Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Obligation and Non-Obligation Structures
Obligation and Non-Obligation Structures
Uploaded by
María Cecilia CarattoliOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Obligation and Non-Obligation Structures
Obligation and Non-Obligation Structures
Uploaded by
María Cecilia CarattoliCopyright:
Available Formats
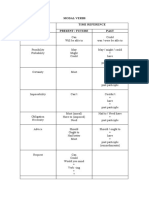
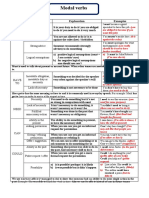
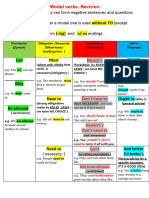
Talking about obligation, permission and prohibition
Must and have to
They are used interchangeably to express obligation. Must is slightly stronger. Sometimes,
there is a slight difference in meaning: must expresses internal obligation or necessity while
have to refers to external obligation, often coming from rules or regulations.
Obligation in the Affirmative Interrogative
present
Must For all persons + infinitive Must + all persons+
infinitive?
Have to For he-she-it: has to + Do I/you/we/they
infinitive +have to + infinitive?
Does he/she/it +
have to + inifinitive?
Obligation in the past Affirmative Interrogative
Must --------------------------- -------------------------------
Have to Had to (for all persons) Did … have to + infinitive?
Negative forms of must and have to: express different meanings
Meaning Form
Must Prohibition Mustn’t : Present
Couldn’t / (be) not allowed
to: Past
Have to No obligation/necessity Don’t/doesn’t have to:
Present
Didn’t have to: Past
1 The law
Change the sentences (if necessary) so that they are true of your country.
a) Passengers in cars don’t have to wear seatbealts.
b) You’re not allowed to drive faster than 100 kph.
c) You don’t have to pay for local phone calls.
d) Everyone has to carry an identity card.
e) Foreigners can’t own land and property.
f) Men and women have to retire at 65.
g) You’re allowed to smoke on buses and trains.
h) Men and women have to do two years’ military service.
2 Obligations at work
What must you do at work?
3 Make and let
Make somebody do something: obligation
Let sb do sth: permission
What are children allowed to do now? What about you? What were you allowed/not allowed
to do? What things did your parents let you do at home?
You might also like
- 01 TAWANG MULTI PURPOSE COOPERATIVE v. LA TRINIDAD WATER DISTRICT GR 166471 Case DigestDocument2 pages01 TAWANG MULTI PURPOSE COOPERATIVE v. LA TRINIDAD WATER DISTRICT GR 166471 Case DigestAl Jay Mejos100% (7)
- Starbucks Marketing Final Project MKT 345 Lydia HarrisDocument17 pagesStarbucks Marketing Final Project MKT 345 Lydia Harrisapi-352111965No ratings yet
- Baby One More Time Chords by Blink-182 @Document4 pagesBaby One More Time Chords by Blink-182 @Eva Magdalena PardedeNo ratings yet
- Apunts Anglès 2n BatxilleratDocument9 pagesApunts Anglès 2n BatxilleratNoèlia Vallverdú BarberàNo ratings yet
- Mapa Conceptual ModalsDocument1 pageMapa Conceptual ModalsAmanda Canlo100% (1)
- Friedrich Schlegel Emergence of Romantic Philosophy: and TheDocument270 pagesFriedrich Schlegel Emergence of Romantic Philosophy: and TheMiguel Alberti100% (2)
- Guest Speaker Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesGuest Speaker Lesson PlanKelley Thompson NeumannNo ratings yet
- Criminal Law - Arts 1-20Document73 pagesCriminal Law - Arts 1-20KrisLarr100% (5)
- Modal Verbs: Always Followed by InfinitiveDocument1 pageModal Verbs: Always Followed by InfinitiveSusannaNo ratings yet
- Modal Verbs: Suggestion and Advice Obligation and Prohibition Lack of Obligation/NecessityDocument26 pagesModal Verbs: Suggestion and Advice Obligation and Prohibition Lack of Obligation/NecessitylidiyaNo ratings yet
- Modals and Other Expressions: Must Mustn' TDocument2 pagesModals and Other Expressions: Must Mustn' TAna MaríaNo ratings yet
- Modal VerbsDocument2 pagesModal VerbsJoeNo ratings yet
- Inglês Resumo Gramática 10ºanoDocument2 pagesInglês Resumo Gramática 10ºanoBeatriz NogueiraNo ratings yet
- Mod Al Ve RBS: Are Auxiliary Verbs That Combined With Other Verbs, Express The "Mode" of The VerbsDocument12 pagesMod Al Ve RBS: Are Auxiliary Verbs That Combined With Other Verbs, Express The "Mode" of The VerbsBrenda Sanabria LeyvaNo ratings yet
- English Grammar: Purpose ClausesDocument5 pagesEnglish Grammar: Purpose ClausesLara CostaNo ratings yet
- Prime Time 3 Work Book 78-138pgDocument60 pagesPrime Time 3 Work Book 78-138pgSalome SamushiaNo ratings yet
- C1.2 U5 GrammarReference-3982234Document3 pagesC1.2 U5 GrammarReference-3982234Gemma PerezNo ratings yet
- Modal Verbs: Modal Function Explanation ExamplesDocument3 pagesModal Verbs: Modal Function Explanation ExamplesSteven Reyes RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Modals I 2ºaDocument4 pagesModals I 2ºaSOFÍA LUACES CARBÓNo ratings yet
- Model Verbs in English Very ImportantDocument9 pagesModel Verbs in English Very ImportantdineshgomberNo ratings yet
- Modal Verbs F4Document2 pagesModal Verbs F4shafiqahdaniar96No ratings yet
- Modal Verbs: Modal Function Explanation ExamplesDocument4 pagesModal Verbs: Modal Function Explanation ExamplesNESTORNo ratings yet
- C8 - Modal Verbs of NecessityDocument5 pagesC8 - Modal Verbs of Necessitypanaitlaurentiu569No ratings yet
- Modal Verbs & Narrative Tenses. (Apuntes)Document23 pagesModal Verbs & Narrative Tenses. (Apuntes)Luis MiguelNo ratings yet
- Skhema Modalnykh Glagolov 3Document6 pagesSkhema Modalnykh Glagolov 3Yakunina OlgaNo ratings yet
- PRACTICE - Modal VerbsDocument4 pagesPRACTICE - Modal VerbsPIR oTECNIANo ratings yet
- Adjectives Adverbs Modal Verbs Past Simples Past ParticipleDocument3 pagesAdjectives Adverbs Modal Verbs Past Simples Past ParticipleJéssica CostaNo ratings yet
- Modal Verbs - Revision (All Rules)Document4 pagesModal Verbs - Revision (All Rules)yarynaNo ratings yet
- Past Perfect ContinousDocument9 pagesPast Perfect Continousdjstgiurgiu2021No ratings yet
- Theory - Modal Verbs For Obligation & ProhibitionDocument2 pagesTheory - Modal Verbs For Obligation & ProhibitionlamanandaNo ratings yet
- Shape The Future 1 - Grammar Map - Unit 5Document1 pageShape The Future 1 - Grammar Map - Unit 5GTA VNo ratings yet
- Functions of Modal Verbs: She Should Learn GreekDocument4 pagesFunctions of Modal Verbs: She Should Learn GreekParty CularNo ratings yet
- English 9 Quarter 1 Modals ModulesDocument5 pagesEnglish 9 Quarter 1 Modals ModulescandonesjohnmarcNo ratings yet
- Theory - Modal Verbs For Obligation & ProhibitionDocument2 pagesTheory - Modal Verbs For Obligation & ProhibitionlamanandaNo ratings yet
- Map Your Grammar - Modal VerbsDocument1 pageMap Your Grammar - Modal Verbssakura.chan190No ratings yet
- 1 ModalsDocument7 pages1 ModalsMaria da LuzAlvesNo ratings yet
- The Use of Modals - ChartDocument3 pagesThe Use of Modals - ChartGuillermina EtcheverriaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Have Has ToDocument16 pagesUnit 1 - Have Has ToMaría José ContrerasNo ratings yet
- Modal Verbs ChartDocument3 pagesModal Verbs ChartLucía CarricartNo ratings yet
- Modal VerbsDocument20 pagesModal Verbsrafael buenoNo ratings yet
- ModalsDocument19 pagesModalsdonya soonNo ratings yet
- Infografia Modal VerbsDocument1 pageInfografia Modal VerbsJAVIER moreno L�pezNo ratings yet
- Level: Second "B" MembersDocument10 pagesLevel: Second "B" MembersMichu SilvyNo ratings yet
- Modal Verbs TH ChartDocument2 pagesModal Verbs TH Chartcarla.martignoni23No ratings yet
- Modal VerbsDocument25 pagesModal VerbsPaulaNo ratings yet
- Lecture ModalsDocument4 pagesLecture ModalsAlwin AsuncionNo ratings yet
- Modal Verb - Ability and PermissionDocument2 pagesModal Verb - Ability and PermissionAnh VuNo ratings yet
- 4.unit V MAV Must Have To 4Document13 pages4.unit V MAV Must Have To 4Fran GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Modal Verbs: Can/couldDocument4 pagesModal Verbs: Can/couldYana DotsenkoNo ratings yet
- ModalsDocument9 pagesModalsElla VorobetsNo ratings yet
- AnglaisDocument9 pagesAnglaisArij OnittoNo ratings yet
- Característica Forma Afirmativa Forma NegativaDocument3 pagesCaracterística Forma Afirmativa Forma NegativaOctavio GuerraNo ratings yet
- I Have Vsi Have vs. I Have Got vs. I Got vs. I GottaDocument4 pagesI Have Vsi Have vs. I Have Got vs. I Got vs. I GottaTới Nguyễn TrọngNo ratings yet
- Lesson 34 Modal Verbs2PDFDocument14 pagesLesson 34 Modal Verbs2PDFEbru D.No ratings yet
- Modal Verbs: Los Verbos Modales YsuDocument28 pagesModal Verbs: Los Verbos Modales YsuNiltze DianaNo ratings yet
- Project Overview Doc in Light Green Blue Vibrant Professional StyleDocument2 pagesProject Overview Doc in Light Green Blue Vibrant Professional Stylen52267408No ratings yet
- Sec 1 Term 2 Grammar 2024sedeek - 105239Document17 pagesSec 1 Term 2 Grammar 2024sedeek - 105239Learn English OnlineNo ratings yet
- We Can To Help You LaterDocument2 pagesWe Can To Help You LaterPIR oTECNIANo ratings yet
- Fisa de Lucru-Modal VerbsDocument1 pageFisa de Lucru-Modal VerbsAnonymous hBLzfGDSirNo ratings yet
- Modal VerbsDocument4 pagesModal VerbsBryan CrespoNo ratings yet
- Modal Verbs Chart With Rephrasing Tips and 20 Sentences To RephraseDocument4 pagesModal Verbs Chart With Rephrasing Tips and 20 Sentences To RephrasempotbNo ratings yet
- ModalsDocument7 pagesModalsNata NagovskaNo ratings yet
- Modal Verbs 2Document7 pagesModal Verbs 2pepemusicaantequeraNo ratings yet
- Present Simple vs. Present ContinuousDocument5 pagesPresent Simple vs. Present ContinuousRita SamorinhaNo ratings yet
- Amanti & Imani Slam Dunk Lazy Talk Mini Dictionary:: Who's Yo Author?From EverandAmanti & Imani Slam Dunk Lazy Talk Mini Dictionary:: Who's Yo Author?No ratings yet
- Practical Work Present and Past Simple and ContinuousDocument2 pagesPractical Work Present and Past Simple and ContinuousMaría Cecilia CarattoliNo ratings yet
- Prepositions 2 Between Under Next ToDocument1 pagePrepositions 2 Between Under Next ToMaría Cecilia CarattoliNo ratings yet
- Strange But True - Past PerfectDocument6 pagesStrange But True - Past PerfectMaría Cecilia CarattoliNo ratings yet
- Comparatives Footballers Sports EtcDocument2 pagesComparatives Footballers Sports EtcMaría Cecilia CarattoliNo ratings yet
- Comparative AdjectivesDocument3 pagesComparative AdjectivesMaría Cecilia CarattoliNo ratings yet
- Passive Mixed TensesDocument1 pagePassive Mixed TensesMaría Cecilia CarattoliNo ratings yet
- WhoseDocument6 pagesWhoseMaría Cecilia CarattoliNo ratings yet
- English WordsDocument2 pagesEnglish WordsMaría Cecilia CarattoliNo ratings yet
- Linking Words of Reason and ResultDocument1 pageLinking Words of Reason and ResultMaría Cecilia CarattoliNo ratings yet
- Lost in The LochDocument1 pageLost in The LochMaría Cecilia CarattoliNo ratings yet
- Description of People, Have GotDocument4 pagesDescription of People, Have GotMaría Cecilia CarattoliNo ratings yet
- JobsDocument1 pageJobsMaría Cecilia CarattoliNo ratings yet
- Happy House StoriesDocument1 pageHappy House StoriesMaría Cecilia CarattoliNo ratings yet
- What Season Is ItDocument2 pagesWhat Season Is ItMaría Cecilia CarattoliNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Physical Description and ComparisonDocument7 pagesUnit 1 Physical Description and ComparisonMaría Cecilia CarattoliNo ratings yet
- JobsDocument1 pageJobsMaría Cecilia CarattoliNo ratings yet
- Animals Pres SDocument2 pagesAnimals Pres SMaría Cecilia CarattoliNo ratings yet
- Revision U 2 My English Trip 1Document2 pagesRevision U 2 My English Trip 1María Cecilia CarattoliNo ratings yet
- FamilyDocument1 pageFamilyMaría Cecilia CarattoliNo ratings yet
- Present Simple and ContinuousDocument1 pagePresent Simple and ContinuousMaría Cecilia CarattoliNo ratings yet
- What Are They Doing Practice Test 3Document1 pageWhat Are They Doing Practice Test 3María Cecilia CarattoliNo ratings yet
- AnimalsDocument2 pagesAnimalsMaría Cecilia CarattoliNo ratings yet
- For SinceDocument1 pageFor SinceMaría Cecilia CarattoliNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 A Place To LiveDocument2 pagesUnit 5 A Place To LiveMaría Cecilia CarattoliNo ratings yet
- Passive Past SimpleDocument2 pagesPassive Past SimpleMaría Cecilia CarattoliNo ratings yet
- Friday 13thDocument1 pageFriday 13thMaría Cecilia CarattoliNo ratings yet
- Passive Present SimpleDocument2 pagesPassive Present SimpleMaría Cecilia CarattoliNo ratings yet
- IO U9 Modal Verbs Grammar and SpeakingDocument1 pageIO U9 Modal Verbs Grammar and SpeakingMaría Cecilia CarattoliNo ratings yet
- Have ToDocument2 pagesHave ToMaría Cecilia CarattoliNo ratings yet
- Revision Use of English IO U 6-8Document1 pageRevision Use of English IO U 6-8María Cecilia CarattoliNo ratings yet
- Linguistic Stylistics-Part1 PDFDocument30 pagesLinguistic Stylistics-Part1 PDFMis Lord93% (14)
- LAW - ON - SALES CH 4 Sec 3Document4 pagesLAW - ON - SALES CH 4 Sec 3MaricrisNo ratings yet
- Examination Pattern - Docx MAPC 1 Cognitive Psychology, Learning and MemoryDocument8 pagesExamination Pattern - Docx MAPC 1 Cognitive Psychology, Learning and MemoryakileshaiyerNo ratings yet
- Ap ch4 SQ PDFDocument17 pagesAp ch4 SQ PDFAdeel AhmedNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic JumpDocument5 pagesHydraulic Jumpsatyam agarwalNo ratings yet
- Gnuradio ProjectosDocument4 pagesGnuradio ProjectosartovolastiNo ratings yet
- WWW - tamilMV.re - Arjun Reddy (2017) Telugu HDRip - 720p - x264 - 5.1 - 1.4GBDocument117 pagesWWW - tamilMV.re - Arjun Reddy (2017) Telugu HDRip - 720p - x264 - 5.1 - 1.4GBMohit SinghNo ratings yet
- Health Care EthicsDocument16 pagesHealth Care EthicsKhenwae Polistico100% (2)
- Monitoring Policy OF Insolvency Professional Agency OF Institute of Cost Accountants of IndiaDocument22 pagesMonitoring Policy OF Insolvency Professional Agency OF Institute of Cost Accountants of IndiaSME 865No ratings yet
- TDA8350QDocument17 pagesTDA8350Qjesad5No ratings yet
- Manila Int Climate PDFDocument3 pagesManila Int Climate PDFLevy SorianoNo ratings yet
- The Hon'Ble Supreme Court of Indiana: BeforeDocument24 pagesThe Hon'Ble Supreme Court of Indiana: BeforeShivani Singh0% (1)
- MKSAP Questions: Intern ReportDocument37 pagesMKSAP Questions: Intern Reportfidelurtecho4881No ratings yet
- Homophobic Transphobic Bullying Pe Focus1Document2 pagesHomophobic Transphobic Bullying Pe Focus1api-440470277No ratings yet
- Workshop WH Question - Simple Present TenseDocument3 pagesWorkshop WH Question - Simple Present TenseSara CastilloNo ratings yet
- ERP - Final Project ReportDocument20 pagesERP - Final Project ReportMohammad Rauf MughalNo ratings yet
- Part IV: About The AuthorDocument380 pagesPart IV: About The AuthorVale MelgozaNo ratings yet
- Ca Inter C0 Audit Question Bank NewDocument14 pagesCa Inter C0 Audit Question Bank NewDaanish Mittal100% (1)
- Solidum Vs People of The Philippines DigestedDocument2 pagesSolidum Vs People of The Philippines DigestedEllen Glae DaquipilNo ratings yet
- Action Plan in MathDocument4 pagesAction Plan in Mathjoanna marie limNo ratings yet
- Paterno Santos V Rod of ManilaDocument4 pagesPaterno Santos V Rod of ManilaDiane Dee YaneeNo ratings yet
- Extrajudicial Executions and Forced Disappearances ReportDocument8 pagesExtrajudicial Executions and Forced Disappearances ReportMariaClaretteJoyMaramagNo ratings yet
- Eng 316 Resume and Cover Letter 2019Document1 pageEng 316 Resume and Cover Letter 2019api-476963060No ratings yet
- Word Study & FluencyDocument16 pagesWord Study & FluencyAmber CastroNo ratings yet