Professional Documents
Culture Documents
487 - Concept, Sources, Nomenclature and Isomerism in Alkanoate (Esters) .
487 - Concept, Sources, Nomenclature and Isomerism in Alkanoate (Esters) .
Uploaded by
emmanuelirem805Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
487 - Concept, Sources, Nomenclature and Isomerism in Alkanoate (Esters) .
487 - Concept, Sources, Nomenclature and Isomerism in Alkanoate (Esters) .
Uploaded by
emmanuelirem805Copyright:
Available Formats
Concept, sources, nomenclature and isomerism in alkanoate (esters).
Concept of Alkanoate: - Alkanoate (esters) are a group of organic compounds formed with an
alkyl group, R’, of an alkanol replaces the ionizable hydrogen atom in an alkanoic acid, RCOOH
to form RCOOR’, where R is H atom or an alkyl group and R’ is an alkyl. The general molecular
formula for alkanoate is CnH2nO2 where n = 2, 3, 4, 5 etc. The first member of the alkanoate
series corresponds to n = 2 and has the molecular formula C2H4O2.
When an alkanol reacts with an alkanoic acid, the products formed are ester and water only, e.g.
O O
║ + H ─ O ─ R’ ║ + H2 O
R─C─O─H R ─ C ─ O ─ R’
Alkanoic acid Alkanol Ester Water
For example, when pentan-1-ol and ethanoic acid react, pentyl ethanoate and water are produced.
H O H H H H H
| ║ | | | | |
H─C ─ C ─O ─H + H ─ O ─ C ─ C ─ C ─ C ─ C ─ H
| | | | | |
H H H H H H
Ethanoic acid Pentan-1-ol
H O H H H H H
| ║ | | | | |
H ─C ─ C ─ O ─ C ─C ─ C ─ C ─ C ─ H + H2O
| | | | | |
H H H H H H
Pentyl ethanoate Water
Esterification: - The formation of an ester by the reaction between an alkanol and an alkanoic
acid is known as esterification. This reaction is extremely slow and reversible at room
temperature, and is catalyzed by a high concentration of hydrogen ions. Simply put, esterification
is the reaction between an alkanol and alkanoic acid to produce an alkanoate/ester and water in
the presence of mineral acid as catalyst.
Esterification
Alkanol + alkanoic acid alkyl alkanoate + water.
Hydrolysis
The above reaction, that is, esterification reaction is quite analogous to the neutralization reaction
between a mineral acid and a base, which produces a salt and water only.
Acid + base salt + water
HCl(aq) + NaOH(aq) NaCl(aq) + H2O(l)
O
║
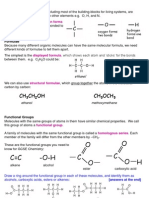
Ester contains R ─ C ─ O ─ R’ as their functional group, where R is hydrogen atom or alkyl
group and R’ is an alkyl group. The r and R’ may be the same or different. It also contains the
polar carbonyl group, C = O and two C ─ O single bonds attached to the same oxygen atom. All
the bonds which make up the functional group are polar. This creates four centers with partial
charge on the atoms. Charged reagents could attack at any of the points. However, the carbonyl
group is the usual site of reaction because of its strong polar nature.
Sources of alkanoate: - Animal and vegetable fats and oils are esters with high relative
molecular masses. Simple esters are present in fruits of plants and are responsible for the natural
sweet smell of flowers.
Homologous series: - The general molecular formula for alkanoate is CnH2nO2; where n = 2, 3,
4…
The first member of the alkanoate series corresponds n = 2 and has the molecular formula
C2H4O2. Its structural formula is HCOOCH3, which is called methyl methanoate. The second
member in the series corresponds to n = 3, and has the molecular formula of C3H6O2. Its
structural formula is either HCOOCH2CH3 which is called ethyl methanoate or CH3COOCH3,
which is called methyl ethanoate respectively.
IUPAC nomenclature of alkanoate (esters): - The name of an alkanoate (ester) is obtained
from the corresponding alkanol and alkanoic acid from where it is formed. The alkanol portion,
R’, is named first as alkyl; and then the link to the alkanoic acid portion, RCOO-, name as
alkanoate. In fact, from the name of an ester, it is very easy to name the alkanol and the alkanoic
acid from where it has been formed as shown below.
S/n Alkanoic acid Alkanol Formula of ester IUPAC name of ester
1. Methanoic acid Methanol HCOOCH3 Methyl methanoate
2. Ethanoic acid Methanol CH4. COOCH3 Methyl ethanoate
3. Methanoic acid Ethanol HCOOCH2CH3 Ethyl methanoate
4. Ethanoic acid Ethanol CH3COOCH2CH3 Ethyl ethanoate
5. Propanoic acid Methanol CH3CH2COOCH3 Methyl propanoate
Estesr are named as alkyl derivatives of alkanoic acids. For example,
H O H H H
| ║ | | |
H─C ─ C ─O ─H + H ─ O ─ C ─ C ─ C ─ H
| | | |
H H H H
Ethanoic acid Propan-1-ol
H O H H H
| ║ | | |
H ─C ─ C ─ O ─ C ─C ─ C ─ H + H2O
| | | |
H H H H
Propyl ethanoate Water
When the ester, that is, propyl ethanoate is divided into two portions, the portion which does not
carry the – COO – is named as the alkyl radical. The portion which contains the – COO – is
named the carboxylate radical. Combining the two parts, our example above is named propyl
ethanoate.
The alkyl groups, R and R’, that is, of the alkanoic acid and alkanol respectively, may be the
same or different. Two other examples are:
(a) Methyl ethanoate; CH3COOCH3, and
(b) Ethyl ethanoate, CH3COOCH2CH3.
Esters are the main constitutes of many naturally occurring fats and oils. Many of them have
pleasant smells and are largely responsible for the fragrance of flowers and the flavors of fruits.
For example, pentyl ethanoate, CH3COOC5H11, has the smell of bananas and is called banana oil
while octyl ethanoate, CH3COOC8H17, has the smell of oranges.
Isomerism in alkanoate: - I. Structural isomerism: - Alkanoate with three (3) or more carbon
atoms exhibit structural isomerism, e.g.
(a) C3H6O2, represents two (2) alkanoate.
1. HCOOCH2CH3 – Ethyl methanoate; and
2. CH3COOCH3 – Methyl ethanoate.
(b) C4H8O2, represents four (4) alkanoate.
1. HCOOCH2CH2CH3 – Propyl methanoate;
2. CH3COOCH2CH3 – Ethyl ethanoate;
3. CH3CH2COOCH3 – Methyl propanoate; and
4. HCOOCH(CH3)CH3 – 2-Methyl ethyl methanoate.
II. Functional isomerism: - Every alkanoate is isomeric with one or more alkanoic acids. For
example,
(a) Methyl methanoate, HCOOCH3, is isomeric with ethanoic acid, CH3COOH; they are
functional isomers, that is, isomers that belong to different homologous series.
(b) Methyl ethanoate, CH3COOCH3, is isomeric with propanoic acid, CH3CH2COOH, both
are functional isomers.
Hence, when the molecular formula of a compound is written as CnH2nO2, it may represent an
alkanoic acid or an alkanoate. However, for an alkanoic acid, n ≥ 1 and for an alkanoate, n ≥ 2.
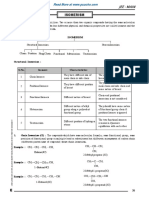
Difference between esterification and neutralization reaction: - The following are the major
difference between esterification and neutralization reaction.
S/n Esterification reaction Neutralization reaction
1. A carboxylic acid reacts with an An acid reacts with a base
alkanol
2. Products of reaction are alkanoate Products of reaction are salt and water.
(ester) and water.
3. Does not require an indicator Require an indicator to show end-point
4. Reaction is reversible Reaction is irreversible
5. It is acid-catalyzed It requires no catalyst
6. Molecules reacts, hence, very slow Ions reacts in a solution, hence, very
fast
7. Requires heating Heating is not required
You might also like
- Organic Chemistry Grade 12 RevisionDocument41 pagesOrganic Chemistry Grade 12 Revisionbennie07100% (3)
- Schaum's Easy Outline of Organic Chemistry, Second EditionFrom EverandSchaum's Easy Outline of Organic Chemistry, Second EditionRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- (Krishna's Text Book) Alok Bariyar, R.P Singh, Babita Agrawal, Babita Agrawal, Prashant Singh - Organic Chemistry-I-Krishna Prakashan Media (2015)Document402 pages(Krishna's Text Book) Alok Bariyar, R.P Singh, Babita Agrawal, Babita Agrawal, Prashant Singh - Organic Chemistry-I-Krishna Prakashan Media (2015)asksankar7857100% (1)
- 5 Hydrocarbon Derivatives 2Document28 pages5 Hydrocarbon Derivatives 2Marivic TayabanNo ratings yet
- Isomerism in Alkanoic AcidsDocument6 pagesIsomerism in Alkanoic AcidsnelsonNo ratings yet
- Cita High School, Port Harcourt Subject: Chemistry Class: Ss3 Week TopicDocument107 pagesCita High School, Port Harcourt Subject: Chemistry Class: Ss3 Week TopicYushau Muhammad LawalNo ratings yet
- Unit 11 - Alcohols, Phenols and EthersDocument41 pagesUnit 11 - Alcohols, Phenols and EthersPoovaraahan RaghuveeranNo ratings yet
- ) Iupac (International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry) - Is Used To Name OrganicDocument11 pages) Iupac (International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry) - Is Used To Name OrganicPkrajen PillaiNo ratings yet
- ESTERSDocument37 pagesESTERSFirdausia Rahma PutriNo ratings yet
- Alcohols & Phenols:: GeneralizationsDocument27 pagesAlcohols & Phenols:: GeneralizationsdoudoudoudouNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry 2 - Chem - f3 - v1Document66 pagesOrganic Chemistry 2 - Chem - f3 - v1Lubanga N JamesNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes Ketones Carboxylic AcidsDocument40 pagesAldehydes Ketones Carboxylic AcidsAlexandrea WynnoevahNo ratings yet
- Note JJ JJDocument23 pagesNote JJ JJms9216974No ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument16 pagesIntroductionAkhtar RazaNo ratings yet
- 04 Organic ChemistryDocument17 pages04 Organic ChemistrysandeepNo ratings yet
- 6 AcidDocument22 pages6 AcidhaslimiNo ratings yet
- Alcohols, Phenols, EthersDocument9 pagesAlcohols, Phenols, Ethersjane kangNo ratings yet
- CI13 5 (Esters)Document12 pagesCI13 5 (Esters)Clint Danniel GuarinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document39 pagesChapter 6c4.arsyadNo ratings yet
- 4.6 Organic Chemistry 2Document30 pages4.6 Organic Chemistry 2Lenah MoiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document28 pagesChapter 3c4.arsyadNo ratings yet
- 4.6 Organic Chemistry 2Document30 pages4.6 Organic Chemistry 2PeterNo ratings yet
- Alcohol, Phenol, and Ethers:: "Their Structures, Physical Properties and Nomenclature"Document33 pagesAlcohol, Phenol, and Ethers:: "Their Structures, Physical Properties and Nomenclature"AmanNo ratings yet
- Catboxylic Acids and Their DerivativesDocument45 pagesCatboxylic Acids and Their DerivativesAnil Kumar VermaNo ratings yet
- PDF Carboxylic AcidsDocument45 pagesPDF Carboxylic AcidsRegina Maree BermudezNo ratings yet
- AldehydesDocument19 pagesAldehydesSeverina MamauagNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16 Lecture NotesDocument30 pagesChapter 16 Lecture NotesJuliaNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry NotesDocument9 pagesOrganic Chemistry NotesBuana SandilaNo ratings yet
- Functional GroupDocument45 pagesFunctional Groupmonasteriomatthew7No ratings yet
- Aariffff FinalDocument28 pagesAariffff Finalsushilshrestha14300No ratings yet
- Alcohols CarbonylDocument8 pagesAlcohols CarbonylmuhajireenNo ratings yet
- Lesson 8 Aldehyds, KetonesDocument54 pagesLesson 8 Aldehyds, KetonesIris BallajNo ratings yet
- Ketones and Aldehydes2022 Copy 1Document56 pagesKetones and Aldehydes2022 Copy 1Camille SolanaNo ratings yet
- 7282 - Carboxylic AcidsDocument6 pages7282 - Carboxylic AcidsGerald DogbeyNo ratings yet
- Experiment #10 - Properties of Carboxylic Acids and EstersDocument5 pagesExperiment #10 - Properties of Carboxylic Acids and EstersJashan LigNo ratings yet
- CHM 123 Lecture Slides 1Document42 pagesCHM 123 Lecture Slides 1christdan75No ratings yet
- Alcohols, Ethers & Phenols: StructureDocument63 pagesAlcohols, Ethers & Phenols: StructureKanika ManochaNo ratings yet
- Alcohol, Phenol and EtherDocument21 pagesAlcohol, Phenol and EtherAditya NandaNo ratings yet
- AlcoholsDocument5 pagesAlcoholsM.zuhair asifNo ratings yet
- Carbon CompoundDocument16 pagesCarbon CompoundAidah AmirNo ratings yet
- Alcohols Phenols and Ethers Anil HssliveDocument16 pagesAlcohols Phenols and Ethers Anil HsslivemartyNo ratings yet
- CH3 Alcohols, Carboxylic Acids and EstersDocument8 pagesCH3 Alcohols, Carboxylic Acids and EstersDoc CrocNo ratings yet
- Carbon and Its Compounds: Chapter - 14Document27 pagesCarbon and Its Compounds: Chapter - 14Swathi VeldhandiNo ratings yet
- Rings, Polymers and Analysis (Unit 4) - OCR Chemistry Notes - Robbie PeckDocument14 pagesRings, Polymers and Analysis (Unit 4) - OCR Chemistry Notes - Robbie Peckrobbiepeck100% (1)
- Nucleophilic Acyl Substitution: The Synthesis of EstersDocument5 pagesNucleophilic Acyl Substitution: The Synthesis of EstersNashDanielSilava100% (2)
- Hsslive Xii CH 7 Alcohols AnilDocument13 pagesHsslive Xii CH 7 Alcohols AnilFathima NithinshaNo ratings yet
- 11.3B AlcoholsDocument34 pages11.3B AlcoholsЕлнур ИкимбаевNo ratings yet
- Aldehid Keton 08Document48 pagesAldehid Keton 08Priagung SetyawanNo ratings yet
- TEST-1 ALCOHOL Physical PropertiesDocument5 pagesTEST-1 ALCOHOL Physical PropertiesFableNo ratings yet
- Reactions of Alcohols, Reactions of Acids and EsterificationDocument11 pagesReactions of Alcohols, Reactions of Acids and EsterificationAlyssa PhillipsNo ratings yet
- Oxygen Containing Organic CompoundsDocument9 pagesOxygen Containing Organic CompoundsmNo ratings yet
- Loaded1-Prof - DO.Moronkola-CHE-176-2023-Course Content1Document58 pagesLoaded1-Prof - DO.Moronkola-CHE-176-2023-Course Content1taiwodamola789No ratings yet
- Alcohol - Britannica Online EncyclopediaDocument16 pagesAlcohol - Britannica Online Encyclopedianoam tiroshNo ratings yet
- Alcohol & PhenolDocument24 pagesAlcohol & Phenolchennivoon00No ratings yet
- Aldehydes and Ketones - Nucleophilic Addition To The Carbonyl GroupDocument55 pagesAldehydes and Ketones - Nucleophilic Addition To The Carbonyl GroupPaul Jhon EugenioNo ratings yet
- Alcohol Alcohol, Any of A Class of Organic CompoundsDocument4 pagesAlcohol Alcohol, Any of A Class of Organic CompoundsJason Orolfo Salvadora HLNo ratings yet
- Chem Notes No6Document31 pagesChem Notes No6AnyhaNo ratings yet
- EP101 Sen LNT 008 Ketone&Aldehyde May11Document18 pagesEP101 Sen LNT 008 Ketone&Aldehyde May11Sàtz ÑÖÑïtNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry 2 PDFDocument15 pagesOrganic Chemistry 2 PDFEnica RichardNo ratings yet
- Alcohol, Esters and Carboxylic AcidsDocument55 pagesAlcohol, Esters and Carboxylic AcidsHuiru ZhaoNo ratings yet
- Alcohols-Phenols and EthersDocument16 pagesAlcohols-Phenols and EthersTr Mazhar PunjabiNo ratings yet
- Part - I: Objective Questions: Section A: Geometrical IsomerismDocument10 pagesPart - I: Objective Questions: Section A: Geometrical IsomerismTejas pawarNo ratings yet
- Course Planner: Target: JEE (Main+Advanced) 2023Document2 pagesCourse Planner: Target: JEE (Main+Advanced) 2023ZzoNo ratings yet
- ACJC H2 CHEM P1 (Worked Solution)Document26 pagesACJC H2 CHEM P1 (Worked Solution)Zach EganNo ratings yet
- Worksheet For Organic SectionDocument17 pagesWorksheet For Organic SectionPramudith Liyanage100% (2)
- MCQs pdf-1 PDFDocument5 pagesMCQs pdf-1 PDFEmman Ann100% (3)
- (PDF) FINAL REPORT INORGANIC LABWORK SYNTHESIS Cis-K (CR (H2O) 2 (C2O4) 2) AND Trans-K (CR (H2O) 2 (C2O4) 2Document1 page(PDF) FINAL REPORT INORGANIC LABWORK SYNTHESIS Cis-K (CR (H2O) 2 (C2O4) 2) AND Trans-K (CR (H2O) 2 (C2O4) 2Tawanda KamutanhoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 Unsaturated Hydrocarbons: Solutions To In-Chapter ProblemsDocument30 pagesChapter 13 Unsaturated Hydrocarbons: Solutions To In-Chapter ProblemsRome Erwin Manalo FestinNo ratings yet
- Coordination CompoundsDocument43 pagesCoordination CompoundsVehlaNo ratings yet
- Competency Test 1Document15 pagesCompetency Test 1Uhu UhuNo ratings yet
- FA-derivatyzacja AChromDocument13 pagesFA-derivatyzacja AChromReza AzghadiNo ratings yet
- Module TwoDocument13 pagesModule TwoKyna PatarataNo ratings yet
- CH62045 Module 1 Polymer Basics 2015Document184 pagesCH62045 Module 1 Polymer Basics 2015sireesha.greenNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 7 Optical Activity and ChiralityDocument15 pagesChapter - 7 Optical Activity and ChiralityManongdo AllanNo ratings yet
- Brocker Hoff 1971Document15 pagesBrocker Hoff 1971yosyNo ratings yet
- Structural IsomerismDocument9 pagesStructural IsomerismJue MayaNo ratings yet
- 16 Introduction To Organic ChemistryDocument9 pages16 Introduction To Organic Chemistryizabel0% (1)
- Activity 4 Introduction To StereochemistryDocument15 pagesActivity 4 Introduction To StereochemistryLyra Ane IlaganNo ratings yet
- BP 401T MCQ Unit1Document32 pagesBP 401T MCQ Unit1Vikash KushwahaNo ratings yet
- (L6) Carbon and Its Compounds Class10 PDFDocument19 pages(L6) Carbon and Its Compounds Class10 PDFRekha MishraNo ratings yet
- CHT Reviewer OChemDocument223 pagesCHT Reviewer OChemChastine CruzNo ratings yet
- 03.01.21 - JR - MPC All - Wtm-26 - Q.paper With KeyDocument14 pages03.01.21 - JR - MPC All - Wtm-26 - Q.paper With KeyNishith Reddy 316No ratings yet
- Isomerism AllenDocument28 pagesIsomerism AllenAshish Ranjan100% (4)
- BS SyllabusDocument66 pagesBS SyllabussabafarooqNo ratings yet
- CAPE Chemistry Study Paper 001αDocument36 pagesCAPE Chemistry Study Paper 001αJerome JAcksonNo ratings yet
- Oi WZ RJJNX S8 B FT FPDocument13 pagesOi WZ RJJNX S8 B FT FPadiiNo ratings yet
- Soal Host Inorganic Chemistry - Group 1 - Cesp 2020Document7 pagesSoal Host Inorganic Chemistry - Group 1 - Cesp 2020AnnisaNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbons NotesDocument15 pagesHydrocarbons Notesarjunrkumar2024No ratings yet
- AITS 23 MAIN SHIFT 1 (2019-21) (DT. 13-03-2021) Question Paper and SolutionDocument25 pagesAITS 23 MAIN SHIFT 1 (2019-21) (DT. 13-03-2021) Question Paper and SolutionSaravanan BNo ratings yet