Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Osi TCP Ip
Osi TCP Ip
Uploaded by
kd ahmedCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- TCP/IP Sockets in Java: Practical Guide for ProgrammersFrom EverandTCP/IP Sockets in Java: Practical Guide for ProgrammersRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- Difference Between Osi and TCPDocument1 pageDifference Between Osi and TCPAlagandula KalyaniNo ratings yet
- Comparison Between IOS & TCPDocument8 pagesComparison Between IOS & TCPMayada GamalNo ratings yet
- 10comparison of OSI and IP Reference ModelDocument3 pages10comparison of OSI and IP Reference ModelJawad SandhuNo ratings yet
- OSI and TCP/IP Models EssayDocument4 pagesOSI and TCP/IP Models EssayannikaNo ratings yet
- Difference Between OSI and TCP/IP Reference ModelDocument2 pagesDifference Between OSI and TCP/IP Reference ModelReign Earl B. Gup-ayNo ratings yet
- Comparison of OSI and TCPDocument3 pagesComparison of OSI and TCPAmit SinghNo ratings yet
- Comparing Tcp-IP & OSIDocument2 pagesComparing Tcp-IP & OSIDan Kimbo Slice MartellNo ratings yet
- OSI Vs TCP - IPDocument3 pagesOSI Vs TCP - IPgullapalli123No ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document14 pagesLecture 2clely fernandesNo ratings yet
- Osi and TCPDocument2 pagesOsi and TCPDnyan navgareNo ratings yet
- Overview of TCP/IP Reference ModelDocument4 pagesOverview of TCP/IP Reference ModelPRODIP DEBNo ratings yet
- Reference Models in Communication NetworkDocument2 pagesReference Models in Communication NetworkJawad SandhuNo ratings yet
- Data Communication & NetworksDocument8 pagesData Communication & Networksrukhsar siddiqueNo ratings yet
- Comparison Between Osi Tcpip ModelDocument10 pagesComparison Between Osi Tcpip ModelVipula RawteNo ratings yet
- Four Layers of TCP/IP Model Explained: Difference Between TCP/IP and OSI ModelDocument3 pagesFour Layers of TCP/IP Model Explained: Difference Between TCP/IP and OSI Modelsundar anandanNo ratings yet
- Which Model Is Better, OSI or TCP - IPDocument5 pagesWhich Model Is Better, OSI or TCP - IPFAYSAL AhamadNo ratings yet
- StanderdsDocument15 pagesStanderdslahiruaioitNo ratings yet
- Cybersecurityassenment 2Document13 pagesCybersecurityassenment 2tataf79300No ratings yet
- 3-Network Models MDocument6 pages3-Network Models Mtwfm578No ratings yet
- Ajay P. GowthamDocument8 pagesAjay P. Gowthamajaay2566No ratings yet
- Wepik The Comprehensive Analysis of Osi and Tcpip Models Unveiling The Purpose Structure and Functiona 20240128161622zfu9Document7 pagesWepik The Comprehensive Analysis of Osi and Tcpip Models Unveiling The Purpose Structure and Functiona 20240128161622zfu9Souvik PalNo ratings yet
- Osi Model and TCP AssignmentDocument7 pagesOsi Model and TCP AssignmentFrancis PulaiziNo ratings yet
- Computer Network Report - CA2 - Tirtharaj Pati - 14201619089 PDFDocument4 pagesComputer Network Report - CA2 - Tirtharaj Pati - 14201619089 PDFTirtharaj PatiNo ratings yet
- Network Communication ModelsDocument7 pagesNetwork Communication ModelsFilipe NahorNo ratings yet
- TCP/IP Model Vs OSI Model: Computer NetworkingDocument5 pagesTCP/IP Model Vs OSI Model: Computer NetworkingRaj KumarNo ratings yet
- Write Down The Advantages of OSI Model Over TCPDocument1 pageWrite Down The Advantages of OSI Model Over TCPgroy4732No ratings yet
- RahulKirtoniya CSE D-03-21Document5 pagesRahulKirtoniya CSE D-03-21Rahul KirtoniyaNo ratings yet
- 6-OSI Model-10-01-2022 (10-Jan-2022) Material - I - 10-01-2022 - OSI - TCP-IP - ModelDocument39 pages6-OSI Model-10-01-2022 (10-Jan-2022) Material - I - 10-01-2022 - OSI - TCP-IP - ModelPrerna SinghNo ratings yet
- TCP IpDocument13 pagesTCP Ipingawalemadhura5722No ratings yet
- 3.4 Notes Other ThanDocument5 pages3.4 Notes Other ThanadvanceshifaNo ratings yet
- Network Layers: The OSI and Internet ModelsDocument33 pagesNetwork Layers: The OSI and Internet ModelsebinVettuchirayilNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1.1.1 and 1.1.2 - OSI Model and TCP-IP Model - DCDocument33 pagesLecture 1.1.1 and 1.1.2 - OSI Model and TCP-IP Model - DCanonymousguyinfinityNo ratings yet
- OSI Model (Open Systems Interconnection) : NetworkDocument22 pagesOSI Model (Open Systems Interconnection) : NetworkStephen ChidhandaraNo ratings yet
- #7 Reference Models in Communication NetworksDocument45 pages#7 Reference Models in Communication NetworksKarrie Mae GolilaoNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2: Lesson 2Document3 pagesAssignment 2: Lesson 2Marijo Bugarso BSIT-3BNo ratings yet
- IPU MCA Advance Computer Network Lecture Wise Notes (Lec03 (TCPIP) )Document3 pagesIPU MCA Advance Computer Network Lecture Wise Notes (Lec03 (TCPIP) )Vaibhav JainNo ratings yet
- Data Communication and Computer Networking LABDocument3 pagesData Communication and Computer Networking LABMuzaffar ChahalNo ratings yet
- TCP IpDocument2 pagesTCP IpfouadbalomiNo ratings yet
- Week 11 UpdatedDocument20 pagesWeek 11 UpdatedSarmmistha TrilochanaNo ratings yet
- The Seven Layers of The OSI ModelDocument4 pagesThe Seven Layers of The OSI ModelShashikant ThakreNo ratings yet
- 2 OSI Reference Model: Computer NetworksDocument26 pages2 OSI Reference Model: Computer NetworksvijayNo ratings yet
- Osi Vs TCP and IpDocument3 pagesOsi Vs TCP and Ipapi-282360558100% (1)
- Data Communication LayersDocument22 pagesData Communication Layersendriasmit_469556062No ratings yet
- Chapter - 05 / Lecture - 03 / Osi - Tcp/IpDocument10 pagesChapter - 05 / Lecture - 03 / Osi - Tcp/IpNagaraj VaratharajNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 UNIT 1 ICT - Student GuideDocument16 pagesTopic 2 UNIT 1 ICT - Student GuideMuhamed MuslimNo ratings yet
- Data Communication & NetworkingDocument71 pagesData Communication & NetworkingShabanaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 NotesDocument9 pagesLecture 1 NotesDiogo PintoNo ratings yet
- The OSI and TCPDocument8 pagesThe OSI and TCPSreejith VaneryNo ratings yet
- Osi ModelDocument10 pagesOsi ModeltayyabNo ratings yet
- Osimodel 170406162300 PDFDocument42 pagesOsimodel 170406162300 PDFPvkkiy EceNo ratings yet
- TCP - IP Model ShubroDocument21 pagesTCP - IP Model ShubroShubrojyoti ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Transport LayerDocument7 pagesTransport LayerMehboob NazimNo ratings yet
- Week # 03: Data Communication & NetworkDocument48 pagesWeek # 03: Data Communication & NetworkSaad Ashfaq XaadNo ratings yet
- Presentation On OSI Model & TCP/ IP ModelDocument42 pagesPresentation On OSI Model & TCP/ IP Modelq_riusNo ratings yet
- OSIReference Model 3Document25 pagesOSIReference Model 3Rizwan KhanNo ratings yet
- 1.1 13. Reference ModelsDocument22 pages1.1 13. Reference Modelshabib kamaieNo ratings yet
- TCP and Osi ModelsDocument4 pagesTCP and Osi Modelsnaki phiphiNo ratings yet
- Deploying IP and MPLS QoS for Multiservice Networks: Theory and PracticeFrom EverandDeploying IP and MPLS QoS for Multiservice Networks: Theory and PracticeNo ratings yet
- Open System LANs and Their Global Interconnection: Electronics and Communications Reference SeriesFrom EverandOpen System LANs and Their Global Interconnection: Electronics and Communications Reference SeriesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Computer Network ArchitectureDocument3 pagesComputer Network Architecturekd ahmedNo ratings yet
- IPv4 Vs IPv6Document3 pagesIPv4 Vs IPv6kd ahmedNo ratings yet
- Bangla Linear AlgebraDocument295 pagesBangla Linear Algebrakd ahmedNo ratings yet
- Advantage and Disadvantage of ComputerDocument2 pagesAdvantage and Disadvantage of Computerkd ahmed100% (1)
- Society and Technology Final Exam QuestionDocument18 pagesSociety and Technology Final Exam Questionkd ahmedNo ratings yet
- Data TypeDocument5 pagesData Typekd ahmedNo ratings yet
- Datasheet of DS 2DE4A225IW DEB - 20201109Document7 pagesDatasheet of DS 2DE4A225IW DEB - 20201109gknsurNo ratings yet
- LogDocument42 pagesLogAziz IsmailNo ratings yet
- Computer Hardware QuestionsDocument19 pagesComputer Hardware Questionsmeethi09No ratings yet
- Icloud Private Relay Overview Dec2021Document11 pagesIcloud Private Relay Overview Dec2021yerafi2991No ratings yet
- 1-Applications of DSPDocument20 pages1-Applications of DSPfigob33370No ratings yet
- ZXR10 M6000-S (V3.00.20) Products at A Glance - 826854Document17 pagesZXR10 M6000-S (V3.00.20) Products at A Glance - 826854danielxxxNo ratings yet
- License Face &sixton Template 5357292Document2 pagesLicense Face &sixton Template 5357292triradiianNo ratings yet
- Data CommunicationDocument17 pagesData CommunicationSnehal KarkiNo ratings yet
- Google AssistantDocument121 pagesGoogle AssistantElmer III PelayoNo ratings yet
- B7 Comp WK7Document6 pagesB7 Comp WK7Nana Yaw Poku JuniorNo ratings yet
- Imane ChtainiLab-Sheet - CSC3371-Fall 2022 - 80083Document47 pagesImane ChtainiLab-Sheet - CSC3371-Fall 2022 - 80083Idriss SefriouiNo ratings yet
- T Rec F.780.1 202203 I!!pdf eDocument42 pagesT Rec F.780.1 202203 I!!pdf eNecroNo ratings yet
- Purpose and Technique of EditingDocument8 pagesPurpose and Technique of EditingjosephsubinNo ratings yet
- Video IP Cores For Altera DE-Series BoardsDocument46 pagesVideo IP Cores For Altera DE-Series BoardsabyNo ratings yet
- Vocabulary Practice Unit 8Document4 pagesVocabulary Practice Unit 8José PizarroNo ratings yet
- NDG Network Virtualization concepts Course Questions اسئلةDocument5 pagesNDG Network Virtualization concepts Course Questions اسئلةMohAmed ReFatNo ratings yet
- ALU Devices and ConfigurationDocument76 pagesALU Devices and ConfigurationRichard ThainkhaNo ratings yet
- A3 Solutions - Representing ImagesDocument3 pagesA3 Solutions - Representing ImagesMykhailo ShapkinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Introduction-1Document28 pagesChapter 1 Introduction-1Abdi HafidNo ratings yet
- 5G Jumpstart: Unofficial Guide To Nokia Certified 5G AssociateDocument34 pages5G Jumpstart: Unofficial Guide To Nokia Certified 5G AssociateAshish JainNo ratings yet
- Visi Misi Ketos 20Document11 pagesVisi Misi Ketos 20haidar alyNo ratings yet
- Connecting FRITZ!Repeater To A Router From Another ManufacturerDocument5 pagesConnecting FRITZ!Repeater To A Router From Another ManufacturerCristian StanNo ratings yet
- Polycom Phone Test LogDocument14 pagesPolycom Phone Test Logثائر هاني فرج اللهNo ratings yet
- Unit 3Document175 pagesUnit 3Bhadra V RajaNo ratings yet
- Bajet 6 Bulan Pentadbiran 2020Document5 pagesBajet 6 Bulan Pentadbiran 2020zatisaadanNo ratings yet
- Ecommission SmartX Controllers Flow Balancer GuideDocument96 pagesEcommission SmartX Controllers Flow Balancer GuideWalter BarbaNo ratings yet
- Angelia Tengara - CVDocument2 pagesAngelia Tengara - CVAngelia TengaraNo ratings yet
- Asynchronous Transfer Mode (Atm) and Frame RelaysDocument15 pagesAsynchronous Transfer Mode (Atm) and Frame RelaysOmar CaabiNo ratings yet
- Intelligent NetworksDocument5 pagesIntelligent Networksdilush ranathunge RanathungeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Ecm413 PDFDocument57 pagesChapter 3 Ecm413 PDFCaha yANo ratings yet
Osi TCP Ip
Osi TCP Ip
Uploaded by
kd ahmedOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Osi TCP Ip
Osi TCP Ip
Uploaded by
kd ahmedCopyright:
Available Formats
What is OSI model?
The OSI stands for Open System Interconnection, which was developed in 1980s. It is a
conceptual model used for network communication. It is not implemented entirely, but it is still
referenced today. This OSI model consists of seven layers, and each layer is connected to each
other. The data moves down the OSI model, and each layer adds additional information. The data
moves down until it reaches the last layer of the OSI model. When the data is received at the last
layer of the OSI model, then the data is transmitted over the network. Once the data is reached on
the other side, then the process will get reversed.
What is TCP/IP model?
The TCP model stands for Transmission Control Protocol, whereas IP stands for Internet
Protocol. A number of protocols that make the internet possibly comes under the TCP/IP model.
Nowadays, we do not hear the name of the TCP/IP model much, we generally hear the name of
the IPv4 or IPv6, but it is still valid. This model consists of 4 layers. Now, we will look at the
diagrammatic representation of the TCP/IP model.
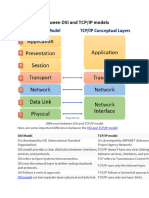
As shown in the above diagram, the TCP/IP model has 4 layers, while the OSI model consists of 7 layers.
Diagrammatically, it looks that the 4 layers of the TCP/IP model exactly fit the 7 layers of the OSI model,
but this is not reality. The application layer of the TCP/IP model maps to the first three layers, i.e.,
application, session, and presentation layer of the OSI model. The transport layer of the TCP maps
directly to the transport layer of the OSI model. The internet layer of the TCP/IP model maps directly to
the network layer of the OSI model. The last two layers of the OSI model map to the network layer of
the TCP/IP model. TCP/IP is the most widely used model as compared to the OSI model for providing
communication between computers over the internet.
Similarities between the OSI and TCP/IP model
The following are the similarities between the OSI and TCP/IP model:
Share common architecture
Both the models are the logical models and having similar architectures as both the models are
constructed with the layers.
Define standards
Both the layers have defined standards, and they also provide the framework used for
implementing the standards and devices.
Simplified troubleshooting process
Both models have simplified the troubleshooting process by breaking the complex function into
simpler components.
Pre-defined standards
The standards and protocols which are already pre-defined; these models do not redefine them;
they just reference or use them. For example, the Ethernet standards were already defined by the
IEEE before the development of these models; instead of recreating them, models have used
these pre-defined standards.
Both have similar functionality of 'transport' and 'network' layers
The function which is performed between the 'presentation' and the 'network' layer is similar
to the function performed at the transport layer.
Differences between the OSI and TCP/IP model
Let's see the differences between the OSI and TCP/IP model in a tabular form:
OSI Model TCP/IP Model
It stands for Transmission Control
It stands for Open System Interconnection.
Protocol.
OSI model has been developed by ISO It was developed by ARPANET (Advanced
(International Standard Organization). Research Project Agency Network).
It consists of standard protocols that lead to
It is an independent standard and generic protocol
the development of an internet. It is a
used as a communication gateway between the
communication protocol that provides the
network and the end user.
connection among the hosts.
The transport layer does not provide the
In the OSI model, the transport layer provides a surety for the delivery of packets. But still,
guarantee for the delivery of the packets. we can say that it is a reliable model.
This model is based on a horizontal
This model is based on a vertical approach.
approach.
In this model, the session and presentation
In this model, the session and presentation layers
layer are not different layers. Both layers are
are separated, i.e., both the layers are different.
included in the application layer.
It is also known as a reference model through
which various networks are built. For example, the It is an implemented model of an OSI
TCP/IP model is built from the OSI model. It is model.
also referred to as a guidance tool.
In this model, the network layer provides both The network layer provides only
connection-oriented and connectionless service. connectionless service.
Protocols in the OSI model are hidden and can be In this model, the protocol cannot be easily
easily replaced when the technology changes. replaced.
It consists of 4 layers.
It consists of 7 layers.
OSI model defines the services, protocols, and In the TCP/IP model, services, protocols,
interfaces as well as provides a proper distinction and interfaces are not properly separated. It
between them. It is protocol independent. is protocol dependent.
This model is highly used.
The usage of this model is very low.
It provides standardization to the devices like It does not provide the standardization to the
router, motherboard, switches, and other hardware devices. It provides a connection between
devices. various computers.
You might also like
- TCP/IP Sockets in Java: Practical Guide for ProgrammersFrom EverandTCP/IP Sockets in Java: Practical Guide for ProgrammersRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- Difference Between Osi and TCPDocument1 pageDifference Between Osi and TCPAlagandula KalyaniNo ratings yet
- Comparison Between IOS & TCPDocument8 pagesComparison Between IOS & TCPMayada GamalNo ratings yet
- 10comparison of OSI and IP Reference ModelDocument3 pages10comparison of OSI and IP Reference ModelJawad SandhuNo ratings yet
- OSI and TCP/IP Models EssayDocument4 pagesOSI and TCP/IP Models EssayannikaNo ratings yet
- Difference Between OSI and TCP/IP Reference ModelDocument2 pagesDifference Between OSI and TCP/IP Reference ModelReign Earl B. Gup-ayNo ratings yet
- Comparison of OSI and TCPDocument3 pagesComparison of OSI and TCPAmit SinghNo ratings yet
- Comparing Tcp-IP & OSIDocument2 pagesComparing Tcp-IP & OSIDan Kimbo Slice MartellNo ratings yet
- OSI Vs TCP - IPDocument3 pagesOSI Vs TCP - IPgullapalli123No ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document14 pagesLecture 2clely fernandesNo ratings yet
- Osi and TCPDocument2 pagesOsi and TCPDnyan navgareNo ratings yet
- Overview of TCP/IP Reference ModelDocument4 pagesOverview of TCP/IP Reference ModelPRODIP DEBNo ratings yet
- Reference Models in Communication NetworkDocument2 pagesReference Models in Communication NetworkJawad SandhuNo ratings yet
- Data Communication & NetworksDocument8 pagesData Communication & Networksrukhsar siddiqueNo ratings yet
- Comparison Between Osi Tcpip ModelDocument10 pagesComparison Between Osi Tcpip ModelVipula RawteNo ratings yet
- Four Layers of TCP/IP Model Explained: Difference Between TCP/IP and OSI ModelDocument3 pagesFour Layers of TCP/IP Model Explained: Difference Between TCP/IP and OSI Modelsundar anandanNo ratings yet
- Which Model Is Better, OSI or TCP - IPDocument5 pagesWhich Model Is Better, OSI or TCP - IPFAYSAL AhamadNo ratings yet
- StanderdsDocument15 pagesStanderdslahiruaioitNo ratings yet
- Cybersecurityassenment 2Document13 pagesCybersecurityassenment 2tataf79300No ratings yet
- 3-Network Models MDocument6 pages3-Network Models Mtwfm578No ratings yet
- Ajay P. GowthamDocument8 pagesAjay P. Gowthamajaay2566No ratings yet
- Wepik The Comprehensive Analysis of Osi and Tcpip Models Unveiling The Purpose Structure and Functiona 20240128161622zfu9Document7 pagesWepik The Comprehensive Analysis of Osi and Tcpip Models Unveiling The Purpose Structure and Functiona 20240128161622zfu9Souvik PalNo ratings yet
- Osi Model and TCP AssignmentDocument7 pagesOsi Model and TCP AssignmentFrancis PulaiziNo ratings yet
- Computer Network Report - CA2 - Tirtharaj Pati - 14201619089 PDFDocument4 pagesComputer Network Report - CA2 - Tirtharaj Pati - 14201619089 PDFTirtharaj PatiNo ratings yet
- Network Communication ModelsDocument7 pagesNetwork Communication ModelsFilipe NahorNo ratings yet
- TCP/IP Model Vs OSI Model: Computer NetworkingDocument5 pagesTCP/IP Model Vs OSI Model: Computer NetworkingRaj KumarNo ratings yet
- Write Down The Advantages of OSI Model Over TCPDocument1 pageWrite Down The Advantages of OSI Model Over TCPgroy4732No ratings yet
- RahulKirtoniya CSE D-03-21Document5 pagesRahulKirtoniya CSE D-03-21Rahul KirtoniyaNo ratings yet
- 6-OSI Model-10-01-2022 (10-Jan-2022) Material - I - 10-01-2022 - OSI - TCP-IP - ModelDocument39 pages6-OSI Model-10-01-2022 (10-Jan-2022) Material - I - 10-01-2022 - OSI - TCP-IP - ModelPrerna SinghNo ratings yet
- TCP IpDocument13 pagesTCP Ipingawalemadhura5722No ratings yet
- 3.4 Notes Other ThanDocument5 pages3.4 Notes Other ThanadvanceshifaNo ratings yet
- Network Layers: The OSI and Internet ModelsDocument33 pagesNetwork Layers: The OSI and Internet ModelsebinVettuchirayilNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1.1.1 and 1.1.2 - OSI Model and TCP-IP Model - DCDocument33 pagesLecture 1.1.1 and 1.1.2 - OSI Model and TCP-IP Model - DCanonymousguyinfinityNo ratings yet
- OSI Model (Open Systems Interconnection) : NetworkDocument22 pagesOSI Model (Open Systems Interconnection) : NetworkStephen ChidhandaraNo ratings yet
- #7 Reference Models in Communication NetworksDocument45 pages#7 Reference Models in Communication NetworksKarrie Mae GolilaoNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2: Lesson 2Document3 pagesAssignment 2: Lesson 2Marijo Bugarso BSIT-3BNo ratings yet
- IPU MCA Advance Computer Network Lecture Wise Notes (Lec03 (TCPIP) )Document3 pagesIPU MCA Advance Computer Network Lecture Wise Notes (Lec03 (TCPIP) )Vaibhav JainNo ratings yet
- Data Communication and Computer Networking LABDocument3 pagesData Communication and Computer Networking LABMuzaffar ChahalNo ratings yet
- TCP IpDocument2 pagesTCP IpfouadbalomiNo ratings yet
- Week 11 UpdatedDocument20 pagesWeek 11 UpdatedSarmmistha TrilochanaNo ratings yet
- The Seven Layers of The OSI ModelDocument4 pagesThe Seven Layers of The OSI ModelShashikant ThakreNo ratings yet
- 2 OSI Reference Model: Computer NetworksDocument26 pages2 OSI Reference Model: Computer NetworksvijayNo ratings yet
- Osi Vs TCP and IpDocument3 pagesOsi Vs TCP and Ipapi-282360558100% (1)
- Data Communication LayersDocument22 pagesData Communication Layersendriasmit_469556062No ratings yet
- Chapter - 05 / Lecture - 03 / Osi - Tcp/IpDocument10 pagesChapter - 05 / Lecture - 03 / Osi - Tcp/IpNagaraj VaratharajNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 UNIT 1 ICT - Student GuideDocument16 pagesTopic 2 UNIT 1 ICT - Student GuideMuhamed MuslimNo ratings yet
- Data Communication & NetworkingDocument71 pagesData Communication & NetworkingShabanaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 NotesDocument9 pagesLecture 1 NotesDiogo PintoNo ratings yet
- The OSI and TCPDocument8 pagesThe OSI and TCPSreejith VaneryNo ratings yet
- Osi ModelDocument10 pagesOsi ModeltayyabNo ratings yet
- Osimodel 170406162300 PDFDocument42 pagesOsimodel 170406162300 PDFPvkkiy EceNo ratings yet
- TCP - IP Model ShubroDocument21 pagesTCP - IP Model ShubroShubrojyoti ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Transport LayerDocument7 pagesTransport LayerMehboob NazimNo ratings yet
- Week # 03: Data Communication & NetworkDocument48 pagesWeek # 03: Data Communication & NetworkSaad Ashfaq XaadNo ratings yet
- Presentation On OSI Model & TCP/ IP ModelDocument42 pagesPresentation On OSI Model & TCP/ IP Modelq_riusNo ratings yet
- OSIReference Model 3Document25 pagesOSIReference Model 3Rizwan KhanNo ratings yet
- 1.1 13. Reference ModelsDocument22 pages1.1 13. Reference Modelshabib kamaieNo ratings yet
- TCP and Osi ModelsDocument4 pagesTCP and Osi Modelsnaki phiphiNo ratings yet
- Deploying IP and MPLS QoS for Multiservice Networks: Theory and PracticeFrom EverandDeploying IP and MPLS QoS for Multiservice Networks: Theory and PracticeNo ratings yet
- Open System LANs and Their Global Interconnection: Electronics and Communications Reference SeriesFrom EverandOpen System LANs and Their Global Interconnection: Electronics and Communications Reference SeriesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Computer Network ArchitectureDocument3 pagesComputer Network Architecturekd ahmedNo ratings yet
- IPv4 Vs IPv6Document3 pagesIPv4 Vs IPv6kd ahmedNo ratings yet
- Bangla Linear AlgebraDocument295 pagesBangla Linear Algebrakd ahmedNo ratings yet
- Advantage and Disadvantage of ComputerDocument2 pagesAdvantage and Disadvantage of Computerkd ahmed100% (1)
- Society and Technology Final Exam QuestionDocument18 pagesSociety and Technology Final Exam Questionkd ahmedNo ratings yet
- Data TypeDocument5 pagesData Typekd ahmedNo ratings yet
- Datasheet of DS 2DE4A225IW DEB - 20201109Document7 pagesDatasheet of DS 2DE4A225IW DEB - 20201109gknsurNo ratings yet
- LogDocument42 pagesLogAziz IsmailNo ratings yet
- Computer Hardware QuestionsDocument19 pagesComputer Hardware Questionsmeethi09No ratings yet
- Icloud Private Relay Overview Dec2021Document11 pagesIcloud Private Relay Overview Dec2021yerafi2991No ratings yet
- 1-Applications of DSPDocument20 pages1-Applications of DSPfigob33370No ratings yet
- ZXR10 M6000-S (V3.00.20) Products at A Glance - 826854Document17 pagesZXR10 M6000-S (V3.00.20) Products at A Glance - 826854danielxxxNo ratings yet
- License Face &sixton Template 5357292Document2 pagesLicense Face &sixton Template 5357292triradiianNo ratings yet
- Data CommunicationDocument17 pagesData CommunicationSnehal KarkiNo ratings yet
- Google AssistantDocument121 pagesGoogle AssistantElmer III PelayoNo ratings yet
- B7 Comp WK7Document6 pagesB7 Comp WK7Nana Yaw Poku JuniorNo ratings yet
- Imane ChtainiLab-Sheet - CSC3371-Fall 2022 - 80083Document47 pagesImane ChtainiLab-Sheet - CSC3371-Fall 2022 - 80083Idriss SefriouiNo ratings yet
- T Rec F.780.1 202203 I!!pdf eDocument42 pagesT Rec F.780.1 202203 I!!pdf eNecroNo ratings yet
- Purpose and Technique of EditingDocument8 pagesPurpose and Technique of EditingjosephsubinNo ratings yet
- Video IP Cores For Altera DE-Series BoardsDocument46 pagesVideo IP Cores For Altera DE-Series BoardsabyNo ratings yet
- Vocabulary Practice Unit 8Document4 pagesVocabulary Practice Unit 8José PizarroNo ratings yet
- NDG Network Virtualization concepts Course Questions اسئلةDocument5 pagesNDG Network Virtualization concepts Course Questions اسئلةMohAmed ReFatNo ratings yet
- ALU Devices and ConfigurationDocument76 pagesALU Devices and ConfigurationRichard ThainkhaNo ratings yet
- A3 Solutions - Representing ImagesDocument3 pagesA3 Solutions - Representing ImagesMykhailo ShapkinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Introduction-1Document28 pagesChapter 1 Introduction-1Abdi HafidNo ratings yet
- 5G Jumpstart: Unofficial Guide To Nokia Certified 5G AssociateDocument34 pages5G Jumpstart: Unofficial Guide To Nokia Certified 5G AssociateAshish JainNo ratings yet
- Visi Misi Ketos 20Document11 pagesVisi Misi Ketos 20haidar alyNo ratings yet
- Connecting FRITZ!Repeater To A Router From Another ManufacturerDocument5 pagesConnecting FRITZ!Repeater To A Router From Another ManufacturerCristian StanNo ratings yet
- Polycom Phone Test LogDocument14 pagesPolycom Phone Test Logثائر هاني فرج اللهNo ratings yet
- Unit 3Document175 pagesUnit 3Bhadra V RajaNo ratings yet
- Bajet 6 Bulan Pentadbiran 2020Document5 pagesBajet 6 Bulan Pentadbiran 2020zatisaadanNo ratings yet
- Ecommission SmartX Controllers Flow Balancer GuideDocument96 pagesEcommission SmartX Controllers Flow Balancer GuideWalter BarbaNo ratings yet
- Angelia Tengara - CVDocument2 pagesAngelia Tengara - CVAngelia TengaraNo ratings yet
- Asynchronous Transfer Mode (Atm) and Frame RelaysDocument15 pagesAsynchronous Transfer Mode (Atm) and Frame RelaysOmar CaabiNo ratings yet
- Intelligent NetworksDocument5 pagesIntelligent Networksdilush ranathunge RanathungeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Ecm413 PDFDocument57 pagesChapter 3 Ecm413 PDFCaha yANo ratings yet