings yet
- Ford V8 302 Adjustable Vacuum Advance KitDocument4 pagesFord V8 302 Adjustable Vacuum Advance Kitandrew_cardoso_3No ratings yet
- 02a. Structure (A)Document34 pages02a. Structure (A)5gk9scnnx9No ratings yet
- Propeller SafetyDocument12 pagesPropeller SafetyHUGO MORANo ratings yet
- CC222 ManualDocument33 pagesCC222 ManualMohamed SaiedNo ratings yet
- Theory of FlightDocument45 pagesTheory of FlightmarshallNo ratings yet
- USARM 405 Propeller QUESTION BANKDocument30 pagesUSARM 405 Propeller QUESTION BANKPathan FatimaNo ratings yet
- Demo Dynapac Ca222Document30 pagesDemo Dynapac Ca222Sri hartatiNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Landing Gear SystemsDocument52 pagesAircraft Landing Gear SystemsJelly MortonNo ratings yet
- pcr200 FurkawaDocument8 pagespcr200 FurkawaadheetteeaNo ratings yet
- Type of Rotor SystemDocument6 pagesType of Rotor SystemAhmadFaisalNo ratings yet
- AUTOMOBILEDocument14 pagesAUTOMOBILEabhinandsofficialNo ratings yet
- 737ngx Groundwork Secondary Controls HandoutDocument15 pages737ngx Groundwork Secondary Controls HandoutDonald MokNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Landing GearDocument33 pagesAircraft Landing GearRoxanne Enero100% (2)
- Aircraft Landing Gear System: Presented By: Rishikesh K. Singh Roll No. 134103054 Guided by Dr. Ujjwal Kumar SahaDocument39 pagesAircraft Landing Gear System: Presented By: Rishikesh K. Singh Roll No. 134103054 Guided by Dr. Ujjwal Kumar SahaindahNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Landing Gear SystemsDocument52 pagesAircraft Landing Gear SystemsMadridSpain67% (3)
- Landing GearDocument129 pagesLanding Gearali amr100% (1)
- 65878202Document48 pages65878202mikepetrivniyNo ratings yet
- Steering GearDocument32 pagesSteering GearBondan AstokaNo ratings yet
- The Initial Stall in Span Wise DirectionDocument8 pagesThe Initial Stall in Span Wise DirectionpareshnathNo ratings yet
- The Initial Stall in Span Wise DirectionDocument8 pagesThe Initial Stall in Span Wise DirectionpareshnathNo ratings yet
- Estabilizadores Más Usados en AerotransportesDocument40 pagesEstabilizadores Más Usados en AerotransportesAngel FerreyraNo ratings yet
- The Instant Handbook of Boat Handling, Navigation, and Seamanship: A Quick-Reference Guide for Sail and PowerFrom EverandThe Instant Handbook of Boat Handling, Navigation, and Seamanship: A Quick-Reference Guide for Sail and PowerRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Section - 6: Undercarriage, Wheels & BrakesDocument26 pagesSection - 6: Undercarriage, Wheels & BrakesrobbertmdNo ratings yet
- Falco Construction DrawingsDocument395 pagesFalco Construction DrawingsPéricles Ferreira Leite100% (1)
- t51 ManualDocument10 pagest51 ManualSteven PentonNo ratings yet
- F 14 HandbookDocument54 pagesF 14 Handbookgerom100% (2)
- Boeing737 ChecklistDocument1 pageBoeing737 ChecklistOsama GhareebNo ratings yet
- AMM10Document278 pagesAMM10Edd AlmoneNo ratings yet
- Dal b712 CHCKLDocument1 pageDal b712 CHCKLAndrew MorreyNo ratings yet
- S6000-Operation-Manual SkyliftDocument50 pagesS6000-Operation-Manual SkyliftSetiawan Tuhu basukiNo ratings yet
- PD-808 Flight ManualDocument49 pagesPD-808 Flight Manualscribd4uallNo ratings yet
- Aviation Maintenance Alerts: Advisory CircularDocument29 pagesAviation Maintenance Alerts: Advisory CircularJessie O.BechaydaNo ratings yet
- Operation Manual Old 140t CRANEDocument43 pagesOperation Manual Old 140t CRANEAshlin Augusty100% (3)
- 3453 Brochure Amphibious Excavator Mrt2019 LR DEF MinDocument12 pages3453 Brochure Amphibious Excavator Mrt2019 LR DEF MinDarkedgeNo ratings yet
- Daily Inspection 737-400 19th September 2016Document24 pagesDaily Inspection 737-400 19th September 2016Iftikhar Jawed100% (1)
- Pilot Operating Handbook For Rockwell Turbo Commander 690BDocument18 pagesPilot Operating Handbook For Rockwell Turbo Commander 690BGuillermo Hernández100% (1)
- King 90Document35 pagesKing 90Carlos Francisco Cedillo Bruzual100% (3)
- Boeing 777-300: Microsoft Flight Simulator 2004Document4 pagesBoeing 777-300: Microsoft Flight Simulator 2004Raph 1123No ratings yet
- Nabh YaanDocument151 pagesNabh Yaanapi-3702832No ratings yet
- Su-33 Key Command List: GeneralDocument6 pagesSu-33 Key Command List: Generalmohit sharmaNo ratings yet
- Bombardier CL-600-2B16 Challenger 604 N999PX 01-24Document23 pagesBombardier CL-600-2B16 Challenger 604 N999PX 01-24tayo_bNo ratings yet
- Transit Card A320 A321 NEO Transit Task Card Issue 23 - Rev 1 - 21-Mar-2023Document4 pagesTransit Card A320 A321 NEO Transit Task Card Issue 23 - Rev 1 - 21-Mar-2023Debasis Roy100% (1)
- Content CHG Code Last Revision Date: Aircraft Characteristics - Airport and Maintenance PlanningDocument1 pageContent CHG Code Last Revision Date: Aircraft Characteristics - Airport and Maintenance PlanningWIN MINNo ratings yet
- A320 Family Ata 33 LigthingDocument54 pagesA320 Family Ata 33 LigthingJOSUÉ CABRERANo ratings yet
- Air Modeller 44 PDFDocument68 pagesAir Modeller 44 PDFdushanero100% (7)
- AMM PeseeDocument9 pagesAMM PeseeCRIPE. MONASTIRNo ratings yet