Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Module 3 - Math 121
Module 3 - Math 121
Uploaded by
AzhelOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Module 3 - Math 121
Module 3 - Math 121
Uploaded by
AzhelCopyright:
Available Formats
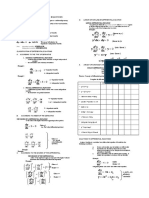
MIDTERM FOOD FOR THE BRAINS: Examples of polynomials having the same
degree.
WEEK/MODULE- 3 • x2-xy+2y2 Homogeneous of 2nd degree
• x4y+3y5 Homogeneous of 5th degree
HOMOGENEOUS DIFFERENTIAL EQUATION
EXAMPLE: Find the general solution of the differential equation, y dx
+ (2x + 3y) dy = 0.
A differential equation of the form f(x,y) dy = g(x,y) dx is said to
be homogeneous differential equation if the degree of f(x,y) and g(x, Solution:
y) is same.
You must have learned to solve the differential equations in
previous sections. To solve a homogeneous differential equation
following steps are followed:
❖ Standard Form: M(x,y) dx + N(x,y) dy = 0, if M and N are
homogeneous of the same degree n.
❖ General Solution: Substitute y = vx or x= vy and the
resulting D.E. is reduced to a variable separable D.E.
Step 1- If M is simpler use: x = vy; dx = vdy + ydv
If N is simpler use: y = vx; dy = vdx + xdv
EXAMPLE: Find the solution of the differential equation, xy dx + (x2 +
Substitute in the given differential equation.
y2) dy = 0.
Step 2 – Differentiating. Now substitute the value of x and y in the Solution:
given differential equation.
Step 3 – Separating the variables
Step 4 – Integrating both side of equation
Step 5 – After integration we replace v = y/x
Note: It is not important using y = vx or x = vy, since both ways will
give the same answer. However, it is sometimes easier to substitute
for the variable whose differential has simpler coefficient.
1 MATH 121 | D I F F E R E N T I A L E Q U A T I O N
You might also like
- Differential Equations BasicDocument4 pagesDifferential Equations BasicBenjaminNo ratings yet
- First Order and First Degree Differential EquationDocument22 pagesFirst Order and First Degree Differential EquationHi HiNo ratings yet
- Differential Equation Area Under The Curve 1645520155242Document50 pagesDifferential Equation Area Under The Curve 1645520155242Abhishek KothariNo ratings yet
- Differential EquationDocument16 pagesDifferential Equationशिवम् सुनील कुमारNo ratings yet
- Elementary Differential Equations-BoyceDocument39 pagesElementary Differential Equations-BoyceNurul HanifahNo ratings yet
- Chapter One 1.1 Differential Equation: (Also, Mention What A Solution of Differential Equation Means)Document10 pagesChapter One 1.1 Differential Equation: (Also, Mention What A Solution of Differential Equation Means)aaryan khanalNo ratings yet
- 202004032250572068siddharth Bhatt Engg Numerical Solution of Ordinary Differential EquationsDocument72 pages202004032250572068siddharth Bhatt Engg Numerical Solution of Ordinary Differential EquationsAnirudh MittalNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1.5 - DE With Homogeneous CoefficientsDocument10 pagesLesson 1.5 - DE With Homogeneous CoefficientsThe BluemanNo ratings yet
- 3.1.Solutions-First Order ODEs-Separable MethodDocument6 pages3.1.Solutions-First Order ODEs-Separable MethodReginald AshongNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Dela Sem. II B.tech. Ma0211Document4 pagesUnit 1 Dela Sem. II B.tech. Ma0211BHADORIYA ADITYASINHNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: Equations With Homogeneous CoefficientsDocument2 pagesThis Study Resource Was: Equations With Homogeneous Coefficientstristan espinosaNo ratings yet
- Sheet - 01 - Differential Equation NJ - 247Document22 pagesSheet - 01 - Differential Equation NJ - 2471qerfdNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 SecondorderlineardeswithconstantcoeffsslideDocument13 pagesChapter 3 SecondorderlineardeswithconstantcoeffsslideIzzul HakimNo ratings yet
- Module 4 - Math 121Document1 pageModule 4 - Math 121AzhelNo ratings yet
- Math 121 Module 4Document1 pageMath 121 Module 4AzhelNo ratings yet
- Differential Equations-1st Order, 1st DegreeDocument9 pagesDifferential Equations-1st Order, 1st DegreeVince Rabin CandidatoNo ratings yet
- Differential Equations: Solution by Direct IntegrationDocument7 pagesDifferential Equations: Solution by Direct IntegrationGlennmark RodriguesNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 - Homogeneous DEDocument15 pagesTopic 3 - Homogeneous DESelaras KyleNo ratings yet
- Math Gre w2015 Lecture7Document11 pagesMath Gre w2015 Lecture7priya dharshiniNo ratings yet
- First Order Differential EquatationsDocument5 pagesFirst Order Differential Equatationsamrin12345No ratings yet
- 2.5 Solutions by SubstitutionsDocument7 pages2.5 Solutions by SubstitutionsNor Azizi Binti ZulkifliNo ratings yet
- Differential Equation - Formula Sheet - MathonGoDocument4 pagesDifferential Equation - Formula Sheet - MathonGoMamtaNo ratings yet
- Best Approach: Differential EquationDocument31 pagesBest Approach: Differential EquationTanmay SagarNo ratings yet
- Differential Equations: 9.1 OverviewDocument25 pagesDifferential Equations: 9.1 OverviewMark Renbel ParanNo ratings yet
- Math 211 - Module 1 - Lesson - 2 - Solution To An OrdinaryDocument5 pagesMath 211 - Module 1 - Lesson - 2 - Solution To An OrdinaryJovy AndoNo ratings yet
- Differential Equations ExemplarDocument25 pagesDifferential Equations ExemplarRitik ChaabraNo ratings yet
- Separable Differential EquationsDocument7 pagesSeparable Differential EquationsLeopold LasetNo ratings yet
- DE Chap1Document13 pagesDE Chap1Corina UrbinaNo ratings yet
- Differential EquationsDocument17 pagesDifferential EquationsNikolai VillegasNo ratings yet
- MATE2A2 HomogeneDocument8 pagesMATE2A2 HomogeneMahlatse Morongwa MalakaNo ratings yet
- "Just The Maths" Slides Number 15.1 Ordinary Differential Equations 1 (First Order Equations (A) ) by A.J.HobsonDocument11 pages"Just The Maths" Slides Number 15.1 Ordinary Differential Equations 1 (First Order Equations (A) ) by A.J.HobsonDon eladioNo ratings yet
- Differential Equations ReviewDocument20 pagesDifferential Equations Reviewsaimom sarkerNo ratings yet
- First Order ODEsDocument11 pagesFirst Order ODEs20kylegarrickNo ratings yet
- Module2 Topic3 Week4 Differential EquationDocument4 pagesModule2 Topic3 Week4 Differential EquationCHEZANIE MIYA ASUNCIONNo ratings yet
- Math 226 Differential Equation: Edgar B. Manubag, Ce, PHDDocument19 pagesMath 226 Differential Equation: Edgar B. Manubag, Ce, PHDJosh T CONLUNo ratings yet
- Buenavista Community College: M (X, Y) DX + N (X, Y) Dy 0Document4 pagesBuenavista Community College: M (X, Y) DX + N (X, Y) Dy 0Oliver EstoceNo ratings yet
- Differential Equations IntroDocument29 pagesDifferential Equations IntroMansi NanavatiNo ratings yet
- De Lec2Document29 pagesDe Lec2Nilo De Mesa NhilNo ratings yet
- Session 2 (20)Document10 pagesSession 2 (20)supriti83No ratings yet
- STEP Support Programme STEP 3 Differential Equations Topic NotesDocument2 pagesSTEP Support Programme STEP 3 Differential Equations Topic NotesNani AhmedNo ratings yet
- Calculus Assignment FinalDocument16 pagesCalculus Assignment FinalYared DemissieNo ratings yet
- First Order Differential EquationsDocument88 pagesFirst Order Differential EquationsAbd AlsaltyNo ratings yet
- 2.ODE of First OrderDocument23 pages2.ODE of First OrderDrew DoroteoNo ratings yet
- Concepts and Formulas - DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONSDocument5 pagesConcepts and Formulas - DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONSPranav KrizzNo ratings yet
- Math 206 - Differential Equations Andy Rosen Please Sign inDocument23 pagesMath 206 - Differential Equations Andy Rosen Please Sign inAston RiceNo ratings yet
- 1.3 NoteDocument9 pages1.3 Notemaityarnab909No ratings yet
- Exact EquationsDocument11 pagesExact EquationsNelsonMoseMNo ratings yet
- Dr. Kavita Gupta FinalDocument46 pagesDr. Kavita Gupta FinalMadhu SharmaNo ratings yet
- 11 - Differential Equations PDFDocument9 pages11 - Differential Equations PDFthinkiitNo ratings yet
- First Order Ordinary Differential EquationsDocument11 pagesFirst Order Ordinary Differential Equationstobianimashaun99No ratings yet
- ES 21 Second Exam D.E.1 - NotesDocument5 pagesES 21 Second Exam D.E.1 - NotesGil Kenneth San MiguelNo ratings yet
- Maths13 02Document14 pagesMaths13 02Random PersonNo ratings yet
- 4 Ordinary Differential EquationsDocument91 pages4 Ordinary Differential EquationsKai CaoNo ratings yet
- 2-0-Solution To Differential EquationsDocument5 pages2-0-Solution To Differential EquationsGedeon BetosNo ratings yet
- 6 Substitution Methods, Homogeneous Equa-Tions, Bernoulli EquationsDocument14 pages6 Substitution Methods, Homogeneous Equa-Tions, Bernoulli EquationsFurkan ErdenNo ratings yet
- MATH3 Lect2Document26 pagesMATH3 Lect2f20221184No ratings yet
- Week 014 Differential Equations - Separable EquationsDocument3 pagesWeek 014 Differential Equations - Separable Equationsvit.chinnajiginisaNo ratings yet
- Mathematics 1St First Order Linear Differential Equations 2Nd Second Order Linear Differential Equations Laplace Fourier Bessel MathematicsFrom EverandMathematics 1St First Order Linear Differential Equations 2Nd Second Order Linear Differential Equations Laplace Fourier Bessel MathematicsNo ratings yet
- Module 4 - Es 125Document1 pageModule 4 - Es 125AzhelNo ratings yet
- Module 5 - Math 121Document1 pageModule 5 - Math 121AzhelNo ratings yet
- Art Appreciation Report 5Document7 pagesArt Appreciation Report 5AzhelNo ratings yet
- Math 121 Module 4Document1 pageMath 121 Module 4AzhelNo ratings yet
- Hydrographic Survey FinalDocument1 pageHydrographic Survey FinalAzhelNo ratings yet
- Theories and Views On GenderDocument2 pagesTheories and Views On GenderAzhelNo ratings yet