Professional Documents
Culture Documents
MIND MAP CHARACTERISTICS OF FATTY ACID (Dick Andrew Rodriguez)
MIND MAP CHARACTERISTICS OF FATTY ACID (Dick Andrew Rodriguez)
Uploaded by
Dick Andrew Rodriguez0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views1 pageLength and degree of unsaturation of fatty acid chains influence properties like melting point and water solubility. Short-chain fatty acids are soluble in water whereas long-chain fatty acids are not. Melting point decreases as the number of double bonds in the chain increases, since more double bonds introduce bends that prevent tight packing and reduce melting point.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentLength and degree of unsaturation of fatty acid chains influence properties like melting point and water solubility. Short-chain fatty acids are soluble in water whereas long-chain fatty acids are not. Melting point decreases as the number of double bonds in the chain increases, since more double bonds introduce bends that prevent tight packing and reduce melting point.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views1 pageMIND MAP CHARACTERISTICS OF FATTY ACID (Dick Andrew Rodriguez)
MIND MAP CHARACTERISTICS OF FATTY ACID (Dick Andrew Rodriguez)
Uploaded by
Dick Andrew RodriguezLength and degree of unsaturation of fatty acid chains influence properties like melting point and water solubility. Short-chain fatty acids are soluble in water whereas long-chain fatty acids are not. Melting point decreases as the number of double bonds in the chain increases, since more double bonds introduce bends that prevent tight packing and reduce melting point.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
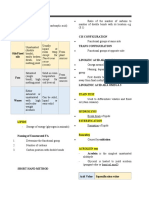
Length and degree of unsaturation of the
Numbering begins at the end
hydrocarbon chain are generally influencing
of -COOH group
factors
MELTING SATURATED Entirely C-C single bonds are bonds
POINT FATTY ACIDS
Melting point of fatty acids decreases as OMEGA
the degree of unsaturation increases OMEGA
(Ω)-6 Essential for optimal membrane
(Ω)-3
FATTY structure
FATTY
ACID
ACID
Short-chain fatty acids are soluble, Numbering begins at the opposite
whereas long-chain fatty acids are FATTY ACIDS end of -COOH
not
WATER UNSATURATED The number C of atoms is indicated
SOLUBILITY FATTY ACIDS using structural notation
Because of the presence of a carboxylic
POLY
group, short-chain fatty acids are only UNSATURATED
sparingly soluble
As the number of double bonds
MONO
increases, so does the number of BENDING UNSATURATED Contains two or more carbon-
"bends" in a fatty acid chain carbon double bonds
There is less
packing
One unsaturated carbon bond in the
The melting molecule, commonly known as a
point is double bond
reduced
You might also like
- Pharmaceutical Organic Chemistry 125.1 Professor Bart David QuibodDocument4 pagesPharmaceutical Organic Chemistry 125.1 Professor Bart David QuibodVNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Amino AcidsDocument13 pagesBiochemistry Amino AcidsApril Aram100% (1)
- Midterm - LipidsDocument7 pagesMidterm - LipidsTherese Vince J. LazosNo ratings yet
- CC Lec-Lipids-And-LipoproteinsDocument7 pagesCC Lec-Lipids-And-LipoproteinsFallen GwiyeobdaNo ratings yet
- Lipids: Theobroma CacaoDocument4 pagesLipids: Theobroma CacaosadburgerNo ratings yet
- SaponificationDocument5 pagesSaponificationTRISHA MARIE CLEMENTENo ratings yet
- LIPIDSDocument8 pagesLIPIDSJona Mae RamosNo ratings yet
- LipidsDocument10 pagesLipidsladyNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry 2Document3 pagesOrganic Chemistry 266rdsmh2mwNo ratings yet
- CH 21 Homologous Series and Structural Formulae (T)Document23 pagesCH 21 Homologous Series and Structural Formulae (T)Lawrence OmegaNo ratings yet
- 5 - B Main Constituents of PetrDocument25 pages5 - B Main Constituents of PetrBogdanAlin100% (1)
- 7.1 Carbon Compounds As Fuels and Feedstock: AlkanesDocument1 page7.1 Carbon Compounds As Fuels and Feedstock: AlkanesAmreen UnnikrishnanNo ratings yet
- Topic 7 Organic Chemistry Revision MatDocument6 pagesTopic 7 Organic Chemistry Revision MatMireiaNo ratings yet
- 1.3 LipidsDocument1 page1.3 LipidsBlitzSZNNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Introduction To Organic Chemistry PDFDocument4 pagesLesson 1 Introduction To Organic Chemistry PDFdela2No ratings yet
- 2.1 Lipid Chemistry Part 1Document6 pages2.1 Lipid Chemistry Part 1Alexandra DalisayNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry of Lipids: Prof. Fritdey Jad Doctolero, RMT, Mls (Ascpi) - April, 2023Document4 pagesBiochemistry of Lipids: Prof. Fritdey Jad Doctolero, RMT, Mls (Ascpi) - April, 2023May Ann EnoserioNo ratings yet
- Carbon CompoundDocument21 pagesCarbon CompoundNur UmairahNo ratings yet
- WOW Notes! DLP Chemistry, Carbon CompoundDocument32 pagesWOW Notes! DLP Chemistry, Carbon Compoundnur asyiqinNo ratings yet
- Lipids: DR Prasheda T Department of Paediatrics PG Part 1Document1 pageLipids: DR Prasheda T Department of Paediatrics PG Part 1KarthikNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Foundation Revision Activity MatDocument2 pagesOrganic Chemistry Foundation Revision Activity MatHồng Ngọc VõNo ratings yet
- Week6 Ch6Document43 pagesWeek6 Ch6jkz8zpbpvbNo ratings yet
- Kech 203Document33 pagesKech 203ankitpp9899No ratings yet
- Lipids: Q: Why Do Lipids Release More Energy Than Carbohydrates or Protein?Document10 pagesLipids: Q: Why Do Lipids Release More Energy Than Carbohydrates or Protein?AlyssaNo ratings yet
- Lipids: MIDTERM ExaminationDocument4 pagesLipids: MIDTERM ExaminationKUZONo ratings yet
- Carbon and Its CompoundsDocument21 pagesCarbon and Its CompoundsrahNo ratings yet
- Chem 123 - LipidsDocument11 pagesChem 123 - LipidsGylene GardonNo ratings yet
- C7-part-1-Organic-Chemistry.265115096 (1)Document7 pagesC7-part-1-Organic-Chemistry.265115096 (1)PuraniNo ratings yet
- FrukDocument33 pagesFrukdaney67299No ratings yet
- Simulation of CO2 For Enhanced Oil RecoveryDocument8 pagesSimulation of CO2 For Enhanced Oil RecoveryMadhaviNo ratings yet
- LipidsDocument7 pagesLipidsHana LunariaNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry ProjectDocument35 pagesOrganic Chemistry Projectapi-703155671No ratings yet
- C7 Part 1 Organic Chemistry.218563238Document2 pagesC7 Part 1 Organic Chemistry.218563238Trudy- Ann CaineNo ratings yet
- 2 IB Molecular BiologyDocument103 pages2 IB Molecular Biologykrishna darji100% (1)
- Unit - 5 Chapter: - 13 Hydrocarbons: Let's RecallDocument39 pagesUnit - 5 Chapter: - 13 Hydrocarbons: Let's RecallHitz D.No ratings yet
- C5 Chem For User N IndustryDocument78 pagesC5 Chem For User N IndustryNUR FASYAREENA BINTI HASHIM MoeNo ratings yet
- LipidsDocument26 pagesLipidsZanie CruzNo ratings yet
- Ch10-Carbohyrates 3eDocument35 pagesCh10-Carbohyrates 3eAditi DubeyNo ratings yet
- MOCRINIS II Mineral Oil and Wax Manufacture LJouanneauDocument45 pagesMOCRINIS II Mineral Oil and Wax Manufacture LJouanneauMohamed SalemNo ratings yet
- LipidsDocument14 pagesLipidsBeverlyNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Carboxylic AcidsDocument5 pagesLesson 1 Carboxylic AcidsMARY JANE ANGELICA SEVANo ratings yet
- C5 Chem For User N IndustryDocument78 pagesC5 Chem For User N Industrynory msNo ratings yet
- Lipids PDFDocument17 pagesLipids PDFEnrico DarylNo ratings yet
- Distillation Basics Distillation Basics: Distillation Side Products Carl Cesar H. BibatDocument11 pagesDistillation Basics Distillation Basics: Distillation Side Products Carl Cesar H. BibatSam Denielle TugaoenNo ratings yet
- Chem123 - LipidsDocument10 pagesChem123 - LipidsCrescinityNo ratings yet
- Carbon and Its CompoundsDocument19 pagesCarbon and Its CompoundsARNAV DEYNo ratings yet
- Module 2 BiochemDocument13 pagesModule 2 BiochemAbby Dimalaluan OquendoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 Amides and AminesDocument69 pagesLecture 6 Amides and AminesJowayriyyahNo ratings yet
- Kfddjopreihjwfihwoifoq'wemn w3 /ifhn3Document9 pagesKfddjopreihjwfihwoifoq'wemn w3 /ifhn3md kuku mumuNo ratings yet
- Biochem TemplateDocument8 pagesBiochem TemplateHyacinth Lei CuynoNo ratings yet
- LIPIDS MidtermDocument8 pagesLIPIDS MidtermMariaGay Albite Delos ReyesNo ratings yet
- Nitro Benzene Preparation, Laboratory & Industrial, Uses and ApplicationsDocument11 pagesNitro Benzene Preparation, Laboratory & Industrial, Uses and Applicationsusman_uet0881% (16)
- IPC (White Spirit Assignment)Document7 pagesIPC (White Spirit Assignment)Humaira AtharNo ratings yet
- imidazoline-based-corrosion-inhibitorsqqqDocument13 pagesimidazoline-based-corrosion-inhibitorsqqqGaurav ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Exxonmobil Premium Hdme 50 Fact SheetDocument2 pagesExxonmobil Premium Hdme 50 Fact SheetЕвгений МасловNo ratings yet
- 2.2 Macromolecules HomeworkDocument4 pages2.2 Macromolecules HomeworkKarolina RachwalNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document4 pagesUnit 1Leen Al-FouzanNo ratings yet
- 6.BiologicalMembranes CompleteDocument68 pages6.BiologicalMembranes Completeazyhuang77No ratings yet
- Org Chem Final ReviewerDocument7 pagesOrg Chem Final ReviewerblessaNo ratings yet
- New Frontiers in Asymmetric CatalysisFrom EverandNew Frontiers in Asymmetric CatalysisKoichi MikamiNo ratings yet
- Nursing As A SC - 202403032228 - 36477Document6 pagesNursing As A SC - 202403032228 - 36477Dick Andrew RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Funda 202401282255 49694Document7 pagesFunda 202401282255 49694Dick Andrew RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Primary and Seconadry SourcesDocument2 pagesPrimary and Seconadry SourcesDick Andrew RodriguezNo ratings yet
- TFN HahahaDocument16 pagesTFN HahahaDick Andrew RodriguezNo ratings yet
- TRIACYLGLYCEROLSDocument3 pagesTRIACYLGLYCEROLSDick Andrew RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Investigation of Optical and Structural PropertiesDocument14 pagesInvestigation of Optical and Structural PropertiesmarcosdavidNo ratings yet
- Calculation of Phase Diagrams of Gas-HydratesDocument9 pagesCalculation of Phase Diagrams of Gas-HydratesMichael ParkerNo ratings yet
- Course Syllabus - : Chem 1Document2 pagesCourse Syllabus - : Chem 1Janea PelpinosasNo ratings yet
- SolutionDocument2 pagesSolutionZuber SheikhNo ratings yet
- Title Improved Color Retention of Hair Dyes With Floraesters K-20W Jojoba in A ShampooDocument1 pageTitle Improved Color Retention of Hair Dyes With Floraesters K-20W Jojoba in A ShampooSANo ratings yet
- Cement and Concrete ResearchDocument10 pagesCement and Concrete ResearchTijani MohammedNo ratings yet
- Nozzle Clogging Behavior of Ti-Bearing Al-Killed ULC SteelDocument8 pagesNozzle Clogging Behavior of Ti-Bearing Al-Killed ULC SteelEstéfano Aparecido VieiraNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper 1 (Solutions Only) - IsC Chemistry 2024Document17 pagesSample Paper 1 (Solutions Only) - IsC Chemistry 2024Dia SureshNo ratings yet
- Gek108792 Gek9250 pb70-80-05-015 20240419034444409Document15 pagesGek108792 Gek9250 pb70-80-05-015 20240419034444409Vero GAtelesisNo ratings yet
- Recovery Boiler History and Future VakkilainenDocument14 pagesRecovery Boiler History and Future VakkilainennotengofffNo ratings yet
- Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0086950 A1Document13 pagesPatent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0086950 A1rat0708No ratings yet
- Manish STUDYONAQUEOUSEXTRACTOFCitrusDocument5 pagesManish STUDYONAQUEOUSEXTRACTOFCitrusZurielle LuboaNo ratings yet
- Edexcel AS Chemistry Note 3 - Different Types of ReactionDocument7 pagesEdexcel AS Chemistry Note 3 - Different Types of ReactionSajaniNo ratings yet
- Quiz HT105: ProblemsDocument17 pagesQuiz HT105: ProblemsZERINA ŠKULJNo ratings yet
- Autopure 96 ManualDocument3 pagesAutopure 96 ManualjarguedasNo ratings yet
- Din Iso 4381Document1 pageDin Iso 4381Soroosh YaghoubiNo ratings yet
- Organic Mind MapDocument37 pagesOrganic Mind Mapkamalia8980% (5)
- Pharmaceutical Chemistry Chapter 1 Introduction To Pharmaceutical Chemistry NotesDocument11 pagesPharmaceutical Chemistry Chapter 1 Introduction To Pharmaceutical Chemistry NoteszartabsocialmediaNo ratings yet
- KS4 Chemistry: 1 of 20 1 of 68Document25 pagesKS4 Chemistry: 1 of 20 1 of 68Maurice Kim CamillonNo ratings yet
- Iodine NUMBER WORKSHEET 2!Document6 pagesIodine NUMBER WORKSHEET 2!lilyrush43No ratings yet
- Heterogeneous NucleationDocument15 pagesHeterogeneous NucleationDimpy KhatriNo ratings yet
- Hapter: Ypes of AintDocument13 pagesHapter: Ypes of AintKali AbdennourNo ratings yet
- Module Trial STPM Biology Term 1 2022 Set 2Document9 pagesModule Trial STPM Biology Term 1 2022 Set 2RuoQi LeeNo ratings yet
- Zinc/Aluminum Corrosion Protective Coatings For FastenersDocument3 pagesZinc/Aluminum Corrosion Protective Coatings For FastenersDarwin DarmawanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry For Engineers - 1 Energy - Topic 02 - Sensible Heat-Heat Capacity-CalorimetryDocument7 pagesChemistry For Engineers - 1 Energy - Topic 02 - Sensible Heat-Heat Capacity-CalorimetryJacob JimenezNo ratings yet
- RBD Tallow PrintDocument37 pagesRBD Tallow PrinthibreNo ratings yet
- ASTM D 4377 - 00 (Reapproved 2006) PDFDocument7 pagesASTM D 4377 - 00 (Reapproved 2006) PDFJulian Felipe Noguera CruzNo ratings yet
- Ball Screw: General CatalogDocument10 pagesBall Screw: General CatalogSueli ZaniNo ratings yet
- BP500C MSDSDocument3 pagesBP500C MSDSMiguel GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Nils Herlenius: IEC 60296 (Ed. 4) From A Transformer Oil Manufacturer's PerspectiveDocument6 pagesNils Herlenius: IEC 60296 (Ed. 4) From A Transformer Oil Manufacturer's Perspectivetaufiqishak09No ratings yet