Professional Documents
Culture Documents
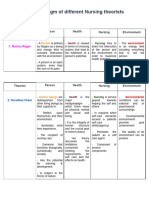
Sister Cakista Roy's Health Adaptation Model
Sister Cakista Roy's Health Adaptation Model
Uploaded by
ysabel.mendozaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Sister Cakista Roy's Health Adaptation Model
Sister Cakista Roy's Health Adaptation Model
Uploaded by
ysabel.mendozaCopyright:
Available Formats
i.
biography
ii. educational background
iii. major concepts
iv. metaparadigm
vi. film showing
Calista Roy's
adaptation model.
MANALASTAS | MARASIGAN | MENDOZA
biography.
— sr. calista roy
Sr. Calista Roy
Born on October 14, 1939
Birthplace: Los Angeles California
A member of the sisters of Saint
Joseph of Carondelet
“God is intimately revealed in the diversity of creation and is the common destiny
of creation; persons use human creative abilities of awareness, enlightenment,
and faith; and persons are accountable for the process of deriving, sustaining,
and transforming the universe.” — (Roy, 2000, p.127)
adaptation model manalastas - marasigan - mendoza
nal back
io g
1963 - she received a bachelor’s degree in nursing at Mount
ro
educa
Saint Mary’s College in Los Angeles.
und
1966 - she received a master’s degree in nursing at the
r•
University of California, Los Angeles.
• ac
ad
ee
She studied Sociology. e mic c a r
1973 - she received her master’s degree in Sociology at the
University of California.
1976 - she developed Sr. Callista Roy’s Adaptation Model of
Nursing.
1977 - she received her doctorate in Sociology at the University
of California.
metaparadigm.
of the adaptation model
Adaptation major concepts
- goal of nursing — sr. calista roy
Person
- adaptive system
Environment
- stimuli
Health
- outcome of adaptation
Nursing
- promoting adaptation and health
adaptation model manalastas - marasigan - mendoza
stimuli sti
mu
li
Role Function
Focal stimuli Physiological -
– refer to immediately confronting the Physical
individual.
COPING
Contextual stimuli PROCESS
be
– these are all other stimuli present that ha
vio
contribute to the effect of the focal r
stimulus. Self - Concept
Inter -
Group Identity
dependence
Residual stimuli
– these are environmental factors of
which the effects are unclear in a given
situation.
adaptation model manalastas - marasigan - mendoza
Innate Coping Mechanisms
- genetically determined sti
mu
li
Acquired Coping Mechanisms Role Function
- developed Physiological -
Physical
Regulator Subsystem COPING
- person’s physiological coping PROCESS
be
mechanism. ha
vio
r
Self - Concept
Cognator Subsystem Group Identity
Inter -
dependence
- person’s mental coping system.
adaptation model manalastas - marasigan - mendoza
adaptive
models
sti
mu
li
Role Function
Physiological -
Physical
1. Physiological-Physical Mode
COPING
2. Role Function Mode PROCESS
be
3. Self-Concept Group Identity Mode ha
vio
4. Interdependence Mode
r
Self - Concept
Inter -
Group Identity
dependence
adaptation model manalastas - marasigan - mendoza
1. Physiological-Physical Mode 2. Role Function Mode 4. Interdependence Mode
Involves the maintenance of the physical
body. 1. Primary Role
Focuses on attaining relational integrity
Five (5) basic needs to promote 2. Secondary Roles
physiological integrity: 3. Tertiary Roles
1. Oxygenation
2. Nutrition
3. Elimination
4. Activity and rest
3. Self-Concept Group Identity Mode
sti
mu
5. Protection li
Role Function
Four (4) processes that help to maintain have a sense of unity Physiological -
physiological integrity: Physical
COPING
1. Physical Self PROCESS
1. Senses
be
2. Fluid and electrolytes 2. Personal Self ha
vio
r
3. Neuro 3. Group-Identity Self - Concept
Inter -
4. Endocrine function Group Identity
dependence
adaptation model manalastas - marasigan - mendoza
ASSESSMENT
Behavior is an action or reaction under specified
circumstances; behavior may be observable, or not.
Nurse identifies stimuli in all 4 adaptive modes; stimuli are
manipulated via interventions to achieve patient goals
m o del
stimuli➡️ coping process ➡️
adaptive modes ➡️output ➡️behaviors
adaptation model manalastas - marasigan - mendoza
🩺 By removing inadequate coping methods, nurses gradually improve results.
ANALYSIS CONCLUSION
Nurses are facilitators of
adaptation
STRENGTH
use observation and interviewing Examine the patient's behaviors
skills for signs of adaptation
WEAKNESS Encourage positive adaptation
many elements, systems, through fostering interactions with
structures, and multiple concepts their surroundings
Support patients in having positive
responses to stimuli
🩺 By removing inadequate coping methods, nurses gradually improve results.
SUMMARY
5 elements: person, the goal of nursing, nursing activities, health, and
environment
These mechanisms work within 4 adaptive modes.
Nursing aims to promote adaptive responses in relation to 4 adaptive modes,
using information about a person’s adaptation level and various stimuli.
Nursing activities involve the manipulation of these stimuli to promote
adaptive responses.
film
showing.
adaptation model manalastas - marasigan - mendoza
You might also like
- Rosemarie Rizzo Parse TheoryDocument3 pagesRosemarie Rizzo Parse TheoryKhrysta CaboNo ratings yet
- Psychology in Modern IndiaDocument547 pagesPsychology in Modern IndiaTarek RahmanNo ratings yet
- Concept of Humanity - Learning and Behavior TheoriesDocument3 pagesConcept of Humanity - Learning and Behavior TheoriesMary Ann AmbitaNo ratings yet
- Sister Callista Roy: Roy Adaptation ModelDocument29 pagesSister Callista Roy: Roy Adaptation Modelyamih0267% (3)
- RPS Phobia Dan Trauma HealingDocument3 pagesRPS Phobia Dan Trauma HealingEfwar Hotib Tokyar0% (1)
- Roy Adaptation ModelDocument4 pagesRoy Adaptation Modelcandy perezNo ratings yet
- ACT Worksheets For CouplesDocument11 pagesACT Worksheets For CouplesLiah Piano-Beast UchihaNo ratings yet
- CISM Case StudiesDocument26 pagesCISM Case StudiesRoventa Florin100% (1)
- TFN - Week 6 - Sister Callista RoyDocument5 pagesTFN - Week 6 - Sister Callista RoyJoy PelpinosasNo ratings yet
- TFN Callista L. RoyDocument4 pagesTFN Callista L. RoyANJELO CYRUS BIARES GARCIANo ratings yet
- TFN-Reviewer MidtermDocument31 pagesTFN-Reviewer MidtermElla ArnocoNo ratings yet
- Roy, Neuman, King ReviewerDocument2 pagesRoy, Neuman, King ReviewerJustine Marie AguilarNo ratings yet
- Calista Roy Adaptation ModelDocument2 pagesCalista Roy Adaptation ModelBryan Dimen88% (8)
- TFN NotesDocument3 pagesTFN Notes1234567890 0987654321No ratings yet
- AdolescentDocument1 pageAdolescentLyka TemonesNo ratings yet
- Sage Publications, Inc. Association For Psychological ScienceDocument18 pagesSage Publications, Inc. Association For Psychological ScienceMomoBeNo ratings yet
- Summary of Psychological Theories and Their Implications/ Contributions To GuidanceDocument4 pagesSummary of Psychological Theories and Their Implications/ Contributions To GuidanceJenny AgadanNo ratings yet
- Govt. College of Nursing Jagdalpur: Subject:-Advance Nursing Practice Seminor On: - Roy'S TheoryDocument10 pagesGovt. College of Nursing Jagdalpur: Subject:-Advance Nursing Practice Seminor On: - Roy'S Theoryaparna100% (1)
- NCMDocument4 pagesNCMCelestina JalemNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument2 pagesUntitledAshley Nicole BeltranNo ratings yet
- Dorothy Johnson - Behavioral System ModelDocument6 pagesDorothy Johnson - Behavioral System ModelNek YasiladNo ratings yet
- SCQ Manual-1 - 231220 - 175941Document8 pagesSCQ Manual-1 - 231220 - 175941VEERNo ratings yet
- Go To PageDocument18 pagesGo To Pageapi-663288067No ratings yet
- Human Develpment CHAPTER 2Document4 pagesHuman Develpment CHAPTER 2Alexa ProvidoNo ratings yet
- Sachser Et Al 2018 The Adaptive Shaping of Social Behavioural Phenotypes During AdolescenceDocument7 pagesSachser Et Al 2018 The Adaptive Shaping of Social Behavioural Phenotypes During AdolescenceWASIS BRATANo ratings yet
- Theory Assignment 1Document2 pagesTheory Assignment 1api-322059527No ratings yet
- Tuguinay, Joshua FLA4 Interpsychic Theory (Concept Map)Document6 pagesTuguinay, Joshua FLA4 Interpsychic Theory (Concept Map)Joshua TuguinayNo ratings yet
- Matrix of Psychological Foundatios of EducationDocument8 pagesMatrix of Psychological Foundatios of EducationSignorina MargaritaNo ratings yet
- Ailawilliams - Ib Psychology Revision SheetDocument3 pagesAilawilliams - Ib Psychology Revision SheetHanie OriginalNo ratings yet
- Calista RoyDocument21 pagesCalista Roydarlenedavid2404No ratings yet
- TFN Trans Part 2Document18 pagesTFN Trans Part 2ree wryNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 2 OutlineDocument9 pagesChapter 1 2 OutlineAlexandra Jayne CortesNo ratings yet
- Behaviorism and CognitivismDocument6 pagesBehaviorism and CognitivismNoviaNo ratings yet
- Chart of Nursing Theories and ModelsDocument3 pagesChart of Nursing Theories and ModelsScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Personal Development 3rd QuarterDocument4 pagesPersonal Development 3rd QuarterSerenity MoonNo ratings yet
- GROUP - 4 MetaparadigmDocument5 pagesGROUP - 4 MetaparadigmRose OrtizNo ratings yet
- Darca & Dimapasoc Roy's Adaptation Theory PresentationDocument26 pagesDarca & Dimapasoc Roy's Adaptation Theory PresentationJandrew Gomez DimapasocNo ratings yet
- The Ecology of Human PerformanceDocument13 pagesThe Ecology of Human PerformanceMariqnNo ratings yet
- FINALSDocument10 pagesFINALSJeameNo ratings yet
- Sister Callista Roy: Adaptation ModelDocument20 pagesSister Callista Roy: Adaptation Modeldarlenedavid2404No ratings yet
- Hypocrisy, Self-Deception, and PerplexityDocument22 pagesHypocrisy, Self-Deception, and PerplexityAnnaNo ratings yet
- Uts Midterm ModuleDocument25 pagesUts Midterm ModuleMika LavadoNo ratings yet
- A Functional Approach To The Assessment of Self-Mutilative BehaviorDocument6 pagesA Functional Approach To The Assessment of Self-Mutilative BehaviorPhillarts LopesNo ratings yet
- Educ 5 (Unit 2)Document16 pagesEduc 5 (Unit 2)George Kevin TomasNo ratings yet
- Sister Callista RoyDocument2 pagesSister Callista RoyZaldivar PenuliarNo ratings yet
- TFN Week 6 Dorothy JohnsonDocument3 pagesTFN Week 6 Dorothy JohnsonJoy PelpinosasNo ratings yet
- Modern Counseling Therapy and TheoriesDocument2 pagesModern Counseling Therapy and TheoriesRommel SarjNo ratings yet
- Renz Morales Module 4Document20 pagesRenz Morales Module 4Renz MoralesNo ratings yet
- Ob CHAPTER 20Document5 pagesOb CHAPTER 20Magandia, Janizah R.No ratings yet
- Dorothy JohnsonDocument5 pagesDorothy JohnsonJoanna Marie TulioNo ratings yet
- Group 11 BSN1 C TFN Activity 3Document11 pagesGroup 11 BSN1 C TFN Activity 3Reibenjay CamoralNo ratings yet
- Psihologia Sociala ArticolDocument71 pagesPsihologia Sociala ArticolLiana Maria DrileaNo ratings yet
- Topic 12 Hbse 4Document15 pagesTopic 12 Hbse 4Mary France Paez CarrilloNo ratings yet
- Prejudice As Self-Image Maintenance (Affirming The Self Through Derogating Others)Document14 pagesPrejudice As Self-Image Maintenance (Affirming The Self Through Derogating Others)Ancer MatasakNo ratings yet
- Sister Callista RoyDocument2 pagesSister Callista RoyJulie Dampo DicdicanNo ratings yet
- An Integrative Approach To PsychopathologyDocument1 pageAn Integrative Approach To PsychopathologyAkheyla GarciaNo ratings yet
- Personality Theories MatrixDocument3 pagesPersonality Theories MatrixChad Lanasa100% (1)
- BeedDocument2 pagesBeedAdrian Joen RapsingNo ratings yet
- A Compare and Contrast Classical Conditioning With Operant ConditioningDocument2 pagesA Compare and Contrast Classical Conditioning With Operant ConditioningAdrian Joen Rapsing100% (1)
- Course Notes - B.F. SkinnerDocument5 pagesCourse Notes - B.F. SkinnerRiva Diva50% (2)
- Obm Vision GeneralDocument9 pagesObm Vision GeneralAlexis Agustin PiraniNo ratings yet
- Johnson and Peplau ReviewerDocument3 pagesJohnson and Peplau ReviewerSofia Marie GalendezNo ratings yet
- Morality and Our Complicated Form of Life: Feminist Wittgensteinian MetaethicsFrom EverandMorality and Our Complicated Form of Life: Feminist Wittgensteinian MetaethicsNo ratings yet
- StressDocument23 pagesStressPoonam RanaNo ratings yet
- Questionnaire On Anger Module 4 PDFDocument3 pagesQuestionnaire On Anger Module 4 PDFanshuNo ratings yet
- Assignment On Ego StateDocument5 pagesAssignment On Ego StatePriyanka NilewarNo ratings yet
- A Life Less Punishing by Matt HeathDocument17 pagesA Life Less Punishing by Matt HeathAllen & UnwinNo ratings yet
- Script For HRD IndiDocument6 pagesScript For HRD IndiNur AzmanNo ratings yet
- Health Psychology - Health Behavior Change AnalysisDocument8 pagesHealth Psychology - Health Behavior Change AnalysisMichele VasconezNo ratings yet
- Discipline Key To SuccessDocument4 pagesDiscipline Key To Successanrigorjeladze88No ratings yet
- Chapter6Document31 pagesChapter6Premkumar KonarNo ratings yet
- Chapter One: Introduction To Determinants of Health: Instructor: Bethlehem Y. (B.SC, MPH)Document22 pagesChapter One: Introduction To Determinants of Health: Instructor: Bethlehem Y. (B.SC, MPH)biniyam bekeleNo ratings yet
- Recreational ActivitiesDocument10 pagesRecreational Activitiespsagubo199xNo ratings yet
- History TakingDocument4 pagesHistory TakingAniqa waheedNo ratings yet
- Rotter Handouts PDFDocument31 pagesRotter Handouts PDFLee Mae BedrijoNo ratings yet
- Massage Therapy-Establishing A BondDocument8 pagesMassage Therapy-Establishing A Bondapi-522933227No ratings yet
- 925 BCE RazésDocument1 page925 BCE RazésJeanelle M.No ratings yet
- Human Sexuality in CounselingDocument6 pagesHuman Sexuality in CounselingJoseph GathuaNo ratings yet
- Communication Studies Expository Piece (Draft)Document3 pagesCommunication Studies Expository Piece (Draft)Martyn PereiraNo ratings yet
- Public SpeakingDocument1 pagePublic SpeakingUmalni Rajarao100% (1)
- Art Comparison Essay ExampleDocument5 pagesArt Comparison Essay Exampleflrzcpaeg100% (2)
- SDP 1 Self Awareness (Who Am I - )Document15 pagesSDP 1 Self Awareness (Who Am I - )Jazzy John C. CurimatmatNo ratings yet
- CopingDocument3 pagesCopingPipit MarianiNo ratings yet
- Enhancing Physical and Mental WellDocument4 pagesEnhancing Physical and Mental WellMAKAR S.No ratings yet
- JPP Self HarmDocument10 pagesJPP Self Harmluthfi anggia sastiwi0% (1)
- 10 Ways To Stop OverthinkingDocument2 pages10 Ways To Stop OverthinkingNhat UyenNo ratings yet
- A Descriptive Study To Assess The Level of Knowledge Regarding Burnout Syndromme Among The Staff NursesDocument8 pagesA Descriptive Study To Assess The Level of Knowledge Regarding Burnout Syndromme Among The Staff NursesIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- Health PsychologyDocument2 pagesHealth PsychologyStephenNo ratings yet
- Perfectionism?: Created With Scanner ProDocument6 pagesPerfectionism?: Created With Scanner ProQuazi Fahim ShahriarNo ratings yet
- Senarai Tajuk JournalDocument11 pagesSenarai Tajuk JournalMusafir AdamNo ratings yet