Professional Documents
Culture Documents
9.redox Reaction
9.redox Reaction
Uploaded by
mansilamba1006Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
9.redox Reaction
9.redox Reaction
Uploaded by
mansilamba1006Copyright:
Available Formats
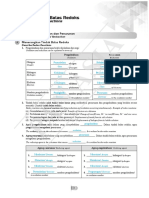
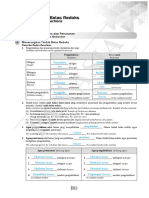
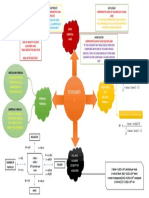
PHYSICS
OXIDISING AGENT
OXIDATION BALANCING OF
REDOX REACTIONS
(OXIDANTS):
NUMBER REDOX REACTION
WALLAH
A reagent which
can increase
RULES TO ASSIGN OXIDATION NUMBER the oxidation
1) Identify oxidation and reduction
1) Oxidation number of an element in free elemental number.
REDUCING AGENT 2) Make total increase and total decrease
state or Uncombined state zera
(REDUCTANTS): in O.N equal
2) In polyatomic ion, the algebraic sum of all the
oxidation numbers of atoms of the ion must equal OXIDATION: A reagent which REDOX REACTIONS: 3) Balance atoms except O & H
the charge on the ion Increase in the can decrease Reactions which 4)
the oxidation ACIDIC BASIC
3) The oxidation number of oxygen in most oxidation number involve change
number. Balance Balance
in oxidation number
PHYSICS
of the compounds is -2
In peroxides -1 - Oxygen with H2O - Charge with OH-
REDUCTION: of the
In superoxides —1/2
In O2 F2 +1 Decrease in the interacting species - Hydrogen with H+ - Oxygen with H2O
In OF2 +2 oxidation number
4) Oxidation number of hydrogen is +1 in
most of its compounds(In metal hydrides -1)
5) Oxidation number of fluorine is always -1 in its
compounds
6) Alkali metals have oxidation number +1 and
alkaline earth metals have oxidation number +2 always
in its compounds
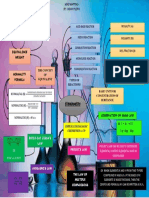
REDOX REACTION
7) The algebraic sum of the oxidation number of all
the atoms in a compound must be zero. TYPES OF REDOX REACTIONS
WALLAH
>
+1 x -2
KMnO4 1 + x + 4x(-2) = 0 x = +7
DECOMPOSITION REACTION DISPLACEMENT REACTION DISPROPORTIONATION REACTIONS
COMBINATION REACTION
Reaction leads to the breakdown of a An ion (or an atom) in a compound In a disproportionation reaction an element
POINTS TO A redox reaction in the form
compound into two or more components is replaced by an ion (or an atom) of
in one oxidation state is simultaneously
REMEMBER A+B→C
at least one of which must be in the another element.
oxidised and reduced.
Either A and B or both A and B must be in elemental state. X + YZ → XZ + Y
It always contains an element that can exist
the elemental form for such a reaction to be eg: H2O → H2 + O2
Fe3O4 in at least three oxidation states.
Carbon suboxide CaOCl2 a redox reaction.
+2 O +2 +2 +3 +1 -1 eg: 2H2O2 → 2H2O + O2
O = C = C = C = O FeO. Fe2O3 Ca(OCl)Cl eg: H2 + Cl2 → 2HCl
Comproportionation reaction:
CrO5 Tribromooctaoxide
A reaction in which an element in a
-2
O
higher oxidation state reacts with the
-1 O O O
-1
O same element in a lower oxidation state to
= =
= =
= =
O +6 +4 +6
O= Br Br =O
Cr
Br
give the element in an intermediate
O
-1
+6 O-1 O O O oxidation state
METAL NON-METAL eg: Pb + PbO2 + 2H2SO4 → 2PbSO4 + 2H2O
DISPLACEMENT DISPLACEMENT
Tetrathionate ion A metal in a compound can be Non-metal in a compound can
O O
Highest O.S— Undergoes Reduction—Oxidising agent displaced by another metal in be displaced by a metal or a
-
O S
+5 O
S
O
S S
+5
O
- the uncombined state. non-metal
Lowest O.S — Undergoes Oxidation—Reducing agent eg: CuSO4 + Zn → Cu + ZnSO4 eg: Zn + H2SO4 → ZnSO4 + H2
O O
Intermediate O.S — Oxidation & Reduction Na + H2O → NaOH + H2
—Oxidising Agent & Reducing Agent
https://t.me/neetwallahpw
You might also like
- Manual Guru Modul A+ Kimia TG 5Document174 pagesManual Guru Modul A+ Kimia TG 5Salina Idris63% (16)
- Amico Pricebook 2018 PDFDocument28 pagesAmico Pricebook 2018 PDFCarlos Guzman CorreaNo ratings yet
- Mba - Banking and Finance: A Work Integrated Learning ProgramDocument6 pagesMba - Banking and Finance: A Work Integrated Learning ProgramPreetam SharmaNo ratings yet
- Observational Report ON: Cardiac Catheterization LaboratoryDocument12 pagesObservational Report ON: Cardiac Catheterization LaboratoryRumela Chakraborty100% (3)
- Security Management Standard - Physical Asset Protection ANSI - ASIS PAP AMERICAN NATIONAL STANDARD - 1 - 部分1Document20 pagesSecurity Management Standard - Physical Asset Protection ANSI - ASIS PAP AMERICAN NATIONAL STANDARD - 1 - 部分1安靖50% (2)
- Basic Acivalent Numbers of Oxidation: EquationDocument1 pageBasic Acivalent Numbers of Oxidation: Equationkrisna divayana105No ratings yet
- REDOXDocument1 pageREDOXeiyda_idrisNo ratings yet
- Class10 Science Notes Chapter1Document6 pagesClass10 Science Notes Chapter1Ganesh Jaishi100% (1)
- Redox Reaction NotesDocument64 pagesRedox Reaction Notesanannya kamathNo ratings yet
- RatesDocument7 pagesRatescwjhgvq964No ratings yet
- Chemical Reactions and EquationsDocument8 pagesChemical Reactions and EquationsDog100% (1)
- Unit 4, Pharmaceutical Analysis, B Pharmacy 1st Sem, Carewell PharmaDocument8 pagesUnit 4, Pharmaceutical Analysis, B Pharmacy 1st Sem, Carewell Pharmavenkat ramanaNo ratings yet
- Interactive Nitrogen Cycle Printable Nitrogen CycleDocument31 pagesInteractive Nitrogen Cycle Printable Nitrogen CycleKevin SanjayaNo ratings yet
- Sir Ica Secc Ref Rev0Document1 pageSir Ica Secc Ref Rev0victorlizcanoNo ratings yet
- Chem 1011Document4 pagesChem 1011Arfa Ali KhanNo ratings yet
- Archivetemp01 Modul A + Kimia Tg5 - Bab 1Document54 pagesArchivetemp01 Modul A + Kimia Tg5 - Bab 1DOROTHY LING YU CHANG Moe0% (1)
- Mega Galvanic Cell 2023Document284 pagesMega Galvanic Cell 2023sibongilesithole983No ratings yet
- Práctica No. 3 CorrosiónDocument18 pagesPráctica No. 3 CorrosiónarbizudanielNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Science Notes - Sa 1 & Sa 2Document132 pagesClass 10 Science Notes - Sa 1 & Sa 2aryan singh100% (1)
- Chm131 - Chapter 4Document37 pagesChm131 - Chapter 4arissa 0503No ratings yet
- Presentation On CmsDocument14 pagesPresentation On Cmsjanu0% (1)
- Principles of N2-PSA: Adsorption Volume by TimeDocument14 pagesPrinciples of N2-PSA: Adsorption Volume by TimeAnonymous KFR3kfkNo ratings yet
- Unit 11 - Redox Titrations - Subjects 0Document79 pagesUnit 11 - Redox Titrations - Subjects 0Siti AmirahNo ratings yet
- Sci 10Document134 pagesSci 10Prabha gNo ratings yet
- An Overview of The Production and Use of Ammonia in NSR + SCR CoupledDocument11 pagesAn Overview of The Production and Use of Ammonia in NSR + SCR CoupledCicero LimaNo ratings yet
- Mind Map Stoikiometri 1Document1 pageMind Map Stoikiometri 1krisna divayana1050% (1)
- Mind Map Stoikiometri 1Document1 pageMind Map Stoikiometri 1krisna divayana105100% (1)
- E. Poster 23017002 IntanDocument1 pageE. Poster 23017002 IntannatayaNo ratings yet
- Equivalence Weight: Boyle-Gay Lussa'S LAWDocument1 pageEquivalence Weight: Boyle-Gay Lussa'S LAWKadek Indah PuspaNo ratings yet
- 5-Post Combustion Methods For Control of NOx EmissionsDocument16 pages5-Post Combustion Methods For Control of NOx EmissionsNojus DekerisNo ratings yet
- Amide BondFormation Via One-Pot Nitrone in SituFormationDocument8 pagesAmide BondFormation Via One-Pot Nitrone in SituFormationvarnish-gearbox-0fNo ratings yet
- Oxidation and ReductionDocument4 pagesOxidation and Reductionmartinmbondjo062No ratings yet
- Selective Catalytic Reduction of Nox: Kushagra AbhishekDocument21 pagesSelective Catalytic Reduction of Nox: Kushagra AbhishekKushagra AbhishekNo ratings yet
- 12 Modul of Pahang For RedoxDocument37 pages12 Modul of Pahang For RedoxkhayranizamNo ratings yet
- 08 Ithink Soalan Bab 7Document6 pages08 Ithink Soalan Bab 7nurulNo ratings yet
- Students Copy Engr1003 Midterms Week 3 LectureDocument27 pagesStudents Copy Engr1003 Midterms Week 3 Lecturecelinewinchester7No ratings yet
- 3B Reactivity of Metals Edrolo Study NotesDocument25 pages3B Reactivity of Metals Edrolo Study NotesMr FiddleNo ratings yet
- Reaction Areas in AodDocument4 pagesReaction Areas in AodPrakash MishraNo ratings yet
- Week 8 - Redox ReactionDocument4 pagesWeek 8 - Redox ReactionThanni AkanbiNo ratings yet
- Redox Reactions and Electrochemistry: JEE SyllabusDocument8 pagesRedox Reactions and Electrochemistry: JEE SyllabusIhtisham Ul HaqNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbons Nitesh Devnani 2Document9 pagesHydrocarbons Nitesh Devnani 2nandkishorjadhav673No ratings yet
- #Ametek Sulfur Recovery AnalyzersDocument4 pages#Ametek Sulfur Recovery AnalyzersCyrix.OneNo ratings yet
- Aging On Lees Best Off-01-1Document16 pagesAging On Lees Best Off-01-1At YugovicNo ratings yet
- RPT Kimia F5Document28 pagesRPT Kimia F5NOR AIDA BINTI HAMIDON KPM-GuruNo ratings yet
- Staged Low Nox Combustion Systems For Coal Fired Boilers and CorrosionDocument9 pagesStaged Low Nox Combustion Systems For Coal Fired Boilers and CorrosionvyshnavkumarNo ratings yet
- Biological Nutrient Removal: Where We Have Been, Where We Are Going? James L. BarnardDocument25 pagesBiological Nutrient Removal: Where We Have Been, Where We Are Going? James L. Barnardjvan migvelNo ratings yet
- ICU One Pager HypoxemiaDocument1 pageICU One Pager HypoxemiaLis Borda MuñozNo ratings yet
- AD-036916 - Refractory Repairs and Terminations - Saudi AramcoDocument1 pageAD-036916 - Refractory Repairs and Terminations - Saudi AramcoAkhil GeorgeNo ratings yet
- HORIBA Emission Monitoring Solutions For Power PlantsDocument1 pageHORIBA Emission Monitoring Solutions For Power PlantsmrafigNo ratings yet
- 07 EnvironmentDocument14 pages07 EnvironmentAmr MokhtarNo ratings yet
- Term 3 Schemes Yr 10 ChemDocument6 pagesTerm 3 Schemes Yr 10 ChemMs Ndung'u PaulineNo ratings yet
- O2 S&D FrameworkDocument1 pageO2 S&D Frameworkmichelle chenNo ratings yet
- Effect of Formaldehyde in Selective Catalytic Reduction of NOx by Ammonia (NH3 SCR) On A Commercial V2O5 WO3/TiO2 Catalyst Under Model ConditionsDocument9 pagesEffect of Formaldehyde in Selective Catalytic Reduction of NOx by Ammonia (NH3 SCR) On A Commercial V2O5 WO3/TiO2 Catalyst Under Model Conditionsadam.zandaniNo ratings yet
- Caton CanJChemEng 73 345-350 1995Document6 pagesCaton CanJChemEng 73 345-350 1995András Szaki SzanthofferNo ratings yet
- RPT Kimia Ting 5 2021Document45 pagesRPT Kimia Ting 5 2021Shafeeqah FadzilNo ratings yet
- Master Plan of Chemistry Versi 1Document1 pageMaster Plan of Chemistry Versi 1bensudinNo ratings yet
- Xi - STD (2M & 3M) - 1Document14 pagesXi - STD (2M & 3M) - 1Prasanth PrasanthNo ratings yet
- Aa 220619 180412Document1 pageAa 220619 180412KeasNo ratings yet
- Phytoremediation 150123100305 Conversion Gate02Document49 pagesPhytoremediation 150123100305 Conversion Gate02Kumar MadhuNo ratings yet
- Reading Passage 1Document13 pagesReading Passage 1Anh Lê Nguyễn KiềuNo ratings yet
- Did You Know?: At&T Fiber InstallationDocument4 pagesDid You Know?: At&T Fiber InstallationAaron SNo ratings yet
- What Algorithms Does ESP Use To Protect Information?Document8 pagesWhat Algorithms Does ESP Use To Protect Information?Vedant popleNo ratings yet
- Product Sheet Damen FCS 5009Document2 pagesProduct Sheet Damen FCS 5009Juan ResendizNo ratings yet
- مذكرة عن السياحة تلمسانDocument23 pagesمذكرة عن السياحة تلمسانdameneyoucef64No ratings yet
- Exclusive Cayenne PorcheDocument22 pagesExclusive Cayenne PorcheRit100% (1)
- Table SettingDocument4 pagesTable SettingBianca FormantesNo ratings yet
- Plato and The Analogy of The ShipDocument1 pagePlato and The Analogy of The ShipEmily LeahNo ratings yet
- Carotenoids: Actual Knowledge On Food Sources, Intakes, Stability and Bioavailability and Their Protective Role in HumansDocument25 pagesCarotenoids: Actual Knowledge On Food Sources, Intakes, Stability and Bioavailability and Their Protective Role in HumansGalinaNo ratings yet
- Development of Atomic TheoryDocument28 pagesDevelopment of Atomic TheoryRenelynn SiloNo ratings yet
- (MY) Malaysia Shopee International PlatformDocument29 pages(MY) Malaysia Shopee International PlatformalexanderNo ratings yet
- Rosary Guide Revised With Intention Per MysteryDocument9 pagesRosary Guide Revised With Intention Per MysteryPatricia Anne Manzo ModinaNo ratings yet
- Mail Merge Feature in Word 2010Document2 pagesMail Merge Feature in Word 2010Gitanjali NayakNo ratings yet
- Courtesy Car AppDocument1 pageCourtesy Car Appadga rwerweNo ratings yet
- Activity 1.1 PhotosynthesisDocument2 pagesActivity 1.1 PhotosynthesisRAMIL BAUTISTANo ratings yet
- LIT 1 FOOTNOTE TO YOUTH With ASSIGNMENTDocument6 pagesLIT 1 FOOTNOTE TO YOUTH With ASSIGNMENTAiel Legaspi EstepaNo ratings yet
- FGD GypsumDocument15 pagesFGD GypsumAnonymous 0vtkoS155No ratings yet
- Understanding Community MediaDocument80 pagesUnderstanding Community MediaJuan Ramos MartínNo ratings yet
- ZXHN F660 V9.2 Datasheet - 2021Document2 pagesZXHN F660 V9.2 Datasheet - 2021Robert LaureanoNo ratings yet
- Case2 Starbucks' MissionDocument13 pagesCase2 Starbucks' Missionsehrish iqbalNo ratings yet
- Antibiotic Classification Mechanism - Sheet1Document2 pagesAntibiotic Classification Mechanism - Sheet1api-329501044No ratings yet
- WFO Global Offshore Wind Report 2022Document10 pagesWFO Global Offshore Wind Report 2022李香浓No ratings yet
- Homeopathy in Dermatology PDFDocument5 pagesHomeopathy in Dermatology PDFlndsNo ratings yet
- Esri Books PDFDocument1 pageEsri Books PDFAnonymous cC2VeA9MBNo ratings yet
- Xenos HunterDocument4 pagesXenos HunterBillthe Something100% (1)
- Regular: Akkurat LL AraDocument23 pagesRegular: Akkurat LL ArablackinNo ratings yet