Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 viewsBotany
Botany
Uploaded by
meirevi3wThe document summarizes 4 major groups of plants:
1. Bryophyta (mosses) - Have no true leaves or roots/stems and reproduce via spores.
2. Filicinophyta (ferns) - Have leaves, roots, and stems and reproduce via spores.
3. Coniferophyta (conifers) - Have leaves, roots, and stems and reproduce via seeds in cones.
4. Angiospermae (flowering plants) - Have leaves, roots, and stems and reproduce via seeds in fruits.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Sean Burke - Online Algae WebquestDocument4 pagesSean Burke - Online Algae Webquestapi-386190429100% (2)
- Ccp1.1: Pharmaceutical Botany With TaxonomyDocument22 pagesCcp1.1: Pharmaceutical Botany With Taxonomyja_Quinine100% (2)
- Lab 7 - Introduction and ProcedureDocument9 pagesLab 7 - Introduction and ProcedureFloyd SeremNo ratings yet
- Botany Reviewer For First Quarter PDFDocument6 pagesBotany Reviewer For First Quarter PDFDale Maristela Peñalosa100% (3)
- Zbook Biology-Unit-03 149aa8Document15 pagesZbook Biology-Unit-03 149aa8Ashok ParasharNo ratings yet
- Bio 11.1 LE 2 NotesDocument7 pagesBio 11.1 LE 2 NotesCode BlueNo ratings yet
- Bio 111 LecDocument50 pagesBio 111 LecFlorence PalomarNo ratings yet
- 1 Botlec ReviewerDocument7 pages1 Botlec ReviewerKamille PobleteNo ratings yet
- General Biology II Midterms PDFDocument16 pagesGeneral Biology II Midterms PDFantonio louise anjella monNo ratings yet
- Plant Growth and Hormone by Garima MamDocument23 pagesPlant Growth and Hormone by Garima Mampolumatlajoy9515No ratings yet
- Anatomy PDFDocument6 pagesAnatomy PDFtrytobeatgamerNo ratings yet
- MRQ LWCT Note 14Document95 pagesMRQ LWCT Note 14Faris AdityaNo ratings yet
- Notes Lesson 6 To 9 Botany LecDocument23 pagesNotes Lesson 6 To 9 Botany LecMohamidin MamalapatNo ratings yet
- Plant Growth and Development - Short NotesDocument5 pagesPlant Growth and Development - Short Notesanusha shankarNo ratings yet
- Science BotanyDocument6 pagesScience BotanybalagbaganjoymargaretNo ratings yet
- PlantsDocument38 pagesPlantsmohamadarafah3No ratings yet
- Bryophytes Kingdom PlantaeDocument8 pagesBryophytes Kingdom PlantaeAnonymous Xlpj86laNo ratings yet
- 11 BryophytesDocument8 pages11 BryophytesAnonymous Xlpj86laNo ratings yet
- Unit 8. SEED GERMINATIONDocument27 pagesUnit 8. SEED GERMINATIONJENELYN BULAWANNo ratings yet
- Transport in PlantsDocument86 pagesTransport in Plantschelsearamdial21No ratings yet
- Roots: Allium (Onion) Root Tip L.S (Mono)Document11 pagesRoots: Allium (Onion) Root Tip L.S (Mono)reeNo ratings yet
- Biology 2 Plant Morphology and Biotechnology Plant SystemsDocument3 pagesBiology 2 Plant Morphology and Biotechnology Plant SystemslarraNo ratings yet
- Plants Morphology & PhysiologyDocument5 pagesPlants Morphology & PhysiologyDonna Mae AbonalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Biology of Agricultural CropsDocument8 pagesChapter 2: Biology of Agricultural CropsDwight Luciano T MendezNo ratings yet
- Biology Notes Alt of Gen Parts 01 - 0307 - 23 1Document12 pagesBiology Notes Alt of Gen Parts 01 - 0307 - 23 1Jon Michael BoboyoNo ratings yet
- Morphology of Flowering Plants 1Document45 pagesMorphology of Flowering Plants 1suresh yadavNo ratings yet
- Ecosystem Q&ADocument6 pagesEcosystem Q&Aberaindrajit583No ratings yet
- II ME NRP B SS 02. Plant KingdomDocument5 pagesII ME NRP B SS 02. Plant KingdomAmit RavindhraNo ratings yet
- Solution Brahmastra SMT-1 22-01-2023Document40 pagesSolution Brahmastra SMT-1 22-01-2023Vaibhav Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Whitehouse: Entrance Preparation ForDocument2 pagesWhitehouse: Entrance Preparation ForLalit ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Plant and Animal BiologyDocument4 pagesPlant and Animal BiologyGina Liza CanamaNo ratings yet
- PromeristemDocument12 pagesPromeristemRosselle NoyoalNo ratings yet
- Plant Structure Adaptations and ResponsesDocument21 pagesPlant Structure Adaptations and ResponsesPheby Alfimay Natysya PutriNo ratings yet
- Unit 04. The Plant Kingdom 1Document21 pagesUnit 04. The Plant Kingdom 1PEPE CISERNo ratings yet
- Bot 3 2 Lec Exam Reviewer: I. Euglenophyta Chlorophyceae Ulvophyceae Charophyceae Iii. BryophytesDocument4 pagesBot 3 2 Lec Exam Reviewer: I. Euglenophyta Chlorophyceae Ulvophyceae Charophyceae Iii. BryophytesXearis SangalangNo ratings yet
- AP Bio Plant Anatomy (KFogler)Document26 pagesAP Bio Plant Anatomy (KFogler)julie rainesNo ratings yet
- Prerequisite Knowledge of The Structure of The Plant.: PlantsDocument11 pagesPrerequisite Knowledge of The Structure of The Plant.: PlantsJohn Bryan JamisonNo ratings yet
- Dizon - Module 5Document9 pagesDizon - Module 5Penelopy DizonNo ratings yet
- Lesson 13. SEEDDocument3 pagesLesson 13. SEEDSamantha Jesi Shania EstradaNo ratings yet
- Transport Water and SolutesDocument4 pagesTransport Water and SolutesAleczandra QuesadaNo ratings yet
- Solution-BTS MT-14-28-04-2024nnDocument41 pagesSolution-BTS MT-14-28-04-2024nnharimohangurjar7073andhanaNo ratings yet
- 1plant Growth and DevelopmentDocument8 pages1plant Growth and Developmentadityaaggarwal821No ratings yet
- Practical Key-2024 Botany FullDocument8 pagesPractical Key-2024 Botany FulluntrustedusageNo ratings yet
- Bagi 'StemsDocument54 pagesBagi 'StemsAlif tiyyah.rNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and VariationDocument6 pagesCell Structure and VariationZ21 Martensen AbigailNo ratings yet
- PGRgucgyDocument6 pagesPGRgucgyCricket MindedNo ratings yet
- 63b90c1bddf56600188f5ac8 ## Plant Growth and Development Short NotesDocument5 pages63b90c1bddf56600188f5ac8 ## Plant Growth and Development Short Noteshyuhgfg349No ratings yet
- Plant EvolutionDocument50 pagesPlant EvolutionjoyfrangonzagaNo ratings yet
- Biology Study GuideDocument1 pageBiology Study Guidekrisamikaela1123No ratings yet
- Roots and StemsDocument14 pagesRoots and StemsSN - 11CC 678197 Meadowvale SSNo ratings yet
- Plant KingdomDocument6 pagesPlant Kingdomrautshreyash22No ratings yet
- Stems: Form & FunctionDocument56 pagesStems: Form & FunctionzubairNo ratings yet
- Vascular and Nonvascular PDFDocument55 pagesVascular and Nonvascular PDFMiedy Corazon TabangNo ratings yet
- Kindgom ProtistaDocument2 pagesKindgom ProtistaAshvine BeddewelaNo ratings yet
- Ticzon-Lab Activity 5Document14 pagesTiczon-Lab Activity 5ANGELA CHRISTIAN LIANILLO TICZONNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2022-01-02 at 5.13.24 PMDocument5 pagesScreenshot 2022-01-02 at 5.13.24 PMViraj PatilNo ratings yet
- Chapter-3-Plant Kingdom (Notes) : Systems of ClassificationDocument9 pagesChapter-3-Plant Kingdom (Notes) : Systems of ClassificationketakiNo ratings yet
- Plant Growth and DevtDocument38 pagesPlant Growth and DevtPatriciaNo ratings yet
- Anatomi TumbuhanDocument30 pagesAnatomi TumbuhanMEISYI DSNo ratings yet
- How Plants Grow - With Information on the Biology of Plant Cells, Roots, Leaves and FlowersFrom EverandHow Plants Grow - With Information on the Biology of Plant Cells, Roots, Leaves and FlowersNo ratings yet
Botany
Botany
Uploaded by
meirevi3w0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views2 pagesThe document summarizes 4 major groups of plants:
1. Bryophyta (mosses) - Have no true leaves or roots/stems and reproduce via spores.
2. Filicinophyta (ferns) - Have leaves, roots, and stems and reproduce via spores.
3. Coniferophyta (conifers) - Have leaves, roots, and stems and reproduce via seeds in cones.
4. Angiospermae (flowering plants) - Have leaves, roots, and stems and reproduce via seeds in fruits.
Original Description:
notes about botany lecture
Original Title
Botany.docx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document summarizes 4 major groups of plants:
1. Bryophyta (mosses) - Have no true leaves or roots/stems and reproduce via spores.
2. Filicinophyta (ferns) - Have leaves, roots, and stems and reproduce via spores.
3. Coniferophyta (conifers) - Have leaves, roots, and stems and reproduce via seeds in cones.
4. Angiospermae (flowering plants) - Have leaves, roots, and stems and reproduce via seeds in fruits.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views2 pagesBotany
Botany
Uploaded by
meirevi3wThe document summarizes 4 major groups of plants:
1. Bryophyta (mosses) - Have no true leaves or roots/stems and reproduce via spores.
2. Filicinophyta (ferns) - Have leaves, roots, and stems and reproduce via spores.
3. Coniferophyta (conifers) - Have leaves, roots, and stems and reproduce via seeds in cones.
4. Angiospermae (flowering plants) - Have leaves, roots, and stems and reproduce via seeds in fruits.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 2
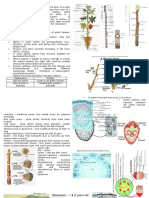
Biology Lecture- Botany 4 Major Groups/ 4 Major Phyla
Photosynthesis Stru Vascul Repro Oth Exa
cture arizatio ductio er mpl
- happens in the chloroplast s n n Feat es
ures
a. Light-dependent
Bryophyt No None Spores Anc Mos
- light is needed for water to be excited a (moss) ‘true’ hore ses
- site: thylakoid leave d by
- reactant: H20 s, rhizo
- product: ATP+ NADPH, O2 roots id
or
b. Light-independent/ Calvin Cycle stem
s
- site: stroma (inner membrane of the chloroplast) Filicinop Have Present Spores Leav Fern
hyta leave es s
- reactant: ATP + NADPH, CO2 (ferns) s, are
roots pinn
- product: C6H12O6 (starch/polysaccharide)
and ate
stem
s
Transpiration Conifero Have Present Seeds Woo Coni
phyta leave (in dy fers
- involves the stomata (gymnos s, cones) stem
- stomata: responsible for the uptake of CO2 perm) roots s
and release of water molecules and
- stomata have guard cells composed of stem
chloroplast which acts as photoreceptors. In s
the presence of light, the chloroplast will be Angiosp Have Present Seeds Hav Flow
excited causing the opening of the stomata ermophy leave (in e ers
- the hormone abscisic acid causes the stomata ta s, fruits) flow
to conserve water especially during the dry (angiosp roots ers
season erm) and and
stem fruits
Plant Major Function s
Hormone
Auxin Establish apical-basal polarity ● Xylem- H2O
● Phloem- food
Cytokinin Promote cell division, influence cell
specialization and plant aging
Gibberellin Stimulate cell division and cell Plant Structure
elongation, and promote seed 1. Root System
germination - holds the plant to the ground
- absorbs water and other minerals crucial to
Abscisic Coordinates defenses against
growth and development
Acid osmotic stress and pathogen
- storehouse for reserve food
attack
- developing root= radicle
Ethylene Induces fruit ripening - the area of the root hairs is the region of
maturation
- the region of the root cap is the region of cell
●
Auxin- Apical growth/ primary growth which division
is the elongation of either the shoot or root - the area between the root hairs and root cap
system; also known as Indole Ascetic Acid is the region of elongation
● Cytokinin- Cell division/ secondary growth PARTS:
which is the lateral or the increase in the a. Primary Root
width or the girt of the stem b. Lateral Root
● Gibberellin- Germination; works with both c. Tertiary Root
Auxin and Cytokinin 2. Shoot System
● Abscisic Acid- think about autumn/ falling of - includes the stem and leaves
the leaves because it coordinates defenses - in flowering plants, it includes the bud, flower,
against osmotic stress and pathogen attack fruits, and seeds
● Ethylene- a gas that induces fruit ripening
- stem, axillary bud, apical/terminal bud, node, ● Complete flower- has both the male and
petiole female parts, and presence of the petal and
a. Stem sepal
- can be an apical or lateral meristem ● Perfect flower- both male and female parts
- Apical Meristem: produces the terminal bud. such as the stamen and the pistil
Growth in this site is called the primary growth
as it increases the stem length
- Lateral Meristem: secondary growth in Monocots vs. Dicots
terms of width and thickness
b. Leaves ● Monocots
- composed of the blade, petiole, stipules, - 1 cotyledon
midrib, vein, and small netted vein - venation: parallel
characterized through monocots and dicot - vascular bundles: complexly arranged
plants o vascular bundle is composed of the
xylem and phloem
- root system: fibrous
Structure of a Flower - floral parts: usually in multiples of 3
1. Pistil ● Dicots
- 2 cotyledons
- the female/gyno part of the plant - venation: netlike
- has an opening called the stigma, and the stalk called - vascular bundles: arranged in ring
the style, the bottom part is the ovary - root system: taproot
- floral prats: usually in multiples of 4 or 5
2. Stamen
- the male/andro part of the plant
- composed of the anther and filament
3. Other parts
a. sepal
b. petal
c. receptacle- holds the flows
d. pedicel- the stalk
- petal and sepal are used for protection, give color to
the plant and acts as an attraction to pollinators
- petals are collectively known as corolla
- sepals are collectively known as calix
Fertilization in Plants
The pollen from the anther it will be taken by the
stigma from the same or different flower. The pollen
could be taken by the stigma through pollination via air,
insects, bugs, and birds. The pollen and the stigma will
form an elongation. This elongation will function as the
passage of the sperm known as the
microgametophyte. It goes in the ovary and form the
ovule known as the macrogametophyte.
In a structure of a flower, the presence of both male
and female parts, fertilization can occur in the same or
different flower
● Double fertilization- 2 sperm and 1 fused
ovule. This will produce seed and 1 polar
nucleus which forms the endosperm for
development. Occurs in angiosperms
You might also like
- Sean Burke - Online Algae WebquestDocument4 pagesSean Burke - Online Algae Webquestapi-386190429100% (2)
- Ccp1.1: Pharmaceutical Botany With TaxonomyDocument22 pagesCcp1.1: Pharmaceutical Botany With Taxonomyja_Quinine100% (2)
- Lab 7 - Introduction and ProcedureDocument9 pagesLab 7 - Introduction and ProcedureFloyd SeremNo ratings yet
- Botany Reviewer For First Quarter PDFDocument6 pagesBotany Reviewer For First Quarter PDFDale Maristela Peñalosa100% (3)
- Zbook Biology-Unit-03 149aa8Document15 pagesZbook Biology-Unit-03 149aa8Ashok ParasharNo ratings yet
- Bio 11.1 LE 2 NotesDocument7 pagesBio 11.1 LE 2 NotesCode BlueNo ratings yet
- Bio 111 LecDocument50 pagesBio 111 LecFlorence PalomarNo ratings yet
- 1 Botlec ReviewerDocument7 pages1 Botlec ReviewerKamille PobleteNo ratings yet
- General Biology II Midterms PDFDocument16 pagesGeneral Biology II Midterms PDFantonio louise anjella monNo ratings yet
- Plant Growth and Hormone by Garima MamDocument23 pagesPlant Growth and Hormone by Garima Mampolumatlajoy9515No ratings yet
- Anatomy PDFDocument6 pagesAnatomy PDFtrytobeatgamerNo ratings yet
- MRQ LWCT Note 14Document95 pagesMRQ LWCT Note 14Faris AdityaNo ratings yet
- Notes Lesson 6 To 9 Botany LecDocument23 pagesNotes Lesson 6 To 9 Botany LecMohamidin MamalapatNo ratings yet
- Plant Growth and Development - Short NotesDocument5 pagesPlant Growth and Development - Short Notesanusha shankarNo ratings yet
- Science BotanyDocument6 pagesScience BotanybalagbaganjoymargaretNo ratings yet
- PlantsDocument38 pagesPlantsmohamadarafah3No ratings yet
- Bryophytes Kingdom PlantaeDocument8 pagesBryophytes Kingdom PlantaeAnonymous Xlpj86laNo ratings yet
- 11 BryophytesDocument8 pages11 BryophytesAnonymous Xlpj86laNo ratings yet
- Unit 8. SEED GERMINATIONDocument27 pagesUnit 8. SEED GERMINATIONJENELYN BULAWANNo ratings yet
- Transport in PlantsDocument86 pagesTransport in Plantschelsearamdial21No ratings yet
- Roots: Allium (Onion) Root Tip L.S (Mono)Document11 pagesRoots: Allium (Onion) Root Tip L.S (Mono)reeNo ratings yet
- Biology 2 Plant Morphology and Biotechnology Plant SystemsDocument3 pagesBiology 2 Plant Morphology and Biotechnology Plant SystemslarraNo ratings yet
- Plants Morphology & PhysiologyDocument5 pagesPlants Morphology & PhysiologyDonna Mae AbonalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Biology of Agricultural CropsDocument8 pagesChapter 2: Biology of Agricultural CropsDwight Luciano T MendezNo ratings yet
- Biology Notes Alt of Gen Parts 01 - 0307 - 23 1Document12 pagesBiology Notes Alt of Gen Parts 01 - 0307 - 23 1Jon Michael BoboyoNo ratings yet
- Morphology of Flowering Plants 1Document45 pagesMorphology of Flowering Plants 1suresh yadavNo ratings yet
- Ecosystem Q&ADocument6 pagesEcosystem Q&Aberaindrajit583No ratings yet
- II ME NRP B SS 02. Plant KingdomDocument5 pagesII ME NRP B SS 02. Plant KingdomAmit RavindhraNo ratings yet
- Solution Brahmastra SMT-1 22-01-2023Document40 pagesSolution Brahmastra SMT-1 22-01-2023Vaibhav Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Whitehouse: Entrance Preparation ForDocument2 pagesWhitehouse: Entrance Preparation ForLalit ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Plant and Animal BiologyDocument4 pagesPlant and Animal BiologyGina Liza CanamaNo ratings yet
- PromeristemDocument12 pagesPromeristemRosselle NoyoalNo ratings yet
- Plant Structure Adaptations and ResponsesDocument21 pagesPlant Structure Adaptations and ResponsesPheby Alfimay Natysya PutriNo ratings yet
- Unit 04. The Plant Kingdom 1Document21 pagesUnit 04. The Plant Kingdom 1PEPE CISERNo ratings yet
- Bot 3 2 Lec Exam Reviewer: I. Euglenophyta Chlorophyceae Ulvophyceae Charophyceae Iii. BryophytesDocument4 pagesBot 3 2 Lec Exam Reviewer: I. Euglenophyta Chlorophyceae Ulvophyceae Charophyceae Iii. BryophytesXearis SangalangNo ratings yet
- AP Bio Plant Anatomy (KFogler)Document26 pagesAP Bio Plant Anatomy (KFogler)julie rainesNo ratings yet
- Prerequisite Knowledge of The Structure of The Plant.: PlantsDocument11 pagesPrerequisite Knowledge of The Structure of The Plant.: PlantsJohn Bryan JamisonNo ratings yet
- Dizon - Module 5Document9 pagesDizon - Module 5Penelopy DizonNo ratings yet
- Lesson 13. SEEDDocument3 pagesLesson 13. SEEDSamantha Jesi Shania EstradaNo ratings yet
- Transport Water and SolutesDocument4 pagesTransport Water and SolutesAleczandra QuesadaNo ratings yet
- Solution-BTS MT-14-28-04-2024nnDocument41 pagesSolution-BTS MT-14-28-04-2024nnharimohangurjar7073andhanaNo ratings yet
- 1plant Growth and DevelopmentDocument8 pages1plant Growth and Developmentadityaaggarwal821No ratings yet
- Practical Key-2024 Botany FullDocument8 pagesPractical Key-2024 Botany FulluntrustedusageNo ratings yet
- Bagi 'StemsDocument54 pagesBagi 'StemsAlif tiyyah.rNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and VariationDocument6 pagesCell Structure and VariationZ21 Martensen AbigailNo ratings yet
- PGRgucgyDocument6 pagesPGRgucgyCricket MindedNo ratings yet
- 63b90c1bddf56600188f5ac8 ## Plant Growth and Development Short NotesDocument5 pages63b90c1bddf56600188f5ac8 ## Plant Growth and Development Short Noteshyuhgfg349No ratings yet
- Plant EvolutionDocument50 pagesPlant EvolutionjoyfrangonzagaNo ratings yet
- Biology Study GuideDocument1 pageBiology Study Guidekrisamikaela1123No ratings yet
- Roots and StemsDocument14 pagesRoots and StemsSN - 11CC 678197 Meadowvale SSNo ratings yet
- Plant KingdomDocument6 pagesPlant Kingdomrautshreyash22No ratings yet
- Stems: Form & FunctionDocument56 pagesStems: Form & FunctionzubairNo ratings yet
- Vascular and Nonvascular PDFDocument55 pagesVascular and Nonvascular PDFMiedy Corazon TabangNo ratings yet
- Kindgom ProtistaDocument2 pagesKindgom ProtistaAshvine BeddewelaNo ratings yet
- Ticzon-Lab Activity 5Document14 pagesTiczon-Lab Activity 5ANGELA CHRISTIAN LIANILLO TICZONNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2022-01-02 at 5.13.24 PMDocument5 pagesScreenshot 2022-01-02 at 5.13.24 PMViraj PatilNo ratings yet
- Chapter-3-Plant Kingdom (Notes) : Systems of ClassificationDocument9 pagesChapter-3-Plant Kingdom (Notes) : Systems of ClassificationketakiNo ratings yet
- Plant Growth and DevtDocument38 pagesPlant Growth and DevtPatriciaNo ratings yet
- Anatomi TumbuhanDocument30 pagesAnatomi TumbuhanMEISYI DSNo ratings yet
- How Plants Grow - With Information on the Biology of Plant Cells, Roots, Leaves and FlowersFrom EverandHow Plants Grow - With Information on the Biology of Plant Cells, Roots, Leaves and FlowersNo ratings yet