Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Paas
Paas
Uploaded by
shaheenashahbas476Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Paas
Paas
Uploaded by
shaheenashahbas476Copyright:
Available Formats
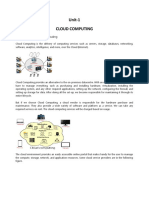
[MUSIC] *Platform as a service,
commonly referred to as P-a-a-S or simply, PaaS,
is a cloud computing model that provides customers a complete platform to develop,
deploy, manage and run applications created by them or
acquired from a third party.
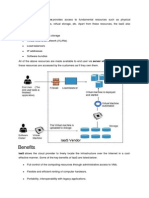
1. The PaaS provider hosts everything:
servers, networks, storage, operating system, application runtimes,
APIs, middleware, databases and
other tools at their data center.
2. The provider also takes responsibility for
the installation, configuration, and operation of
the application infrastructure, leaving the user responsible for only
the application code and its maintenance.
3. Customers pay for this service on a usage
basis and purchase resources on demand. With IaaS, the cloud provider
offers access to raw computing resources such as servers,
storage, and networking, while the user is responsible for
the platform and application software.
4. With P-a-a-S or PaaS,
the cloud service provider delivers and manages the entire
platform infrastructure, abstracting users from the lower
level details of the environment.
5. Let's look at some essential characteristics
of platform as a service or PaaS.
• PaaS clouds are distinguished by the high
level of abstraction they provide to the users, eliminating the complexity
of deploying applications, configuring infrastructure,
and provisioning and configuring supporting technologies like load balancers and databases.
• PaaS clouds provide services and APIs
that help simplify the job of developers in delivering elastically scalable and
highly available cloud applications. These services typically include a variety
of capabilities such as APIs for distributing, caching,
queuing and messaging, file and data storage,
workload management, user identity, and analytics, thus eliminating the need
to integrate disparate components.
• The PaaS runtime environment
executes end user code according to policies set by the application owner and
cloud provider. Many of the PaaS offerings provide
developers with rapid deployment mechanisms or push and run mechanism for
deploying and running applications.
• PaaS offerings support a range of
application infrastructure or middleware capabilities such as application servers,
database management systems, business analytics servers,
mobile backend services, integration services,
business process management systems, rules engines, and
complex event processing systems. Such an application infrastructure assists
developers by reducing the amount of code that must be written while expanding
the application's functional capabilities.
6. The most important use case for
PaaS is strategic, build, test, deploy, enhance and scale applications
rapidly and cost effectively.
7. Let's look at some more use cases for
PaaS. API development and management.
• Organizations are using PaaS to develop,
run, manage and secure APIs and microservices, which are loosely coupled, independently
deployable components and services.
• Internet of Things, or IoT: PaaS clouds support a broad range
of application environments, programming languages, and
tools used for IoT deployments.
• Business analytics, or intelligence: PaaS tools allow organizations to
analyze their data to find business insights that enable more informed
business decisions and predictions.
• Business Process management, or BPM. Organizations are using
the PaaS cloud to access BPM platform delivered as a service.
• Master data management, or MDM: Organizations are leveraging the PaaS
cloud to provide a single point of reference for critical business data,
such as information about customer transactions and analytical
data to support decision-making.
8. Let's look at some
advantages of using PaaS.
• Scalability, made possible because
of the rapid allocation and deallocation of resources with
a pay-as-you-use model offered by PaaS.
• The APIs support services and middleware
capabilities that PaaS clouds provide assist developers in focusing their
efforts on application development and testing, resulting in faster time-to-market
for their products and services. Middleware capabilities also reduce
the amount of code that need to be written while expanding the application's
functional capabilities.
• Greater agility and innovation:
because using PaaS platforms means that you can experiment with
multiple operating systems, languages and tools without having
to invest in these resources. You can evaluate and prototype
ideas with very low risk exposure, resulting in faster, easier, less risky
adoption of a wider range of resources.
9. Some of the key PaaS offerings
available in the market today include AWS Elastic Beanstalk,
Cloud Foundry, IBM Cloud Paks, Windows Azure,
Red Hat OpenShift, Magento Commerce Cloud,
force.com, and Apache Stratos.
10. PaaS clouds do come with some risks,
risks that all cloud offerings have in general, such as
• information security threats and
• dependency on the service
provider's infrastructure. Services can get impacted when
a service provider's infrastructure experiences downtime.
• Customers also don't have any direct
control over the changes that may take place when a provider makes changes in
its strategy, service offerings or tools. But the benefits can far
outweigh these risks.
11. PaaS continues to experience
strong growth and is predicted to become the prevailing
platform delivery model moving forward. In the next video, we will look
at software as a service model, its features, benefits,
and some use cases. [MUSIC]
You might also like
- Red Hat OpenShift Training Workshop SlidesDocument95 pagesRed Hat OpenShift Training Workshop Slideskaralyh100% (1)
- Platform As A ServiceDocument4 pagesPlatform As A ServiceSuganya PeriasamyNo ratings yet
- UNIT 3 Cloud Service ModelsDocument8 pagesUNIT 3 Cloud Service ModelsBharat KumarNo ratings yet
- Unit3 Cloud Computing PDFDocument42 pagesUnit3 Cloud Computing PDFonlyfor collegeuseNo ratings yet
- What Is Paas?Document15 pagesWhat Is Paas?Tarang ShahNo ratings yet
- Cloud BitDocument7 pagesCloud Bitnithikuttan29No ratings yet
- Cloud ComputingDocument66 pagesCloud ComputingMadhav Madhausudhan Reddy KNo ratings yet
- Platform As A ServiceDocument7 pagesPlatform As A ServicechandraNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8Document6 pagesLecture 8Haidr abed alkarimNo ratings yet
- Cloud 2Document22 pagesCloud 2Sudhanshu KumarNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Cloud Architecture Not of UseDocument51 pagesUnit 2 Cloud Architecture Not of UseAnonymous FKWVgNnSjo100% (1)
- Summary of Key Differences: Platform Type Common ExamplesDocument6 pagesSummary of Key Differences: Platform Type Common ExamplesajaygavNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing Paas Cloud Demand PaperDocument14 pagesCloud Computing Paas Cloud Demand PaperKrkrNo ratings yet
- 18 Describe Platform As A ServiceDocument2 pages18 Describe Platform As A ServiceevamariaestabansienesNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing ServicesDocument25 pagesCloud Computing ServicesSakshi KakadeNo ratings yet
- Platform As A Service PaaS FaqDocument5 pagesPlatform As A Service PaaS FaqMoinuddin MirzaNo ratings yet
- Unit - II (Cloud Computing)Document46 pagesUnit - II (Cloud Computing)NikitaNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing (All Questions)Document54 pagesCloud Computing (All Questions)SahilNo ratings yet
- CC Unit 3Document11 pagesCC Unit 3Harsh RajputNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 PPTDocument30 pagesChapter 3 PPTKotireddy vinthaNo ratings yet
- CC Unit-4Document16 pagesCC Unit-4Kanduri shirisha GoudNo ratings yet
- SnorlaxDocument3 pagesSnorlaxdomainexpansion00000No ratings yet
- Mengenal SaaS, IaaS, Dan PaaS Dalam Cloud ComputingDocument3 pagesMengenal SaaS, IaaS, Dan PaaS Dalam Cloud ComputingHans Christian IrawanNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing Platform As A Service (PaaS) - TutorialspointDocument4 pagesCloud Computing Platform As A Service (PaaS) - Tutorialspointsepoged319No ratings yet
- Cloud ServicesDocument10 pagesCloud Servicesthumpsup1223No ratings yet
- Cloud Computing PresentationDocument34 pagesCloud Computing PresentationWaleed EducationalNo ratings yet
- Unit-I CCDocument8 pagesUnit-I CCnarendra sahuNo ratings yet
- CC Week 06Document22 pagesCC Week 06Muhammad ShehzadNo ratings yet
- Cloud ServicesDocument5 pagesCloud Servicessankit120kNo ratings yet
- Azure PaaSDocument3 pagesAzure PaaSNew sonNo ratings yet
- Cloud-Computing-Architecture - Services - HypervisiorDocument11 pagesCloud-Computing-Architecture - Services - Hypervisioruserdemo12334No ratings yet
- Cloud Service ModelsDocument10 pagesCloud Service ModelsmanasyogiNo ratings yet
- WhitePaper SaaSHub Final 5Document7 pagesWhitePaper SaaSHub Final 5Spencer YangNo ratings yet
- KazisaymaDocument2 pagesKazisaymaMahpara Rahman RafaNo ratings yet
- Platform As A Service: Presented By: N Kalyan Gupta 1602-17-733-314 B Madhukumar 1602-17-733-323Document22 pagesPlatform As A Service: Presented By: N Kalyan Gupta 1602-17-733-314 B Madhukumar 1602-17-733-323Kalyan NarlaNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing v.1Document6 pagesCloud Computing v.1infusionNo ratings yet
- SaaS PaaS and IaaSDocument3 pagesSaaS PaaS and IaaSpamulasNo ratings yet
- UNIT3 NotesDocument8 pagesUNIT3 NotesHarsh AryanNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing Platform As A Service (PaaS)Document5 pagesCloud Computing Platform As A Service (PaaS)Kavya MamillaNo ratings yet
- CC Platform As A ServiceDocument8 pagesCC Platform As A ServiceTushar MircheNo ratings yet
- Assignment (IaaS, PaaS)Document5 pagesAssignment (IaaS, PaaS)Ahmad AbbasiNo ratings yet
- IaaS vs. PaaS vs. SaaSDocument4 pagesIaaS vs. PaaS vs. SaaSleonardo.russoNo ratings yet
- IaaS PaaS SaaSDocument6 pagesIaaS PaaS SaaSajaybm1No ratings yet
- CHAP - I I (Cloud Computing)Document24 pagesCHAP - I I (Cloud Computing)baharNo ratings yet
- Basics of Cloud ComputingDocument16 pagesBasics of Cloud Computingisimarkaur21No ratings yet
- Unit1 1Document30 pagesUnit1 1HimajanaiduNo ratings yet
- Iaas Vs Paas Vs SaasDocument5 pagesIaas Vs Paas Vs SaasSreekantNo ratings yet
- Cloud - Computing UNIT-3 Material .Document17 pagesCloud - Computing UNIT-3 Material .kavists20No ratings yet
- Unit 3 Cloud ComputingDocument99 pagesUnit 3 Cloud Computingadarsh tiwariNo ratings yet
- PG Cloud Computing Unit-IDocument33 pagesPG Cloud Computing Unit-Ideepthi sanjeevNo ratings yet
- Pengantar Cloud #3Document13 pagesPengantar Cloud #3wulandariweniNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing - Unit4 - NewDocument16 pagesCloud Computing - Unit4 - New028maloth ramNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing Paper2Document4 pagesCloud Computing Paper2Akanksha SharmaNo ratings yet
- 01 (B) Other PlatformsDocument3 pages01 (B) Other PlatformsTanNo ratings yet
- 23PCA11-Unit-2-Cloud Computing-10-01-2024Document62 pages23PCA11-Unit-2-Cloud Computing-10-01-2024l2845610No ratings yet
- Cloud Computing Service ModelsDocument6 pagesCloud Computing Service ModelsAshwaq Saqib KhanNo ratings yet
- Cloud Service ModelDocument10 pagesCloud Service ModelridihimaNo ratings yet
- Categories of Cloud Computing UNIT-IIIDocument11 pagesCategories of Cloud Computing UNIT-IIIDr. Lakshmi Narayana Reddy BNo ratings yet
- 2nd Assignment PDFDocument8 pages2nd Assignment PDFWahab KhanNo ratings yet
- SaaS: Everything You Need to Know About Building Successful SaaS Company in One Place.From EverandSaaS: Everything You Need to Know About Building Successful SaaS Company in One Place.No ratings yet
- The Ultimate Guide to Unlocking the Full Potential of Cloud Services: Tips, Recommendations, and Strategies for SuccessFrom EverandThe Ultimate Guide to Unlocking the Full Potential of Cloud Services: Tips, Recommendations, and Strategies for SuccessNo ratings yet
- Block StorageDocument8 pagesBlock Storageshaheenashahbas476No ratings yet
- Bare ServersDocument7 pagesBare Serversshaheenashahbas476No ratings yet
- Basics of Cloud StorageDocument6 pagesBasics of Cloud Storageshaheenashahbas476No ratings yet
- Hybrid CloudDocument6 pagesHybrid Cloudshaheenashahbas476No ratings yet
- Introduction To SSRFDocument9 pagesIntroduction To SSRFdawasov843No ratings yet
- Static Routing ConfigurationDocument3 pagesStatic Routing Configurationalimad0900No ratings yet
- Debug LogDocument144 pagesDebug LogEvan JusephcaNo ratings yet
- Opera:ng Systems: Dr. P. Sateesh KumarDocument26 pagesOpera:ng Systems: Dr. P. Sateesh KumarSurendra ParlaNo ratings yet
- SDMC RDK-B OverviewDocument5 pagesSDMC RDK-B OverviewgocenikNo ratings yet
- Operating System - Lab Manual # 11Document7 pagesOperating System - Lab Manual # 11bsef21m008No ratings yet
- Internet TechnologyDocument4 pagesInternet Technologyphilip abrahamsNo ratings yet
- LogDocument58 pagesLogTheresiaNo ratings yet
- Instructor Materials Chapter 7: IP Addressing: CCNA Routing and Switching Introduction To Networks v6.0Document21 pagesInstructor Materials Chapter 7: IP Addressing: CCNA Routing and Switching Introduction To Networks v6.0Honey ShineNo ratings yet
- IR8831 LTE RoamingDocument36 pagesIR8831 LTE RoamingRex FengNo ratings yet
- DS BBDocument62 pagesDS BBNiranjan mohiteNo ratings yet
- Creating A Virtual Private Cloud ActivityDocument9 pagesCreating A Virtual Private Cloud ActivityProf.Anup KunteNo ratings yet
- ccna 1 Chapter 9 v5 0 AnswersDocument8 pagesccna 1 Chapter 9 v5 0 AnswersPriscila Beatriz Cabrera CabralNo ratings yet
- RouterOS by Example Stephen Discher PDFDocument236 pagesRouterOS by Example Stephen Discher PDFAntonioNo ratings yet
- SRWE - Module - 11-Switch Security Configuration-ModifiedDocument45 pagesSRWE - Module - 11-Switch Security Configuration-ModifiedLama Ahmad100% (1)
- Quality of ServiceDocument40 pagesQuality of ServiceYsrael HuancaNo ratings yet
- Health - Check - NE40E-05.05.13 08-30-00Document118 pagesHealth - Check - NE40E-05.05.13 08-30-00K.m.khizir AhmedNo ratings yet
- PDC Final DocumentDocument21 pagesPDC Final DocumentMannanNo ratings yet
- LogDocument102 pagesLogAbdullah SelamatNo ratings yet
- CH 20Document62 pagesCH 20ADNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing SyllabusDocument2 pagesCloud Computing Syllabushappylife 123No ratings yet
- DNS Server Global Query Block ListDocument10 pagesDNS Server Global Query Block ListSławek TurekNo ratings yet
- CCNA Discovery 4 Final ExamDocument22 pagesCCNA Discovery 4 Final ExamAbraham Gebreyohanes100% (1)
- LogDocument10 pagesLogrizal rausanNo ratings yet
- VPC ArchitectureDocument10 pagesVPC ArchitectureSamNo ratings yet
- Operating Systems ProcessesDocument30 pagesOperating Systems ProcessesZoe NyadziNo ratings yet
- Miercom ISR 4000 Lab Test (20150817)Document16 pagesMiercom ISR 4000 Lab Test (20150817)kanggodolananNo ratings yet
- Mansi Kadam PC Lab Assignment 1Document4 pagesMansi Kadam PC Lab Assignment 1SAMINA ATTARINo ratings yet
- Fortinet NSE4Document34 pagesFortinet NSE4Hamed Ghabi100% (1)