Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Class 12 DDP 1
Class 12 DDP 1
Uploaded by
sumitsorout2940 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views4 pagesThe document contains questions related to DNA, RNA, and protein synthesis. It asks about the structure of DNA and RNA, experiments that proved DNA is the genetic material like those by Griffith, Hershey and Chase, semi-conservative DNA replication, transcription, translation, and the roles of mRNA, tRNA, and rRNA in protein synthesis. It also contains questions about DNA and RNA polymerases, replication, transcription, the genetic code, and molecular biology concepts like the central dogma.
Original Description:
Pdf of high quality and content
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document contains questions related to DNA, RNA, and protein synthesis. It asks about the structure of DNA and RNA, experiments that proved DNA is the genetic material like those by Griffith, Hershey and Chase, semi-conservative DNA replication, transcription, translation, and the roles of mRNA, tRNA, and rRNA in protein synthesis. It also contains questions about DNA and RNA polymerases, replication, transcription, the genetic code, and molecular biology concepts like the central dogma.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views4 pagesClass 12 DDP 1
Class 12 DDP 1
Uploaded by
sumitsorout294The document contains questions related to DNA, RNA, and protein synthesis. It asks about the structure of DNA and RNA, experiments that proved DNA is the genetic material like those by Griffith, Hershey and Chase, semi-conservative DNA replication, transcription, translation, and the roles of mRNA, tRNA, and rRNA in protein synthesis. It also contains questions about DNA and RNA polymerases, replication, transcription, the genetic code, and molecular biology concepts like the central dogma.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 4
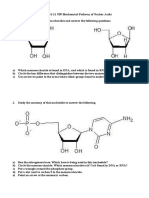
Q: 1 Group the following as nitrogenous bases and nucleosides: Adenine, Cytidine,
Thymine, Guanosine, Uracil and Cytosine, Guanine
Q: 2 What is the difference between DNAs and DNase ?
Q: 3 What are characteristics of prokaryotic chromosome/nucleoid ?
Q: 4 What is the role of NHC (Non-Histone chromsomal) other than histones proteins?
Q: 5 Give examples of nitrogenous bases.
Q: 6 What is the major compositional difference in DNA or RNA?
Q: 7 Who first identified DNA? Q: 8 What are histones?
Q: 9 . How many base pairs are present in a nucleosome ?
Q: 10 Name amino acid residues of histone proteins.
Q: 11 Who proposed central dogma of molecular biology?
Q: 12 . What is the linkage between nitrogenous base and pentose sugar called?
Q.13. It is sequence of the sequence of mRNA.
5–ATGCATGCAIGCATGCATGCATGIANG 3 .Write down the sequence of mRNA.
Q: 14 Mention the carbon positions to which the nitrogenous base and phosphate
molecule are respectively linked in the nucleotide.
Q: 15 Who proposed the famous double stranded helical structure of DNA?
Q: 16 How does the flow of genetic information in HIV deviate from the 'Central
dogma' proposed by Francis Crick? [C.B.S.E. 2011)
Q: 17 Draw double helix structures OR Draw only DNA Double Helix.
OR Describe Watson and Crick model with the help of suitable diagram
OR Draw the well labelled diagrams of B- DNA .
Q: 18 Differentiate between prokaryotic DNA and eukaryotic DNA.
Q: 19 What are Chargaff's rules?
Q: 20 How does a prokaryotic chromosome differ from an eukaryotic chromosome?
Q: 21 Define mention what enable histone to acquire a positive charge.
Q: 22 In the eukaryotes the DNA molecules are organised within the nucleus. How is
the DNA molecule organised in a bacterial of in absence of a nucleus ?
Q: 23 Explain the structure of nucleoside and nucleotide.
Q: 24 What is the role of RNA? How many bp's are present in bacteriophage ?
Q: 25 Which property of DNA double helix led Watson and Crick to hypothesise semi-
conservative mode of DNA replication? Explain.
OR
What background information did Watson and Crick had available with them for
developing a model of DNA? What was their own contribution? [N.C.E.R.T. Exemplar]
Q: 26 Why flowers are important for human beings?
Q: 27 Define flower and its floral parts with the help of diagram.
Q: 28 List the functions of a flower.
Q: 26 Explain the two factros responsible for conferring stability to double helix
structure of DNA.
Q: 27 Retrovirus do not follows central dogma. Comment.
Q: 28 The base sequence on one of the strands of DNA is ATGTCTATA.
(i) Give the base sequence of its complementary strand.
(ii) If an RNA strand is transcribed by this strand, what would be the base sequence of
RNA ? (iii) In what other respect, an RNA molecule differs from a DNA molecule ?
Q: 29 Draw a schematic representation of dinucleotide. Label the following: (i) The
components of a nucelotide (ii) 5' end (ii) N-glycosidic linkage (iv) Phosphodiester
linkage.
Q: 30 Why does RNA express the characters easily?
Q: 31 Why RNA viruses have high evolution rate?
Q:32 Why RNA is more reactive than DNA?
Q: 33 What suggested the copying mechanism of genetic material to Watson and
Crick?
Q:34 Which property of RNA helps it to work as catalyst?
Q: 35 Though RNA can directly code for proteins still DNA is preferred as storage
genetic material. Why ?
Q: 36 What are NHC proteins ? Q: 37 What are bacteriophages ?
Q: 38 What do you understand by transformation?
Q: 39 Who discovered the phenomenon of transformation?
Q: 40 Recall the experiment done by Frederick Griffith. If RNA, instead of DNA was the
genetic material, would the heat killed strain of Streptococcus have transformed the
R-strain into virulent strain? Explain your answer.
Q: 41 What is the nature of genetic material?
Q: 42 Differentiate between euchromatin and heterochromatin ?
Q: 43 How did Hershey and Chase differentiate between DNA and protein in their
experiment while proving that DNA is the genetic material?(C.B.S.E. 2016; N.C.E.R.T.)
Q: 44 Distinguish between transformation and transduction.
Q:45 You are repeating the Hershey-Chase experiment and are provided with two
isotopes: 32P and 15N (in place of 35S in the original experiment). How do you expect
your results to be different? [C.B.S.E. 2016]
Q: 46 It is established that RNA is the first genetic material. Explain giving three
reasons.[C.B.S.E. 2012/
Q: 47 Explain the role of 35S and 32P in the experiments conducted by Hershey and
Chase. [C.B.S.E. 2019; 2020]
Q: 48 Why is DNA considered a better materia than RNA l IC.B.S.E. 2016]
Q: 49 Discuss Griffith experiment to prove DNA is genetic material.
Q: 50 Explain Hershey and Chase experiment to prove that DNA is genetic material.
IC.B.S.E. 2018; 20201
Q: 51 List the three major functions of a DNA.
Q: 52 (a) Write the scientific name of the bacterium used by Fredrick Griffith in his
experiment.
(b) How did he prove that some "transforming principle' is responsible for
transformation of the non-violent strains of bacteria into the virulent form?
(c) State the biochemical nature of transforming principle'? (d) Name the scientists
who proved it.IC.B.S.E. 2016, 2011]
Q: 53 Describe Fredrick Griffith's experiment on Streptococcus pneumoniae. Discuss
the conclusion he arrive at[C.B.S.E. 2014]
Or
Describe the experiment with Streptococcus pneumoniae that demonstrated the
existence of some "transforming principle".
Q: 54 How did Griffith explain the trans- formation of R-strain (non-virulent) bacteria
into S-strain (virulent)?
(b) Explain how MacLeod, McCarty and Avery determined the biochemical nature of
the molecule responsible for transforming R-strain bacteria linto S-strain bacteria.
Q:55 How did Alfred Hershey and Martha Chase arrive at the conclusion that DNA is
the genetic material [C.B.S.E. 2009). OR. Write the conclusion they
arrive at after the experiment.
Q:56 Give an example where ribosome acts as catalyst.
Q: 57 Name two viruses that have RNA as genetic material
Q:58 Which of the following RNA acts as structural RNA as well as enzyme in bacteria
Q: 59 Which enzyme initiates transcription?
Q: 60 Differentiate between mRNA and RNA
Q: 61 Draw the structure of a RNA charged with methionine.[C.B.S.E. 2012)
Q:62 (a) Draw the structure of the initiator rRNA adaptor molecule.
(b) Draw a clover leaf structure of RNA showing the following:
(b) Why is RNA called an adaptor molecule ? [C.B.S.E. 2017)
Q: 63 State the functions of the following in a prokaryote :tRNA and rRNA (C.B.S.2012]
Q: 64 (a) Name the scientist who called RNA an adaptor molecule.
b) Draw a clover leaf structure of RNA showing the following:
1) Tyrosine attached to its amino acid site.
ii) Anticodon for this amino acid in its correct site (codon for tyrosine is UAC).
c) What does the actual structure of RNA look like ?[C.B.S.E. 2014]
Q:65 Enlist the role of following in protein synthesis:(1) mRNA (ii) RNA.(i) tRNA
Q:66 Q.84. (i) What are the three types of RNAs? (ii) Which one of these has the shape
of a clover-leaf in two dimensional structure? (iii) How is each RNA related in the
information flow during protein
Q:67 Describe the structure of a RNA polynucleotide chain having different types of
nucleotides.
Q: 68 To prove semi-conservative replication of DNA in chromosomes, Taylor and his
colleagues conducted experimentation:
Q:69 Define semi-conservative DNA Replication.
Q:70 What are two functions of DNA polymerase?
Q: 71 How does DNA polymerase functions within a replication fork of DNA during
replication?
Q:72 What is the direction of DNA/RNA replication by polymerases?
Q:73 Which of the two DNA strands is called coding strand?
Q:74 At which phase of cell division DNA replicates ?
Q: 75 Can DNA polymerase initiate DNA replication?
Q: 76 If the sequence of one strand of DNA is written as follows:
5-AIGCATGCATGCATGCATGCATGCATGE-31 [C.B.S.E. 2020; N.C.E.R.T.]
Write down the sequence of complementary strand in 5'-3' direction.
Q:77 Name the types of synthesis 'a' and 'b' occuring in the replication fork of DNA as
shown below
Q: 78 What are exons ? Q: 79 Name the enzyme involved in the continuous
replication of DNA srand. Mention the polarity lof the template strand. [C.B.S.E. 2010]
Q:80 Name the enzyme and state its property that is responsible for continuous and
discontinuous replication of the two strandsof a DNA molecule.[C.B.S.E. 2013]
Q:81 Mention the function of DNA ligase ? Q:82 What is origin of replication or ori?
Q:83 What is replication fork?
Q:84 In a nucleus, the number of RNA nucleoside triphosphates is 10 times more than
the number of DNA nucleoside triphosphates, still only DNA nucleotides are added
during the DNA replication and not the RNA nucleotides. Why?
Q:85 Differentiate Leading and Lagging strand.
Q:86 Why only one strand of DNA acts as template for transcription?
Q:87 Differentiate between Replication and Transcription.
Q:88 Depending upon the chemical nature of the template (DNA or RNA) and the
nature of nucleic acids synthesised from it (DNA or RNA), list the types of nucleic acid
polymerases. IN.C.E.R.T.J
Q:89 Name indicating their functions, a few additional enzymes, other than DNA
polymerase and ligase, that are involved in the replication of DNA with high degree of
processivity and accuracy.IN.C.E.R.T. Exemplar]
Q:90 During in vitro synthesis of DNA, a researcher used 2',3'-deoxycytidine
triphosphate as raw nucleotide in place of 2'-deoxy cytidine triphosphate, other
conditions remaining as standard. Will further polymerisation of DNA continue up to
end or not? Explain.IN.C.E.R.T. Exemplar]
Q:91 Why do you see two differfent types of replicating strands in the given DNA
replication fork? Explain. Name these strands.(C.B.S.E. 2011
Q:92 (a) Explain the process of DNA replication with the help of a schematic diagram.
(b) In which phase of the cell cycle does replication occur in Eucaryotes? What would
happen if cell division is not followed after DNA replication?(C.B.S.E. 2014]
Q:93 Answer the following questions based on Meselon and Stahl's experiment:
(a) Write the name of the chemical substance used as a source of nitrogen in the
experiment by them. (b) Why did the scientists synthesise the light and the heavy
DNA molecules in the organism used in the experiment? (c) How did the scientists
make it possible to distinguish the heavy DNA molecule from the light DNA molecule
? Explain. (d) Write the conclusion the scientists arrived at after completing the
experiment. [C.B.S.E. 2016]
Q:94 State the dual role of deoxyribonucleoside triphosphates during DNA replication.
[C.B.S.E. 2018]
Q:95 In a nucleus, the number of RNA nuceoside triphosphates is 10 times more than
the number of DNA nucleoside triphosphates, still only DNA nucleotides are added
during the DNA replication, and not the RNA nucleotides. Why? IN.C.E.R.T. Exemplar
Q:96 Describe the discontinuous synthesis of DNA.
Q:97 Describe the process of DNA Replication. [C.B.S.E. 2020]
Q:98 Draw a labelled schematic sketch of replication fork of DNA. Explain the role of
the enzymes involved in DNA replication.[C.B.S.E. 2019]
Q:99 Describe semi conservative nature of DNA replication.[C.B.S.E. 20201
Or
Write note that mode of DNA replication is semiconservative.
Or
State the aim and describe Meselson and Stahl's experiment.
Q:100 a) Why did the scientists use 15NH4Cl and 14NH,Cl as source of nitrogen in the
© Write the conclusion drawn by them at the end of their experiment.culture medium
for growing E. coli?
(b) Name the molecule(s) that 15N got incorporated into.
D Write the observations made by them from the samples taken at the end of 20
minutes and 40 minutes respectively
E How did they distinguish between 15N To labelled molecules from 14N ones?
F Mention the significance of taking the E. coli samples at definite time intervals for
this observations
You might also like
- Biology Concepts and Investigations 5Th Edition Marielle Hoefnagels Full ChapterDocument67 pagesBiology Concepts and Investigations 5Th Edition Marielle Hoefnagels Full Chapteroscar.gokey720100% (6)
- Michael Lynch - The Origins of Genome Architecture-Sinauer (2007)Document403 pagesMichael Lynch - The Origins of Genome Architecture-Sinauer (2007)SashaNo ratings yet
- Final Study Guide 13Document8 pagesFinal Study Guide 13tlyons1188No ratings yet
- Curriculum Map in Science 10 S.Y.2021-2022Document32 pagesCurriculum Map in Science 10 S.Y.2021-2022NEL TVNo ratings yet
- DNA Structure of PolynucleotidechainDocument22 pagesDNA Structure of PolynucleotidechainNasla AbdulsalamNo ratings yet
- Homework 4 Chapt 10, 11, 12Document2 pagesHomework 4 Chapt 10, 11, 12ButterlesstoastNo ratings yet
- D.A.V School: Sree Nandeeswarar Campus, Adambakkam, Chennai 88 Class 12 BIOLOGY Chapter 11 BIOTECHNOLOGYDocument9 pagesD.A.V School: Sree Nandeeswarar Campus, Adambakkam, Chennai 88 Class 12 BIOLOGY Chapter 11 BIOTECHNOLOGYMaheswari RajnarayananNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGYDocument3 pagesBIOLOGYAadit “ThePROkiller”No ratings yet
- Study Guide For Dna Unit 1Document3 pagesStudy Guide For Dna Unit 1юрий локтионовNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Biology Zoology EM Chapter 5. Molecular Genetics Question Bank by Rana Sakthi Durga, Puducherry.Document2 pagesClass 12 Biology Zoology EM Chapter 5. Molecular Genetics Question Bank by Rana Sakthi Durga, Puducherry.joshan jayapaul pandiyan100% (1)
- Combine PDFDocument106 pagesCombine PDFМөнхгэрэл ГанбатNo ratings yet
- Pyq Cbse 2021-1-2Document19 pagesPyq Cbse 2021-1-2Yuvraj MehtaNo ratings yet
- Molecular Genetics ReviewDocument1 pageMolecular Genetics Reviewshya3640 shya3640No ratings yet
- Molecular Biology Previous Year QuestionsDocument7 pagesMolecular Biology Previous Year QuestionsKrutika SNo ratings yet
- Hapter 7 Essay Questions Enzyme, Dna N RnaDocument6 pagesHapter 7 Essay Questions Enzyme, Dna N Rnamaxwell amponsahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Molecular Basis of Inheritance Unsolved Important QuestionsDocument9 pagesChapter 6 Molecular Basis of Inheritance Unsolved Important QuestionsDeep Kumar BasakNo ratings yet
- Molecular Biology: Principles and PracticeDocument34 pagesMolecular Biology: Principles and PracticesabweedNo ratings yet
- DNA - RNA Practice Q SolutionsDocument16 pagesDNA - RNA Practice Q SolutionschibuyeNo ratings yet
- Homework 4 Chapters 10, 11,12 AnswersDocument5 pagesHomework 4 Chapters 10, 11,12 AnswersButterlesstoastNo ratings yet
- Question BankDocument7 pagesQuestion Bankapi-3699290No ratings yet
- SEHH2231-22 T09 Biochemical Pathway of Nucleic Acid Exercise (Question)Document6 pagesSEHH2231-22 T09 Biochemical Pathway of Nucleic Acid Exercise (Question)Brian Chi Yan Cheng 鄭智仁No ratings yet
- Dna Review AnswersDocument2 pagesDna Review AnswersShi Jie100% (1)
- Genetics A Conceptual Approach 5Th Edition Pierce Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument41 pagesGenetics A Conceptual Approach 5Th Edition Pierce Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFsoojeebeautied9gz3h100% (8)
- (B) Explain How The Biochemnical Characterization (Nature) of Transforming Principle 'WasDocument3 pages(B) Explain How The Biochemnical Characterization (Nature) of Transforming Principle 'WasBhavna BeniwalNo ratings yet
- Microbiology 2nd Edition Wessner Test BankDocument18 pagesMicrobiology 2nd Edition Wessner Test Bankeugenephedrayy2bfk100% (28)
- Bio 218 Review For CH 9Document1 pageBio 218 Review For CH 9BrandonNo ratings yet
- 107普生期末Document4 pages107普生期末Rose FuNo ratings yet
- Molecular Basis of InheritanceeDocument4 pagesMolecular Basis of InheritanceePROFESSORNo ratings yet
- BioK DP Notes 2.7Document18 pagesBioK DP Notes 2.7Lal ÖzşahinNo ratings yet
- DNA Replication Review WorksheetDocument8 pagesDNA Replication Review WorksheetSamya SehgalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16 Molecular Basis of InheritanceDocument8 pagesChapter 16 Molecular Basis of InheritanceMahesh T MadhavanNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis Review Worksheet 3Document5 pagesProtein Synthesis Review Worksheet 3api-249583770No ratings yet
- Fred Review 16Document8 pagesFred Review 16Justin HsuNo ratings yet
- XII Biology PT2Document2 pagesXII Biology PT2Richi SahooNo ratings yet
- Ls3 Midterm I Exam: InstructionsDocument8 pagesLs3 Midterm I Exam: InstructionsArmaanGurayaNo ratings yet
- Microbiology 1st Edition Wessner Test BankDocument18 pagesMicrobiology 1st Edition Wessner Test Bankthomasmayoaecfpmwgn100% (32)
- Review SheetDocument2 pagesReview Sheetapi-289866381No ratings yet
- Name: SurnameDocument2 pagesName: SurnameMichele Leigh ChenaultNo ratings yet
- BIO3170 - Practice Midterm 1 PDFDocument5 pagesBIO3170 - Practice Midterm 1 PDFJohn DoeNo ratings yet
- Assignment-2 XII Molecular Basis of InheritanceDocument2 pagesAssignment-2 XII Molecular Basis of InheritanceJai Bharat0% (1)
- Module 4 KKKDocument32 pagesModule 4 KKKbhrayancachero100% (1)
- Class Xii Biology Chapter 6 - Molecular Basis of InheritanceDocument8 pagesClass Xii Biology Chapter 6 - Molecular Basis of InheritanceAkshit Sharma VIII Diasy Roll no 6No ratings yet
- DNA: Structure & FunctionDocument3 pagesDNA: Structure & Function孙美美Ezra Paola TaysonNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Introduction To Genetic Analysis Eleventh EditionDocument18 pagesTest Bank For Introduction To Genetic Analysis Eleventh Editiondaonhatc2ddrq100% (29)
- Essentials of Genetics 9th Edition Klug Test Bank DownloadDocument7 pagesEssentials of Genetics 9th Edition Klug Test Bank DownloadEmanuel Maples100% (25)
- Sbi 4u Exam Review UpdateDocument2 pagesSbi 4u Exam Review UpdateKevin KocotNo ratings yet
- DNA Quiz ReviewDocument2 pagesDNA Quiz ReviewsvitlanaNo ratings yet
- 1-Nucleotides and Nucleic AcidsDocument46 pages1-Nucleotides and Nucleic AcidsFair PisuttisarunNo ratings yet
- COMPETANCE BASED QUESTION Chapter 6 Molecular Basis of InheritanceDocument9 pagesCOMPETANCE BASED QUESTION Chapter 6 Molecular Basis of InheritanceKarthika UmashankarNo ratings yet
- Molecular Basis of InheritanceDocument22 pagesMolecular Basis of InheritancePavithraNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acids.Q&A Part1Document102 pagesNucleic Acids.Q&A Part1dhainey80% (5)
- Answer 1:: (Class - XII)Document9 pagesAnswer 1:: (Class - XII)Subhadip MurmuNo ratings yet
- DisadvantagesDocument9 pagesDisadvantagesSubhadip MurmuNo ratings yet
- Nuclec Asids Revision ListsDocument6 pagesNuclec Asids Revision ListsFULYA YALDIZNo ratings yet
- Molecular Basis of InheritanceDocument142 pagesMolecular Basis of InheritanceKanmani SathiachandranNo ratings yet
- Science-10 Q3 Week-4 Lessons-8-11 27Document16 pagesScience-10 Q3 Week-4 Lessons-8-11 27Azhell VillasotoNo ratings yet
- Science10 Q3 Week4Document22 pagesScience10 Q3 Week4Samad Recca T. NatividadNo ratings yet
- Chapter - Biology Xii PyqDocument16 pagesChapter - Biology Xii Pyqalina jamalNo ratings yet
- Bioscience Imp QuesDocument2 pagesBioscience Imp QuesdearsaswatNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 - A1.2 Nucleic AcidsDocument63 pagesTopic 1 - A1.2 Nucleic AcidsOlatundeNo ratings yet
- 1.5 Nucleic AcidDocument28 pages1.5 Nucleic AcidLak Judin IINo ratings yet
- Exercise 5 Molecular Basis of HeredityDocument6 pagesExercise 5 Molecular Basis of HeredityHiroshi MatsushimaNo ratings yet
- De Guzman, John MichaelDocument3 pagesDe Guzman, John MichaelMiko de GuzmanNo ratings yet
- CH 3Document14 pagesCH 3Qais Bani HaniNo ratings yet
- Advanced PCR - Methods and ApplicationsDocument21 pagesAdvanced PCR - Methods and ApplicationsNT RavindranNo ratings yet
- MCQ ADocument357 pagesMCQ Aankitraj318No ratings yet
- TUTORIAL 3 MicrobiologyDocument8 pagesTUTORIAL 3 MicrobiologyJOSEPH TING FU KIONGNo ratings yet
- DNA Replication WorksheetDocument2 pagesDNA Replication WorksheetMaktoumNo ratings yet
- Mechanism of Semiconservative ReplicationDocument12 pagesMechanism of Semiconservative ReplicationKhadija ShoaibNo ratings yet
- Dwnload Full Introduction To Biotechnology 3rd Edition Thieman Test Bank PDFDocument36 pagesDwnload Full Introduction To Biotechnology 3rd Edition Thieman Test Bank PDFemmapricehzv3c100% (16)
- MH SET 2011 Aug Environmental Science Question Paper IIDocument12 pagesMH SET 2011 Aug Environmental Science Question Paper IIsamritiNo ratings yet
- Archer Fusionplex Ngs Assays BrochureDocument4 pagesArcher Fusionplex Ngs Assays Brochurealivio141960No ratings yet
- Differences Between DNA and RNADocument2 pagesDifferences Between DNA and RNAmonishaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 14Document19 pagesLecture 14DIMPHO ZILWANo ratings yet
- Schneider Review of Moore's The Dependent Gene PDFDocument15 pagesSchneider Review of Moore's The Dependent Gene PDFfuck offNo ratings yet
- 4.biotechnology - Principle and ProcessesDocument6 pages4.biotechnology - Principle and ProcessesIndrajith MjNo ratings yet
- CENG 1600 Lecture 12Document19 pagesCENG 1600 Lecture 12Roxanna LevineNo ratings yet
- Instant Download Ebook PDF Essentials of The Living World 4th Edition PDF ScribdDocument37 pagesInstant Download Ebook PDF Essentials of The Living World 4th Edition PDF Scribdjudy.wilson397100% (46)
- Biology Notebook: 03.05 DNA ReplicationDocument3 pagesBiology Notebook: 03.05 DNA ReplicationGaurav ChaudhuriNo ratings yet
- LT Adm 16.1Document10 pagesLT Adm 16.1Bayani VicencioNo ratings yet
- PCR Mycoplasma Test Kit I/C: Instruction ManualDocument8 pagesPCR Mycoplasma Test Kit I/C: Instruction ManualAslam MikraniNo ratings yet
- Ba - Bacterial Identification Lab WorksheetDocument12 pagesBa - Bacterial Identification Lab WorksheetFay SNo ratings yet
- Food Prevention Age RelatedDocument378 pagesFood Prevention Age Relatedaintzane.ezkurdiaNo ratings yet
- Bacterial PlasmidsDocument9 pagesBacterial PlasmidsspanishinqNo ratings yet
- CRISPR HandbookDocument18 pagesCRISPR Handbookgoucloud100% (1)
- Module 2 Lesson Plan: Session Title Date LocationDocument2 pagesModule 2 Lesson Plan: Session Title Date LocationshruthiNo ratings yet
- Efficient Adaptor Ligation For The Preparation of DsDNA Libraries Using Blunt-TA Ligase Master MixDocument10 pagesEfficient Adaptor Ligation For The Preparation of DsDNA Libraries Using Blunt-TA Ligase Master MixMoni Becerra WongNo ratings yet
- Ebook PDF Understanding Bioinformatics by Marketa Zvelebil PDFDocument41 pagesEbook PDF Understanding Bioinformatics by Marketa Zvelebil PDFrichard.rogers744100% (37)
- Bio Notes 3.1.2 Pro Vs EukDocument1 pageBio Notes 3.1.2 Pro Vs EukKari Kristine Hoskins BarreraNo ratings yet