Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lab 7
Lab 7
Uploaded by
joy002anuOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lab 7
Lab 7
Uploaded by
joy002anuCopyright:
Available Formats
Conductance of pure H2O = 18.
62 µohm -1cm-1
Conductance of BaSO4 solution = 176.4 µohm -1cm-1
Table 1: To determining Specific and equivalent conductance of KCl solution of various
concentrations
Specific Equivalent
Observation Concentration, √C conductance conductance, Λ
No. C (N) LS (Ω-1cm2eq-1)
(µΩ-1cm-1)
01 0.001 0.03 189 189
02 0.005 0.07 633 126.6
03 0.01 0.10 1172 117.2
04 0.05 0.22 5765 115.3
05 0.1 0.32 11180 111.8
06 0.25 0.50 26620 106.48
Equivalent Conductance (Λ) vs √C
200
180
160
140 f(x) = − 110.714345114345 x + 150.610964656965
(Ω-1cm2eq-1)
120 R² = 0.415850875040444
100
Λ
80
60
40
20
0
0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6
√C (N)
Figure 1: Graph for determining ɅKCl at infinite dilution
Calculation:
K = (176.4-18.62) µohm -1cm-1
Concentration of BaSO4:
k ×1000
CBaSO4 =
Ʌ
(k × 1000)
=
¿¿
(1000 1.5778 10−4 )
=
(127.2+160)
= 5.4910-4 N
Solubility product:
Ksp = C2 = 3.014×10-7 mol2L-2
From the intercept of the graph,
Equivalent conductance at infinite dilution, Ʌo = 147 Ω-1cm2eq-1
Result:
Equivalent conductance of KCl solution at infinite dilution, Λ°KCl =147 Ω-1cm2eq-1
The solubility product of BaSO4, Ksp= 3.014×10-7 mol 2L2
You might also like
- Design Based Research in Education Theory and Applications PhilippakosDocument349 pagesDesign Based Research in Education Theory and Applications PhilippakosFaznah MursyidiNo ratings yet
- Tugas II Fenomena Transport LanjutDocument3 pagesTugas II Fenomena Transport Lanjutزينل الغزاليNo ratings yet
- 2023 TPM351ppyDocument7 pages2023 TPM351ppyJenyver LappyNo ratings yet
- Reactor Type: Reactor With Specified Constant Temperature of 150 CDocument8 pagesReactor Type: Reactor With Specified Constant Temperature of 150 CJay MaradiyaNo ratings yet
- Pd1 (KN) Pu (KN) M1s (KN-M) M1ns (KN-M) M2ns (KN-M) M2s (KN-M)Document21 pagesPd1 (KN) Pu (KN) M1s (KN-M) M1ns (KN-M) M2ns (KN-M) M2s (KN-M)Kayla DimaanoNo ratings yet
- Phenol and PhotocatalysisDocument12 pagesPhenol and PhotocatalysisMerul ShahNo ratings yet
- Otk KuisDocument7 pagesOtk KuisRenaufal 18No ratings yet
- Worked Example For Unbraced Frame Designed Colum Wind Moment MethodDocument22 pagesWorked Example For Unbraced Frame Designed Colum Wind Moment MethodAce LowNo ratings yet
- Piling 2Document3 pagesPiling 2Aek JanNo ratings yet
- Class Room 1 8M Minimum Thickness of SlabDocument7 pagesClass Room 1 8M Minimum Thickness of Slabdiego lopezNo ratings yet
- Physical Chemistry Assignment 2Document5 pagesPhysical Chemistry Assignment 2Dick HardwoodNo ratings yet
- Perhitungan Asam KuatDocument6 pagesPerhitungan Asam KuatYulle RachmaNo ratings yet
- The Conductance of Strong and Weak ElectrolytesDocument8 pagesThe Conductance of Strong and Weak Electrolytessexycassie100% (6)
- Juano - RC2 - DDM Method - Final ReqDocument15 pagesJuano - RC2 - DDM Method - Final ReqJohn Lloyd JuanoNo ratings yet
- Design of Slab Using DDM: CE 158 Reinforced Concreted Design IiDocument15 pagesDesign of Slab Using DDM: CE 158 Reinforced Concreted Design IiJohn Lloyd JuanoNo ratings yet
- Table & FigureDocument5 pagesTable & FigureNabilla Putri AndiniNo ratings yet
- Vol I-Chapter 8 ExamplesDocument9 pagesVol I-Chapter 8 Examplesotokar2No ratings yet
- EXAMPLE 4.1 - Batch KineticsDocument15 pagesEXAMPLE 4.1 - Batch KineticsfaninaninaninaNo ratings yet
- Pedestal 1Document3 pagesPedestal 1EakJhuanNo ratings yet
- Bui Viet Phuong HW11Document6 pagesBui Viet Phuong HW11Bùi Việt PhươngNo ratings yet
- Pubdoc 10 23773 250Document6 pagesPubdoc 10 23773 250Irfan GulNo ratings yet
- Ejemplo N 20Document1 pageEjemplo N 20Toby BobyNo ratings yet
- Kapal Pole and Line: Disp Disp Disp Disp DispDocument5 pagesKapal Pole and Line: Disp Disp Disp Disp DispSyarifah Raudhah AlkhairidNo ratings yet
- CHEM-E6105 Exercise-2-SolutionsDocument4 pagesCHEM-E6105 Exercise-2-SolutionsEdwin R RiveraNo ratings yet
- Contoh Regresi Kap Angkut Vs Bahan BakarDocument14 pagesContoh Regresi Kap Angkut Vs Bahan Bakaradelita adrianaNo ratings yet
- Beams On Elastic Foundation: Mechanics Equations Material Variabless Slab Thickness Slab WidthDocument2 pagesBeams On Elastic Foundation: Mechanics Equations Material Variabless Slab Thickness Slab WidthDC1234No ratings yet
- Task 4Document3 pagesTask 4mysteries of spaceNo ratings yet
- Conduct IV I DadDocument7 pagesConduct IV I DadEder E. AguilarNo ratings yet
- Concentration Vs Conductivity: 1.0 Results, Discussion and Analysis 1.1 Calibration CurveDocument9 pagesConcentration Vs Conductivity: 1.0 Results, Discussion and Analysis 1.1 Calibration CurveAhZaiSkyNo ratings yet
- Spektroskopsko Određivanje Ibuprofena U Neofen Dražejama: 0.14 F (X) 0.2528 X 0.00028 R 0.999995618710111Document1 pageSpektroskopsko Određivanje Ibuprofena U Neofen Dražejama: 0.14 F (X) 0.2528 X 0.00028 R 0.999995618710111saraahNo ratings yet
- Design For S-7 4M Minimum Thickness of SlabDocument24 pagesDesign For S-7 4M Minimum Thickness of Slabdiego lopezNo ratings yet
- P MMHG: Constantes de Antoine Parámetros Binarios: (G - G) (Cal/Mol K) Parámetros Binarios: AlfaDocument14 pagesP MMHG: Constantes de Antoine Parámetros Binarios: (G - G) (Cal/Mol K) Parámetros Binarios: AlfaXiime WalburgNo ratings yet
- Transferencia de MasaDocument6 pagesTransferencia de MasaJonyzhitop TenorioNo ratings yet
- TOS Lecture 11Document19 pagesTOS Lecture 11Shaina Mariz Serrano PanaliganNo ratings yet
- TSAI HSIANG en Biochemical EngineeringDocument22 pagesTSAI HSIANG en Biochemical EngineeringTSAI, HSIANGEN(대학원학생/일반대학원 화공생명공학) No ratings yet
- Jawaban Biofar Pertemuan 7Document2 pagesJawaban Biofar Pertemuan 7yoga refiNo ratings yet
- Axis Title Axis TitleDocument2 pagesAxis Title Axis TitleAnnisah Yuliana SaidNo ratings yet
- Supplementary MaterialDocument7 pagesSupplementary MaterialInigo JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Semibatch KRD LabDocument7 pagesSemibatch KRD LabPritiNo ratings yet
- 2.5 Eadie (1942) Measured The Initial Reaction Rate of Hydrolysis of Acetylcholme (Substrate) byDocument6 pages2.5 Eadie (1942) Measured The Initial Reaction Rate of Hydrolysis of Acetylcholme (Substrate) byRoxan Bueno MoraNo ratings yet
- Exp 3Document2 pagesExp 3Wing Yin CHEUNGNo ratings yet
- Design SpreadsheetDocument6 pagesDesign SpreadsheetWinnieNo ratings yet
- Experiment Eight: Spectrophotometric Analysis of A Complex MixtureDocument12 pagesExperiment Eight: Spectrophotometric Analysis of A Complex MixtureMark AwNo ratings yet
- Validasi H2SDocument18 pagesValidasi H2Sseptian_bbyNo ratings yet
- Kellogg Synthesis Reactor PropertiesDocument9 pagesKellogg Synthesis Reactor PropertiesMainul HaqueNo ratings yet
- Calculations TFP260S AssignmentDocument5 pagesCalculations TFP260S AssignmentKelly AbrahamsNo ratings yet
- Gauge Repeteability and ReprouctibilityDocument7 pagesGauge Repeteability and ReprouctibilityAdrián JarablaNo ratings yet
- Ahmad Naufal - Hambatan Dan Propulsi - 029Document3 pagesAhmad Naufal - Hambatan Dan Propulsi - 029UmarNo ratings yet
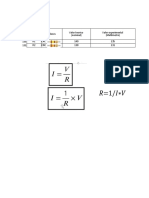
- Electrolytic Conductance Weak ElectrolytesDocument3 pagesElectrolytic Conductance Weak ElectrolytesmylodNo ratings yet
- UOA Distillation Tutorial SolutionsDocument12 pagesUOA Distillation Tutorial SolutionsutewwtrNo ratings yet
- Distillation TowerDocument28 pagesDistillation TowerSYED ASGHAR ALI SULTAN100% (1)
- Example 4.1Document21 pagesExample 4.1M Iqbal ANo ratings yet
- Lab 1Document4 pagesLab 1JOHANN STIVEN OCAMPO GARCIANo ratings yet
- 10Document4 pages10ZenPhiNo ratings yet
- 1psi q Q a Capa Ei Ei tnf/cm2 Vi Ki Bi λiDocument2 pages1psi q Q a Capa Ei Ei tnf/cm2 Vi Ki Bi λiCleison Armando Manrique AguirreNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 2: ObjectDocument3 pagesExperiment No. 2: ObjectAlia KhanNo ratings yet
- Flas K# Mass of Charcoa L (G) Initial Concentrati On of Acoh (M) Volume of Naoh Used (ML) Run 1 Run 2Document2 pagesFlas K# Mass of Charcoa L (G) Initial Concentrati On of Acoh (M) Volume of Naoh Used (ML) Run 1 Run 2shaiNo ratings yet
- 1psi q Q a Capa Ei Ei tnf/cm2 Vi Ki Bi λiDocument2 pages1psi q Q a Capa Ei Ei tnf/cm2 Vi Ki Bi λiCleison Armando Manrique AguirreNo ratings yet
- Exercicis UVvis - SoluciãDocument17 pagesExercicis UVvis - SoluciãclerrosseNo ratings yet
- Volume Molar ParsialDocument8 pagesVolume Molar ParsialEco Generasi BiruNo ratings yet
- BA42-Linear Programming - Practice Problem Answer KeyDocument6 pagesBA42-Linear Programming - Practice Problem Answer KeyMa Gemma ApaapNo ratings yet
- Simplex MethodDocument24 pagesSimplex MethodAce Maynard Dianco50% (2)
- PMI RMP RiskManagementStandardAndCertificationOverviewDocument27 pagesPMI RMP RiskManagementStandardAndCertificationOverviewsurajthakur100% (2)
- Anachem NeutralizationDocument2 pagesAnachem NeutralizationChristian Ghail MacapagalNo ratings yet
- Probability Theory: STAT310/MATH230 September 12, 2010Document151 pagesProbability Theory: STAT310/MATH230 September 12, 2010RocApplyNo ratings yet
- Midterm SolutionDocument8 pagesMidterm SolutionranvNo ratings yet
- CALCULUS 2 LM Chapter 1Document12 pagesCALCULUS 2 LM Chapter 1Ella FelicianoNo ratings yet
- On The Numerical Solution of Picard Iteration Method For Fractional Integro - Differential EquationDocument7 pagesOn The Numerical Solution of Picard Iteration Method For Fractional Integro - Differential EquationDavid Ilejimi ONo ratings yet
- IME634 Statistics UnivariateDocument238 pagesIME634 Statistics UnivariateAbhishek aryaNo ratings yet
- 5 Boundary Value Problems and Green's FunctionsDocument6 pages5 Boundary Value Problems and Green's FunctionsArun TyagiNo ratings yet
- A First Course in Calculus PDFDocument103 pagesA First Course in Calculus PDFG skids eggNo ratings yet
- CALCUTTA UNIVERSITY Mathematics Honours TextbooksDocument4 pagesCALCUTTA UNIVERSITY Mathematics Honours TextbooksADITI Library100% (2)
- Probablistic Number TheoryDocument85 pagesProbablistic Number TheoryShreerang ThergaonkarNo ratings yet
- PG 27-07-2016Document1 pagePG 27-07-2016trianNo ratings yet
- Mth101 Mid Term 4Document8 pagesMth101 Mid Term 4Zafran Aslam KhanNo ratings yet
- L-6 de Series SolutionDocument88 pagesL-6 de Series SolutionRiju VaishNo ratings yet
- 30 Sample Questions - RMPDocument9 pages30 Sample Questions - RMPyaghoobNo ratings yet
- Generation of Complex ExponentialDocument5 pagesGeneration of Complex Exponentialirum jafriNo ratings yet
- Calculus Volume 2-OP PDFDocument830 pagesCalculus Volume 2-OP PDFkebarcla100% (1)
- Pid PDFDocument22 pagesPid PDFmansoorNo ratings yet
- Space-Filling CurvesDocument10 pagesSpace-Filling CurvesAlexBowringNo ratings yet
- Powell Ku 0099D 15918 DATA 1Document267 pagesPowell Ku 0099D 15918 DATA 1Mariana RomoNo ratings yet
- Manajemen Penjualan Chapter 9 123Document16 pagesManajemen Penjualan Chapter 9 123jae cantikNo ratings yet
- Structural Restoration of MonumentsDocument16 pagesStructural Restoration of MonumentsIdaHodzicNo ratings yet
- Form4 Add Maths Chapter 1Document20 pagesForm4 Add Maths Chapter 1Murugan RSNo ratings yet
- MGMT 6250 Financial Modeling and Optimization: Aparna GuptaDocument6 pagesMGMT 6250 Financial Modeling and Optimization: Aparna GuptabhathiyaengNo ratings yet
- Math489/889 Stochastic Processes and Advanced Mathematical Finance Homework 7Document3 pagesMath489/889 Stochastic Processes and Advanced Mathematical Finance Homework 7poma7218No ratings yet
- B Tech - Polymer-R2021-CS - 14 06 2023Document310 pagesB Tech - Polymer-R2021-CS - 14 06 2023Faraj HaiderNo ratings yet