Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1 Musculoskeletal Mind Map
1 Musculoskeletal Mind Map
Uploaded by
vn6jydy5gk0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views1 pageThe skeletal and muscular systems work together to enable movement of the body. The skeleton provides structure, protection, movement, and blood production. There are three main types of joints in the body - fixed/immovable, slightly movable, and freely movable - which connect bones and allow different degrees of movement. Muscles are attached to bones via tendons and contract to create movement. They work in pairs of agonists, which contract to create movement, and antagonists, which relax to allow movement.
Original Description:
Original Title
1%20Musculoskeletal%20mind%20map
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe skeletal and muscular systems work together to enable movement of the body. The skeleton provides structure, protection, movement, and blood production. There are three main types of joints in the body - fixed/immovable, slightly movable, and freely movable - which connect bones and allow different degrees of movement. Muscles are attached to bones via tendons and contract to create movement. They work in pairs of agonists, which contract to create movement, and antagonists, which relax to allow movement.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views1 page1 Musculoskeletal Mind Map
1 Musculoskeletal Mind Map
Uploaded by
vn6jydy5gkThe skeletal and muscular systems work together to enable movement of the body. The skeleton provides structure, protection, movement, and blood production. There are three main types of joints in the body - fixed/immovable, slightly movable, and freely movable - which connect bones and allow different degrees of movement. Muscles are attached to bones via tendons and contract to create movement. They work in pairs of agonists, which contract to create movement, and antagonists, which relax to allow movement.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
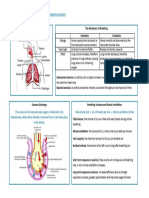
IGCSE PE Chapter 1 – Skeletal and Muscular System
The Skeleton Joint Types, Structure and Formation Muscles
A point in the body where two or more bones are joined in a
way that permits movement
Fixed or Bones cannot move at all, Between plates
immoveable joined by fibrous tissue of the cranium
Irregular Flat (Fibrous)
Slightly Small amount of Between
moveable movement, linked by vertebrae
(Cartilaginous) ligaments and cartilage
Freely Greater amount of Ball and socket –
Long moveable movement shoulder & hip
(Synovial)
Hinge – elbow
and knee
Short
Antagonistic Muscle Action
-Shape and support Agonist: the muscle that contracts to create movement
Movement at Joints
-Movement Antagonist: the muscle that relaxes during movement
-Protection
Antagonistic: pairs of muscles work in opposition to
-Blood production
create movement
Muscle Fibre Types Origin: where a muscle joins a stationary bone
Insertion: where a muscle joins a moving bone
Slow twitch (Type I) Fast twitch (Type II)
Contract slowly Contract quickly Isotonic contraction: where muscles change length as
they contract
Produce a little force Produce a large amount of
Concentric contraction: muscle contraction where the
force
High fatigue tolerance Lower fatigue tolerance muscle shortens
(Don’t tire easily) (Tire quickly) Eccentric contraction: muscle contraction where the
Good for endurance Good for strength and muscle lengthens
sports power Isometric contraction: where the muscles contract but
stay the same length
You might also like
- Tennis Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesTennis Lesson Planmanaftergod100% (2)
- D2066 Truck Engine enDocument4 pagesD2066 Truck Engine enDani Nch57% (14)
- The Pilates Mat ExercisesDocument76 pagesThe Pilates Mat ExercisesHeatherKnifer67% (3)
- Mind Map. Skeletal SystemDocument1 pageMind Map. Skeletal SystemMayeliz Urvina50% (2)
- GCSE PE Paper 1 ContentDocument18 pagesGCSE PE Paper 1 Contentshiven.solankiNo ratings yet
- 11.2 Movement: Essential Idea: The Roles ofDocument20 pages11.2 Movement: Essential Idea: The Roles ofReshma DookarranNo ratings yet
- Muscular System Handout Part IIDocument4 pagesMuscular System Handout Part IIDeenaNo ratings yet
- Nelson VCE PEDocument23 pagesNelson VCE PEPNo ratings yet
- Generalities MyologyDocument14 pagesGeneralities MyologyScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Muscles Anatomy-Dr - NdukuiDocument62 pagesMuscles Anatomy-Dr - Ndukuiglenian560No ratings yet
- Reading Assignment 4Document17 pagesReading Assignment 4John Chris LuminangNo ratings yet
- Kinesiology: Chapter 2 (An Introduction To Movement) : DR: Iqra KaramatDocument14 pagesKinesiology: Chapter 2 (An Introduction To Movement) : DR: Iqra KaramatNimra TariqNo ratings yet
- Structure of The BodyDocument7 pagesStructure of The BodyKarina TakemuraNo ratings yet
- Muscular ConsiderationsDocument59 pagesMuscular ConsiderationsThor ManlangitNo ratings yet
- Skeleto-Syste Loco: Muscular Ms and MotionDocument26 pagesSkeleto-Syste Loco: Muscular Ms and MotionmeriiNo ratings yet
- Muscle SystemDocument2 pagesMuscle Systemapi-428138727No ratings yet
- PE Movement Analysis RevisionDocument15 pagesPE Movement Analysis Revisionkunal ramcharunNo ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal System Glossary - AcllDocument3 pagesMusculoskeletal System Glossary - AcllAna Carolina Londoño LopezNo ratings yet
- 1.15 (Surgery) Review of The Musculoskeletal SystemDocument5 pages1.15 (Surgery) Review of The Musculoskeletal SystemLeo Mari Go LimNo ratings yet
- Introduction To MusclesDocument1 pageIntroduction To MusclesMaria Jesus Bustamante MussoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Module - Intro To Basics II - Intro To Skin, Fascia and Muscle - 2020Document14 pagesAnatomy Module - Intro To Basics II - Intro To Skin, Fascia and Muscle - 2020chau418No ratings yet
- Skeletal System - KODocument1 pageSkeletal System - KOGift Munyinda (G-Man)No ratings yet
- 2.1 (B) - Role of Muscles, Ligaments & Tendons inDocument19 pages2.1 (B) - Role of Muscles, Ligaments & Tendons inliefeng81100% (1)
- Anatomi - Olah Raga 1st MeetingDocument79 pagesAnatomi - Olah Raga 1st MeetingR DarmawanNo ratings yet
- Physical EducationDocument3 pagesPhysical EducationLei Yunice NorberteNo ratings yet
- Muscular SystemDocument1 pageMuscular SystemHanin Farhani Binti AhmadNo ratings yet
- Sport Science NotesDocument5 pagesSport Science NotesSpicyChildrenNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Muscular System BrochureDocument2 pagesAnatomy Muscular System Brochureapi-462608096No ratings yet
- Anaphy Reviewer Muscular SystemDocument4 pagesAnaphy Reviewer Muscular SystemJoyce Kathreen Ebio LopezNo ratings yet
- Applications To Functional Anatomy Lecture 2Document13 pagesApplications To Functional Anatomy Lecture 2joshNo ratings yet
- Core 2 Body in Motion 65026f0d1277cDocument61 pagesCore 2 Body in Motion 65026f0d1277careebah.shahbaz1No ratings yet
- Introduction To ANATOMY. Part-IIIDocument42 pagesIntroduction To ANATOMY. Part-IIIHASSET SHIFERAWNo ratings yet
- '18. Movement in humans: What is endoskeleton made up of? 內⾻骼由什麼組成?Document7 pages'18. Movement in humans: What is endoskeleton made up of? 內⾻骼由什麼組成?thanks btNo ratings yet
- ANPH MIDTERMS 1 NOTESpdfDocument5 pagesANPH MIDTERMS 1 NOTESpdfcunanankaye11No ratings yet
- General Anatomy of Muscles: By: Dr. Sana KashifDocument15 pagesGeneral Anatomy of Muscles: By: Dr. Sana KashifUSAMA AHMEDNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Presentation WeeblyDocument85 pagesUnit 1 Presentation Weeblyapi-276945651No ratings yet
- Triathlon Movement and Its Coordination 1PP ColourDocument19 pagesTriathlon Movement and Its Coordination 1PP Colourjshemm1No ratings yet
- CHP 11Document71 pagesCHP 11Sophia YounNo ratings yet
- Modeling of The Musculoskeletal System - 1Document9 pagesModeling of The Musculoskeletal System - 1Shyam PolacondaNo ratings yet
- 316 FinalsDocument21 pages316 FinalsKatherine BautistaNo ratings yet
- TriChapter27 09 Muscular SystemDocument18 pagesTriChapter27 09 Muscular Systembao.nguyenthienadamsNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy Study Guide: Chapter 10: Muscle Tissue and OrganizationDocument5 pagesHuman Anatomy Study Guide: Chapter 10: Muscle Tissue and OrganizationSuperjunior8No ratings yet
- Ana - Joints ClassificationsDocument12 pagesAna - Joints ClassificationsMahmoud hilmyNo ratings yet
- The Skeletal SystemDocument11 pagesThe Skeletal SystemAbhi LiteNo ratings yet
- Proprioceptive SensesDocument2 pagesProprioceptive Senseslawrencedragon4No ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal SystemDocument2 pagesMusculoskeletal SystemJames Wilstar Delicano SandovalNo ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal System. Assessing The MusculoskeletalDocument11 pagesMusculoskeletal System. Assessing The MusculoskeletalLorenz Jude CańeteNo ratings yet
- LECTURE 7 Types of Muscle ContractionDocument3 pagesLECTURE 7 Types of Muscle ContractionAtharva kengarNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Ligaments The Revolutionary Re-Vision of Jaap Van Der Wal 2011 EN Article PDFDocument6 pagesDynamic Ligaments The Revolutionary Re-Vision of Jaap Van Der Wal 2011 EN Article PDFJorge Flores TorresNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 - JointsDocument5 pagesLesson 4 - JointsMuffaddal MustafaNo ratings yet
- Muscular SystemDocument22 pagesMuscular Systembenhassennada44No ratings yet
- JointsDocument11 pagesJointsCelina NassarNo ratings yet
- Locomotion and MovementDocument3 pagesLocomotion and MovementYouTutor PSNo ratings yet
- Types of Muscle ContractionDocument12 pagesTypes of Muscle Contractions_saikalyanNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy & Physiology of Hip JointDocument4 pagesHuman Anatomy & Physiology of Hip JointZed P. EstalillaNo ratings yet
- Behavioral Properties of The Musculotendinous Unit: 1) Extensibility: Ability To Be Stretched or To IncreaseDocument6 pagesBehavioral Properties of The Musculotendinous Unit: 1) Extensibility: Ability To Be Stretched or To IncreasechandanNo ratings yet
- Biomechanics LectureDocument3 pagesBiomechanics LectureOmar OsamaNo ratings yet
- A&P Presentation 20-11-23Document24 pagesA&P Presentation 20-11-23jordanmcmillan04No ratings yet
- Skeletal & Muscular Systems: First Year ScienceDocument15 pagesSkeletal & Muscular Systems: First Year Scienceapi-406307933No ratings yet
- Joints of The Body & Functional Muscle GroupsDocument20 pagesJoints of The Body & Functional Muscle GroupsOmar Ali AyoubkhanNo ratings yet
- Note, Unit 5 Topic 7B, Muscle, Movement and HeartDocument24 pagesNote, Unit 5 Topic 7B, Muscle, Movement and HeartNour AtassiNo ratings yet
- Quick Study Guide To The Muscular SystemDocument8 pagesQuick Study Guide To The Muscular SystemMc Luis Glen AserdanoNo ratings yet
- 5 Elasticities 2Document5 pages5 Elasticities 2vn6jydy5gkNo ratings yet
- 4 ElasticitiesDocument4 pages4 Elasticitiesvn6jydy5gkNo ratings yet
- 3 Circulatory Mind MapDocument1 page3 Circulatory Mind Mapvn6jydy5gkNo ratings yet
- 2 Respiratory Mind MapDocument1 page2 Respiratory Mind Mapvn6jydy5gkNo ratings yet
- FAQ and Often Forgotten Rules: Clan Action Pawn Building Field CardsDocument8 pagesFAQ and Often Forgotten Rules: Clan Action Pawn Building Field CardsDia VargaNo ratings yet
- Hell On Earth - Cardstock Cowboys #02 - Horrors of The Wasted WestDocument8 pagesHell On Earth - Cardstock Cowboys #02 - Horrors of The Wasted WestEdu ConNo ratings yet
- Warmuster Issue 1Document17 pagesWarmuster Issue 1francisco100% (3)
- Afl Round 7 - Friday - Pacific RacingDocument1 pageAfl Round 7 - Friday - Pacific RacingjoanalcarazNo ratings yet
- Life of EminemDocument1 pageLife of EminemTurvashuNo ratings yet
- AconcaguaDocument5 pagesAconcaguaAbiyyu Muhammad HarisNo ratings yet
- IAP Cracker CompatibleDocument591 pagesIAP Cracker Compatiblejamaica46No ratings yet
- Bruford: EnglishDocument6 pagesBruford: EnglishPalos DoseNo ratings yet
- Adult Song DragonDocument4 pagesAdult Song DragonRegual Llegna100% (1)
- Racquet Sports IndustryDocument52 pagesRacquet Sports IndustryLiya DavidovNo ratings yet
- Slides Da Aula - MetroDocument120 pagesSlides Da Aula - MetroElen SilvaNo ratings yet
- LabyrinthDocument1 pageLabyrinthJonathan JanssenNo ratings yet
- !welcome To StonetopDocument1 page!welcome To StonetopSteven GinNo ratings yet
- Carta OrganisasiDocument3 pagesCarta OrganisasiHafizahSyaza Mohd GhazalliNo ratings yet
- Pathfinder Chronicles Extracted Artwork PDFDocument54 pagesPathfinder Chronicles Extracted Artwork PDFZechariah Ho100% (2)
- huong dẫn topic 1.2Document19 pageshuong dẫn topic 1.2Tieu Thi Thanh Thao (FPL DN)100% (1)
- LPL QuizDocument78 pagesLPL QuizGaurav PatowariNo ratings yet
- Myferrari - Purosangue - S0rbunzDocument10 pagesMyferrari - Purosangue - S0rbunzGreggs ShopukNo ratings yet
- Beowulf Study Guide-1Document6 pagesBeowulf Study Guide-1Maykel FalcónNo ratings yet
- M0001D 2019 - Game Design AnalysisDocument49 pagesM0001D 2019 - Game Design Analysiseandmsz100% (1)
- Model Name: GA-B75M-D3V: Revision 2.01Document32 pagesModel Name: GA-B75M-D3V: Revision 2.01leminhtrildbNo ratings yet
- 911700899348all - Result - January-2024Document11 pages911700899348all - Result - January-2024Mahmudul Hassan MehediNo ratings yet
- PLANET FIST v1.0 - SinglesDocument60 pagesPLANET FIST v1.0 - SinglescarlosNo ratings yet
- Parts Catalog of YC6A260-33 (A1016) Diesel EngineDocument73 pagesParts Catalog of YC6A260-33 (A1016) Diesel Enginem h habib m h kassamNo ratings yet
- Cardiology 2: OutlineDocument5 pagesCardiology 2: Outlinevinnie0905No ratings yet
- Dimitri Bertsekas and John N Tsitsiklis - Introduction To ProbabilityDocument6 pagesDimitri Bertsekas and John N Tsitsiklis - Introduction To ProbabilityKAUSHIKNo ratings yet
- AP Physics1 KE and PE WorksheetDocument3 pagesAP Physics1 KE and PE WorksheetTrevor RivardNo ratings yet