Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Decision Making - Stepladder Method
Decision Making - Stepladder Method
Uploaded by
LUCA ANDRADEOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Decision Making - Stepladder Method
Decision Making - Stepladder Method
Uploaded by
LUCA ANDRADECopyright:
Available Formats
DECISION MAKING - STEPLADDER METHOD
Making decisions within a group can often be challenging. When things go
well, they can go very well. However, when things go wrong, you can end
up mired in conflict. Some people may fight for recognition and position,
others may be over-critical or disruptive, while others may sit quietly and
not contribute anything to the overall effort. Because of this, groups can
often spin out of control and make worse decisions than individuals
working on their own.
When this happens, it's easy to see why some people throw their hands up
in frustration and give up. However, when a group works in the right way, it
really WORKS. Groups that function effectively together can outperform
individuals and make much better decisions.
But how do you make your group effective? How do you get all group
members to contribute and inspire one another to create great ideas and
solutions?
The Stepladder Technique is a useful method for encouraging individual
participation in group decision making.
What Is the Stepladder Technique?
The Stepladder Technique is a simple tool that manages how members
enter the decision-making group. Developed by Steven Rogelberg, Janet
Barnes-Farrell and Charles Lowe in 1992, it encourages all members to
contribute on an individual level BEFORE being influenced by anyone else.
This results in a wider variety of ideas, it prevents people from "hiding"
within the group, and it helps people avoid being "stepped on" or
overpowered by stronger, louder group members.
All of this helps the group make better decisions.
How to Use the Tool
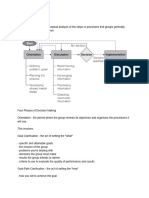
The Stepladder Technique has five basic steps. Here's how it works:
Finding This Article Useful?
You can learn another 53 decision-making skills, like this, by joining the
Mind Tools Club.
Join the Mind Tools Club Today!
Step 1: Before getting together as a group, present the task or problem to
all members. Give everyone sufficient time to think about what needs to be
done and to form their own opinions on how to best accomplish the task or
solve the problem.
Step 2: Form a core group of two members. Have them discuss the
problem.
Step 3: Add a third group member to the core group. The third member
presents ideas to the first two members BEFORE hearing the ideas that have
already been discussed. After all three members have laid out their
solutions and ideas, they discuss their options together.
Step 4: Repeat the same process by adding a fourth member, and so on, to
the group. Allow time for discussion after each additional member has
presented his or her ideas.
Step 5: Reach a final decision only after all members have been brought in
and presented their ideas.
The Stepladder Technique is similar to the Delphi Method, another tool
that's often used in groups to prevent Groupthink and to encourage
participation. While both tools have the same objective, they differ in a few
key ways:
• In the Delphi Method, an objective facilitator or leader manages the
group. In the Stepladder Technique, all members are equal.
• The Delphi Method keeps members anonymous. The facilitator manages
the flow of information, and members may have no idea who else is in
the group. The Stepladder Technique involves face-to-face meetings, so
everyone knows who the other members are.
• The Delphi Method is a lengthy process, while the Stepladder Technique
is much quicker.
• The Delphi Method is often used for major decisions that need input
from a large number of people. The Stepladder Technique works best
with smaller groups that make a wide range of decisions.
Tip:
Groups can begin to lose their effectiveness and ability to make good
quality decisions if they have too many members. Keep your group small –
four to seven team members – to maximize effectiveness.
Key Points
The Stepladder Technique is a step-by-step approach that helps you ensure
that all members of a group participate and are heard. The technique allows
shy, quiet people to present their ideas before other group members can
influence them, and it allows everyone to hear many different viewpoints
before reaching a final decision.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Ul_z4TJmwzs
You might also like
- Teamwork PPT PresentationDocument26 pagesTeamwork PPT PresentationMuhayarHeracles100% (4)
- 5 Stages of Team DevelopmentDocument6 pages5 Stages of Team Developmentaniszar6668100% (1)
- Basic Facilitation Skills: Developing Facilitative LeadershipDocument44 pagesBasic Facilitation Skills: Developing Facilitative LeadershipMasilamani RamasamyNo ratings yet
- SAP Dictionary FrenchDocument747 pagesSAP Dictionary FrenchClaudio Di FrancescoNo ratings yet
- 5 Stages of Group DevelopmentDocument4 pages5 Stages of Group DevelopmentMegala TheviNo ratings yet
- Making Group DecisionsDocument7 pagesMaking Group DecisionsyugalkishorNo ratings yet
- Facilitation 101Document6 pagesFacilitation 101Dilan Türkan YuNo ratings yet
- Group Decision MakingDocument9 pagesGroup Decision MakingmymadhavaNo ratings yet
- Assignment#2: Organizational BehaviourDocument12 pagesAssignment#2: Organizational Behaviouraimma-tur-rehmanNo ratings yet
- Decision - Making StyleDocument29 pagesDecision - Making Stylejme_pescasioNo ratings yet
- Teamwork Module Student Guide: Preparation For This ModuleDocument8 pagesTeamwork Module Student Guide: Preparation For This ModuleRrhh EstNo ratings yet
- Applied Psychology CP-2 - 223377 (Himanshi Lahora) MA Psychology Sem 4Document8 pagesApplied Psychology CP-2 - 223377 (Himanshi Lahora) MA Psychology Sem 4Himanshi LahoraNo ratings yet
- Group FunctionsDocument24 pagesGroup FunctionsVani Madhavi Avasarala100% (1)
- Group Communication: Presented By: Kanika Sood Gundeep Singh KapoorDocument48 pagesGroup Communication: Presented By: Kanika Sood Gundeep Singh KapoorKanika SoodNo ratings yet
- BrainstormingDocument29 pagesBrainstormingAyu MutiaNo ratings yet
- Yasmin - Summary Ch. 10, Techniques, Strategies and Systems of Group ConsultingDocument7 pagesYasmin - Summary Ch. 10, Techniques, Strategies and Systems of Group ConsultingScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Decision Making TechniquesDocument6 pagesDecision Making Techniquesfathima.ahamed1926No ratings yet
- Decision Making ProcessDocument11 pagesDecision Making ProcessDianne MethosNo ratings yet
- Group Counseling ProDocument25 pagesGroup Counseling ProMartus Doulos75% (4)
- WIN SEM (2022-23) FRESHERS STS6001 TH AP2022237000730 Reference Material I 15-Mar-2023 Emotional Intelligence - All ContentDocument17 pagesWIN SEM (2022-23) FRESHERS STS6001 TH AP2022237000730 Reference Material I 15-Mar-2023 Emotional Intelligence - All ContentDendiNo ratings yet
- EXERCISESDocument65 pagesEXERCISESlehsem20006985No ratings yet
- Working With Groups and TeamsDocument38 pagesWorking With Groups and TeamsJasielleNo ratings yet
- 214 Group Dynamics and Human Behavior - CORNITODocument12 pages214 Group Dynamics and Human Behavior - CORNITOMARY ROSE CORNITONo ratings yet
- Group Work GuideDocument6 pagesGroup Work GuideNatasha JamesNo ratings yet
- Group Decision MakingDocument4 pagesGroup Decision MakingwanifaizanNo ratings yet
- Group Techniques: in Decision MakingDocument32 pagesGroup Techniques: in Decision MakingMa Marisa Arbalate100% (1)
- Chapter 9Document30 pagesChapter 9nurfarhanaali0% (1)
- TTT Phase 42 PDFDocument16 pagesTTT Phase 42 PDFakshita ramdasNo ratings yet
- Management of Engineering Projects: TeamworkDocument33 pagesManagement of Engineering Projects: Teamworkavinash_k007No ratings yet
- Nominal Group Technique & BrainstormingDocument16 pagesNominal Group Technique & BrainstormingAjayNo ratings yet
- 07-Group CommunicationDocument114 pages07-Group CommunicationArshad Ali0% (1)
- De BriefingDocument6 pagesDe Briefingjohnsonkkuriakose50% (2)
- AS2 NTKVân FB1200003Document11 pagesAS2 NTKVân FB1200003Jolie NguyễnNo ratings yet
- What Is Brainstorming?Document3 pagesWhat Is Brainstorming?Nerick AducalNo ratings yet
- Team MGMT & Group DynamicsDocument13 pagesTeam MGMT & Group DynamicsAbhinav BansalNo ratings yet
- What Is A TemDocument8 pagesWhat Is A TembantiebduNo ratings yet
- Effective Team DecisionDocument3 pagesEffective Team DecisionMia BogdanovicNo ratings yet
- Defining The ProblemDocument2 pagesDefining The Problemfaraherh amberNo ratings yet
- Nominal Group Technique & BrainstormingDocument20 pagesNominal Group Technique & BrainstormingAjayNo ratings yet
- Stages of Group FormationDocument5 pagesStages of Group FormationPrashant Singh JadonNo ratings yet
- Becoming An Excellent Facilitator: by Adam Fletcher, President, Commonaction ConsultingDocument6 pagesBecoming An Excellent Facilitator: by Adam Fletcher, President, Commonaction ConsultingvaleriaNo ratings yet
- Effective Teamwork: Farrokh Alemi, PH.DDocument16 pagesEffective Teamwork: Farrokh Alemi, PH.DShivam DwivediNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Group Decision MakingDocument22 pagesChapter 3 - Group Decision MakingAzwandiHarryNo ratings yet
- Facilitation The BasicsDocument26 pagesFacilitation The BasicsPoonam NaiduNo ratings yet
- Basic Conversation Method DescriptionDocument4 pagesBasic Conversation Method DescriptionIstiak AhmedNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - Work in A Team EnvironmentDocument6 pagesModule 2 - Work in A Team EnvironmentHenrissa Granado TalanNo ratings yet
- 10 Tips To Improve Your Meeting or CoordinationsDocument7 pages10 Tips To Improve Your Meeting or CoordinationsLynn N DavidNo ratings yet
- Advantages of Group DiscussionDocument8 pagesAdvantages of Group Discussionsmjega50% (2)
- MKTG Team PPT 1 ShannonDocument78 pagesMKTG Team PPT 1 ShannonNoah Gene Del RioNo ratings yet
- TJD Effective Group FacilitationDocument39 pagesTJD Effective Group FacilitationgjabyNo ratings yet
- Final Examination in EDUC 313Document4 pagesFinal Examination in EDUC 313Mark Anthony RagudoNo ratings yet
- Group Work GuidanceDocument5 pagesGroup Work GuidancepooshNo ratings yet
- OB - Groups and TeamsDocument102 pagesOB - Groups and TeamsShraddha RawatNo ratings yet
- Total Quality ManagementDocument65 pagesTotal Quality Managementp ganeshNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 HBODocument37 pagesChapter 7 HBOAlyssa TiadNo ratings yet
- Principle of ManagementDocument14 pagesPrinciple of ManagementKARTHINA A/P C.RAJOO STUDENTNo ratings yet
- Grou D Namics: Whether A TeamDocument4 pagesGrou D Namics: Whether A TeamBryan KingstonNo ratings yet
- Behaviour OptionsDocument57 pagesBehaviour OptionsHarold Dela FuenteNo ratings yet
- Understanding and Improving Group Decision-MakingFrom EverandUnderstanding and Improving Group Decision-MakingNo ratings yet
- Developmental Counseling Form: The Leader's Facts and Observations Prior To The Counseling.)Document3 pagesDevelopmental Counseling Form: The Leader's Facts and Observations Prior To The Counseling.)Anonymous EpKfz0LNo ratings yet
- Tata PowerDocument9 pagesTata PowerAnkita SinghNo ratings yet
- Anhang Amel 55Document12 pagesAnhang Amel 55frankNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Introduction To HTML5Document46 pagesChapter 1 Introduction To HTML5alhinai676No ratings yet
- IMO Test Reports LSADocument12 pagesIMO Test Reports LSAMd AmirulNo ratings yet
- Engine Performance Data at 1500 RPM: B3.9 1 Cummins IncDocument4 pagesEngine Performance Data at 1500 RPM: B3.9 1 Cummins IncJosé CarlosNo ratings yet
- FFT - Constructing A Secure SD-WAN Architecture v6.2 r6Document91 pagesFFT - Constructing A Secure SD-WAN Architecture v6.2 r6Pepito CortizonaNo ratings yet
- Pas Airpack 2 Pi 9046599 en GBDocument8 pagesPas Airpack 2 Pi 9046599 en GBForum PompieriiNo ratings yet
- Benefit of Trunked Radio TechnologyDocument4 pagesBenefit of Trunked Radio TechnologyOrpheo NgadimanNo ratings yet
- IMC 2014 Brochure JB 1Document16 pagesIMC 2014 Brochure JB 1tristanmaharajNo ratings yet
- Patricia Eldridge 4.19.23Document3 pagesPatricia Eldridge 4.19.23abhi kumarNo ratings yet
- Payment Advice: Labour Solutions Australia PTY LTDDocument1 pagePayment Advice: Labour Solutions Australia PTY LTDZulfiqar AliNo ratings yet
- SCHLETTER Solar Mounting Systems Roof EN WebDocument19 pagesSCHLETTER Solar Mounting Systems Roof EN WebcharlesbenwariNo ratings yet
- Surface Defects in Steel ProductsDocument41 pagesSurface Defects in Steel ProductsShilaj PNo ratings yet
- Air France v. CA (1983)Document10 pagesAir France v. CA (1983)8111 aaa 1118No ratings yet
- BOQ For Bought Out Items (Purified Water) PDFDocument1 pageBOQ For Bought Out Items (Purified Water) PDFsppatilNo ratings yet
- Economics: I Brrvewy EDocument712 pagesEconomics: I Brrvewy EVania GomesNo ratings yet
- Wine Marketing PlanDocument17 pagesWine Marketing PlanAdib M Basbous100% (2)
- Christian Andrei Abiad BSCE-1Document2 pagesChristian Andrei Abiad BSCE-1Eddie GuiribaNo ratings yet
- C5G Tech Specs enDocument65 pagesC5G Tech Specs enСања БанковићNo ratings yet
- Structure Gad DrawingsDocument56 pagesStructure Gad Drawingsdheeraj sehgalNo ratings yet
- X40235D ChinookCompact ENDocument60 pagesX40235D ChinookCompact ENMartin Renner WallaceNo ratings yet
- Pplication ORM: Ersonal EtailsDocument5 pagesPplication ORM: Ersonal EtailsAnaz KalliyathNo ratings yet
- S TR GEN STC (Spec Tech Requ's) (Rev.2 2009) - LampsDocument10 pagesS TR GEN STC (Spec Tech Requ's) (Rev.2 2009) - LampsRaghu NathNo ratings yet
- Doing Business in IndiaDocument20 pagesDoing Business in IndiarasheedNo ratings yet
- Management of Cybersecurity in Medical Devices - Diec 2020Document13 pagesManagement of Cybersecurity in Medical Devices - Diec 2020Haris Hamidovic100% (1)
- Vinyl Ester Epovia Data SheetDocument32 pagesVinyl Ester Epovia Data SheetAmjad MehmoodNo ratings yet
- 2nd Year Civil Engineering Course Detail of IOE, TU NepalDocument20 pages2nd Year Civil Engineering Course Detail of IOE, TU NepalSunil Kharbuja100% (1)
- Gujarat Technological University: W.E.F. AY 2018-19Document3 pagesGujarat Technological University: W.E.F. AY 2018-19Bhavesh PatelNo ratings yet