Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ch3 OL Revision
Ch3 OL Revision
Uploaded by
zuhra123cool0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views11 pagesThe document discusses several cellular transport processes including diffusion, osmosis, and active transport, explaining how they allow molecules to move across cell membranes down concentration gradients or against them using energy. It provides details on factors that affect rates of diffusion and osmosis, how osmosis allows plant cells to remain turgid, and how active transport uses carrier proteins to move molecules against their concentration gradient.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses several cellular transport processes including diffusion, osmosis, and active transport, explaining how they allow molecules to move across cell membranes down concentration gradients or against them using energy. It provides details on factors that affect rates of diffusion and osmosis, how osmosis allows plant cells to remain turgid, and how active transport uses carrier proteins to move molecules against their concentration gradient.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views11 pagesCh3 OL Revision
Ch3 OL Revision
Uploaded by
zuhra123coolThe document discusses several cellular transport processes including diffusion, osmosis, and active transport, explaining how they allow molecules to move across cell membranes down concentration gradients or against them using energy. It provides details on factors that affect rates of diffusion and osmosis, how osmosis allows plant cells to remain turgid, and how active transport uses carrier proteins to move molecules against their concentration gradient.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 11
Movement Into & Out the Cell
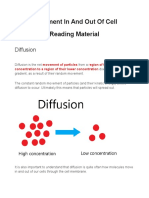
Diffusion is the movement of molecules from a region of its
higher concentration to a region of its lower concentration.
Molecules move down a concentration gradient.
•Diffusion helps living organisms to:
1) Obtain many of their requirements.
2) Get rid of many of their waste products.
3) Carry out gas exchange for respiration.
Dr. Ahmad Salem – Biology OL
Factors that Affect the Rate of Diffusion
1. Distance
The shorter the distance the substances have to
move, the faster the rate of diffusion.
2. Temperature
The higher the temperature, the faster molecules move
as they have more energy.
Therefore, as the temperature increases, the rate of
diffusion increases.
3. Concentration Gradient
The greater the concentration gradient, the quicker
diffusion takes place.
4. The surface area of the membrane affects the rate
of diffusion.
As the surface area of the membrane increases, the rate of
diffusion also increases, as there is more space for molecules
to diffuse across the membrane.
Osmosis
Net movement of water molecules from area of high
concentration of water (dilute solution) to area of low
concentration of water (concentrated solution) through
partially permeable membrane. Water is moving down its
concentration gradient
Water potential: The ability of
water molecules to move from
one place to another.
Water potential gradient:
Presence in water potential of
different media.
Importance of water as a solvent:
•75% of cell components is water
•Many substances move around the cell dissolved
•Many needed reactions occur in water
In plant tissues Plant Osmosis
When water moves into a plant cell, the vacuole gets
bigger, pushing the cell membrane against the cell
wall, by osmosis makes the cell rigid and firm.
Plant cells that are turgid are full of water and contain
a high turgor pressure (the pressure of the cytoplasm
pushing against the cell wall).
This pressure prevents any more water entering the
cell by osmosis. This preventing taking in too much
water and bursting.
Plant roots are surrounded by soil water and the
cytoplasm of root cells has a lower water potential than
the soil water. Turgor pressure within cells, Water pressure acting against an in
elastic cell wall needed to support plant.
In plant tissues
This means water will move across the cell membrane
of root hair cells into the root by osmosis
The water moves across the root from cell to cell by
osmosis until it reaches the xylem
Once they enter the xylem they are transported away
from the root by the transpiration stream, helping to
maintain a concentration gradient between the root cells
and the xylem vessels.
If plants do not receive enough water the cells cannot
remain rigid and firm (turgid) and the plant wilts.
Plant cell doesn’t burst as it
has a cell wall that is elastic as
it’s made of cellulose so it’s
stretched and never break.
Flaccid: soft and limp; not firm
Plasmolysis
Plasmolysis: It is the shrinking of cytoplasm of plant cell so that
cell membrane tears away from cell wall.
Features of plasmolysis:
1. Sap vacuole shrinks.
2. Cytoplasm is pulled away from cell wall.
3. Cell membrane is seen
4. There is a space between cell wall and cell membrane that contains
outer solution as water Importance of osmosis for plants:
5. No change in cell wall. •Absorption of water by root hair cells
•Preventing plants’ wilting
•Provide support by turgidity.
In animal tissues
Animal cells also lose and gain water as a result of osmosis.
However, animal cells do not have a supporting cell wall.
1) If an animal cell is placed into a strong sugar solution, it will lose
water by osmosis, Cytoplasm shrinks and the cell shrivels up.
and cell become crenated.
2) If an animal cell is placed into distilled water , it will gain water
by osmosis and, as it has no cell wall to create turgor pressure,
will continue to do so until the cell membrane is stretched too far
and it bursts.
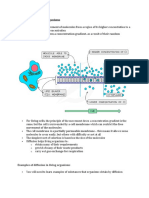
Active Transport
Active transport is the movement of particles through a cell
membrane from a region of lower concentration to a region of
higher concentration using energy from respiration.
Carrier protein:
• Protein found in cell membrane that forces particles against their
concentration gradient.
• They’re specific.
• How ? The solute is taken in the binding site of the carrier. The carrier
molecules rotate using energy to transfer the solute from lower
concentration area to its higher concentration area.
Factors affecting active transport:
1. Number of mitochondria: (increasing mitochondria leads to release more
energy; this causes more active uptake to occur)
2. Concentration of O2: When it increases, the rate of aerobic respiration
increases so more released energy is produced and fast active uptake
occurs.
3. Number of carrier proteins: This increase the rate of active transport.
Active transport works by using carrier proteins embedded in the cell
membrane to pick up specific molecules and take them through the cell
membrane against their concentration gradient:
1. Substance combines with carrier protein molecule in the cell membrane
2. Carrier transports substances across membrane using energy from
respiration to give them the kinetic energy needed to change shape and
move the substance through the cell membrane
3. Substance released into cell
The differences between uptake of water and uptake of minerals
by the root hair cells!
•Uptake of water takes place by the process of osmosis which is a
passive process while uptake of minerals takes place by the process
of active uptake which is an active process.
•In uptake of water, the molecules of water move from regions of
their higher concentration (potential), while in uptake of minerals
the molecules move from regions of their lower concentrations to
regions of their higher concentrations (against their concentration
gradient).
Osmosis Experiments
The most common osmosis practical involves cutting cylinders of potato and placing
them into distilled water and sucrose solutions of increasing concentration.
The potato cylinders are weighed before placing into the solutions.
They are left in the solutions for 20 – 30 minutes and then removed, dried to remove
excess liquid and reweighed.
You might also like
- Module 05 - Macros 1 Rev 03Document14 pagesModule 05 - Macros 1 Rev 03ercanpekNo ratings yet
- ZF ADM 2: Automatic Drive-Train Management: All-Wheel Drive Systems Business Unit Special Driveline TechnologyDocument11 pagesZF ADM 2: Automatic Drive-Train Management: All-Wheel Drive Systems Business Unit Special Driveline TechnologylatNo ratings yet
- Bio OL Chapter 3 & 4Document9 pagesBio OL Chapter 3 & 4zuhra123coolNo ratings yet
- 3 Movement Into & Out of CellsDocument4 pages3 Movement Into & Out of CellsmeerzasarahNo ratings yet
- Bio NotasDocument34 pagesBio NotasDhuhaa YusufNo ratings yet
- Movement in and Out of Cells - NOTESDocument5 pagesMovement in and Out of Cells - NOTESAnonymousNo ratings yet
- Movement Into and Out of Cells Objectives:3.1Document12 pagesMovement Into and Out of Cells Objectives:3.1Army ForeverNo ratings yet
- Biology Info Sheet 18.11.23Document5 pagesBiology Info Sheet 18.11.23jhoyvanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Movement in and Out of CellsDocument6 pagesChapter 3 Movement in and Out of CellsWezu heavenNo ratings yet
- Movement in and Out of Cells NotesDocument9 pagesMovement in and Out of Cells Notesmanarehab35No ratings yet
- MOvement in and Out of Cells - Osmosis & Active TransportDocument4 pagesMOvement in and Out of Cells - Osmosis & Active TransportTshepo O MotsemmeNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 BioDocument13 pagesGrade 9 BioMohammad Hamza AwanNo ratings yet
- 2 D Movement in and Out of CellsDocument39 pages2 D Movement in and Out of Cellsyippee.ndi13No ratings yet
- CELL PHYSIOLOGY@starDocument6 pagesCELL PHYSIOLOGY@starDENIS KIPKOSGEINo ratings yet
- Movement Into and Out of CellsDocument12 pagesMovement Into and Out of Cellsf8sdh6xvzyNo ratings yet
- Diffusion Diffusion in Living Organisms: Diffusion Across The Cell MembraneDocument11 pagesDiffusion Diffusion in Living Organisms: Diffusion Across The Cell MembraneRahil BhavanNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 3diffusion in Living OrganismsDocument10 pagesChapter - 3diffusion in Living OrganismsBoney StephenNo ratings yet
- 3 - Movement in and Out of CellsDocument22 pages3 - Movement in and Out of CellsRashed Nada100% (1)
- 04 NotesDocument6 pages04 NotesAirus SamaNo ratings yet
- Movement in and Out of CellsDocument10 pagesMovement in and Out of CellsarhampracticeNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Biology Chapter 3: Movement in & Out of CellsDocument7 pagesIGCSE Biology Chapter 3: Movement in & Out of CellsNabil Ahmed100% (1)
- Movement in and Out of CellDocument6 pagesMovement in and Out of CellMahamudul HassanNo ratings yet
- Diffusion: AlveoliDocument5 pagesDiffusion: Alveoliaby251188No ratings yet
- Movement Into and Out of CellsDocument9 pagesMovement Into and Out of CellsMuhammad Ahmad NoorNo ratings yet
- 2.1.5 Biology Ocr ADocument5 pages2.1.5 Biology Ocr AFatima AfifiNo ratings yet
- Movement Across The Cell MembraneDocument3 pagesMovement Across The Cell MembraneUmi Zaheera AzharNo ratings yet
- Absorption by RootsDocument7 pagesAbsorption by RootsSaswatNo ratings yet
- Movement in and Out of CellsDocument40 pagesMovement in and Out of CellslubaajamesNo ratings yet
- 4.3 Modes of Absorption and Conduction of WaterDocument60 pages4.3 Modes of Absorption and Conduction of WaterankurbiologyNo ratings yet
- Absorption by Roots - Summary NotesDocument5 pagesAbsorption by Roots - Summary NotesSanjayNo ratings yet
- Bio Exchange of MaterialsDocument12 pagesBio Exchange of Materials3.4 (2022) LAU JING XUAN DESTINEENo ratings yet
- AkdogDocument10 pagesAkdognorhain4.aNo ratings yet
- Cell and Its EnvironmentDocument13 pagesCell and Its EnvironmentAgim OnyekaNo ratings yet
- Transport Mind MapDocument49 pagesTransport Mind MapMiryaNo ratings yet
- Movement in and Out of CellsDocument10 pagesMovement in and Out of CellsMoni VillalbaNo ratings yet
- Biological ProcessesDocument2 pagesBiological ProcessesIsra OmerNo ratings yet
- CH 3 Movement in and Out of The CellDocument10 pagesCH 3 Movement in and Out of The CellAmal HassanNo ratings yet
- 3.movement in & Out of Cells PDFDocument3 pages3.movement in & Out of Cells PDFAntrika YadavNo ratings yet
- Ch-3 Movement Into & Out of CellDocument27 pagesCh-3 Movement Into & Out of CellHaziq KhanNo ratings yet
- Cells and Its Environment Ss1 NoteDocument14 pagesCells and Its Environment Ss1 NoteEllaNo ratings yet
- Movement in and OutDocument35 pagesMovement in and OutzefanyaNo ratings yet
- 2 2 OsmosisDocument25 pages2 2 OsmosisAyah FNo ratings yet
- Movement in and Out of CellsDocument25 pagesMovement in and Out of Cellsmajanga johnNo ratings yet
- Bios - Transport of MaterialDocument46 pagesBios - Transport of MaterialNeseriani AndersonNo ratings yet
- Movement of MoleculesDocument16 pagesMovement of MoleculeslibanNo ratings yet
- Cell TransportDocument19 pagesCell TransportOctavio ManciniNo ratings yet
- Cell Classix Notes Session2 Made by Purnima SharmaDocument4 pagesCell Classix Notes Session2 Made by Purnima Sharmajeetjyoti787No ratings yet
- Week 6 Cell MembraneDocument23 pagesWeek 6 Cell Membranesabeera.ahmadNo ratings yet
- Movement in and Out of CellsDocument2 pagesMovement in and Out of CellsMandla RebirthNo ratings yet
- Absorption by RootsDocument3 pagesAbsorption by Rootsthe lillyNo ratings yet
- REVISION NOTES - B2.2MovementInAndOutOfTheCellDocument4 pagesREVISION NOTES - B2.2MovementInAndOutOfTheCellDavé TranNo ratings yet
- Bio CH 3Document15 pagesBio CH 3SourabhiNo ratings yet
- MOVEMENT IN & OUT OF CELLS - Ch.3Document48 pagesMOVEMENT IN & OUT OF CELLS - Ch.3Yassin Al fekyNo ratings yet
- 6 OsmosisDocument3 pages6 OsmosisQuino AmarelaNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two ThreeDocument50 pagesChapter Two Threerue pattinsonNo ratings yet
- Diffusion & Osmosis PDFDocument18 pagesDiffusion & Osmosis PDFmapanga2807No ratings yet
- Cellular Transport PowerpointDocument50 pagesCellular Transport PowerpointPortia EgkenNo ratings yet
- Cell TransportDocument27 pagesCell TransportAnne HidalgoNo ratings yet
- B2.2 Revision Notes Zzsc27Document2 pagesB2.2 Revision Notes Zzsc27GwendaNo ratings yet
- Movement in and Out of Cells 1Document10 pagesMovement in and Out of Cells 1saadNo ratings yet
- Cell PhysiologyDocument12 pagesCell PhysiologyJaseme OtoyoNo ratings yet
- Ch12 OL SummaryDocument47 pagesCh12 OL Summaryzuhra123coolNo ratings yet
- Pale Pink and Blue Brushstrokes Daily PlannerDocument2 pagesPale Pink and Blue Brushstrokes Daily Plannerzuhra123coolNo ratings yet
- Human Nutrition Lesson SummaryDocument19 pagesHuman Nutrition Lesson Summaryzuhra123coolNo ratings yet
- WavessssDocument1 pageWavesssszuhra123coolNo ratings yet
- Bio OL Chapter 3 & 4Document9 pagesBio OL Chapter 3 & 4zuhra123coolNo ratings yet
- Assistants API in OpenAI-1Document35 pagesAssistants API in OpenAI-1Yussuf AbdirizakNo ratings yet
- 3511-A4-3 Iss1 Deck Plate Cut Out Mk2020S BinnacleDocument1 page3511-A4-3 Iss1 Deck Plate Cut Out Mk2020S BinnacleyanuNo ratings yet
- Control Tutorials For MATLAB and Simulink - Suspension - Simulink ControlDocument1 pageControl Tutorials For MATLAB and Simulink - Suspension - Simulink ControlMohamed Amine ZouhriNo ratings yet
- 00-Different SIEMENS GIS TypesDocument44 pages00-Different SIEMENS GIS TypesPélagie DAH SERETENONNo ratings yet
- Mus 105 HandoutsDocument91 pagesMus 105 HandoutsPablo Gambaccini100% (1)
- Wa0004 PDFDocument2 pagesWa0004 PDFAli MansoorNo ratings yet
- Incorporating Artificial Intelligence in ShoppingDocument6 pagesIncorporating Artificial Intelligence in ShoppingGaby HayekNo ratings yet
- GeopolymerDocument20 pagesGeopolymerAhmed TahaNo ratings yet
- Statistics and Probability W2Document15 pagesStatistics and Probability W2Juhan BisonNo ratings yet
- Intensity ModulationDocument3 pagesIntensity Modulationanon-323096100% (1)
- GC PresentationDocument9 pagesGC PresentationSomnath BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- ρ r r Cov (X,Y) V (x) .V (Y) X X) (Y Y) X X n Y Y: xy xyDocument13 pagesρ r r Cov (X,Y) V (x) .V (Y) X X) (Y Y) X X n Y Y: xy xyStatistics and EntertainmentNo ratings yet
- United States Patent: CarverDocument4 pagesUnited States Patent: CarverwewewewNo ratings yet
- Die Casting: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument6 pagesDie Casting: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediagodseNo ratings yet
- Homework 1Document10 pagesHomework 1شمس صبيح عبد الرحيمNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Computer MCQsDocument5 pagesIntroduction To Computer MCQsNoor KhanNo ratings yet
- MuJava Supporting DocumentationDocument22 pagesMuJava Supporting DocumentationKhushboo KhannaNo ratings yet
- Notes On SetsDocument8 pagesNotes On SetsJpricarioNo ratings yet
- LCM HCFDocument3 pagesLCM HCFtejareddyNo ratings yet
- Rman DocumentDocument11 pagesRman Documentsantababu100% (2)
- Sheet Pile Calc Sheet - 2 (Propped Cantiliver) - REV1Document5 pagesSheet Pile Calc Sheet - 2 (Propped Cantiliver) - REV1channajayamangalaNo ratings yet
- Testing The Software With X-Ray GlassesDocument19 pagesTesting The Software With X-Ray Glassesmuhammad umairNo ratings yet
- Average Mcqs CssDocument6 pagesAverage Mcqs CssHuria MalikNo ratings yet
- Points, Pixels, and Gray Levels: Digitizing Image Data: James B. PawleyDocument22 pagesPoints, Pixels, and Gray Levels: Digitizing Image Data: James B. PawleyÖner AyhanNo ratings yet
- IOR & EOR in Tight Reservoirs - BakkenDocument47 pagesIOR & EOR in Tight Reservoirs - Bakkennitin lahkarNo ratings yet
- Enqueue and Dequeue Function ModuleDocument16 pagesEnqueue and Dequeue Function ModulePeng Qiong LuNo ratings yet
- IA Vector Calculus Lecture Notes 2000 (Cambridge)Document139 pagesIA Vector Calculus Lecture Notes 2000 (Cambridge)ucaptd3No ratings yet
- Sitrans RD200 Manual - 20180911 102347Document106 pagesSitrans RD200 Manual - 20180911 102347Alvaro S. CáceresNo ratings yet