Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Light - Class Work
Light - Class Work
Uploaded by
arunkumar0909iq0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views6 pagesThis document provides information about light reflection and refraction through a physics lesson on light for Class X students. It includes very short answer questions about the laws of reflection, refractive index, types of mirrors used in car headlights, why light bends when changing mediums, and more. Longer questions are also provided about the types of mirrors preferred for rear view mirrors and shaving mirrors. Additional questions cover topics like where an image will be located based on magnification, how light bends when entering water, the definition of a dioptre of power for a lens, drawing ray diagrams, and more. Sign conventions for spherical mirrors and an example calculation are also outlined.
Original Description:
Original Title
Light - Class Work (1)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides information about light reflection and refraction through a physics lesson on light for Class X students. It includes very short answer questions about the laws of reflection, refractive index, types of mirrors used in car headlights, why light bends when changing mediums, and more. Longer questions are also provided about the types of mirrors preferred for rear view mirrors and shaving mirrors. Additional questions cover topics like where an image will be located based on magnification, how light bends when entering water, the definition of a dioptre of power for a lens, drawing ray diagrams, and more. Sign conventions for spherical mirrors and an example calculation are also outlined.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views6 pagesLight - Class Work
Light - Class Work
Uploaded by
arunkumar0909iqThis document provides information about light reflection and refraction through a physics lesson on light for Class X students. It includes very short answer questions about the laws of reflection, refractive index, types of mirrors used in car headlights, why light bends when changing mediums, and more. Longer questions are also provided about the types of mirrors preferred for rear view mirrors and shaving mirrors. Additional questions cover topics like where an image will be located based on magnification, how light bends when entering water, the definition of a dioptre of power for a lens, drawing ray diagrams, and more. Sign conventions for spherical mirrors and an example calculation are also outlined.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 6
1|Page
SHAKTHI PUBLIC SCHOOL
SESSION: 2021-2022
CLASS: X
PHYSICS
LIGHT-REFLECTION & REFRACTION
I) Very short answer questions
1. State laws of reflection of light. List four characteristics of the image
formed by a plane mirror.
Ans: Laws of Reflection:
1) The angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection. ( i = r)
2) The incident angle, reflected angle and normal all lie in a same
plane.
Characteristics of images formed by plane MIRROR:
1) The image is of the same size as the object, 2) The image is virtual,
3) The image is laterally inverted, 4) The distance between the image
and the mirror is equal to the distance between the object and the
mirror
2. “The refractive index of diamond is 2.42”. What is the meaning of this
statement in relation to speed of light?
3. Which kind of mirrors are used in the headlights of a motor-car and
why?
Ans: Concave mirror, to get the parallel beam of light.
4. Why does a ray of light bend when it travels from one medium into
another?
Ans: Due to change in velocity in the medium and to reduce the time
taken to travel the same
5. Explain why a ray of light passing through the centre of curvature of a
concave mirror, gets reflected along the same path.
Ans: The ray passing through the centre of curvature incident to the
mirror along its normal so ∠i= ∠r = 0. Therefore, the ray retraces its
path.
6. The outer surface of a hollow sphere of aluminium of radius 50 cm is to
be used as a mirror. What will be the focal length of this mirror? Which
type of spherical mirror will it provide?
Ans: f = R/2 = 25 cm. It will form a convex mirror.
2|Page
7. A ray of light enters a rectangular glass slab of refractive index 1.5. It is
found that the ray emerges from the opposite face of the slab without
being displaced. If its speed in air is 3 x 10^8 ms-1 then what is its
speed in glass?
8. What is the magnification of the images formed by plane mirrors and
why?
Ans: Magnification, m = 1 because size of image is equal to size of
object in case of a plane mirror.
II) Answer the following questions in about 40 to 50 words.
1. State the type of mirror preferred as (i) rear view mirror in vehicles,
(shaving mirror. Justify your answer giving two reasons in each case.
Ans: (i) Convex mirror (ii) Concave mirror
Justification:
(i) Convex mirror is used as a rear view mirror because:
(a) it gives a wider field of view as it is curved outwards and
(b) it produces erect and diminished image of the traffic behind the
driver of the vehicle.
(ii) Concave mirror is used as a shaving mirror to see a large size
image of the face. When the object lies in between pole and principal
focus of a concave mirror, it forms a virtual, erect and enlarged image
behind it.
2. A concave mirror produces three times magnified (enlarged) real
image of an object placed at 10 cm in front of it. Where is the image
located?
Ans: Magnification produced by a spherical mirror:
3|Page
Object distance (u) = – 10 cm
v = 3 × (- 10) = – 30 cm
Therefore, the negative sign indicates that an inverted image is formed
in front of the given concave mirror at a distance of 30 cm.
3. A ray of light travelling in air enters obliquely into water. Does the
light ray bends towards the normal or away from the normal? Why?
Ans: The light ray bends towards the normal. When a light ray enters
from an optically rarer medium (which has low refractive index) to an
optically denser medium (which has a high refractive index), its speed
slows down and bends towards the normal. As water is optically
denser than air, a ray of light entering from air into water will bend
towards the normal.
4. Define 1 dioptre of power of a lens. A convex lens forms a real and
inverted image of a needle at a distance of 50 cm from it. Where is the
needle placed in front of the convex lens if the image is equal to the
size of the object? Also, find the power of the lens.
Ans: Dioptre is the SI unit of power of lens is denoted by the letter D. 1
dioptre can be defined as the power of a lens of focal length 1 metre.
Ans: The position of the image should be at 2F since the image is the
real and same size.
It is given that the image of the needle is formed at a distance of 50 cm
from the convex lens. Therefore, the needle is placed in front of the
lens at a distance of 50 cm.
Object distance (u) = – 50 cm
Image distance, (v) = 50 cm
Focal length = f
According to the lens formula,
5. An object 5 cm in length is held 25 cm away from a converging lens of
focal length 10 cm. Draw the ray diagram and find the position, size
and the nature of the image formed.
Ans: Height of the Object, h0 = 5 cm
Distance of the object from converging lens, u = -25 cm
Focal length of a converging lens, f = 10 cm
4|Page
Using lens formula,
Thus, the image is inverted and formed at a distance of 16.7 cm behind
the lens and measures 3.3 cm. The ray diagram is shown below.
6. A concave lens of focal length 15 cm forms an image 10 cm from the
lens. How far is the object placed from the lens? Draw the ray diagram.
Ans: Focal length of concave lens (OF1), f = – 15 cm
Image distance, v= – 10 cm
According to the lens formula,
The negative value of u indicates that the object is placed 30 cm in
front of the lens. This is shown in the following ray diagram.
5|Page
III) Answer the following questions in 80 words.
1. (a) What is meant by ‘power of a lens’?
(b) State and define the S.I. unit of power of a lens.
(c) A convex lens of focal length 25 cm and a concave lens of focal
length 10 cm are placed in close contact with each other. Calculate the
lens power of this combination.
Ans: (a) The power of a lens is a measure of the degree of convergence
or divergence of light rays falling on it.
(b) The SI unit of the power of a lens is dioptre. One dioptre is the
power of a lens whose focal length is 1 metre.
(c) Focal length of the convex lens:
f1 = +25 cm = + m = +0.25 m
Focal length of the concave lens:
f2 = -10 cm = – m = -0.10 m
P1 = = +4D
P2 = = -10D
Power of combination, P = P1 + P2 = 4 + (-10) = -6D
2. State Snell's law of refraction of light. Express it mathematically. Write
the relationship between absolute refractive index of a medium and
speed of light in vacuum.
Ans. Snell’s law: The ratio of sine of angle of incidence (i.e. sin i) to
the sine of angle of refraction (i.e. sin r) is always constant for the
light of given colour and for the given pair of media.
Mathematically, sin i/ sin r = constant = n21
The constant n21 is called refractive index of the second medium
with respect to the first medium.
Absolute refractive index of the medium is given by
6|Page
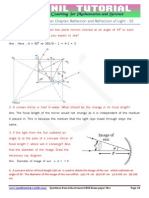
3. List the sign conventions for reflection of light by spherical mirrors.
Draw a diagram and apply these conventions in the determination of
focal length of a spherical mirror which forms a three times magnified
real image of an object placed 16 cm in front of it.
Ans: Sign conventions for reflection of light by spherical mirror are:
1. The object is always placed to the left of the mirror.
2. All the distances parallel to the principal axis are always measured
from the pole of the spherical mirror.
3. All the distances measured along the direction of incident light
(along +ve x-axis), are considered to be positive.
4. Those distances measured opposite to the direction of incidence
light (i.e. along -ve x-axis), are taken as negative.
5. The distances measured in upward direction, i.e. perpendicular to
and above the principal axis (along +ve y-axis), are taken as
positive.
6. The distances measured in the downward direction, (along -ve y-
axis), i.e. perpendicular to and below the principal axis are taken
as negative.
So, focal length of spherical mirror is 12 cm. Negative sign of focal length
indicates that mirror is concave in nature.
You might also like
- Earth's Curvature and Atmospheric RefractionDocument11 pagesEarth's Curvature and Atmospheric RefractionCharles Carpo67% (3)
- Lecture Notes 7 - 203 OpticsDocument33 pagesLecture Notes 7 - 203 OpticsGramoz Cubreli100% (1)
- GR 10 - CH 10-Light QB With Solution-SubjectiveDocument25 pagesGR 10 - CH 10-Light QB With Solution-SubjectiveKishan MishraNo ratings yet
- CbseDocument15 pagesCbseYaaroNo ratings yet
- Reflection and Refraction NCERT Book SolutionDocument5 pagesReflection and Refraction NCERT Book Solutionहर्षित चौहानNo ratings yet
- Cbse Test Paper-02 10 Light Reflection and RefractionDocument6 pagesCbse Test Paper-02 10 Light Reflection and RefractionAchyut SinghNo ratings yet
- 5+mark+questions +CBSE+X +light +25 12 2019 PDFDocument45 pages5+mark+questions +CBSE+X +light +25 12 2019 PDFPiyushNo ratings yet
- Class X Science (Physics) Ch10 Question-AnswersDocument9 pagesClass X Science (Physics) Ch10 Question-AnswersAnkur MondalNo ratings yet
- Short Answer Questions - I (PYQ) : - F RespectivelyDocument18 pagesShort Answer Questions - I (PYQ) : - F Respectivelyashok pradhanNo ratings yet
- 2 Ii We 7 TKB Es 6 CSN G3 S EoDocument6 pages2 Ii We 7 TKB Es 6 CSN G3 S Eony9197171No ratings yet
- Padhle 10th - Light - Reflection & RefractionDocument33 pagesPadhle 10th - Light - Reflection & Refractionshreyasbandi0904No ratings yet
- G-10 Physics Important Questions FinalDocument29 pagesG-10 Physics Important Questions FinalRohan SenapathiNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Science Chapter 10 Intext QuestionsDocument8 pagesClass 10 Science Chapter 10 Intext QuestionsDebsuvro RoyNo ratings yet
- FAQ PhysicsDocument30 pagesFAQ Physicsamit21oct2005No ratings yet
- Light - Intext & ExerciseDocument8 pagesLight - Intext & ExerciseTapas BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Exercise Solution of Reflection and RefractionDocument17 pagesExercise Solution of Reflection and RefractioniTutor Classes BapiNo ratings yet
- X PhyDocument6 pagesX PhyTapas BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Ray Optics Questions STD Xii Holiday HWDocument5 pagesRay Optics Questions STD Xii Holiday HWamritmohanty1000No ratings yet
- Extra Questions - Refraction - Lens - Answers - 230610 - 042208Document5 pagesExtra Questions - Refraction - Lens - Answers - 230610 - 042208Zoha AzizNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Reflection and Refraction of Light Cbse Test Paper Solved-05Document5 pagesClass 10 Reflection and Refraction of Light Cbse Test Paper Solved-05ashokNo ratings yet
- Light Worksheet Padhleakshay PDFDocument18 pagesLight Worksheet Padhleakshay PDFanandatulNo ratings yet
- Most Repeated PYQS Science - LIGHTDocument6 pagesMost Repeated PYQS Science - LIGHTpvkff1234No ratings yet
- Light - Reflection and Refraction Part 2Document7 pagesLight - Reflection and Refraction Part 2Saji JayarajNo ratings yet
- Light ReflectionDocument37 pagesLight Reflectionimraan smNo ratings yet
- Light QBDocument3 pagesLight QBAngad SinghNo ratings yet
- GHJGJHDocument9 pagesGHJGJHKaran RanaNo ratings yet
- 09 Light Reflection and Refraction Chapter Wise Important QuestionsDocument17 pages09 Light Reflection and Refraction Chapter Wise Important QuestionsKrsna JaiswalNo ratings yet
- H1 Sxfoijozxr 8 Oi R6 NVDDocument56 pagesH1 Sxfoijozxr 8 Oi R6 NVDnaughtynaman420No ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Physics Important Questions Only (3 Marks) of OPTICSDocument4 pagesCBSE Class 12 Physics Important Questions Only (3 Marks) of OPTICSPramit RanjanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9Document84 pagesChapter 9rohit murmuNo ratings yet
- Back Exercise Questions NCERT LightDocument9 pagesBack Exercise Questions NCERT LightMinakshi TiwariNo ratings yet
- OpticsDocument23 pagesOpticsanubhavmaheshwariNo ratings yet
- All Questions Are Compulsory: Topic - Reflection & RefractionDocument3 pagesAll Questions Are Compulsory: Topic - Reflection & Refractionshivanshu kushwahaNo ratings yet
- Physics Cl10 Assign2Document2 pagesPhysics Cl10 Assign2Tapas BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- LightDocument6 pagesLightVivek saklaniNo ratings yet
- Phy - Wave OpticsDocument2 pagesPhy - Wave Opticsdebadrita senguptaNo ratings yet
- G10 - Refraction - Q BankDocument21 pagesG10 - Refraction - Q BankUrmila GNo ratings yet
- Physics Worksheet - LightDocument3 pagesPhysics Worksheet - Lightcartooncompany73No ratings yet
- 12 Physics Notes Ch09 Rayoptics and Optical InstrumentsDocument5 pages12 Physics Notes Ch09 Rayoptics and Optical InstrumentsMayank SainiNo ratings yet
- Reflection Light 3Document31 pagesReflection Light 3api-296824694No ratings yet
- Ilovepdf Merged PDFDocument48 pagesIlovepdf Merged PDFSomik JainNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 29-Jun-2023Document6 pagesAdobe Scan 29-Jun-2023kpssgaming923No ratings yet
- Light Reflection and RefractionDocument77 pagesLight Reflection and Refractionmasuma.bvbvnird21No ratings yet
- 10 LightDocument50 pages10 LightNaveen Kumar100% (1)
- 2013 Optics Assignment 1Document9 pages2013 Optics Assignment 1Marcos Aaron TherthensNo ratings yet
- Ray OpticsDocument11 pagesRay OpticsxkryxxzNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 - D - E - MAINS - TB - EXERCISESDocument9 pagesChapter 10 - D - E - MAINS - TB - EXERCISESAmey IngoleNo ratings yet
- Assignment-Ray OpticsDocument2 pagesAssignment-Ray OpticstejvanshsandhuNo ratings yet
- OptikDocument48 pagesOptikdarwishmajidNo ratings yet
- Light - Padhle TenthiesDocument92 pagesLight - Padhle Tenthiesa9758127118No ratings yet
- Light Reflection - C10 Q&aDocument36 pagesLight Reflection - C10 Q&aumaNo ratings yet
- Assignment LightDocument1 pageAssignment Lightshubhutams2No ratings yet
- ISC Board Questions On Ray Optics Grade 12Document6 pagesISC Board Questions On Ray Optics Grade 12iraNo ratings yet
- Physics Cl10 Assign1Document2 pagesPhysics Cl10 Assign1Tapas BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- 23.ray OpticsDocument50 pages23.ray OpticsRakesh Ranjan Mishra100% (1)
- Optics Important QuestionsDocument25 pagesOptics Important Questionsmohitkumarr2411No ratings yet
- Light PresentationDocument91 pagesLight PresentationRohan SinghNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 1 - Physics 12Document2 pagesWorksheet 1 - Physics 12Harshit SinghalNo ratings yet
- Cylindrical Perspective: Cylindrical Perspective: Exploring Visual Perception in Computer VisionFrom EverandCylindrical Perspective: Cylindrical Perspective: Exploring Visual Perception in Computer VisionNo ratings yet
- Optics and Optical Instruments: An IntroductionFrom EverandOptics and Optical Instruments: An IntroductionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- Optics (EM) 230613 002017Document11 pagesOptics (EM) 230613 002017Dharsitth AshvinNo ratings yet
- Check Out This File: MCQ OF POLARISATION, LASER, SOLID STATE PHYSICSDocument44 pagesCheck Out This File: MCQ OF POLARISATION, LASER, SOLID STATE PHYSICSNikhil SatbhaiNo ratings yet
- Ray Optics: PhysicsDocument3 pagesRay Optics: Physicsmalanga.bangaNo ratings yet
- Propagation and AntennaDocument105 pagesPropagation and AntennaSagnik ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- 8 PDFDocument10 pages8 PDFMolec Hazard MosleyNo ratings yet
- Finals Assignment 1 - Bu3Document3 pagesFinals Assignment 1 - Bu3Jhossa EpondulanNo ratings yet
- 614202015946PM-Class 10 Physics Notes-Reflection and RefractionDocument10 pages614202015946PM-Class 10 Physics Notes-Reflection and RefractionMd ShariqueNo ratings yet
- T23731 QData Part 1 PDFDocument59 pagesT23731 QData Part 1 PDFAshok GuptaNo ratings yet
- Snell's Law (Also Known As Snell-Descartes Law and The Law of Refraction) IsDocument3 pagesSnell's Law (Also Known As Snell-Descartes Law and The Law of Refraction) IsLalaine MamaedNo ratings yet
- Chief Examiner's Report: Summer Series 2017Document16 pagesChief Examiner's Report: Summer Series 2017Mark McKinsnkeyNo ratings yet
- Activity ZoneDocument9 pagesActivity ZonePrathamNo ratings yet
- Alpo in Silica Glass Optical Fibers: Deduction of Additional Material PropertiesDocument14 pagesAlpo in Silica Glass Optical Fibers: Deduction of Additional Material PropertiesRahmad HidayatNo ratings yet
- CSEC Physics P2 2013 JanuaryDocument22 pagesCSEC Physics P2 2013 JanuaryBill BobNo ratings yet
- RefractometryDocument2 pagesRefractometryLoveFreequencyNo ratings yet
- 4 Term 1 Test QuestionsDocument11 pages4 Term 1 Test QuestionstinoNo ratings yet
- 10 Science Imp Ch11 HotsDocument2 pages10 Science Imp Ch11 HotsUday JoshiNo ratings yet
- U4AOS1 - How Can Waves Explain The Behaviour of LightDocument55 pagesU4AOS1 - How Can Waves Explain The Behaviour of LightPraveen RavichandranNo ratings yet
- Secret BankingDocument8 pagesSecret BankingberryberryNo ratings yet
- What Is A Mirage?: Presented By: Emilia Ronafel TatadDocument15 pagesWhat Is A Mirage?: Presented By: Emilia Ronafel TatadEmmanuel John DiwaNo ratings yet
- Physics Ch4 NotesDocument22 pagesPhysics Ch4 NotesAli GorganiNo ratings yet
- Physics Worksheet Reflection and Refraction Section: NameDocument1 pagePhysics Worksheet Reflection and Refraction Section: NamewelsyaNo ratings yet
- PolarizationDocument7 pagesPolarizationrajesh.v.v.kNo ratings yet
- Propertiesof Glass MaterialsDocument13 pagesPropertiesof Glass MaterialsElva Diany SyamsudinNo ratings yet
- Fiitjee: Common Test - VDocument9 pagesFiitjee: Common Test - VAnirudh WaliaNo ratings yet
- Particle Monitoring in Liquids: Liquid Particle Counter: Author: Professor: David Pui TA: Poshin Lee Lab MembersDocument17 pagesParticle Monitoring in Liquids: Liquid Particle Counter: Author: Professor: David Pui TA: Poshin Lee Lab MembersSeethaNo ratings yet
- STM 004 LAST QUIZ With AswersDocument2 pagesSTM 004 LAST QUIZ With AswersJv BiasuraNo ratings yet
- Light WorksheetDocument11 pagesLight Worksheetkobayashirei602No ratings yet
- 2010 - Katie - Useful Estimations and Rules of Thumb For Optomechanics PDFDocument92 pages2010 - Katie - Useful Estimations and Rules of Thumb For Optomechanics PDFodormicchiNo ratings yet