Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Answer Key
Answer Key
Uploaded by
Sansen ColipanoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Answer Key
Answer Key
Uploaded by
Sansen ColipanoCopyright:
Available Formats
It is a Relationship between the angles of incidence and refraction is described by a formula.
Snells law
the process of separating colors from light by diffraction or refraction and creating a spectrum
Dispersion
a technique for figuring out how waves or particles would travel through a system with different
propagation speeds, absorption properties, and reflecting surfaces
Ray Tracing
examines light's behavior and characteristics, particularly how it interacts with matter and how to build
tools to use or detect it.
Optics
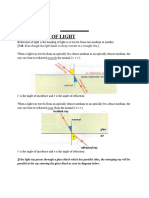
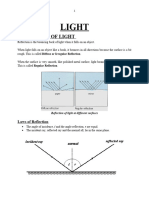
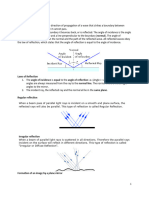
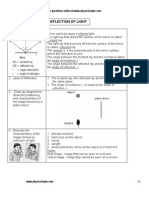
the angle of the reflected ray is identical to the angle of the incident ray upon reflection from a smooth
surface
the law of reflection
a surface that reflects almost all incident light
mirror
What are the two types of mirrors that exist?
Spherical and plane mirror
Additional categories for spherical mirrors include
Convex and concave
a mirror with a curved shape, the reflecting surface of which is on the inside. It features an inwardly
curved surface that resembles the interior surface of a hollow sphere.
Concave mirror
This are found in a huge array of optical instruments, ranging from a simple
magnifying glass to the eye to a camera’s zoom.
Lenses
Is Snell's Law only for solid materials?
No
Which direction will light bend (towards or away from the normal) if the index of
refraction for the second material in the interface is higher than the first? Why?
1. The transmitted angle will be smaller than the incident angle. So the light will
bend towards the normal. This is because the a higher index of refraction in the
second material causes a decrease in the speed of the light in the second
material.
for a material, the ratio of the speed of light in vacuum to that in the material
Index of Refraction
changing of a light ray’s direction when it passes through variations in matter
Refraction
Determine the image distance and image height for a 5.00-cm tall object placed 45.0
cm from a concave mirror having a focal length of 15.0 cm.
Answer: di = 22.5 cm and hi = -2.5 cm
Use 1/f = 1/do + 1/di where f = 15 cm and do = 45 cm
Then use hi / ho = - di / do where ho = 5 cm, do = 45 cm, and di = 22.5 cm
NOTE: this is "Case 1"
You might also like
- Optics Egt22460Document14 pagesOptics Egt22460vimukthi gunasinghaNo ratings yet
- LIGHT PART II: Reflection, Refraction, Mirrors and Lenses The Big IdeaDocument24 pagesLIGHT PART II: Reflection, Refraction, Mirrors and Lenses The Big IdeanidharshanNo ratings yet
- WP2; Light Waves (SDA) 1Document11 pagesWP2; Light Waves (SDA) 1ellenjune632No ratings yet
- WP2 Light Waves (SDA) 2Document11 pagesWP2 Light Waves (SDA) 2matsweamogelang89No ratings yet
- Physics 72.1 Peer ReviewDocument12 pagesPhysics 72.1 Peer Reviewviviene24No ratings yet
- CHAPTER 7 Geometrical Optics UpdatedDocument40 pagesCHAPTER 7 Geometrical Optics UpdatedPriyaa JayasankarNo ratings yet
- Light - Reflection and RefractionDocument4 pagesLight - Reflection and RefractionRounak BasuNo ratings yet
- Phy161 Lab Report 11Document10 pagesPhy161 Lab Report 11Javier Luis SantosNo ratings yet
- Reflection and Refraction of LightDocument44 pagesReflection and Refraction of LightArman Akram100% (1)
- Snell's Law Lab ReportDocument22 pagesSnell's Law Lab ReportSaransh JainNo ratings yet
- Notes: Introduction To Light - Reflection & RefractionDocument10 pagesNotes: Introduction To Light - Reflection & RefractionShardul SumantNo ratings yet
- Physics 11 Chapter 18: Ray Optics: Reading: OutlineDocument6 pagesPhysics 11 Chapter 18: Ray Optics: Reading: OutlinesenjicsNo ratings yet
- WP4 Light WavesDocument16 pagesWP4 Light Waveswarona letangNo ratings yet
- Basic Tools and TechniquesDocument33 pagesBasic Tools and TechniquesAditi MishraNo ratings yet
- OpticsDocument56 pagesOpticsahsan shahNo ratings yet
- Physics Form 4 Chapter 5: Light: Prepared By: Sharvinder SinghDocument28 pagesPhysics Form 4 Chapter 5: Light: Prepared By: Sharvinder SinghSharvinder SinghNo ratings yet
- Thin Lens Focus DistanceDocument13 pagesThin Lens Focus DistanceselniNo ratings yet
- Phy161 Lab Report 11Document9 pagesPhy161 Lab Report 11Javier Luis SantosNo ratings yet
- Explain How Refraction and Reflection Phenomenon Could Be Used in Transmission SystemsDocument10 pagesExplain How Refraction and Reflection Phenomenon Could Be Used in Transmission SystemsJuan Jose PerdomoNo ratings yet
- What Is Reflection of Light?Document3 pagesWhat Is Reflection of Light?MD: Rabiul Awal ShuvoNo ratings yet
- Ray OpyicsDocument56 pagesRay OpyicsDhruv JainNo ratings yet
- Light PUREDocument9 pagesLight PUREtalithaonkabetse723No ratings yet
- The Ray Model of LightDocument8 pagesThe Ray Model of LightNikoli MajorNo ratings yet
- Ray Optics by Kshitij Chandel (Physics)Document8 pagesRay Optics by Kshitij Chandel (Physics)Kshitij ChandelNo ratings yet
- Light PresentationDocument91 pagesLight PresentationRohan SinghNo ratings yet
- Light ReflectionandnrhehrDocument16 pagesLight ReflectionandnrhehrRaghav NegiNo ratings yet
- 3.1 Light (1) (1) - 2Document10 pages3.1 Light (1) (1) - 2Dark VariantNo ratings yet
- Reflection & Refraction of LightDocument43 pagesReflection & Refraction of Lightgbokoyiayomide17No ratings yet
- Physics Investigatory ProjectDocument11 pagesPhysics Investigatory Projectakash singh50% (2)
- Light, Optics & ColourDocument38 pagesLight, Optics & ColourKrish ChopraNo ratings yet
- Refraction and Reflection of LightDocument9 pagesRefraction and Reflection of LightShenNo ratings yet
- LightDocument6 pagesLightNishi ShahNo ratings yet
- Archivos PASCO - CA-6787 PDF Files - 3 Thermo., WavDocument8 pagesArchivos PASCO - CA-6787 PDF Files - 3 Thermo., WavChess ManNo ratings yet
- Termpaper-Light Optical Microscope TechniquesDocument39 pagesTermpaper-Light Optical Microscope TechniquesPopang WernaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7 5Document29 pagesLecture 7 5mysaustine1No ratings yet
- LightDocument17 pagesLightAhmad ZebNo ratings yet
- Isc Physics ProjectDocument15 pagesIsc Physics ProjectBhoomi Dhoka100% (1)
- Reflection RefractionDocument38 pagesReflection RefractionHandini Novita SariNo ratings yet
- Wilmer Nossa Pino Paso - 3Document7 pagesWilmer Nossa Pino Paso - 3Eder SolisNo ratings yet
- Byjus Optics Notes CAPFDocument5 pagesByjus Optics Notes CAPFPhani GopalNo ratings yet
- Physics Project Class 12th 'E' Anupam GuptaDocument36 pagesPhysics Project Class 12th 'E' Anupam Guptaguptaanupam552No ratings yet
- Physics Chapter LightDocument25 pagesPhysics Chapter LightNurliyana Zairul AfendiNo ratings yet
- 12 Physics Imp Ch9 2Document9 pages12 Physics Imp Ch9 2Amar PandeyNo ratings yet
- Reflection RefractionDocument7 pagesReflection Refractionmanuel.velasquezNo ratings yet
- L Principles MicrosDocument60 pagesL Principles MicrosRasul AmirovNo ratings yet
- Phy161 Lab Report 10Document10 pagesPhy161 Lab Report 10Javier Luis SantosNo ratings yet
- Make Your Own ProjectorDocument9 pagesMake Your Own ProjectorswapnasridharanNo ratings yet
- WP2 Light Waves (SDA) 1Document10 pagesWP2 Light Waves (SDA) 1botswanaboy9No ratings yet
- Physics - Geometric-Optics Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesPhysics - Geometric-Optics Lesson PlanBeing MotivatedNo ratings yet
- 2096 Light MicrosDocument49 pages2096 Light MicrosSaad Zafar AwanNo ratings yet
- Reflection of LightDocument8 pagesReflection of LightShivani ChaurasiaNo ratings yet
- Lenses LectureDocument6 pagesLenses LectureMarcuz ValdezNo ratings yet
- E112 - AgustinDocument19 pagesE112 - AgustinSeth Jarl G. AgustinNo ratings yet
- Slit Lampbiomicroscopy 140720101817 Phpapp01Document77 pagesSlit Lampbiomicroscopy 140720101817 Phpapp01Kevin JawanNo ratings yet
- Light - Reflection and Refraction NotesDocument9 pagesLight - Reflection and Refraction NotesRaviraj Desai100% (3)
- EF Lens Work Book 10 enDocument25 pagesEF Lens Work Book 10 enSilvana HadžićNo ratings yet
- Cylindrical Perspective: Cylindrical Perspective: Exploring Visual Perception in Computer VisionFrom EverandCylindrical Perspective: Cylindrical Perspective: Exploring Visual Perception in Computer VisionNo ratings yet
- Crave MuchDocument40 pagesCrave MuchSansen ColipanoNo ratings yet
- Study HabitsDocument3 pagesStudy HabitsSansen ColipanoNo ratings yet
- 1st Law - Never Outshine A MasterDocument8 pages1st Law - Never Outshine A MasterSansen ColipanoNo ratings yet
- Equations of Simple Harmonic MotionDocument15 pagesEquations of Simple Harmonic MotionSansen ColipanoNo ratings yet